Deep Learning -- 数据增强
数据增强
- 旋转|反射变换(Rotation/reflection):随机旋转图像一定角度;改变图像的内容朝向;
- 翻转变换(flip):沿这水平或者垂直方向翻转图像
- 缩放变换(zoom):按照一定的比例放大或者缩小图像
- 平移变换(shift):在图像平面上对图像以一定方式进行平移
数据增强的代码实现
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 数据增强
# 1.翻转变换flip
# 2.随机修剪random crop
# 3.色彩抖动color jittering
# 4.平移变换shift
# 5.尺度变换scale
# 6.对比度变换contrast
# 7.噪声扰动noise
# 8.旋转变换/反射变换 Rotation/reflection from PIL import Image,ImageEnhance,ImageOps,ImageFile
import numpy as np
import random
import threading,os,time
import logging logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True class DataAugmentation:
#包含数据增强的八种方式
def __init__(self):
pass @staticmethod
def openImage(image):
return Image.open(image,mode="r") @staticmethod
def randomRotation(image,mode=Image.BICUBIC):
# 对图像进行任意0~360度旋转
# param mode 邻近插值,双线性插值,双三次B样条插值(default)
# param image PIL的图像image
# return 旋转之后的图像
random_angle = np.random.randint(1,360)
return image.rotate(random_angle,mode) @staticmethod
def randomCrop(image):
#对图像随意剪切,考虑到图像大小范围(68*68),使用一个一个大于(36*36)的窗口进行截图
#param image:PIL的图像image
#return:剪切之后的图像
image_width = image.size[0]
image_height = image.size[1]
crop_win_size = np.random.randint(40,68)
random_region = ((image_width - crop_win_size ) >> 1 , (image_height - crop_win_size) >> 1 ,(image_width + crop_win_size) >> 1 , (image_height + crop_win_size) >> 1)
return image.crop(random_region) @staticmethod
def randomColor(image):
#对图像进行颜色抖动
#param image:PIL的图像image
#return:有颜色色差的图像image #随机因子
random_factor = np.random.randint(0, 31) / 10.
#调整图像的饱和度
color_image = ImageEnhance.Color(image).enhance(random_factor)
#随机因子
random_factor = np.random.randint(10,21) / 10.
#调整图像的亮度
brightness_image = ImageEnhance.Brightness(color_image).enhance(random_factor)
#随机因子
random_factor = np.random.randint(10,21) / 10.
#调整图像的对比度
contrast_image = ImageEnhance.Contrast(brightness_image).enhance(random_factor)
#随机因子
random_factor = np.random.randint(0,31) / 10.
#调整图像锐度
sharpness_image = ImageEnhance.Sharpness(contrast_image).enhance(random_factor)
return sharpness_image @staticmethod
def randomGaussian(image,mean=0.2,sigma=0.3):
#对图像进行高斯噪声处理
#param image:
#return def gaussianNoisy(im,mean=0.2,sigma=0.3):
#对图像做高斯噪音处理
# param im:单通道图像
# param mean:偏移量
# param sigma:标准差
#return:
for _i in range(len(im)):
im[_i] += random.gauss(mean,sigma)
return im #将图像转化为数组
img = np.asanyarray(image)
#将数组改为读写模式
img.flags.writeable = True
width,height = img.shape[:2]
#对image的R,G,B三个通道进行分别处理
img_r = gaussianNoisy(img[:,:,0].flatten(), mean, sigma)
img_g = gaussianNoisy(img[:,:,1].flatten(), mean, sigma)
img_b = gaussianNoisy(img[:,:,2].flatten(), mean, sigma)
img[:,:,0] = img_r.reshape([width,height])
img[:,:,1] = img_g.reshape([width,height])
img[:,:,2] = img_b.reshape([width,height])
return Image.fromarray(np.uint8(img)) @staticmethod
def saveImage(image,path):
image.save(path) def makeDir(path):
try:
if not os.path.exists(path):
if not os.path.isfile(path):
os.makdirs(path)
return 0
else:
return 1
except Exception, e:
print str(e)
return -1 def imageOps(func_name, image, des_path, file_name, times = 5):
funcMap = {"randomRotation": DataAugmentation.randomRotation,
"randomCrop":DataAugmentation.randomCrop,
"randomColor":DataAugmentation.randomColor,
"randomGaussian":DataAugmentation.randomGaussian
}
if funcMap.get(func_name) is None:
logger.error("%s is not exist" , func_name)
return -1 for _i in range(0,times,1):
new_image = funcMap[func_name](image)
DataAugmentation.saveImage(new_image,os.path.join(des_path,func_name + str(_i) + file_name)) opsList = {"randomRotation", "randomCrop", "randomColor", "randomGaussian"} def threadOPS(path,new_path):
#多线程处理事务
#param src_path:资源文件
#param des_path:目的地文件
#return: if os.path.isdir(path):
img_names = os.listdir(path)
else:
img_names = [path]
for img_name in img_names:
print img_name
tmp_img_name = os.path.join(path,img_name)
print tmp_img_name
if os.path.isdir(tmp_img_name):
if makeDir(os.path.join(new_path,img_name)) != -1:
threadOPS(tmp_img_name,os.path.join(new_path,img_name))
else:
print 'create new dir failure'
return -1
elif tmp_img_name.split('.')[1] != "DS_Store":
image = DataAugmentation.openImage(tmp_img_name)
threadImage = [0] * 5
_index = 0
for ops_name in opsList:
threadImage[_index] = threading.Thread(target=imageOps,args=(ops_name,image,new_path,img_name))
threadImage[_index].start()
_index += 1
time.sleep(0.2) if __name__ == '__main__':
threadOPS("C:\Users\Acheron\PycharmProjects\CNN\pic-image\\train\images","C:\Users\Acheron\PycharmProjects\CNN\pic-image\\train\\newimages")
数据增强实验
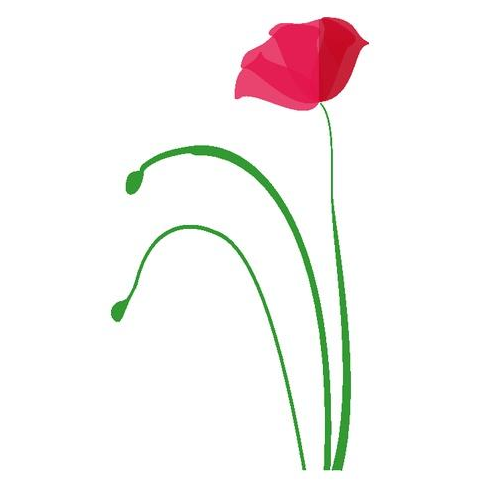
原始的待进行数据增强的图像:

1.对图像进行颜色抖动
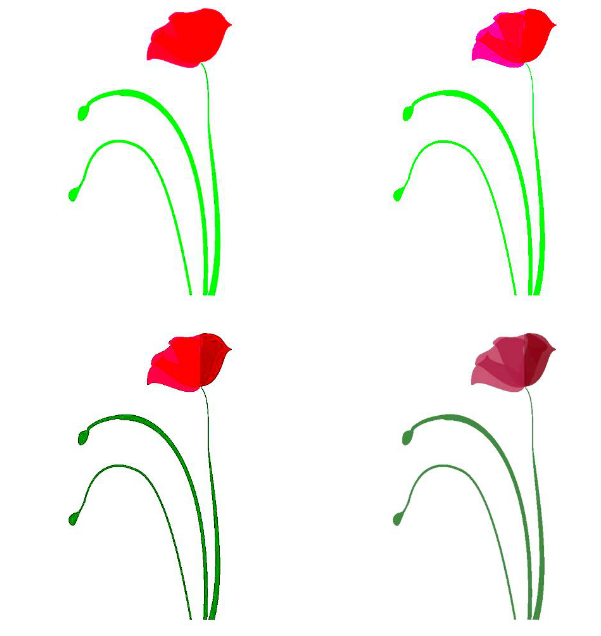
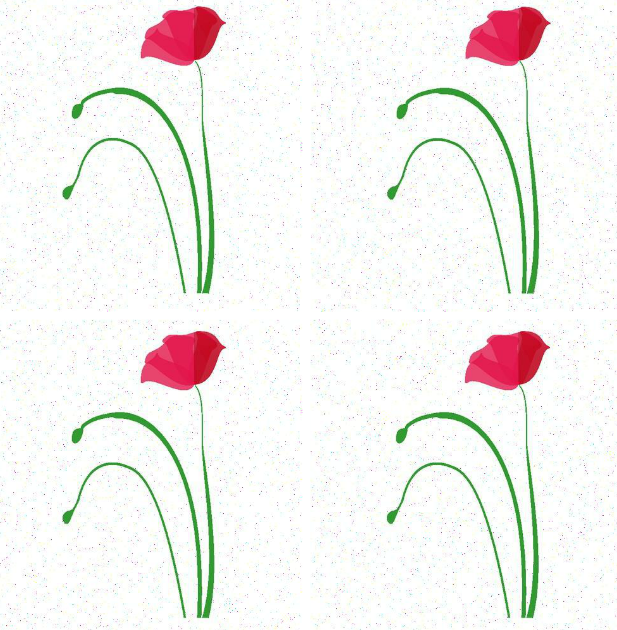
2.对图像进行高斯噪声处理
Deep Learning -- 数据增强的更多相关文章
- [基础]Deep Learning的基础概念
目录 DNN CNN DNN VS CNN Example 卷积的好处why convolution? DCNN 卷积核移动的步长 stride 激活函数 active function 通道 cha ...
- Generalizing from a Few Examples: A Survey on Few-Shot Learning 小样本学习最新综述 | 三大数据增强方法
目录 原文链接:小样本学习与智能前沿 01 Transforming Samples from Dtrain 02 Transforming Samples from a Weakly Labeled ...
- Deep Learning 16:用自编码器对数据进行降维_读论文“Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks”的笔记
前言 论文“Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks”是深度学习鼻祖hinton于2006年发表于<SCIENCE > ...
- Deep Learning 11_深度学习UFLDL教程:数据预处理(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
理论知识:UFLDL数据预处理和http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/04/20/3033149.html 数据预处理是深度学习中非常重要的一 ...
- Deep learning:三十四(用NN实现数据的降维)
数据降维的重要性就不必说了,而用NN(神经网络)来对数据进行大量的降维是从2006开始的,这起源于2006年science上的一篇文章:reducing the dimensionality of d ...
- 收藏:左路Deep Learning+右路Knowledge Graph,谷歌引爆大数据
发表于2013-01-18 11:35| 8827次阅读| 来源sina微博 条评论| 作者邓侃 数据分析智能算法机器学习大数据Google 摘要:文章来自邓侃的博客.数据革命迫在眉睫. 各大公司重兵 ...
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
CNN的发展史 上一篇回顾讲的是2006年Hinton他们的Science Paper,当时提到,2006年虽然Deep Learning的概念被提出来了,但是学术界的大家还是表示不服.当时有流传的段 ...
- Deep Learning(深度学习)学习笔记整理
申明:本文非笔者原创,原文转载自:http://www.sigvc.org/bbs/thread-2187-1-3.html 4.2.初级(浅层)特征表示 既然像素级的特征表示方法没有作用,那怎样的表 ...
- 【转载】Deep Learning(深度学习)学习笔记整理
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/8775360 一.概述 Artificial Intelligence,也就是人工智能,就像长生不老和星际漫 ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发中如遇到频繁的Http请求,取消之前已经发送的Http
主要精髓在于 第一点:不要initialize a new AFHTTPSessionManager object everytime 一定要把manager用成全局的 第二点:把请求返回的task对 ...
- 初探csrf学习笔记
以下是学习了对CSRF的理解,大家切勿作为标准,如有出错请告之! 严禁转载.不想拿自己刚学到的知识去[误人子弟]之所以写出来是让自己巩固和增加理解,他日对此文有不当之处自会修改. [00x1]csrf ...
- IPC之信号量
无名信号量 POSIX标准提出了有名信号量和无名信号量来同步进程和线程,而linux(2.6以前)只实现了无名信号量. sem_overview中有详细介绍:man 7 sem_overview. S ...
- poj3020 Antenna Placement 匈牙利算法求最小覆盖=最大匹配数(自身对应自身情况下要对半) 小圈圈圈点
/** 题目:poj3020 Antenna Placement 链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3020 题意: 给一个由'*'或者'o'组成的n*m大小的图,你可以用一个 ...
- SpringBoot 获取前端页面参数的集中方式总结
SpringBoot的一个好处就是通过注解可以轻松获取前端页面的参数,之后尅将参数经过一系列处理传送到后台数据库,前端时间正好用到.大致分为一下几种: 1.指定前端URL请求参数名称与方法名称一致,这 ...
- Matlab之合并音频
程序功能: 1.读入wav下的所有音频 2.每个音频截取前0.6秒 3.合并每个音频 clear all; cd = 'wav'; waveFiles = dir(fullfile(cd,'*.wav ...
- ASP.NET动态添加控件一例
第一次单击页面中有3个Label,第二次单击有6个,第三次单击有9个,也就是每次单击要在上次的状态下再添加3个. 我的方法是,可以通过Session来保存上次的状态,一种解法如下: Test.aspx ...
- 在系统重装后为什么ChemDraw用不了
作为一款非常受欢迎的化学绘图软件ChemDraw需要在满足运行条件的电脑上运行,但是一些用户发现自己在给自己的电脑重装系统之后,ChemDraw运行不了呢.导致ChemDraw用不了的原因比较多样,不 ...
- ChemDraw在苹果电脑上能不能用
很多ChemDraw 15.1 Pro用户都Windows操作系统用户,近年来随着苹果公司的影响力越来越大,使用苹果电脑的朋友越来越多.一些ChemDraw用户可能会使用苹果电脑,因此特别的关注在苹果 ...
- webpack 从入门到工程实践
from:https://www.jianshu.com/p/9349c30a6b3e?utm_campaign=maleskine&utm_content=note&utm_medi ...
