【LeetCode】72. Edit Distance 编辑距离(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛
id: fuxuemingzhu
个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/edit-distance/description/
题目描述
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
题目大意
给了两个字符串,现在有三种操作,问最少做多少次操作,能使word1变成word2。三种操作是:
- 插入一个字符
- 删除一个字符
- 替换一个字符
解题方法
程序的世界真是其妙无穷。
很多人的解法直接上来就是动态规划,其实少了这个动态规划怎么想出来的过程。动态规划的思路就是 递归 => 记忆化搜索 => 动态规划,一步步提升转化出来的,大家都在讲动态规划,其实少了前两步的思考过程。
我现在详细讲解下递归 => 记忆化搜索 => 动态规划的优化过程。
递归
这个题和最长公共子序列非常相似,需要判断最后的一个字符是否相等:
- 如果相等,则最后一个字符不用做任何操作,那么只用计算除去最后一个字符外的前面的子串的编辑距离即可。
- 如果不等,则最后一个字符需要进行替换操作,那么只用计算除去最后一个字符外的前面的子串的编辑距离 ,再 +1(最后一个字符的替换操作),即可把word1变成word2。
图源花花酱:
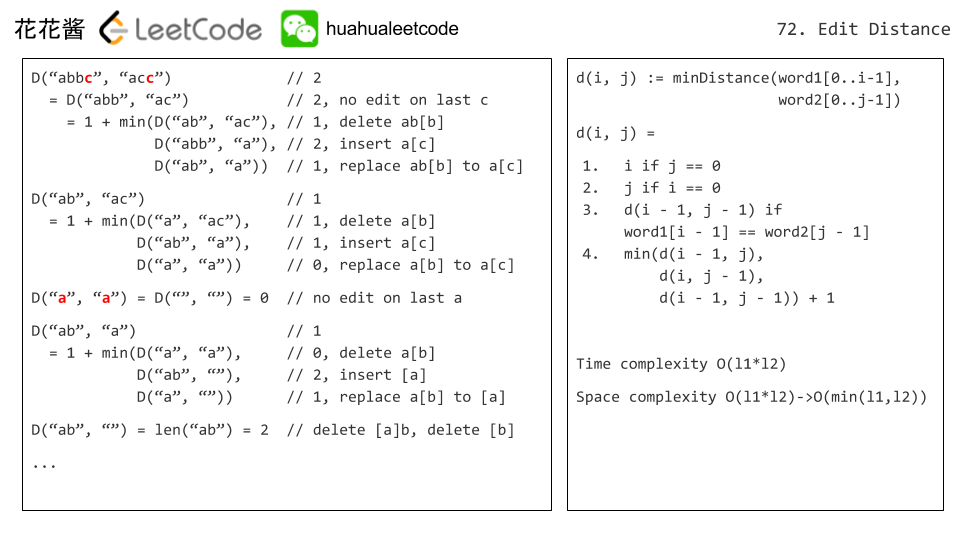
代码比较简单,需要注意的是初始化的数组大小是 L1 + 1 和 L2 + 1,因为函数的意义是 [0, L1], [0, L2] 区间变成相等的最小操作次数,闭区间。
可以按照上面的思路,进行暴力的求解。但是会超时 TLE。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
// cout << "word1: " << word1 << " word2: " << word2 << endl;
int M = word1.size();
int N = word2.size();
if (M == 0) return N;
if (N == 0) return M;
if (word1[M - 1] == word2[N - 1]) {
return minDistance(word1.substr(0, M - 1), word2.substr(0, N - 1));
}
return 1 + min(min(minDistance(word1.substr(0, M - 1), word2),
minDistance(word1, word2.substr(0, N - 1))),
minDistance(word1.substr(0, M - 1), word2.substr(0, N - 1)));
}
};
记忆化搜索
上面的超时的原因是会有重复的计算,同样的一个状态会被不同的分支走多次,因此可以使用记忆化搜索,保存一下走过的状态的结果,如果另外一个分支走到了这个状态,那么可以直接查找之前的计算结果。
Python代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
"""
:type word1: str
:type word2: str
:rtype: int
"""
L1, L2 = len(word1), len(word2)
dp = [[-1] * (L2 + 1) for _ in range(L1 + 1)]
return self.getDistance(word1, word2, dp, L1, L2)
def getDistance(self, word1, word2, dp, pos1, pos2):
if pos1 == 0: return pos2
if pos2 == 0: return pos1
if dp[pos1][pos2] >= 0: return dp[pos1][pos2]
res = 0
if word1[pos1 - 1] == word2[pos2 - 1]:
res = self.getDistance(word1, word2, dp, pos1 - 1, pos2 - 1)
else:
res = min(self.getDistance(word1, word2, dp, pos1 - 1, pos2 - 1),
self.getDistance(word1, word2, dp, pos1, pos2 - 1),
self.getDistance(word1, word2, dp, pos1 - 1, pos2)) + 1
dp[pos1][pos2] = res
return res
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
const int L1 = word1.size();
const int L2 = word2.size();
dp_ = vector<vector<int>>(L1 + 1, vector<int>(L2 + 1, -1));
return getDistance(word1, word2, L1, L2);
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> dp_;
int getDistance(string& word1, string& word2, int l1, int l2) {
if (l1 == 0) return l2;
if (l2 == 0) return l1;
if (dp_[l1][l2] >= 0) return dp_[l1][l2];
int res = 0;
if (word1[l1 - 1] == word2[l2 - 1])
res = getDistance(word1, word2, l1 - 1, l2 - 1);
else
res = min(getDistance(word1, word2, l1 - 1, l2 - 1),
min(getDistance(word1, word2, l1 - 1, l2),
getDistance(word1, word2, l1, l2 - 1))) + 1;
dp_[l1][l2] = res;
return res;
}
};
动态规划
记忆化搜索是自顶向下的操作,即如果求 word1 和 word2 的编辑距离 需要求除掉最后一个字符外的字符串的 编辑距离,依次递归下去。是个把问题规模逐渐变小的过程。
动态规划是自底向上的操作,即先求出最开始的边界条件,然后一步步添加字符,直到添加成 word1 和 word2 的时候,最后的编辑距离。是个把问题规模逐渐变大的过程。
知道了记忆化搜索之后,很容易改成动态规划。这两者的边界是一样的,只不过从递归转成了循环。
python代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
"""
:type word1: str
:type word2: str
:rtype: int
"""
L1, L2 = len(word1), len(word2)
dp = [[0] * (L2 + 1) for _ in range(L1 + 1)]
for i in range(L1 + 1):
dp[i][0] = i
for j in range(L2 + 1):
dp[0][j] = j
for i in range(1, L1 + 1):
for j in range(1, L2 + 1):
if word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]
else:
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + 1
return dp[L1][L2]
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
const int L1 = word1.size();
const int L2 = word2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(L1 + 1, vector<int>(L2 + 1, -1));
for (int i = 0; i <= L1; i++)
dp[i][0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= L2; j++)
dp[0][j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= L1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= L2; j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[L1][L2];
}
};
日期
2018 年 12 月 10 日 —— 又是周一!
2020 年 4 月 6 日 —— 又是周一!
【LeetCode】72. Edit Distance 编辑距离(Python & C++)的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 72. Edit Distance 编辑距离
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to ...
- leetCode 72.Edit Distance (编辑距离) 解题思路和方法
Edit Distance Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to convert ...
- [LeetCode] 72. Edit Distance(最短编辑距离)
传送门 Description Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to conver ...
- LeetCode - 72. Edit Distance
最小编辑距离,动态规划经典题. Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to conver ...
- [leetcode]72. Edit Distance 最少编辑步数
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to ...
- 72. Edit Distance(编辑距离 动态规划)
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to ...
- 第十八周 Leetcode 72. Edit Distance(HARD) O(N^2)DP
Leetcode72 看起来比较棘手的一道题(列DP方程还是要大胆猜想..) DP方程该怎么列呢? dp[i][j]表示字符串a[0....i-1]转化为b[0....j-1]的最少距离 转移方程分三 ...
- [leetcode] 72. Edit Distance (hard)
原题 dp 利用二维数组dp[i][j]存储状态: 从字符串A的0~i位子字符串 到 字符串B的0~j位子字符串,最少需要几步.(每一次删增改都算1步) 所以可得边界状态dp[i][0]=i,dp[0 ...
- 【Leetcode】72 Edit Distance
72. Edit Distance Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to conv ...
随机推荐
- /etc/sudoers 文件
sudo的权限控制可以在/etc/sudoers文件中查看到 如果想要控制某个用户(或某个组用户)只能执行root权限中的一部分命令, 或者允许某些用户使用sudo时不需要输入密码 格式一般都是 ro ...
- (转载)java中判断字符串是否为数字的方法的几种方法
java中判断字符串是否为数字的方法: 1.用JAVA自带的函数 public static boolean isNumeric(String str){ for (int i = 0; i < ...
- 关于写SpringBoot+Mybatisplus+Shiro项目的经验分享一:简单介绍
这次我尝试写一个原创的项目 the_game 框架选择: SpringBoot+Mybatisplus+Shiro 首先是简单的介绍(素材灵感来自英雄联盟) 5个关键的表: admin(管理员): l ...
- SCRDet——对小物体和旋转物体更具鲁棒性的模型
引言 明确提出了三个航拍图像领域内面对的挑战: 小物体:航拍图像经常包含很多复杂场景下的小物体. 密集:如交通工具和轮船类,在航拍图像中会很密集.这个DOTA数据集的发明者也提到在交通工具和轮船类的检 ...
- Python中的随机采样和概率分布(一)
Python(包括其包Numpy)中包含了了许多概率算法,包括基础的随机采样以及许多经典的概率分布生成.我们这个系列介绍几个在机器学习中常用的概率函数.先来看最基础的功能--随机采样. 1. rand ...
- 学习java 7.27
学习内容: 创建树 Swing 使用JTree对象来代表一棵树,JTree树中结点可以使用TreePath来标识,该对象封装了当前结点及其所有的父结点. 当一个结点具有子结点时,该结点有两种状态: 展 ...
- HDFS【概述、数据流】
目录 概述 定义 优缺点 HDFS组成架构 HDFS文件块大小 HDFS数据流 写数据 读数据 网络拓扑-节点距离计算 机架感知(写数据的副本存储节点选择) 概述 定义 HDFS是一个分布式文件管理系 ...
- 『学了就忘』Linux启动引导与修复 — 70、grub启动引导程序的配置文件说明
目录 1.grub中分区的表示方法 2.grub的配置文件 3.grub的配置文件内容说明 (1)grub的整体设置 (2)CentOS系统的启动设置 1.grub中分区的表示方法 在说grub启动引 ...
- Simulating final class in C++
Ever wondered how can you design a class in C++ which can't be inherited. Java and C# programming la ...
- 【Java】面向类与对象
一.面向对象 对象封装:私有变量+公共方法 方法与构造方法 this变量 Animal.java public class Animal { String name; int age; void mo ...
