Flink学习笔记:Operators串烧
本文为《Flink大数据项目实战》学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程:
Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz
1. DataStream Transformation
1.1 DataStream转换关系
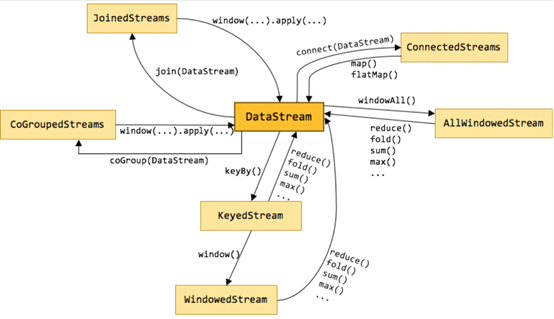
上图标识了DataStream不同形态直接的转换关系,也可以看出DataStream主要包含以下几类:
1.keyby就是按照指定的key分组
2.window是一种特殊的分组(基于时间)
3.coGroup
4.join Join是cogroup 的特例
5.Connect就是松散联盟,类似于英联邦
1.2 DataStream
DataStream 是 Flink 流处理 API 中最核心的数据结构。它代表了一个运行在多个分区上的并行流。
一个 DataStream 可以从 StreamExecutionEnvironment 通过env.addSource(SourceFunction) 获得。
1.3 map&flatMap
含义:数据映射(1进1出和1进n出)
转换关系:DataStream → DataStream
使用场景:
ETL时删减计算过程中不需要的字段
案例1:
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Long> input=env.generateSequence(0,10);
DataStream plusOne=input.map(new MapFunction<Long, Long>() {
@Override
public Long map(Long value) throws Exception {
System.out.println("--------------------"+value);
return value+1;
}
});
plusOne.print();
env.execute();
}
}
案例2:
public class TestFlatmap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<String> input=env.fromElements(WORDS);
DataStream<String> wordStream=input.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
String[] tokens = value.toLowerCase().split("\\W+");
for (String token : tokens) {
if (token.length() > 0) {
out.collect(token);
}
}
}
});
wordStream.print();
env.execute();
}
public static final String[] WORDS = new String[] {
"To be, or not to be,--that is the question:--",
"Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer",
"The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune",
"And by opposing end them?--To die,--to sleep,--",
"Be all my sins remember'd."
};
}
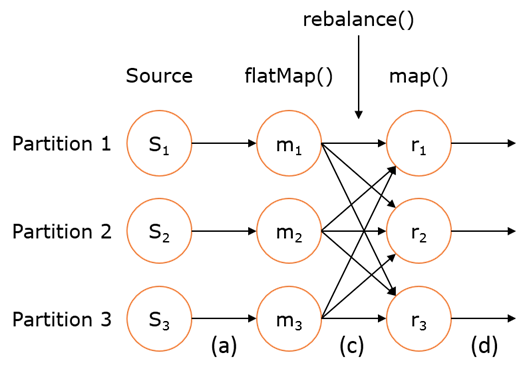
如右上图所示,DataStream 各个算子会并行运行,算子之间是数据流分区。如 Source 的第一个并行实例(S1)和 flatMap() 的第一个并行实例(m1)之间就是一个数据流分区。而在 flatMap() 和 map() 之间由于加了 rebalance(),它们之间的数据流分区就有3个子分区(m1的数据流向3个map()实例)。这与 Apache Kafka 是很类似的,把流想象成 Kafka Topic,而一个流分区就表示一个 Topic Partition,流的目标并行算子实例就是 Kafka Consumers。
1.4 filter
含义:数据筛选(满足条件event的被筛选出来进行后续处理),根据FliterFunction返回的布尔值来判断是否保留元素,true为保留,false则丢弃
转换关系: DataStream → DataStream
使用场景:
过滤脏数据、数据清洗等
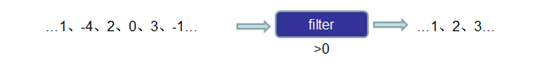
案例:
public class TestFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Long> input=env.generateSequence(-5,5);
input.filter(new FilterFunction<Long>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(Long value) throws Exception {
return value>0;
}
}).print();
env.execute();
}
}
1.5 keyBy
含义:
根据指定的key进行分组(逻辑上把DataStream分成若干不相交的分区,key一样的event会被划分到相同的partition,内部采用hash分区来实现)
转换关系: DataStream → KeyedStream
限制:
1.可能会出现数据倾斜,可根据实际情况结合物理分区来解决(后面马上会讲到)
2.Key的类型限制:
1)不能是没有覆盖hashCode方法的POJO
2)不能是数组
使用场景:
1.分组(类比SQL中的分组
案例:
public class TestKeyBy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//统计各班语文成绩最高分是谁
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>> input=env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPT);
KeyedStream<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>,Tuple> keyedStream = input.keyBy("f0");
keyedStream.maxBy("f3").print();
env.execute();
}
public static final Tuple4[] TRANSCRIPT = new Tuple4[] {
Tuple4.of("class1","张三","语文",100),
Tuple4.of("class1","李四","语文",78),
Tuple4.of("class1","王五","语文",99),
Tuple4.of("class2","赵六","语文",81),
Tuple4.of("class2","钱七","语文",59),
Tuple4.of("class2","马二","语文",97)
};
}
1.6 KeyedStream
KeyedStream用来表示根据指定的key进行分组的数据流。
一个KeyedStream可以通过调用DataStream.keyBy()来获得。
在KeyedStream上进行任何transformation都将转变回DataStream。
在实现中,KeyedStream是把key的信息写入到了transformation中。
每个event只能访问所属key的状态,其上的聚合函数可以方便地操作和保存对应key的状态。
1.7 reduce&fold& Aggregations
分组之后当然要对分组之后的数据也就是KeyedStream进行各种聚合操作啦(想想SQL)。
KeyedStream → DataStream
对于KeyedStream的聚合操作都是滚动的(rolling,在前面的状态基础上继续聚合),千万不要理解为批处理时的聚合操作(DataSet,其实也是滚动聚合,只不过他只把最后的结果给了我们)。

案例1:
public class TestReduce {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>> input=env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPT);
KeyedStream<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>,Tuple> keyedStream = input.keyBy(0)
keyedStream.reduce(new ReduceFunction<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> reduce(Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> value1, Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> value2) throws Exception {
value1.f3+=value2.f3;
return value1;
}
}).print();
env.execute();
}
public static final Tuple4[] TRANSCRIPT = new Tuple4[] {
Tuple4.of("class1","张三","语文",100),
Tuple4.of("class1","李四","语文",78),
Tuple4.of("class1","王五","语文",99),
Tuple4.of("class2","赵六","语文",81),
Tuple4.of("class2","钱七","语文",59),
Tuple4.of("class2","马二","语文",97)
};
}
案例2:
public class TestFold {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>> input=env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPT);
DataStream<String> result =input.keyBy(0).fold("Start", new FoldFunction<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>,String>() {
@Override
public String fold(String accumulator, Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> value) throws Exception {
return accumulator + "=" + value.f1;
}
});
result.print();
env.execute();
}
public static final Tuple4[] TRANSCRIPT = new Tuple4[] {
Tuple4.of("class1","张三","语文",100),
Tuple4.of("class1","李四","语文",78),
Tuple4.of("class1","王五","语文",99),
Tuple4.of("class2","赵六","语文",81),
Tuple4.of("class2","钱七","语文",59),
Tuple4.of("class2","马二","语文",97)
};
}
1.8 Interval join
KeyedStream,KeyedStream → DataStream
在给定的周期内,按照指定的key对两个KeyedStream进行join操作,把符合join条件的两个event拉到一起,然后怎么处理由用户你来定义。
key1 == key2 && e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound
场景:把一定时间范围内相关的分组数据拉成一个宽表
案例:
public class TestIntervalJoin {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
DataStream<Transcript> input1=env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPTS).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor<Transcript>() {
@Override
public long extractAscendingTimestamp(Transcript element) {
return element.time;
}
});
DataStream<Student> input2=env.fromElements(STUDENTS).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor<Student>() {
@Override
public long extractAscendingTimestamp(Student element) {
return element.time;
}
});
KeyedStream<Transcript,String> keyedStream=input1.keyBy(new KeySelector<Transcript, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Transcript value) throws Exception {
return value.id;
}
});
KeyedStream<Student,String> otherKeyedStream=input2.keyBy(new KeySelector<Student, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Student value) throws Exception {
return value.id;
}
});
//e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound
// key1 == key2 && leftTs - 2 < rightTs < leftTs + 2
keyedStream.intervalJoin(otherKeyedStream)
.between(Time.milliseconds(-2), Time.milliseconds(2))
.upperBoundExclusive()
.lowerBoundExclusive()
.process(new ProcessJoinFunction<Transcript, Student, Tuple5<String,String,String,String,Integer>>()
@Override
public void processElement(Transcript transcript, Student student, Context ctx, Collector<Tuple5<String, String, String, String, Integer>> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(Tuple5.of(transcript.id,transcript.name,student.class_,transcript.subject,transcript.score));
}
}).print();
env.execute();
}
public static final Transcript[] TRANSCRIPTS = new Transcript[] {
new Transcript("1","张三","语文",100,System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Transcript("2","李四","语文",78,System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Transcript("3","王五","语文",99,System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Transcript("4","赵六","语文",81,System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Transcript("5","钱七","语文",59,System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Transcript("6","马二","语文",97,System.currentTimeMillis())
};
public static final Student[] STUDENTS = new Student[] {
new Student("1","张三","class1",System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Student("2","李四","class1",System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Student("3","王五","class1",System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Student("4","赵六","class2",System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Student("5","钱七","class2",System.currentTimeMillis()),
new Student("6","马二","class2",System.currentTimeMillis())
};
private static class Transcript{
private String id;
private String name;
private String subject;
private int score;
private long time;
public Transcript(String id, String name, String subject, int score, long time) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
this.score = score;
this.time = time;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(long time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
private static class Student{
private String id;
private String name;
private String class_;
private long time;
public Student(String id, String name, String class_, long time) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.class_ = class_;
this.time = time;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClass_() {
return class_;
}
public void setClass_(String class_) {
this.class_ = class_;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(long time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
}
1.9 connect & union(合并流)
connect之后生成ConnectedStreams,会对两个流的数据应用不同的处理方法,并且双流 之间可以共享状态(比如计数)。这在第一个流的输入会影响第二个流 时, 会非常有用; union 合并多个流,新的流包含所有流的数据。
union是DataStream* → DataStream。
connect只能连接两个流,而union可以连接多于两个流 。
connect连接的两个流类型可以不一致,而union连接的流的类型必须一致。
案例:
public class TestConnect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Long> someStream = env.generateSequence(0,10);
DataStream<String> otherStream = env.fromElements(WORDS);
ConnectedStreams<Long, String> connectedStreams = someStream.connect(otherStream);
DataStream<String> result=connectedStreams.flatMap(new CoFlatMapFunction<Long, String, String>() {
@Override
public void flatMap1(Long value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(value.toString());
}
@Override
public void flatMap2(String value, Collector<String> out) {
for (String word: value.split("\\W+")) {
out.collect(word);
}
}
});
result.print();
env.execute();
}
public static final String[] WORDS = new String[] {
"And thus the native hue of resolution",
"Is sicklied o'er with the pale cast of thought;",
"And enterprises of great pith and moment,",
"With this regard, their currents turn awry,",
"And lose the name of action.--Soft you now!",
"The fair Ophelia!--Nymph, in thy orisons",
"Be all my sins remember'd."
};
}
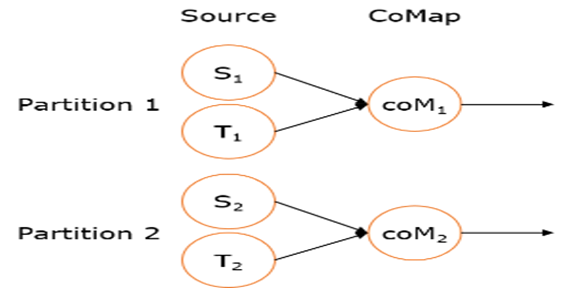
1.10 CoMap, CoFlatMap
跟map and flatMap类似,只不过作用在ConnectedStreams上
ConnectedStreams → DataStream
1.11 split & select(拆分流)
split
1.DataStream → SplitStream
2.按照指定标准将指定的DataStream拆分成多个流用SplitStream来表示
select
1.SplitStream → DataStream
2.跟split搭配使用,从SplitStream中选择一个或多个流
案例:
public class TestSplitAndSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Long> input=env.generateSequence(0,10);
SplitStream<Long> splitStream = input.split(new OutputSelector<Long>() {
@Override
public Iterable<String> select(Long value) {
List<String> output = new ArrayList<String>();
if (value % 2 == 0) {
output.add("even");
}
else {
output.add("odd");
}
return output;
}
});
//splitStream.print();
DataStream<Long> even = splitStream.select("even");
DataStream<Long> odd = splitStream.select("odd");
DataStream<Long> all = splitStream.select("even","odd");
//even.print();
odd.print();
//all.print();
env.execute();
}
}
1.12 project
含义:从Tuple中选择属性的子集
限制:
1.仅限event数据类型为Tuple的DataStream
2.仅限Java API
使用场景:
ETL时删减计算过程中不需要的字段

案例:
public class TestProject {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStreamSource<Tuple4<String,String,String,Integer>> input=env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPT);
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out = input.project(1,3);
out.print();
env.execute();
}
public static final Tuple4[] TRANSCRIPT = new Tuple4[] {
Tuple4.of("class1","张三","语文",100),
Tuple4.of("class1","李四","语文",78),
Tuple4.of("class1","王五","语文",99),
Tuple4.of("class2","赵六","语文",81),
Tuple4.of("class2","钱七","语文",59),
Tuple4.of("class2","马二","语文",97)
};
}
1.13 assignTimestampsAndWatermarks
含义:提取记录中的时间戳作为Event time,主要在window操作中发挥作用,不设置默认就是ProcessingTim
限制:
只有基于event time构建window时才起作用
使用场景:
当你需要使用event time来创建window时,用来指定如何获取event的时间戳
案例:讲到window时再说
1.14 window相关Operators
放在讲解完Event Time之后在细讲
构建window
1.window
2.windowAl
window上的操作
1.Window ApplyWindow Reduce
2.Window Fold
3.Aggregations on windows(sum、min、max、minBy、maxBy)
4.Window Join
5.Window CoGroup
2. 物理分区
2.1回顾 Streaming DataFlow
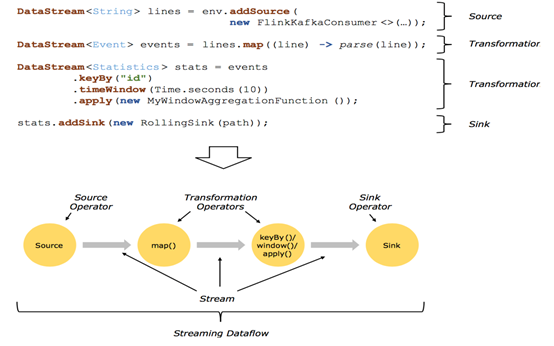
2.2并行化DataFlow
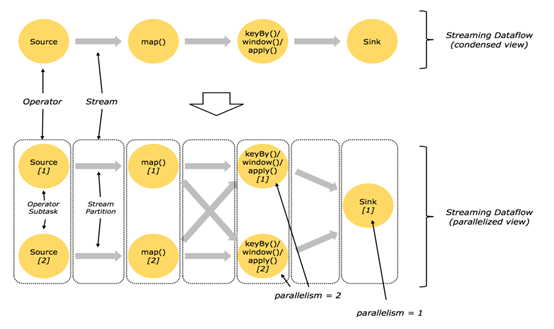
2.3算子间数据传递模式
One-to-one streams
保持元素的分区和顺序
Redistributing streams
1.改变流的分区
2.重新分区策略取决于使用的算子
a)keyBy() (re-partitions by hashing the key)
b)broadcast()
c)rebalance() (which re-partitions randomly)
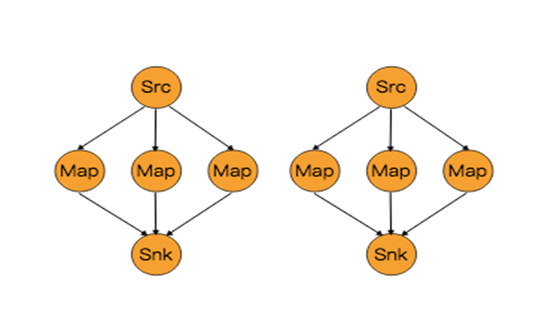
2.4物理分区
能够对分区在物理上进行改变的算子如下图所示:

上面算子都是Transformation,只是改变了分区。它们都是DataStream → DataStream。
2.5 rescale
通过轮询调度将元素从上游的task一个子集发送到下游task的一个子集。
原理:
第一个task并行度为2,第二个task并行度为6,第三个task并行度为2。从第一个task到第二个task,Src的子集Src1 和 Map的子集Map1,2,3对应起来,Src1会以轮询调度的方式分别向Map1,2,3发送记录。从第二个task到第三个task,Map的子集1,2,3对应Sink的子集1,这三个流的元素只会发送到Sink1。假设我们每个TaskManager有三个Slot,并且我们开了SlotSharingGroup,那么通过rescale,所有的数据传输都在一个TaskManager内,不需要通过网络。
2.6任务链和资源组相关操作
startNewChain()表示从这个操作开始,新启一个新的chain。
someStream.filter(...).map(...).startNewChain().map(...)
如上一段操作,表示从map()方法开始,新启一个新的chain。
如果禁用任务链可以调用disableChaining()方法。
如果想单独设置一个SharingGroup,可以调用slotSharingGroup("name")方法。

Flink学习笔记:Operators串烧的更多相关文章
- flink学习笔记-数据源(DataSource)
说明:本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKh ...
- Apache Flink学习笔记
Apache Flink学习笔记 简介 大数据的计算引擎分为4代 第一代:Hadoop承载的MapReduce.它将计算分为两个阶段,分别为Map和Reduce.对于上层应用来说,就要想办法去拆分算法 ...
- Flink学习笔记:Operators之CoGroup及Join操作
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
- Flink学习笔记:Operators之Process Function
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
- flink学习笔记:DataSream API
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
- Flink学习笔记:Time的故事
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
- flink学习笔记-split & select(拆分流)
说明:本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKh ...
- Flink学习笔记-新一代Flink计算引擎
说明:本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKh ...
- Flink学习笔记:Flink Runtime
本文为<Flink大数据项目实战>学习笔记,想通过视频系统学习Flink这个最火爆的大数据计算框架的同学,推荐学习课程: Flink大数据项目实战:http://t.cn/EJtKhaz ...
随机推荐
- 什么是响应式编程——响应式Spring的道法术器
响应式编程之道 1.1 什么是响应式编程? 在开始讨论响应式编程(Reactive Programming)之前,先来看一个我们经常使用的一款堪称“响应式典范”的强大的生产力工具——电子表格. 举个简 ...
- 钉钉开发笔记(六)使用Google浏览器做真机页面调试
注: 参考文献:https://developers.google.com/web/ 部分字段为翻译文献,水平有限,如有错误敬请指正 步骤1: 从Windows,Mac或Linux计算机远程调试And ...
- 636. Exclusive Time of Functions 进程的执行时间
[抄题]: Given the running logs of n functions that are executed in a nonpreemptive single threaded CPU ...
- MYSQL中GROUP BY的细节及SELECT语句顺序
一.GROUP BY语句的细节 我们知道,在sql中,GROUP BY语句主要用来给数据分组,以便能对每个组进行聚集计算,但是GROUP BY也有一些限制需要知道: 1. GROUP BY字句可以包含 ...
- 利用SHELL脚本修改当前环境变量
转自http://www.chinaunix.net/old_jh/7/21485.html 1.背景 ---- 在日常的工作中,为了设置一大批环境变量,我们通常编辑了一个shell程序,包含了多个的 ...
- webapi限流框架WebApiThrottle
为了防止网站意外暴增的流量比如活动.秒杀.攻击等,导致整个系统瘫痪,在前后端接口服务处进行流量限制是非常有必要的.本篇主要介绍下Net限流框架WebApiThrottle的使用. WebApiThro ...
- JavaScript中的shift()、unshift()和pop()函数
JavaScript中的shift()和pop()函数 1.shift()函数 定义 该函数从从数组中删除第一项,并返回该删除项. 用法示例 var fruits = ["Banana& ...
- 如何在IIS中承载WCF NetTcpBinding 服务
这篇博客将介绍如何在IIS中承载NetTcpBinding的服务. 1. 首先准备服务代码. Contract namespace Contract { [ServiceContract] publi ...
- bootstrap缩略图及警示框制作
缩略图在网站中最常用的地方就是产品列表页面,一行显示几张图片,有的在图片底下(左侧或右侧)带有标题.描述等信息.Bootstrap框架将这一部独立成一个模块组件.并通过“thumbnail”样式配合b ...
- QT学习之窗口部件
对话框--QDialog 模态对话框与非模态对话框 模态对话框:就是相当于没关闭它之前,不能再和该应用程序的其他窗口进行交互(比如新建项目时弹出的对话框) 非模态对话框:可以与它交互,也可以与该程序中 ...
