[Tensorflow] RNN - 04. Work with CNN for Text Classification
Ref: Combining CNN and RNN for spoken language identification
Ref: Convolutional Methods for Text
[1] CONVOLUTIONAL, LONG SHORT-TERM MEMORY, FULLY CONNECTED DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
[2] Efficient Character-level Document Classification by Combining Convolution and Recurrent Layers
结合此文,对sentiment prediction做进一步的性能提升。
一个近似的例子:https://github.com/LopezGG/NN_NER_tensorFlow/blob/master/network.py
#Embedding layer (is always built on CPU. There is bug that makes embedding fail on GPU)
with tf.device('/cpu:0'), tf.name_scope("char_embedding"):
#plus 1 becuase 0 is for unknown char
self.W_char = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([char_vocab_size+1, char_embedd_dim],-1,1),trainable=True, name="W_char")
self.char_embedding_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [char_vocab_size+1, char_embedd_dim])
char_embedding_init = self.W_char.assign(self.char_embedding_placeholder)
self.embedded_char = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W_char, self.input_x_char_flat,name="embedded_char") #shape [batch_size,max_char_per_word*sequence_length,char_embedd_dim]
self.embedded_char_dropout =tf.nn.dropout(self.embedded_char, self.dropout_keep_prob,name="embedded_char_dropout")
#Add CNN get filters and combine with word
with tf.name_scope("char_conv_maxPool"):
filter_shape = [filter_size, char_embedd_dim, num_filters]
W_conv = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(filter_shape, stddev=0.1), name="W_conv")
b_conv = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_filters]), name="b_conv") conv = tf.nn.conv1d(self.embedded_char_dropout,
W_conv,
stride=1,
padding="SAME",
name="conv") #will have dimensions [batch_size,out_width,num_filters] out_width is a function of max_words,filter_size and stride_size #(?, 3051, 20)
#out_width for same padding iwth stride 1 given by (max_char_per_word*sequence_length)
print("conv.get_Shape(): ",conv.get_shape())
# Apply nonlinearity TODO: Test without relu
#h = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b_conv,name="add bias")#does not change dimensions
h_expand = tf.expand_dims(conv, -1)
print("h_expand.get_Shape(): ",h_expand.get_shape())
pooled = tf.nn.max_pool(
h_expand,
#[batch, height, width, channels]
ksize=[1,sequence_length * max_char_per_word,1, 1], #On the batch size dimension and the channels dimension, ksize is 1 because we don't want to take the maximum over multiple examples, or over multiples channels.
strides=[1, max_char_per_word, 1, 1],
padding='SAME',
name="pooled")
#print("pooled.get_Shape(): ",pooled.get_shape())
#[batch_size,(max_char_per_word*sequence_length), num_filters, 1] --> [batch, sequence_length, num_filters] , same as word_embedding layer (?, 113, 20, 1) --> (?, 113, 20)
self.char_pool_flat = tf.reshape(pooled, [-1,sequence_length,num_filters],name="char_pool_flat")
#print("self.char_pool_flat.get_shape(): ",self.char_pool_flat.get_shape())
#[batch, sequence_length, word_embedd_dim+num_filters]
self.word_char_features = tf.concat([self.embedded_words, self.char_pool_flat], axis=2) #we mean that the feature with index 2 i/e num_filters is variable
#print("self.word_char_features.get_shape(): ",self.word_char_features.get_shape())
self.word_char_features_dropout =tf.nn.dropout(self.word_char_features, self.dropout_keep_prob,name="word_char_features_dropout")
Combinations of CNN and RNN
The general architecture of these combinations is a convolutional feature extractor applied on the input, then some recurrent network on top of the CNN’s output, then an optional fully connected layer on RNN’s output and finally a softmax layer.
The output of the CNN is a set of several channels (also known as feature maps). We can have separate GRUs acting on each channel (with or without weight sharing) as described in this picture (Left).
Another option is to interpret CNN’s output as a 3D-tensor and run a single GRU on 2D slices of that tensor, picture (Right).
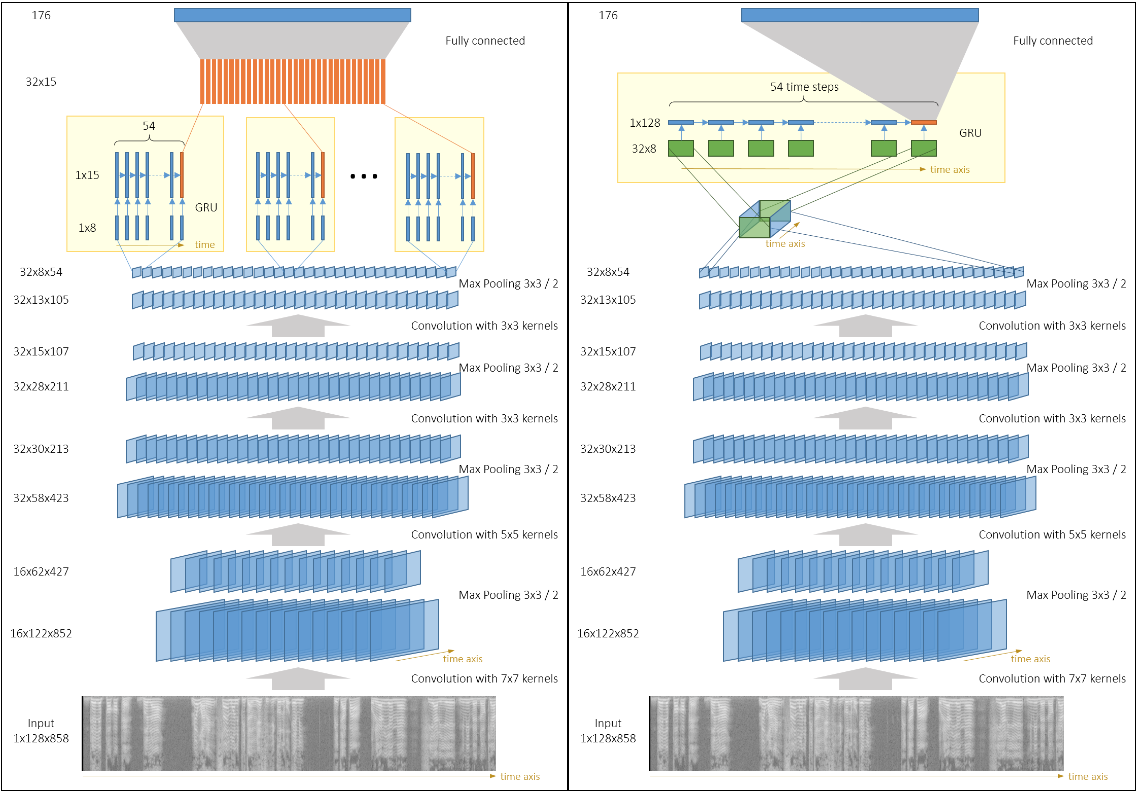
The latter option has more parameters,but the information from different channels is mixed inside the GRU, and it seems to improve performance. 【后者貌似好】
This architecture is similar to the one described in this paper[1] on speech recognition,
except that they also use some residual connections (“shortcuts”) from input to RNN and from CNN to fully connected layers.
It is interesting to note that recently it was shown that similar architectures work well for text classification[2].
| Network | Accuracy | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| tc_net_rnn | 92.4 | CNN consists of 3 convolutional blocks and outputs 32 channels of size 104x13. Each of these channels is fed to a separate GRU as a sequence of 104 vectors of size 13. The outputs of GRUs are combined and fed to a fully connected layer |
| tc_net_rnn_nodense | 91.94 | Same as above, except there is no fully connected layer on top of GRUs. Outputs of GRU are fed directly to the softmax layer |
| tc_net_rnn_shared | 96.96 | Same as above, but the 32 GRUs share weights. This helped to fight overfitting |
| tc_net_rnn_shared_pad | 98.11 | 4 convolutional blocks in CNN using pad=2 instead of ignore_broder=False(which enabled CuDNN and the training became much faster). The output of CNN is a set of 32 channels of size 54x8. 32 GRUs are applied (one for each channel) with shared weights and there is no fully connected layer |
| tc_net_deeprnn_shared_pad | 95.67 | 4 convolutional block as above, but 2-layer GRUs with shared weights are applied on CNN’s outputs. Overfitting became stronger because of this second layer |
| tc_net_shared_pad_augm | 98.68 | Same as tc_net_rnn_shared_pad, but the network randomly crops the input and takes 9s interval. The performance became a bit better due to this |
| tc_net_rnn_onernn | 99.2 | The outputs of a CNN with 4 convolutional blocks are grouped into a 32x54x8 3D-tensor and a single GRU runs on a sequence of 54 vectors of size 32*8 |
| tc_net_rnn_onernn_notimepool | 99.24 | Same as above, but the stride along the time axis is set to 1 in every pooling layer. Because of this the CNN outputs 32 channels of size 852x8 |
The second layer of GRU in this setup didn’t help due to the overfitting.
It seems that subsampling in the time dimension is not a good idea. The information that is lost during subsampling can be better used by the RNN.
In the paper on text classification[2] by Yijun Xiao and Kyunghyun Cho, the authors even suggest that maybe all pooling/subsampling layers can be replaced by recurrent layers.
训练技巧
These networks were trained using SGD with momentum only. The learning rate was set to 0.003 for around 10 epochs, then it was manually decreased to 0.001 and then to 0.0003. On average, it took 35 epochs to train these networks.
Ensembling
The best single model had 99.24% accuracy on the validation set. We had 33 predictions by all these models (there were more than one predictions for some models, taken after different epochs) and we just summed up the predicted probabilities and got 99.67% accuracy. Surprisingly, our other attempts of ensembling (e.g. majority voting, ensemble only on some subset of all models) didn’t give better results.
[Tensorflow] RNN - 04. Work with CNN for Text Classification的更多相关文章
- [转] Implementing a CNN for Text Classification in TensorFlow
Github上的一个开源项目,文档讲得极清晰 Github - https://github.com/dennybritz/cnn-text-classification-tf 原文- http:// ...
- Implementing a CNN for Text Classification in TensorFlow
参考: 1.Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks for NLP 2.Implementing a CNN for Text Classificati ...
- CNN tensorflow text classification CNN文本分类的例子
from:http://deeplearning.lipingyang.org/tensorflow-examples-text/ TensorFlow examples (text-based) T ...
- [Tensorflow] RNN - 01. Spam Prediction with BasicRNNCell
Ref: http://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/60780813 Ref: https://medium.com/@erikhallstrm/hell ...
- TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CRF 实现 sequence labeling 序列标注问题 源码下载
http://blog.csdn.net/scotfield_msn/article/details/60339415 在TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习下 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CR ...
- tensorflow rnn 最简单实现代码
tensorflow rnn 最简单实现代码 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import tensorflow as tf from te ...
- TensorFlow RNN MNIST字符识别演示快速了解TF RNN核心框架
TensorFlow RNN MNIST字符识别演示快速了解TF RNN核心框架 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4b0020f30102wv4l.html
- Ubuntu16.04下搜狗输入法、Sublime Text 3的安装
Ubuntu16.04下搜狗输入法.Sublime Text 3的安装 一.搜狗输入法 1. 安装中文语言 默认在Ubuntu16.04下是没有中文的,需要安装中文,在System Settings- ...
- 论文列表——text classification
https://blog.csdn.net/BitCs_zt/article/details/82938086 列出自己阅读的text classification论文的列表,以后有时间再整理相应的笔 ...
随机推荐
- Asp.Net Core 通过自定义中间件防止图片盗链的实例(转)
一.原理 要实现防盗链,我们就必须先理解盗链的实现原理,提到防盗链的实现原理就不得不从HTTP协议说起,在HTTP协议中,有一个表头字段叫referer,采用URL的格式来表示从哪儿链接到当前的网页或 ...
- canvas应用——将方形图片处理为圆形
上段时间在项目中需要将方形图片处理为圆形图片,你可能会说直接用css设置border-radius: 50%就可以了,但是项目中还要将此图片的圆形图片作为一部分利用canvas将其绘制到一张背景图上面 ...
- 如何在Windows 10上访问NFS的share
大致过程是: 1. 开启名为"Services for NFS"的Windows Feature. 2. 如果需要拥有写权限,需要修改注册表. 3. Mount即可. 具体步骤详见 ...
- WIN10平板系统 如何自定义分辨率,修改分辨率
从以下网址下载Intel网卡驱动,注意只要下载zip版本的(如果是exe版本的,双击将提示win10无法为此计算机验证正在安装的驱动程序,也包括你用驱动精灵这种软件,也会安装的时候由于这个问题装不上) ...
- Spark机器学习(10):ALS交替最小二乘算法
1. Alternating Least Square ALS(Alternating Least Square),交替最小二乘法.在机器学习中,特指使用最小二乘法的一种协同推荐算法.如下图所示,u表 ...
- pycharm调整代码长度分割线
1.File -> Settings -> Code Style -> Right margin (columns) 的值为80,大功告成. 2.具体设置的数值可以根据个人电脑 ...
- Linux下利用backtrace追踪函数调用堆栈以及定位段错误[转]
来源:Linux社区 作者:astrotycoon 一般察看函数运行时堆栈的方法是使用GDB(bt命令)之类的外部调试器,但是,有些时候为了分析程序的BUG,(主要针对长时间运行程序的分析),在程序 ...
- 基于CentOS搭建私有云服务
系统版本:CentOS 7.2 64 位操作系统 部署 XAMPP 服务 下载 XAMPP(XAMPP 是个集成了多个组件的开发环境,包括 Apache + MariaDB + PHP + Perl. ...
- Android Studio 常用快捷键 for mac
Android Studio 常用快捷键 for mac 查找/查看相关 ⌘O: 全局查找class类名<使用率非常高> ⌘F: 在当前编辑文件中查找<使用率非常高> | 对应 ...
- 解决zabbix的中文乱码
CentOS7.1 x64上下载了zabbix官方的rpm包,导入后使用yum安装了zabbix 3.2.6,但是启动zabbix server的时候报了个段错误的错,谷歌了一会儿,发现段错误不止一次 ...
