interrupted()和isInterrupted()比较+终止线程的正确方法+暂停线程
interrupted():测试当前线程【运行此方法的当前线程】是否已经是中断状态,执行后具有将状态标志清除为false的功能。
isInterrupted():测试线程对象是否已经是中断状态,但不清除状态标志。
interrupted()的例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
syso(thread.interrupted());
syso(thread.interrupted());
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//运行结果
false
false
从上可以看出thread.interrupted()执行的是运行当前方法的线程,而不是thread线程,而由于main线程一直没有停止,所以一直是false。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
syso(Thread.interrupted());
syso(Thread.interrupted());
}
//运行结果
true
false
从上可以看出Thread.currentTrhead().interrupt()将main线程停止了,所以下面第一个是true状态,而第二个是false状态,就是因为interrupted()方法有清空状态标志的功能。
isInterrupted()的例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
syso(thread.isInterrupted());
syso(thread.isInterrupted());
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//运行结果
true
true
从上面可以看出isInterrupted()就是线程对象是否中断。
interrupt()并不能真正的结束线程:
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(this.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("已经是停止状态了!我要退出了!");
break;
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
System.out.println("for之后代码");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
thread.interrupt();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束了");
}
}
运行结果:
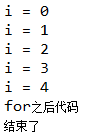
可以发现interrupt()并没有真正终止线程。下面介绍几种可以终止线程的方法:
1.异常法【建议使用】:
if(this.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("已经是停止状态了!我要退出了!");
throw new InterruptedException();
break;
}
在上面需要正常终止的地方抛出异常即可。
此方法最推荐使用,因为在catch块中还可以将异常向上抛,使线程停止的事件得以传播。
2.在sleep中interrupt():
public class SleepThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
System.out.println("run begin");
Thread.sleep(200000);
System.out.println("run end");
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("沉睡中停止,进入catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SleepMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SleepThread thread = new SleepThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread.interrupt();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束了");
}
}
运行结果:

3.使用作废的stop()方法:
调用stop()方法会强制让线程停止则有可能使一些清理性的工作得不到完成。并且有可能对锁定对象进行了“解锁”,导致数据得不到同步处理,出现数据不一致问题。
4.return法:
public class ReturnThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
while(true) {
if(this.isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("停止了!");
return;
}
System.out.println("timer" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
public class ReturnMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReturnThread thread = new ReturnThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(20);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
在需要停止的地方return即可。

暂停线程所使用的suspend()和resume()已经弃用,这里看一下suspend()方法:
当某个线程的suspend()方法被调用时,该线程会被挂起。如果该线程占有了锁,则它不会释放锁。即,线程在挂起的状态下还持有锁。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
private long i = 0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
i++;
//syso是一个同步方法
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();//启动一个线程'thread'
Thread.sleep(1000);//使当前线程(main线程)睡眠
thread.suspend();//挂起线程'thread'
//下面这一行不会执行,因为println一直被占用
System.out.println("main end!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
下面看一下println()源码:
public void println(long x) {
synchronized (this) {
print(x);
newLine();
}
}
从上可以看出suspend()暂停线程之后不会释放锁。
而在main中调用resume(),可以恢复线程,线程执行完毕就会释放锁。
interrupted()和isInterrupted()比较+终止线程的正确方法+暂停线程的更多相关文章
- java多线线程停止正确方法
//军队线程 //模拟作战双方的行为 public class ArmyRunnable implements Runnable { //volatile保证了线程可以正确的读取其他线程写入的值 // ...
- 零基础学习java------day18------properties集合,多线程(线程和进程,多线程的实现,线程中的方法,线程的声明周期,线程安全问题,wait/notify.notifyAll,死锁,线程池),
1.Properties集合 1.1 概述: Properties类表示了一个持久的属性集.Properties可保存在流中或从流中加载.属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串 一个属性列表可包含另 ...
- java线程interrupt、interrupted 、isInterrupted区别
前言 在分析interrupt之前,应该先了解java里线程有5种状态,其中有一个阻塞状态,interrupt和阻塞有关. interrupt() 方法 作用于要中断的那个线程. interrupt( ...
- interrupt ,interrupted 和 isInterrupted
1.interrupt interrupt方法用于中断线程.调用该方法的线程的状态为将被置为"中断"状态. 注意:线程中断仅仅是置线程的中断状态位,不会停止线程.需要用户自己去监 ...
- java---interrupt、interrupted和isInterrupted的区别
1.interrupt() interrupt方法用于中断线程.调用该方法的线程的状态为将被置为"中断"状态. 注意:线程中断仅仅是置线程的中断状态位,不会停止线程.需要用户自己 ...
- Java并发编程之线程生命周期、守护线程、优先级、关闭和join、sleep、yield、interrupt
Java并发编程中,其中一个难点是对线程生命周期的理解,和多种线程控制方法.线程沟通方法的灵活运用.这些方法和概念之间彼此联系紧密,共同构成了Java并发编程基石之一. Java线程的生命周期 Jav ...
- java线程相关基本方法
java线程中常用的基本方法有wait,notify,notifyAll,sleep,join,yield等. 线程的生命周期一共分为五个部分,分别是:新建(New).就绪(Runnable).运行( ...
- 线程概念( 线程的特点,进程与线程的关系, 线程和python理论知识,线程的创建)
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao987334176/p/9041318.html 线程概念的引入背景 进程 之前我们已经了解了操作系统中进程的概念,程序并不能单独运 ...
- python 全栈开发,Day41(线程概念,线程的特点,进程和线程的关系,线程和python 理论知识,线程的创建)
昨日内容回顾 队列 队列 : 先进先出.数据进程安全 队列实现方式: 管道 + 锁 生产者消费者模型 : 解决数据供需不平衡 管道 双向通信 数据进程不安全 EOFError: 管道是由操作系统进行引 ...
随机推荐
- 1040: [ZJOI2008]骑士
首先是因为想学仙人掌图才来先拿这题热热身,结果&……竟然调了一个晚上我的傻叉!(其中一大半的时候是在郁闷hzwer和Greens的代码画风不一样,后来才发现一个用拓扑一个用树dp23333,以 ...
- Unity3D LOD Group
今天下了一个4.0破解版,然后看到一个Demo Level of Detail 就研究了一下 以前用的是Unity3.5 free版本,没有这个功能,真实泪奔....... As your s ...
- ContestHunter暑假欢乐赛 SRM 15
菜菜给题解,良心出题人!但我还是照常写SRM一句话题解吧... T1经典题正解好像是贪心...我比较蠢写了个DP,不过还跑的挺快的 f[i]=min( f[j-a[j]-1] )+1 { j+a[j ...
- 关于springmvc下服务器文件打包成zip格式下载功能
关于springmvc下服务器文件打包成zip格式下载功能 2016年09月21日 11:22:14 toxic_guantou 阅读数:5731更多 个人分类: 技术点存储 版权声明:本文为博主 ...
- django-jet 中文文档
关于 JET是新式的Django管理界面并且增强了功能. 内容 文档 开始 安装django-jet 安装仪表盘 配置 配置文件 自动补全 紧凑内联 过滤器 仪表盘 自定义仪表盘 仪表盘模块 ...
- 洛谷P3396 哈希冲突 (分块)
洛谷P3396 哈希冲突 题目背景 此题约为NOIP提高组Day2T2难度. 题目描述 众所周知,模数的hash会产生冲突.例如,如果模的数p=7,那么4和11便冲突了. B君对hash冲突很感兴趣. ...
- Apple Tree POJ - 3321 dfs序列构造树状数组(好题)
There is an apple tree outside of kaka's house. Every autumn, a lot of apples will grow in the tree. ...
- 【IntelliJ IDEA 12使用】导入外部包
以前用eclipse,现在用IntelliJ IDEA,发现它确实是个很不错的工具. 用IntelliJ IDEA12这个版本导入外部JAR包,这样来操作,打开Project Structure,在m ...
- nodejs formidable混合表单提交
废话不多说,直接上代码: 前端页面: <!DOCTYPE html><html><head><link rel=’stylesheet’ href=’/sty ...
- codevs 1332 上白泽慧音
1332 上白泽慧音 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目描述 Description 在幻想乡,上白泽慧音是以知识渊博闻名的老师.春雪异变导致人间之里的很多道路都被大 ...
