sharding-jdbc读写分离原理解读
原帖地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yanyan19880509/article/details/78170233
前言
很多时候,为了应付DB的高并发读写,我们会采用读写分离技术。读写分离指的是利用数据库主从技术(把数据复制到多个节点中),分散读多个库以支持高并发的读,而写只在master库上。DB的主从技术只负责对数据进行复制和同步,而读写分离技术需要业务应用自身去实现。sharding-jdbc通过简单的开发,可以方便的实现读写分离技术。本篇主要介绍其实现的原理。
sharding-jdbc读写分离特性说明
sharding-jdbc官方对其支持的读写分离技术进行了说明:
支持项
提供了一主多从的读写分离配置,可独立使用,也可配合分库分表使用。
同个调用线程,执行多条语句,其中一旦发现有非读操作,后续所有读操作均从主库读取。
Spring命名空间。
基于Hint的强制主库路由。
不支持范围
主库和从库的数据同步。
主库和从库的数据同步延迟导致的数据不一致。
主库双写或多写。
简单说明
sharding-jdbc实现读写分离技术的思路比较简洁,不支持类似主库双写或多写这样的特性,但目前来看,已经可以满足一般的业务需求了。
读写分离实现demo
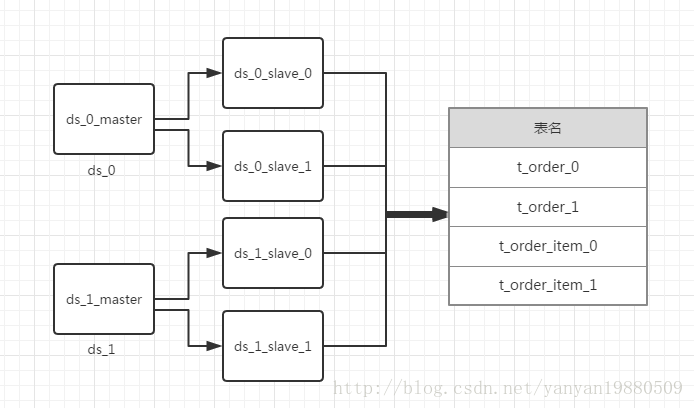
库和表的设计结构如下:
简单的java代码示例:
public final class MasterSlaveMain {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = getShardingDataSource();
printSimpleSelect(dataSource);
}
private static void printSimpleSelect(final DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT i.* FROM t_order o JOIN t_order_item i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.user_id=? AND o.order_id=?";
try (
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 1001);
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println(rs.getInt(2));
System.out.println(rs.getInt(3));
}
}
}
}
private static ShardingDataSource getShardingDataSource() throws SQLException {
DataSourceRule dataSourceRule = new DataSourceRule(createDataSourceMap());
TableRule orderTableRule = TableRule.builder("t_order").actualTables(Arrays.asList("t_order_0", "t_order_1")).dataSourceRule(dataSourceRule).build();
TableRule orderItemTableRule = TableRule.builder("t_order_item").actualTables(Arrays.asList("t_order_item_0", "t_order_item_1")).dataSourceRule(dataSourceRule).build();
ShardingRule shardingRule = ShardingRule.builder().dataSourceRule(dataSourceRule).tableRules(Arrays.asList(orderTableRule, orderItemTableRule))
.databaseShardingStrategy(new DatabaseShardingStrategy("user_id", new ModuloDatabaseShardingAlgorithm()))
.tableShardingStrategy(new TableShardingStrategy("order_id", new ModuloTableShardingAlgorithm())).build();
return new ShardingDataSource(shardingRule);
}
private static Map<String, DataSource> createDataSourceMap() throws SQLException {
Map<String, DataSource> result = new HashMap<>(2, 1);
Map<String, DataSource> slaveDataSourceMap1 = new HashMap<>(2, 1);
slaveDataSourceMap1.put("ds_0_slave_0", createDataSource("ds_0_slave_0"));
slaveDataSourceMap1.put("ds_0_slave_1", createDataSource("ds_0_slave_1"));
result.put("ds_0", MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory.createDataSource("ds_0", "ds_0_master", createDataSource("ds_0_master"), slaveDataSourceMap1));
Map<String, DataSource> slaveDataSourceMap2 = new HashMap<>(2, 1);
slaveDataSourceMap2.put("ds_1_slave_0", createDataSource("ds_1_slave_0"));
slaveDataSourceMap2.put("ds_1_slave_1", createDataSource("ds_1_slave_1"));
result.put("ds_1", MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory.createDataSource("ds_1", "ds_1_master", createDataSource("ds_1_master"), slaveDataSourceMap2));
return result;
}
private static DataSource createDataSource(final String dataSourceName) {
BasicDataSource result = new BasicDataSource();
result.setDriverClassName(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getName());
result.setUrl(String.format("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/%s", dataSourceName));
result.setUsername("root");
result.setPassword("123456");
return result;
}
} private static DataSource createDataSource(final String dataSourceName) {
BasicDataSource result = new BasicDataSource();
result.setDriverClassName(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getName());
result.setUrl(String.format("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/%s", dataSourceName));
result.setUsername("root");
result.setPassword("123456");
return result;
}
}读写分离实现原理
一般我们是这样来执行sql语句的:
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeQuery();这是利用原生jdbc操作数据库查询语句的一般流程,获取一个连接,然后生成Statement,最后再执行查询。那么sharding-jdbc是在哪一块进行扩展从而实现读写分离的呢?
想一下,想要实现读写分离,必然会涉及到多个底层的Connection,从而构造出不同连接下的Statement语句,而很多第三方软件,如Spring,为了实现事务,调用dataSource.getConnection()之后,在一次请求过程中,可能就不会再次调用getConnection方法了,所以在dataSource.getConnection中做读写扩展是不可取的。为了更好的说明问题,看下面的例子:
Connection conn = getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
preparedStatement1.executeQuery();
Connection conn2 = getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = conn2.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement2.executeUpdate();一次请求过程中,为了实现事务,一般的做法是当线程第一次调用getConnection方法时,获取一个底层连接,然后存储到ThreadLocal变量中去,下次就直接在ThreadLocal中获取了。为了实现一个事务中,针对一个数据源,既可能获取到主库连接,也可能获取到从库连接,还能够切换,sharding-jdbc在PreparedStatement(实际上为ShardingPreparedStatement)的executeXX层进行了主从库的连接处理。
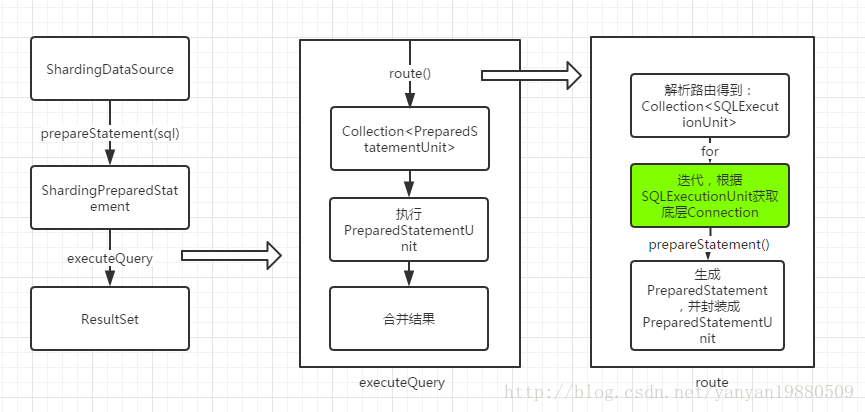
下图为sharding-jdbc执行的部分流程:
sharding-jdbc使用ShardingPreparedStatement来替代PreparedStatement,在执行ShardingPreparedStatement的executeXX方法时,通过路由计算,得到PreparedStatementUnit单元列表,然后执行后合并结果返回,而PreparedStatementUnit只不过封装了原生的PreparedStatement。读写分离最关键的地方在上图标绿色的地方,也就是生成PreparedStatement的地方。
在使用SQLEcecutionUnit转换为PreparedStatement的时候,有一个重要的步骤就是必须先获取Connection,源码如下:
public Connection getConnection(final String dataSourceName, final SQLType sqlType) throws SQLException {
if (getCachedConnections().containsKey(dataSourceName)) {
return getCachedConnections().get(dataSourceName);
}
DataSource dataSource = shardingContext.getShardingRule().getDataSourceRule().getDataSource(dataSourceName);
Preconditions.checkState(null != dataSource, "Missing the rule of %s in DataSourceRule", dataSourceName);
String realDataSourceName;
if (dataSource instanceof MasterSlaveDataSource) {
NamedDataSource namedDataSource = ((MasterSlaveDataSource) dataSource).getDataSource(sqlType);
realDataSourceName = namedDataSource.getName();
if (getCachedConnections().containsKey(realDataSourceName)) {
return getCachedConnections().get(realDataSourceName);
}
dataSource = namedDataSource.getDataSource();
} else {
realDataSourceName = dataSourceName;
}
Connection result = dataSource.getConnection();
getCachedConnections().put(realDataSourceName, result);
replayMethodsInvocation(result);
return result;
}如果发现数据源对象为MasterSlaveDataSource类型,则会使用如下方式获取真正的数据源:
public NamedDataSource getDataSource(final SQLType sqlType) {
if (isMasterRoute(sqlType)) {
DML_FLAG.set(true);
return new NamedDataSource(masterDataSourceName, masterDataSource);
}
String selectedSourceName = masterSlaveLoadBalanceStrategy.getDataSource(name, masterDataSourceName, new ArrayList<>(slaveDataSources.keySet()));
DataSource selectedSource = selectedSourceName.equals(masterDataSourceName) ? masterDataSource : slaveDataSources.get(selectedSourceName);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(selectedSource, "");
return new NamedDataSource(selectedSourceName, selectedSource);
}
private static boolean isMasterRoute(final SQLType sqlType) {
return SQLType.DQL != sqlType || DML_FLAG.get() || HintManagerHolder.isMasterRouteOnly();
}有三种情况会认为一定要走主库:
1. 不是查询类型的语句,比如更新字段
2. DML_FLAG变量为true的时候
3. 强制Hint方式走主库
当执行了更新语句的时候,isMasterRoute()==true,这时候,Connection为主库的连接,并且引擎会强制设置DML_FLAG的值为true,这样一个请求后续的所有读操作都会走主库。
有些时候,我们想强制走主库,这时候在请求最开始执行Hint操作即可,如下所示:
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly();在获取数据源的时候,如果走的是从库,会使用从库负载均衡算法类进行处理,该类的实现比较简单,如下所示:
public final class RoundRobinMasterSlaveLoadBalanceStrategy implements MasterSlaveLoadBalanceStrategy {
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, AtomicInteger> COUNT_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public String getDataSource(final String name, final String masterDataSourceName, final List<String> slaveDataSourceNames) {
AtomicInteger count = COUNT_MAP.containsKey(name) ? COUNT_MAP.get(name) : new AtomicInteger(0);
COUNT_MAP.putIfAbsent(name, count);
count.compareAndSet(slaveDataSourceNames.size(), 0);
return slaveDataSourceNames.get(count.getAndIncrement() % slaveDataSourceNames.size());
}
}其实就是一个简单的轮循机制进行从库的负载均衡。
总结
sharding-jdbc进行主从读写分离的特性实现比较简洁易懂,对spring这种上层框架而言是无感知的,而且由于它是在路由得到SQLExecutionUtil后再处理的,所以使用了读写分离特性,可以同时使用分库分表。
参考
sharding-jdbc官方文档和demo
sharding-jdbc读写分离原理解读的更多相关文章
- Spring boot项目集成Sharding Jdbc
环境 jdk:1.8 framework: spring boot, sharding jdbc database: MySQL 搭建步骤 在pom 中加入sharding 依赖 <depend ...
- MySQL - 主从复制及读写分离原理
1.MySQL主从复制与读写分离原理 首先,我们看一个图: 影响MySQL-A数据库的操作,在数据库执行后,都会写入本地的日志系统A中. 假设,实时的将变化了的日志系统中的数据库事件操作,在MYSQL ...
- [转载]JDBC读写Oracle的CLOB、BLOB
JDBC读写Oracle10g的CLOB.BLOB http://lavasoft.blog.51cto.com/62575/321882/ 在Oracle中存取BLOB对象实现文件的上传和下载 ht ...
- JavaEE JDBC 读写LOB大对象
JDBC 读写LOB大对象 @author ixenos LOB 除了数字.字符串和日期之外,许多数据库还可以存储大对象,例如图片或其他数据, 在SQL中,二进制(字节型)大对象称为BLOB,字符型大 ...
- JDBC读写MySQL的大字段数据
JDBC读写MySQL的大字段数据 不管你是新手还是老手,大字段数据的操作常常令你感到很头痛.因为大字段有些特殊,不同数据库处理的方式不一样,大字段的操作常常是以流的方式 来处理的.而非一般的字段 ...
- sharding demo 读写分离 U (分库分表 & 不分库只分表)
application-sharding.yml sharding: jdbc: datasource: names: ds0,ds1,dsx,dsy ds0: type: com.zaxxer.hi ...
- sharding jdbc(sphere) 3.1.0 spring boot配置
sharding jdbc 2.x系列详解参见https://www.cnblogs.com/zhjh256/p/9221634.html. 最近将sharding jdbc的配置从xml切换到了sp ...
- Sharding JDBC整合SpringBoot 2.x 和 MyBatis Plus 进行分库分表
Sharding JDBC整合SpringBoot 2.x 和 MyBatis Plus 进行分库分表 交易所流水表的单表数据量已经过亿,选用Sharding-JDBC进行分库分表.MyBatis-P ...
- spring boot:配置shardingsphere(sharding jdbc)使用druid数据源(druid 1.1.23 / sharding-jdbc 4.1.1 / mybatis / spring boot 2.3.3)
一,为什么要使用druid数据源? 1,druid的优点 Druid是阿里巴巴开发的号称为监控而生的数据库连接池 它的优点包括: 可以监控数据库访问性能 SQL执行日志 SQL防火墙 但spring ...
随机推荐
- 利用mysql行级锁创建数据库主键id
存储函数: CREATE FUNCTION `getSerialNo`(`serialName` VARCHAR(50), `skip` INT) RETURNS bigint(20) COMMENT ...
- 小文笔记 - phantomjs
小文笔记 - phantomjs 视频推荐: http://www.intalesson.com/compedium/phantom 2017-05-13 第一节:安装 Windows安装: 下载解压 ...
- python学习 day07打卡 文件操作
本节主要内容: 初识文件操作 只读(r,rb) 只读(w,wb) 追加(a,ab) r+读写 w+写读 a+追加写读 其他操作方法 文件的修改以及另一种打开文件句柄的方法 一. 初识文件操作 使用py ...
- 【BZOJ】3295: [Cqoi2011]动态逆序对
题目链接:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3295 mamaya,弱鸡xrdog终于会写树套树啦.... 将树状数组中每一个节点看成一棵 ...
- 《深入理解JVM虚拟机》读书笔记
前言:<深入理解JVM虚拟机>是JAVA的经典著作之一,因为内容更偏向底层,所以之前一直没有好好的阅读过.最近因为刚好有空,又有了新目标.所以打算和<构架师的12项修炼>一起看 ...
- 《剑指offer》第六十七题(把字符串转换成整数)
// 面试题67:把字符串转换成整数 // 题目:请你写一个函数StrToInt,实现把字符串转换成整数这个功能.当然,不 // 能使用atoi或者其他类似的库函数. #include <ios ...
- (转)C# 之泛型详解
什么是泛型 我们在编写程序时,经常遇到两个模块的功能非常相似,只是一个是处理int数据,另一个是处理string数据,或者其他自定义的数据类型,但我们没有办法,只能分别写多个方法处理每个数据类型,因为 ...
- 雷林鹏分享:现实生活中的 XML
现实生活中的 XML 如何使用 XML 来交换信息的一些实例. 实例:XML 新闻 XMLNews 是用于交换新闻和其他信息的规范. 对新闻的供求双方来说,通过使用这种标准,可以使各种类型的新闻信息通 ...
- p1468 Party Lamps
就是模拟.同一个开关按2下相当于没按,那么,如果一共按0下,就是没按,按1下就是4个开关的1个,按2下可能相当于实际按了0下或按2下,按3下实际按了1下或3下,之后如果是奇数,相当于按1或3下,偶数相 ...
- Nginx安装与使用 及在redhat 中的简单安装方式
首先说下在redhat中的安装方法, 正常安装nginx 需要安装很多的依赖,最后再安装nginx,而且很容易出错. 在nginx官方上有这么一段描述: Pre-Built Packages for ...