openstack--2--控制节点安装mysql和rabbitmq
生产中可以把mysql数据库单独安装到一台机器上,这里因为实验机器有限,就把mysql安装到了控制节点
其实openstack每个组件都可以安装到单独的机器上。
RabbitMQ介绍
RabbitMQ是一个消息队列产品
MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专用连接来链接它们。
消息传递指的是程序之间通过在消息中发送数据进行通信,而不是通过直接调用彼此来通信,直接调用通常是用于诸如远程过程调用的技术。排队指的是应用程序通过 队列来通信。
队列的使用除去了接收和发送应用程序同时执行的要求
MQ是消费-生产者模型的一个典型的代表,一端往消息队列中不断写入消息,而另一端则可以读取或者订阅队列中的消息。
消息队列让程序做到异步处理,而这种异步处理的方式大大的节省了服务器的请求响应时间,从而提高了系统的吞吐量。

安装和配置mariadb
大多数 OpenStack 服务使用 SQL 数据库来存储信息。 典型地,数据库运行在控制节点上。OpenStack 服务也支持其他 SQL 数据库,包括PostgreSQL
安装下面3个包。mariadb这里精确到版本号了,是因为最新版的(mariadb-server-10.1.18-3.el7.x86_64.rpm) 安装和一些lib文件有冲突
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install mariadb-5.5.52-1.el7.x86_64 -y
Package 1:mariadb-5.5.52-1.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install mariadb-server-5.5.52-1.el7.x86_64 -y
Package 1:mariadb-server-5.5.52-1.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install python2-PyMySQL -y
Package python2-PyMySQL-0.7.9-2.el7.noarch already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
# Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used.
# If you need to run mysqld under a different user or group,
# customize your systemd unit file for mariadb according to the
# instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd [mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
pid-file=/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid #
# include all files from the config directory
#
!includedir /etc/my.cnf.d [root@linux-node1 ~]#
default-storage-engine = innodb 默认存储引擎innodb
innodb_file_per_table 设置独享的表空间,如果不设置,会是共享表空间
collation-server = utf8_general_ci 校对规则
init-connect = 'SET NAMES utf8' 链接字符集
character-set-server = utf8 数据库建库字符集
max_connections = 4096 最大连接数
bind-address mysql监听地址
[root@linux-node1 ~]# touch /etc/my.cnf.d/openstack.cnf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/openstack.cnf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat /etc/my.cnf.d/openstack.cnf
[mysqld]
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
default-storage-engine = innodb
innodb_file_per_table
max_connections = 4096
collation-server = utf8_general_ci
character-set-server = utf8
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl enable mariadb.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -lntp | grep 3306
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1965/mysqld
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
为了保证数据库服务的安全性,运行mysql_secure_installation脚本,进行一些安全方面的配置,删除匿名用户,删除test库,设置root密码等
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mysql_secure_installation NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation. Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB!
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
Openstack组件建库和授权
建库和授权,之前说过,除了Horizon,其它组件都用到了数据库。 可以在安装响应组件之前建库和授权。
这里我们提前建好,复制下面语句,直接在命令行执行即可,注意root密码根据自己的密码。
这里M版本的openstack,除了新建nova库,还需要新建一个nova_api库。
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "CREATE DATABASE keystone;"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON keystone.* TO 'keystone'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'keystone';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON keystone.* TO 'keystone'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'keystone';" mysql -u root -p123456 -e "CREATE DATABASE glance;"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON glance.* TO 'glance'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'glance';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON glance.* TO 'glance'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'glance';" mysql -u root -p123456 -e "CREATE DATABASE nova;"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON nova.* TO 'nova'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'nova';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON nova.* TO 'nova'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'nova';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "CREATE DATABASE nova_api;"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON nova_api.* TO 'nova'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'nova';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON nova_api.* TO 'nova'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'nova';" mysql -u root -p123456 -e "CREATE DATABASE neutron;"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON neutron.* TO 'neutron'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'neutron';"
mysql -u root -p123456 -e "GRANT ALL ON neutron.* TO 'neutron'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'neutron';"
检查库和用户
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e "show databases ;" |egrep "glance|keystone|neutron|nova|nova_api"
glance
keystone
neutron
nova
nova_api
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e "select user,host from mysql.user ;" |egrep "cinder|glance|keystone|neutron|nova"
glance %
keystone %
neutron %
nova %
glance localhost
keystone localhost
neutron localhost
nova localhost
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
OpenStack 使用 message queue 协调操作和各服务的状态信息。消息队列服务一般运行在控制节点上。OpenStack支持好几种消息队列服务包括 RabbitMQ, Qpid, 和 ZeroMQ。
不过,大多数发行版本的OpenStack包支持特定的消息队列服务。本指南安装 RabbitMQ 消息队列服务,因为大部分发行版本都支持它。
1. 安装包:
yum install rabbitmq-server -y
2. 启动消息队列服务并将其配置为随系统启动:
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server.service
systemctl start rabbitmq-server.service
3. 添加 openstack 用户,并设置密码(这里我实验环境设置密码也是openstack):
rabbitmqctl add_user openstack openstack
4. 给openstack用户配置写和读权限:
rabbitmqctl set_permissions openstack ".*" ".*" ".*"
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl enable rabbitmq-server.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/rabbitmq-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/rabbitmq-server.service.
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start rabbitmq-server.service
[root@linux-node1 ~]# rabbitmqctl add_user openstack openstack
Creating user "openstack" ...
[root@linux-node1 ~]# rabbitmqctl set_permissions openstack ".*" ".*" ".*"
Setting permissions for user "openstack" in vhost "/" ...
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2607/beam.smp
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1580/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4369 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1656/dnsmasq
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1158/sshd
tcp6 0 0 :::5672 :::* LISTEN 2607/beam.smp
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1158/sshd
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
rabbitmq默认带了个web的插件,可以通过web来看rabbit的状态
它有下面这么多插件
列出rabbitmq的插件:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# rabbitmq-plugins list
Configured: E = explicitly enabled; e = implicitly enabled
| Status: * = running on rabbit@linux-node1
|/
[ ] amqp_client 3.6.5
[ ] cowboy 1.0.3
[ ] cowlib 1.0.1
[ ] mochiweb 2.13.1
[ ] rabbitmq_amqp1_0 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_auth_backend_ldap 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_auth_mechanism_ssl 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_consistent_hash_exchange 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_event_exchange 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_federation 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_federation_management 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_jms_topic_exchange 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_management 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_management_agent 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_management_visualiser 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_mqtt 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_recent_history_exchange 1.2.1
[ ] rabbitmq_sharding 0.1.0
[ ] rabbitmq_shovel 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_shovel_management 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_stomp 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_top 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_tracing 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_trust_store 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_web_dispatch 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_web_stomp 3.6.5
[ ] rabbitmq_web_stomp_examples 3.6.5
[ ] sockjs 0.3.4
[ ] webmachine 1.10.3
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
开机自启动rabbitmq的管理插件(这些官方文档没有):
[root@linux-node1 ~]# rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
The following plugins have been enabled:
mochiweb
webmachine
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
amqp_client
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_management Applying plugin configuration to rabbit@linux-node1... started 6 plugins.
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart rabbitmq-server.service
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3455/beam.smp
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1965/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4369 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1337/dnsmasq
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1153/sshd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3455/beam.smp
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1277/master
tcp6 0 0 :::5672 :::* LISTEN 3455/beam.smp
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1153/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1277/master
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
用户名 guest 密码 guest
现在使用openstack用户是无法登录的
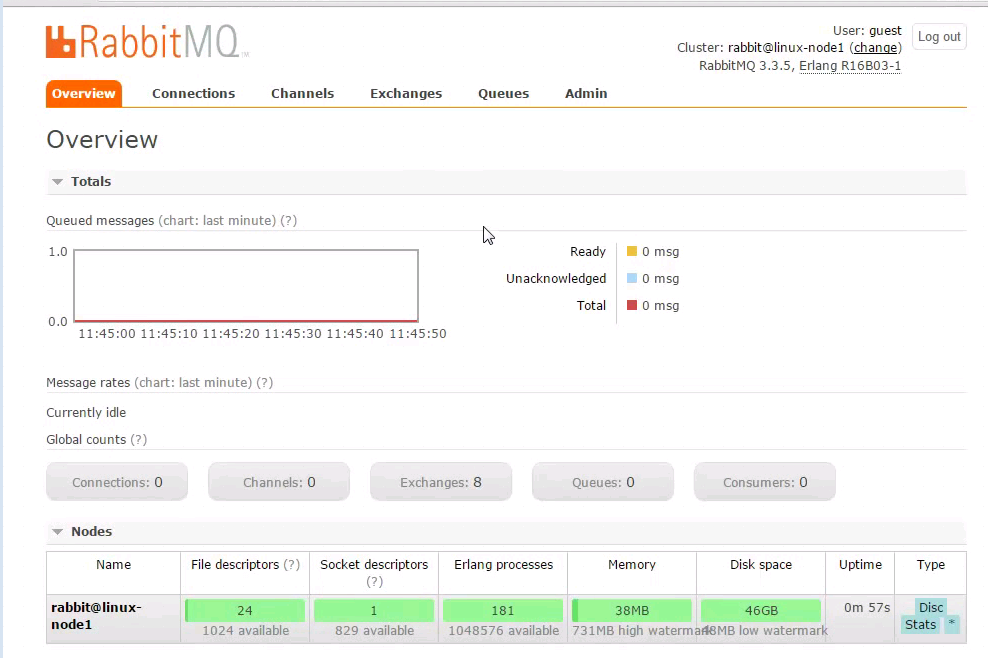

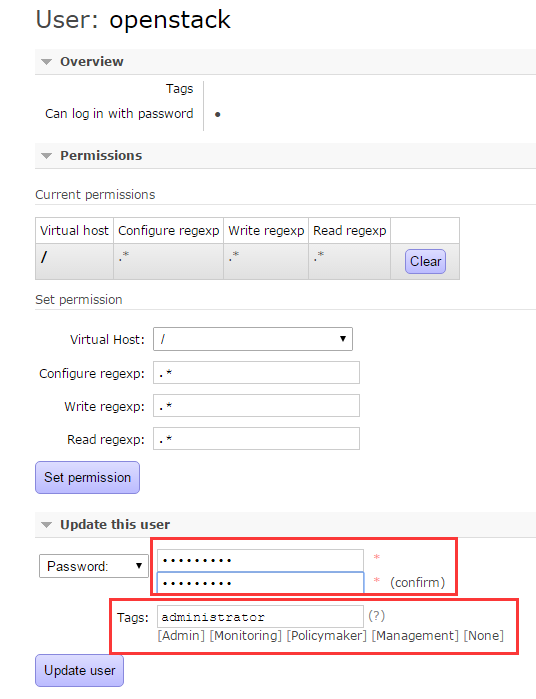
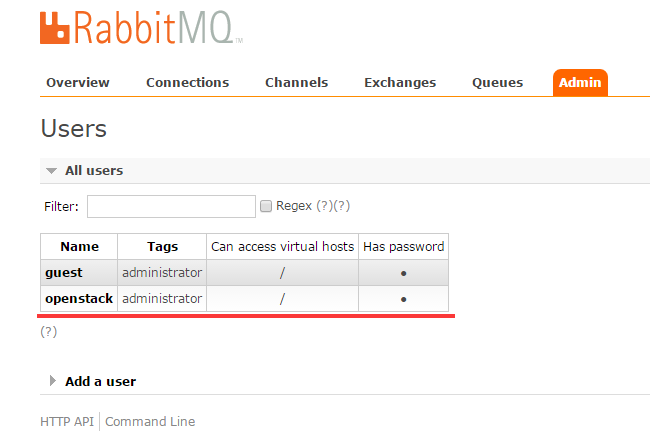


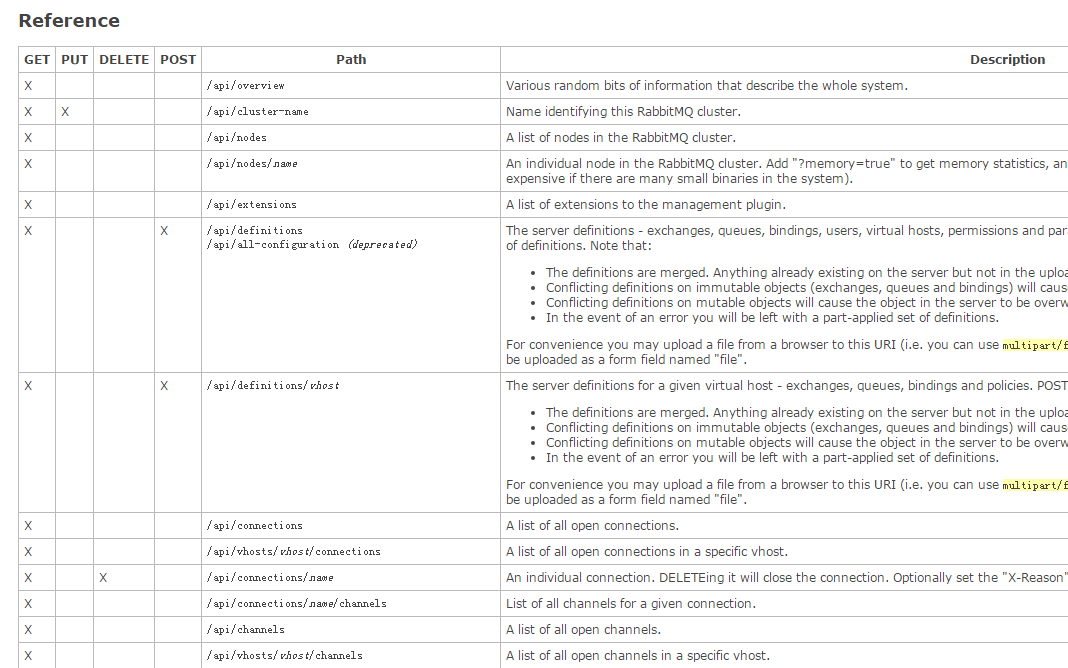
点击进去,看到如下所示,暂时和我们的实验无关。就不深入研究它了
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install ntpdate -y
[root@linux-node1 ~]# ntpdate time1.aliyun.com
17 Feb 16:32:15 ntpdate[3951]: adjust time server 115.28.122.198 offset 0.010747 sec
[root@linux-node1 ~]# ntpdate time1.aliyun.com
17 Feb 16:32:28 ntpdate[3962]: adjust time server 115.28.122.198 offset 0.007115 sec
[root@linux-node1 ~]# date
Fri Feb 17 16:32:29 CST 2017
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
openstack--2--控制节点安装mysql和rabbitmq的更多相关文章
- openstack grizzly版cloud控制节点安装
openstack-ubuntu-create 参考官方文档 三个节点:cloud :控制节点内网:10.10.10.10外网:172.16.56.252 network:网络节点内网:10.10.1 ...
- OpenStack之三: 安装MySQL,rabbitmq, memcached
官网地址:https://docs.openstack.org/install-guide/environment-sql-database-rdo.html #:安装mysql [root@mysq ...
- 安装Rocky版OpenStack 1控制节点+1计算节点环境部署脚本
在上一篇文章中叙述了具体的安装部署过程,在这里把相应的部署脚本写出来,供大家参考: 一.执行部署的setup.sh脚本: #!/bin/bash ########################### ...
- 脚本安装Rocky版OpenStack 1控制节点+1计算节点环境部署
视频安装指南请访问: http://39.96.203.138/wordpress/document/%E8%84%9A%E6%9C%AC%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85rocky%E7%89%8 ...
- openstack的控制节点部署
openstack的控制节点部署 主要是使用了本地安装的那个镜像. 会出现几个问题, 1.重启服务无法启动. 2.环境变量无法正确配置可以自己配置
- Openstak(M版)控制节点安装
#############修改hosts文件 # controller10.0.0.11 controller# compute110.0.0.31 compute1# block110.0.0.41 ...
- Kubernetes控制节点安装配置
#环境安装Centos 7 Linux release 7.3.1611网络: 互通配置主机名设置各个服务器的主机名hosts#查找kubernetes支持的docker版本Kubernetes v1 ...
- openstack ocata版(脚本)控制节点安装
一.初始化环境: 1.更换yum源: yum install -y wget mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS- ...
- CentOS7安装OpenStack(Rocky版)-01.控制节点的系统环境准备
分享一下Rocky版本的OpenStack安装管理经验: OpenStack每半年左右更新一版,目前是版本是201808月发布的版本-R版(Rocky),目前版本安装方法优化较好,不过依然是比较复杂 ...
随机推荐
- MATLAB中mexFunction函数的接口规范(转)
reference:https://www.cnblogs.com/haoyul/p/5606720.html https://www.cnblogs.com/zeakey/p/3984733.htm ...
- MyEclipse使用教程:在Web项目中使用Web片段
MyEclipse 在线订购年终抄底促销!火爆开抢>> MyEclipse最新版下载 本教程向用户展示了使用关联的Web项目创建Web片段项目的机制.用户还可以获得要检查的示例项目.在本教 ...
- 组队项目——黄金点(叶雨&王浩)
代码来源:自己编写 运行环境:win10 编译软件:VC++6.0 使用语言:C语言 功能:可多次运行,由用户决定退出与否,可以记录玩家的姓名与分数并显示. BUG:暂未发现 GitHub地址:htt ...
- 点击li ,父辈出现; 子级,子辈不出现. prevUntil ---> 前面多个, 截止到 截止元素 , prev([expr]) --> 前面一个.
要求: 1. 点击第一级 [1知识点] 的时候, [1知识点] 前有 圆圈. 点击 第二级 [1-1知识点, 1-2知识点, 1-3知识点] 时 , [1知识点]出现 圆圈. 2. 点击 第一级 ...
- django面试四
Django的优点 功能完善.要素齐全:自带大量常用工具和框架(比如分页,auth,权限管理), 适合快速开发企业级网站. 完善的文档:经过十多年的发展和完善,Django有广泛的实践案例和完善的在线 ...
- Day9作业及默写
1,整理函数相关知识点,写博客. 2,写函数,检查获取传入列表或元组对象的所有奇数位索引对应的元素,并将其作为新列表返回给调用者. def func(obj): return obj[1::2] 3, ...
- Java学习笔记11(this,super)
this在构造方法间的使用, public class Person { private String name; private int age; public Person() { //this( ...
- python day03--字符串
一.字符串 1.索引 s1 = "python最牛B" S1[0]第0个,从零开始算 s1[8]“B” 2.切片 语法: str[start: end]规则: 顾头不顾腚, 从st ...
- natapp 穿透访问 vue项目 Invalid Host header
由于要近期开发微信小程序,所以今天了解了一下这个netapp 内网映射这个东西,所以一开始自己就在网上看,然后想把环境部署起来,参考https://natapp.cn/ ,看了一分钟教程以后,然后自己 ...
- spring-dao.xml配置问题(一)
问题描述:对mapper扫描器进行配置时,sqlSessionFactory依赖报错 <!-- 配置sqlSessionFactory --> <bean id="sqlS ...
