Codeforces 804D Expected diameter of a tree
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Pasha is a good student and one of MoJaK's best friends. He always have a problem to think about. Today they had a talk about the following problem.
We have a forest (acyclic undirected graph) with n vertices and m edges. There are q queries we should answer. In each query two vertices v and u are given. Let V be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains v, and U be the set of vertices in the connected component of the graph that contains u. Let's add an edge between some vertex 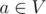 and some vertex in
and some vertex in 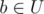 and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
and compute the value d of the resulting component. If the resulting component is a tree, the value d is the diameter of the component, and it is equal to -1 otherwise. What is the expected value of d, if we choose vertices a and b from the sets uniformly at random?
Can you help Pasha to solve this problem?
The diameter of the component is the maximum distance among some pair of vertices in the component. The distance between two vertices is the minimum number of edges on some path between the two vertices.
Note that queries don't add edges to the initial forest.
The first line contains three integers n, m and q(1 ≤ n, m, q ≤ 105) — the number of vertices, the number of edges in the graph and the number of queries.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n), that means there is an edge between vertices ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the given graph is a forest.
Each of the next q lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) — the vertices given in the i-th query.
For each query print the expected value of d as described in the problem statement.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6. Let's assume that your answer is a, and the jury's answer is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 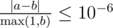 .
.
3 1 2
1 3
3 1
2 3
-1
2.0000000000
5 2 3
2 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
2 5
-1
2.6666666667
2.6666666667
In the first example the vertices 1 and 3 are in the same component, so the answer for the first query is -1. For the second query there are two options to add the edge: one option is to add the edge 1 - 2, the other one is 2 - 3. In both ways the resulting diameter is 2, so the answer is 2.
In the second example the answer for the first query is obviously -1. The answer for the second query is the average of three cases: for added edges 1 - 2 or 1 - 3 the diameter is 3, and for added edge 1 - 4 the diameter is 2. Thus, the answer is 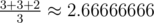 .
.
题意:
给出一个森林,q次询问,每次问把x,y两点所属的树之间任意连接一条边形成新的树的直径的期望,如果x和y在同一棵树中输出-1;
代码:
//这题算出复杂度也就解出来了。先枚举一棵树中的节点然后二分找另一棵树中的节点满足两个节点之间的距离不小于max(树1直径,
//树2直径),他们的贡献就是各自在自己树中最远能到达的端点的距离相加再+1,否则贡献就是max(树1直径,树2直径),这样看似是
//q*n*long(n),但是注意到所有的树的大小总和是n所以最坏是sqrt(n)棵树每棵树大小是sqrt(n),所以是q*sqrt(n)*long(n);
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN=;
int fa[MAXN],head[MAXN],tot,n,cnt,m,q,d[MAXN],f[MAXN],deep,o,oo,root[MAXN];
int a[MAXN],aa;
double size[MAXN];
map<pair<int,int>,double>mp;
vector<ll>v[MAXN],vv[MAXN];
struct Edge { int u,v,next; }edge[MAXN*];
void init()
{
tot=cnt=;
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
memset(fa,-,sizeof(fa));
memset(f,,sizeof(f));
memset(d,-,sizeof(d));
}
void add(int x,int y)
{
edge[tot].u=x;edge[tot].v=y;
edge[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot++;
edge[tot].u=y;edge[tot].v=x;
edge[tot].next=head[y];
head[y]=tot++;
}
void dfs1(int x,int father,int p)
{
v[p].push_back(x);
for(int i=head[x];i!=-;i=edge[i].next){
int y=edge[i].v;
if(y==father) continue;
fa[y]=p;
dfs1(y,x,p);
}
}
void dfs2(int x,int father,int sum,bool w)
{
if(w!=) f[x]=max(f[x],sum);
if(sum>=deep){
deep=sum;
if(w==) o=x;
else if(w==) oo=x;
}
for(int i=head[x];i!=-;i=edge[i].next){
int y=edge[i].v;
if(y==father) continue;
dfs2(y,x,sum+,w);
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
init();
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
for(int i=;i<m;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
if(fa[i]!=-) continue;
fa[i]=++cnt;
v[cnt].clear();vv[cnt].clear();
dfs1(i,,cnt);
root[cnt]=i;
}
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++){
deep=;
dfs2(root[i],,,);
deep=;
dfs2(o,,,);
d[i]=deep;
dfs2(oo,,,);
aa=v[i].size();
for(int j=;j<aa;j++) a[j]=f[v[i][j]];
v[i].clear();
for(int j=;j<aa;j++) v[i].push_back(a[j]);
sort(v[i].begin(),v[i].end());
a[aa]=;
for(int j=aa-;j>=;j--) a[j]=a[j+]+v[i][j]+;
for(int j=;j<=aa;j++) vv[i].push_back(a[j]);
}
while(q--){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(fa[x]==fa[y]) printf("-1\n");
else{
pair<int,int>p1(fa[x],fa[y]);
if(mp[p1]>) printf("%.6f\n",mp[p1]);
else{
double ans=;
int xx=fa[x],yy=fa[y];
if(v[xx].size()<=v[yy].size()){
for(int i=;i<v[xx].size();i++){
ll tmp=lower_bound(v[yy].begin(),v[yy].end(),max(d[xx],d[yy])-v[xx][i]-)-v[yy].begin();
ans+=(vv[yy][tmp]+v[xx][i]*(v[yy].size()-tmp))+tmp*max(d[xx],d[yy]);
}
}else{
for(int i=;i<v[yy].size();i++){
ll tmp=lower_bound(v[xx].begin(),v[xx].end(),max(d[xx],d[yy])-v[yy][i]-)-v[xx].begin();
ans+=(vv[xx][tmp]+v[yy][i]*(v[xx].size()-tmp))+tmp*max(d[xx],d[yy]);
}
}
double tmp1=v[xx].size(),tmp2=v[yy].size();
ans/=(tmp1*tmp2);
printf("%.6f\n",ans);
mp[p1]=ans;
}
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces 804D Expected diameter of a tree的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 804D Expected diameter of a tree(树的直径 + 二分 + map查询)
题目链接 Expected diameter of a tree 题目意思就是给出一片森林, 若把任意两棵树合并(合并方法为在两个树上各自任选一点然后连一条新的边) 求这棵新的树的树的直径的期望长度. ...
- Codeforces 804D Expected diameter of a tree(树形DP+期望)
[题目链接] http://codeforces.com/contest/804/problem/D [题目大意] 给你一个森林,每次询问给出u,v, 从u所在连通块中随机选出一个点与v所在连通块中随 ...
- Codeforces 840D Expected diameter of a tree 分块思想
Expected diameter of a tree 我们先两次dfs计算出每个点能到达最远点的距离. 暴力计算两棵树x, y连边直径的期望很好求, 我们假设SZ(x) < SZ(y) 我们枚 ...
- CodeForces 805F Expected diameter of a tree 期望
题意: 给出一个森林,有若干询问\(u, v\): 从\(u, v\)中所在子树中随机各选一个点连起来,构成一棵新树,求新树直径的期望. 分析: 回顾一下和树的直径有关的东西: 求树的直径 从树的任意 ...
- CF804D Expected diameter of a tree 树的直径 根号分治
LINK:Expected diameter of a tree 1e5 带根号log 竟然能跑过! 容易想到每次连接两个联通快 快速求出直径 其实是 \(max(D1,D2,f_x+f_y+1)\) ...
- Codeforces Round #411 (Div. 1) D. Expected diameter of a tree
题目大意:给出一个森林,每次询问给出u,v,问从u所在连通块中随机选出一个点与v所在连通块中随机选出一个点相连,连出的树的直径期望(不是树输出-1).(n,q<=10^5) 解法:预处理出各连通 ...
- codeforces804D Expected diameter of a tree
本文版权归ljh2000和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 本文作者:ljh2000 作者博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljh2000-jump/ ...
- 543. Diameter of Binary Tree
https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/#/description Given a binary tree, you need to ...
- LeetCode 543. Diameter of Binary Tree (二叉树的直径)
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a b ...
随机推荐
- 编写webpack 插件
Webpack插件为第三方开发者释放了Webpack的最大可能性.利用多级回调开发者可以把他们自己的需要的功能引入到Webpack里面来.Build插件比Build loader 更进一步.因为你需要 ...
- [leetcode-921-Minimum Add to Make Parentheses Valid]
Given a string S of '(' and ')' parentheses, we add the minimum number of parentheses ( '(' or ')', ...
- url的param与dict转换
urllib.parse.urlencode urlencode from urllib import parse from urllib.request import urlopen from ur ...
- 互评beta版本 - 探路者【贪吃蛇】
基于NABCD评论,及改进建议 1)N(Need 需求) 开发本软件一方面是为了让80,90后用户重温童年的美好记忆,另一方面也是为了增加对英语学习兴趣较弱.意志力薄弱的中小学生学习英语的兴趣和动力, ...
- TCP/IP,HTTP,HTTPS,WEBSocket协议
我看看着挺多的,我暂时没时间自己写,有需要的请借鉴 http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI0MDQ4MTM5NQ==&mid=2247486927&id ...
- myeclipse 导入 import maven web project
用google才收到了这个.. http://stackoverflow.com/questions/12197662/maven-java-web-project-not-recognised-wh ...
- 剑指offer:旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述: 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转. 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素. 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个 ...
- js获取浏览器窗口属性
网页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth;网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight;网页可见区域宽: document.body.offset ...
- Mac配置环境变量
Mac配置环境变量,以ant和maven为例 1.编辑 .bash_profile文件 cd vi .bash_profile 编辑内容为 ------------------------- ...
- python3.6执行AES加密及解密方法
python版本:3.6.2 首先安装pycryptodome cmd执行命令:pip install pycryptodome 特别简单,代码如下: #!/usr/bin/python # -*- ...
