Linux-进程间通信(二): FIFO
1. FIFO:
FIFO也被成为命名管道,因其通过路径关系绑定,可以用于任意进程间通信,而普通无名管道只能用于有共同祖先的进行直接通信;
命名管道也是半双工的,open管道的时候不要以读写方式打开,这种操作是未定义的;
2. FIFO创建:
#include <sys/stat.h> int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); ret = 成功返回0,失败返回-
FIFO是一种文件类型,mode参数与open函数中的mode参数相同,并且一般文件的操作函数(close, read, write, unlink等)都以用于FIFO;
3. 非阻塞标志(O_NONBLOCK):
(1) 阻塞模式:只读open要阻塞到某个进程为写而打开此FIFO,只写open要阻塞到某个进程为读而打开此FIFO;
(2) 非阻塞模式:只读立即返回,如果没有进程为读而打开FIFO,则只写open返回-1,erron=ENXIO;
4. 一端关闭:
(1) 若读一个已经关闭写端的FIFO,则读取完数据后,会读到文件结束符,read返回0;
(2) 若写一个已经关闭读端的FIFO,则产生SIGPIPE;
5. 用途:
(1) FIFO由shell命令使用以便将数据从一条管道传送到另一条,而无需创建临时文件;
(2) FIFO用于客户进程和服务器进程进行数据传递;
6. 测试代码:两个进程间通信;
fifo_writer.c -- 向fifo中写入字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -;
int fifoid = -; char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { }; if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < ){
fifoid = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, );
if (fifoid < ){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -;
}
} pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (pipeid < ){
perror("open pipeid error\n");
return -;
} int read_bytes = read(STDIN_FILENO, buffer, BUF_LEN);
if (read_bytes < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} const char * buff_send = buffer;
int no_write_bytes = read_bytes;
while (no_write_bytes > ){
int n = write(pipeid, buff_send, no_write_bytes);
if (n < ){
perror("write error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} no_write_bytes -= n;
buff_send += n;
} close(pipeid); return ;
}
fifo_reader.c -- 从fifo中读出字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -; char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { }; pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY); int n = read(pipeid, buffer, BUF_LEN - );
if (n < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} write(STDOUT_FILENO, buffer, n); close(pipeid); return ;
}
7. 测试代码:多个客户端与服务器通信
模型如下图所示:
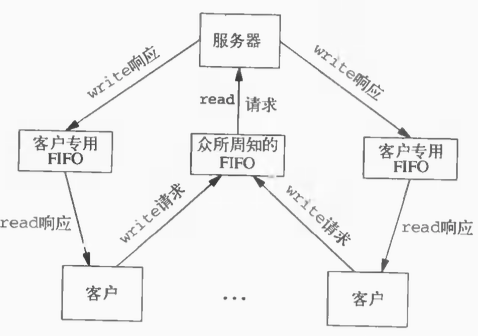
common.h--公共头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string.h> #define SERVER_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoServer"
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoClient%d"
#define BUFF_SIZE PIPE_BUF
#define MSG_LEN 64
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN 64 typedef struct fifo_msg{
pid_t client_pid;
char msg[MSG_LEN];
}fifo_msg_t;
fifo_server.c
#include "common.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fifo_id = -;
int server_fifo_fd = -; if (access(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < ){
fifo_id = mkfifo(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, );
if (fifo_id < ){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -;
}
} server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open fifo error\n");
return -;
} fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, , sizeof(client_msg));
int read_bytes = ; do {
read_bytes = read(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (read_bytes < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -;
} char *tmp_msg = client_msg.msg;
while (*tmp_msg){
*tmp_msg = toupper(*tmp_msg);
tmp_msg++;
} char client_fifo[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = { };
snprintf(client_fifo, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - , CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_msg.client_pid); int client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo, O_WRONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
} write(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
printf("write to client:%d\n", client_msg.client_pid);
close(client_fifo_fd); } while (read_bytes > ); close(server_fifo_fd);
return ;
}
fifo_client.c
#include "common.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pid_t client_pid = -;
int server_fifo_fd = -;
int client_fifo_fd = -; server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open server fifo error\n");
return -;
} client_pid = getpid(); char client_fifo_name[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = {};
snprintf(client_fifo_name, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - , CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_pid);
if (mkfifo(client_fifo_name, ) < ){
perror("mkfifo client error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -;
} fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, , sizeof(client_msg));
client_msg.client_pid = client_pid; #define TRY_TIMES 3
int times = ;
for (times = ; times < TRY_TIMES; times++){
snprintf(client_msg.msg, MSG_LEN - , "client_pid:%d\n", client_pid);
write(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg)); client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo_name, O_RDONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return -;
} int n = read(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (n > ){
printf("reveive msg from server:%s", client_msg.msg);
} close(client_fifo_fd);
} close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return ;
}
Linux-进程间通信(二): FIFO的更多相关文章
- Linux 进程间通信(二) 管道
Linux 进程间通信-管道 进程是一个独立的资源分配单位,不同进程之间的资源是相互独立的,没有关联,不能在一个进程中直接访问另一个进程中的资源.但是,进程不是孤立的,不同的进程之间需要信息的交换以及 ...
- linux 进程间通信 之fifo
上一篇博客已经介绍了一种进程间通信的方式,但是那只是针对于有血缘关系的进程,即父子进程间的通信,那对于没有血缘关系的进程,那要怎么通信呢? 这就要创建一个有名管道,来解决无血缘关系的进程通信, fi ...
- Linux进程间通信(二) - 消息队列
消息队列 消息队列是Linux IPC中很常用的一种通信方式,它通常用来在不同进程间发送特定格式的消息数据. 消息队列和之前讨论过的管道和FIFO有很大的区别,主要有以下两点(管道请查阅我的另一篇文章 ...
- Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(SVR4 信号量)
Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(SVR4 信号量)
- Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(Posix 信号量)
Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(Posix 信号量)
- Linux 进程间通信之管道(pipe),(fifo)
无名管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允许无亲缘关系进程间的通信: 定义函数: int pipe(int f ...
- Linux进程间通信(二)
信号 信号的概念 信号是Linux进程间通信的最古老的一种方式.信号是软件中断,是一种异步通信的方式.信号可以导致一个正在运行的进程被另一个正在运行的异步进程中断,转而处理某个突发事件. 一旦产生信号 ...
- Linux进程间通信(二):信号集函数 sigemptyset()、sigprocmask()、sigpending()、sigsuspend()
我们已经知道,我们可以通过信号来终止进程,也可以通过信号来在进程间进行通信,程序也可以通过指定信号的关联处理函数来改变信号的默认处理方式,也可以屏蔽某些信号,使其不能传递给进程.那么我们应该如何设定我 ...
- Linux进程间通信之管道(pipe)、命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal)
整理自网络 Unix IPC包括:管道(pipe).命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal) 管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道 ...
- Linux进程间通信(四):命名管道 mkfifo()、open()、read()、close()
在前一篇文章—— Linux进程间通信 -- 使用匿名管道 中,我们看到了如何使用匿名管道来在进程之间传递数据,同时也看到了这个方式的一个缺陷,就是这些进程都由一个共同的祖先进程启动,这给我们在不相关 ...
随机推荐
- SQL SERVER 的操作复习
一.数据库的创建(SQL语句)CREATE DATABASE AON PRIMARY --主文件组( NAME='A_data',--逻辑文件名 --物理文件名 FILENAME=' ...
- 02-Mysql数据库----初识
什么是数据(Data) 描述事物的符号记录称为数据,描述事物的符号既可以是数字,也可以是文字.图片,图像.声音.语言等,数据由多种表现形式,它们都可以经过数字化后存入计算机 在计算机中描述一个事物,就 ...
- HDFS伪分布式环境搭建
(一).HDFS shell操作 以上已经介绍了如何搭建伪分布式的Hadoop,既然环境已经搭建起来了,那要怎么去操作呢?这就是本节将要介绍的内容: HDFS自带有一些shell命令,通过这些命令我们 ...
- 关键词提取TF-IDF算法/关键字提取之TF-IDF算法
TF-IDF(term frequency–inverse document frequency)是一种用于信息检索与信息探勘的常用加权技术.TF的意思是词频(Term - frequency), ...
- gitbook生成的_book文件本地打开后链接失效问题
Gitbook 生成本地 html 的问题 在本地用 gitbook-cli根据 Summary 生成目录 然后在每个 md 文件里书写内容 然后用 gitbook serve .生成本地 html ...
- BZOJ 3809 Gty的二逼妹子序列 莫队算法+分块
Description Autumn和Bakser又在研究Gty的妹子序列了!但他们遇到了一个难题. 对于一段妹子们,他们想让你帮忙求出这之内美丽度∈[a,b]的妹子的美丽度的种类数. 为了方便,我们 ...
- 【集训试题】exam 信心考 最小割
题意概述: 有N个人,A,B两个考场.如果学生i在A考场,总信心值增加xi:如果学生i在B考场,总信心值增加yi.其中还有m对好友,当第i对好友的两个人都在A考场时,总信心值增加ai:如果两人都在B考 ...
- 使用github同步网站
今天刚刚完成了自己的一个小项目,想把他上传到服务器上,想到到我使用的Visual Stdio Code具有git功能,于是想到使用github作为代码仓库来同步代码. 大体步骤分为这几步:创建远程代码 ...
- 玩lua
https://my.oschina.net/wangxuanyihaha/blog/186401
- JavaScript 执行环境(作用域)总结
所有变量(包括基本类型和引用类型)都存在一个执行环境(也称为作用域)当中,这个执行环境决定了变量的生命周期,以及哪一部分可以访问其中的变量. 以下是关于执行环境的几点总结: 执行环境有全局执行环境(全 ...
