HADOOP 2.6 INSTALLING ON UBUNTU 14.04 (hadoop 2.6 部署到ubuntu 14.04上面)
In this chapter, we'll install a single-node Hadoop cluster backed by the Hadoop Distributed File System on Ubuntu.
Hadoop framework is written in Java!!
k@laptop:~$ cd ~ # Update the source list
k@laptop:~$ sudo apt-get update # The OpenJDK project is the default version of Java
# that is provided from a supported Ubuntu repository.
k@laptop:~$ sudo apt-get install default-jdk k@laptop:~$ java -version
java version "1.7.0_65"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (IcedTea 2.5.3) (7u71-2.5.3-0ubuntu0.14.04.1)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.65-b04, mixed mode)
k@laptop:~$ sudo addgroup hadoop
Adding group `hadoop' (GID 1002) ...
Done. k@laptop:~$ sudo adduser --ingroup hadoop hduser
Adding user `hduser' ...
Adding new user `hduser' (1001) with group `hadoop' ...
Creating home directory `/home/hduser' ...
Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Changing the user information for hduser
Enter the new value, or press ENTER for the default
Full Name []:
Room Number []:
Work Phone []:
Home Phone []:
Other []:
Is the information correct? [Y/n] Y
ssh has two main components:
- ssh : The command we use to connect to remote machines - the client.
- sshd : The daemon that is running on the server and allows clients to connect to the server.
The ssh is pre-enabled on Linux, but in order to start sshd daemon, we need to install sshfirst. Use this command to do that :
k@laptop:~$ sudo apt-get install ssh
This will install ssh on our machine. If we get something similar to the following, we can think it is setup properly:
k@laptop:~$ which ssh
/usr/bin/ssh k@laptop:~$ which sshd
/usr/sbin/sshd
Hadoop requires SSH access to manage its nodes, i.e. remote machines plus our local machine. For our single-node setup of Hadoop, we therefore need to configure SSH access to localhost.
So, we need to have SSH up and running on our machine and configured it to allow SSH public key authentication.
Hadoop uses SSH (to access its nodes) which would normally require the user to enter a password. However, this requirement can be eliminated by creating and setting up SSH certificates using the following commands. If asked for a filename just leave it blank and press the enter key to continue.
k@laptop:~$ su hduser
Password:
hduser@laptop:~$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ""
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/hduser/.ssh'.
Your identification has been saved in /home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
50:6b:f3:fc:0f:32:bf:30:79:c2:41:71:26:cc:7d:e3 hduser@laptop
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| .oo.o |
| . .o=. o |
| . + . o . |
| o = E |
| S + |
| . + |
| O + |
| O o |
| o.. |
+-----------------+ hduser@laptop:/home/k$ cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
The second command adds the newly created key to the list of authorized keys so that Hadoop can use ssh without prompting for a password.
We can check if ssh works:
hduser@laptop:/home/k$ ssh localhost
The authenticity of host 'localhost (127.0.0.1)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is e1:8b:a0:a5:75:ef:f4:b4:5e:a9:ed:be:64:be:5c:2f.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-40-generic x86_64)
...
hduser@laptop:~$ wget http://mirrors.sonic.net/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-2.6.0/hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz
hduser@laptop:~$ tar xvzf hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz
We want to move the Hadoop installation to the /usr/local/hadoop directory using the following command:
hduser@laptop:~/hadoop-2.6.0$ sudo mv * /usr/local/hadoop
[sudo] password for hduser:
hduser is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported.
Oops!... We got:
"hduser is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported."
This error can be resolved by logging in as a root user, and then add hduser to sudo:
hduser@laptop:~/hadoop-2.6.0$ su k
Password: k@laptop:/home/hduser$ sudo adduser hduser sudo
[sudo] password for k:
Adding user `hduser' to group `sudo' ...
Adding user hduser to group sudo
Done.
Now, the hduser has root priviledge, we can move the Hadoop installation to the /usr/local/hadoop directory without any problem:
k@laptop:/home/hduser$ sudo su hduser hduser@laptop:~/hadoop-2.6.0$ sudo mv * /usr/local/hadoop
hduser@laptop:~/hadoop-2.6.0$ sudo chown -R hduser:hadoop /usr/local/hadoop
The following files will have to be modified to complete the Hadoop setup:
- ~/.bashrc
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
1. ~/.bashrc:
Before editing the .bashrc file in our home directory, we need to find the path where Java has been installed to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable using the following command:
hduser@laptop update-alternatives --config java
There is only one alternative in link group java (providing /usr/bin/java): /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java
Nothing to configure.
Now we can append the following to the end of ~/.bashrc:
hduser@laptop:~$ vi ~/.bashrc #HADOOP VARIABLES START
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64
export HADOOP_INSTALL=/usr/local/hadoop
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_INSTALL/bin
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_INSTALL/sbin
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL
export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL
export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL
export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_INSTALL/lib/native
export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=$HADOOP_INSTALL/lib"
#HADOOP VARIABLES END hduser@laptop:~$ source ~/.bashrc
note that the JAVA_HOME should be set as the path just before the '.../bin/':
hduser@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ javac -version
javac 1.7.0_75 hduser@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ which javac
/usr/bin/javac hduser@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ readlink -f /usr/bin/javac
/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/bin/javac
2. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
We need to set JAVA_HOME by modifying hadoop-env.sh file.
hduser@laptop:~$ vi /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64
Adding the above statement in the hadoop-env.sh file ensures that the value of JAVA_HOME variable will be available to Hadoop whenever it is started up.
3. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml:
The /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml file contains configuration properties that Hadoop uses when starting up.
This file can be used to override the default settings that Hadoop starts with.
hduser@laptop:~$ sudo mkdir -p /app/hadoop/tmp
hduser@laptop:~$ sudo chown hduser:hadoop /app/hadoop/tmp
Open the file and enter the following in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
hduser@laptop:~$ vi /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml <configuration>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name>
<value>/app/hadoop/tmp</value>
<description>A base for other temporary directories.</description>
</property> <property>
<name>fs.default.name</name>
<value>hdfs://localhost:54310</value>
<description>The name of the default file system. A URI whose
scheme and authority determine the FileSystem implementation. The
uri's scheme determines the config property (fs.SCHEME.impl) naming
the FileSystem implementation class. The uri's authority is used to
determine the host, port, etc. for a filesystem.</description>
</property>
</configuration>
4. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
By default, the /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/ folder contains
/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template
file which has to be renamed/copied with the name mapred-site.xml:
hduser@laptop:~$ cp /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
The mapred-site.xml file is used to specify which framework is being used for MapReduce.
We need to enter the following content in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>mapred.job.tracker</name>
<value>localhost:54311</value>
<description>The host and port that the MapReduce job tracker runs
at. If "local", then jobs are run in-process as a single map
and reduce task.
</description>
</property>
</configuration>
5. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
The /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml file needs to be configured for each host in the cluster that is being used.
It is used to specify the directories which will be used as the namenode and the datanode on that host.
Before editing this file, we need to create two directories which will contain the namenode and the datanode for this Hadoop installation.
This can be done using the following commands:
hduser@laptop:~$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode
hduser@laptop:~$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/datanode
hduser@laptop:~$ sudo chown -R hduser:hadoop /usr/local/hadoop_store
Open the file and enter the following content in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
hduser@laptop:~$ vi /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml <configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Default block replication.
The actual number of replications can be specified when the file is created.
The default is used if replication is not specified in create time.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/datanode</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Now, the Hadoop file system needs to be formatted so that we can start to use it. The format command should be issued with write permission since it creates current directory
under /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode folder:
hduser@laptop:~$ hadoop namenode -format
DEPRECATED: Use of this script to execute hdfs command is deprecated.
Instead use the hdfs command for it. 15/04/18 14:43:03 INFO namenode.NameNode: STARTUP_MSG:
/************************************************************
STARTUP_MSG: Starting NameNode
STARTUP_MSG: host = laptop/192.168.1.1
STARTUP_MSG: args = [-format]
STARTUP_MSG: version = 2.6.0
STARTUP_MSG: classpath = /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop
...
STARTUP_MSG: java = 1.7.0_65
************************************************************/
15/04/18 14:43:03 INFO namenode.NameNode: registered UNIX signal handlers for [TERM, HUP, INT]
15/04/18 14:43:03 INFO namenode.NameNode: createNameNode [-format]
15/04/18 14:43:07 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
Formatting using clusterid: CID-e2f515ac-33da-45bc-8466-5b1100a2bf7f
15/04/18 14:43:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: No KeyProvider found.
15/04/18 14:43:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: fsLock is fair:true
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.DatanodeManager: dfs.block.invalidate.limit=1000
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.DatanodeManager: dfs.namenode.datanode.registration.ip-hostname-check=true
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: dfs.namenode.startup.delay.block.deletion.sec is set to 000:00:00:00.000
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: The block deletion will start around 2015 Apr 18 14:43:10
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map BlocksMap
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO util.GSet: 2.0% max memory 889 MB = 17.8 MB
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^21 = 2097152 entries
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: dfs.block.access.token.enable=false
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: defaultReplication = 1
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxReplication = 512
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: minReplication = 1
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxReplicationStreams = 2
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: shouldCheckForEnoughRacks = false
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: replicationRecheckInterval = 3000
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: encryptDataTransfer = false
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxNumBlocksToLog = 1000
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: fsOwner = hduser (auth:SIMPLE)
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: supergroup = supergroup
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: isPermissionEnabled = true
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: HA Enabled: false
15/04/18 14:43:10 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Append Enabled: true
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map INodeMap
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: 1.0% max memory 889 MB = 8.9 MB
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^20 = 1048576 entries
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.NameNode: Caching file names occuring more than 10 times
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map cachedBlocks
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: 0.25% max memory 889 MB = 2.2 MB
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^18 = 262144 entries
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.threshold-pct = 0.9990000128746033
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.min.datanodes = 0
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.extension = 30000
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache on namenode is enabled
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache will use 0.03 of total heap and retry cache entry expiry time is 600000 millis
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map NameNodeRetryCache
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: 0.029999999329447746% max memory 889 MB = 273.1 KB
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^15 = 32768 entries
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.NNConf: ACLs enabled? false
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.NNConf: XAttrs enabled? true
15/04/18 14:43:11 INFO namenode.NNConf: Maximum size of an xattr: 16384
15/04/18 14:43:12 INFO namenode.FSImage: Allocated new BlockPoolId: BP-130729900-192.168.1.1-1429393391595
15/04/18 14:43:12 INFO common.Storage: Storage directory /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode has been successfully formatted.
15/04/18 14:43:12 INFO namenode.NNStorageRetentionManager: Going to retain 1 images with txid >= 0
15/04/18 14:43:12 INFO util.ExitUtil: Exiting with status 0
15/04/18 14:43:12 INFO namenode.NameNode: SHUTDOWN_MSG:
/************************************************************
SHUTDOWN_MSG: Shutting down NameNode at laptop/192.168.1.1
************************************************************/
Note that hadoop namenode -format command should be executed once before we start using Hadoop.
If this command is executed again after Hadoop has been used, it'll destroy all the data on the Hadoop file system.
Now it's time to start the newly installed single node cluster.
We can use start-all.sh or (start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh)
k@laptop:~$ cd /usr/local/hadoop/sbin k@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ ls
distribute-exclude.sh start-all.cmd stop-balancer.sh
hadoop-daemon.sh start-all.sh stop-dfs.cmd
hadoop-daemons.sh start-balancer.sh stop-dfs.sh
hdfs-config.cmd start-dfs.cmd stop-secure-dns.sh
hdfs-config.sh start-dfs.sh stop-yarn.cmd
httpfs.sh start-secure-dns.sh stop-yarn.sh
kms.sh start-yarn.cmd yarn-daemon.sh
mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start-yarn.sh yarn-daemons.sh
refresh-namenodes.sh stop-all.cmd
slaves.sh stop-all.sh k@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ sudo su hduser hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ start-all.sh
hduser@laptop:~$ start-all.sh
This script is Deprecated. Instead use start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh
15/04/18 16:43:13 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
Starting namenodes on [localhost]
localhost: starting namenode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-namenode-laptop.out
localhost: starting datanode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-datanode-laptop.out
Starting secondary namenodes [0.0.0.0]
0.0.0.0: starting secondarynamenode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-secondarynamenode-laptop.out
15/04/18 16:43:58 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
starting yarn daemons
starting resourcemanager, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/yarn-hduser-resourcemanager-laptop.out
localhost: starting nodemanager, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/yarn-hduser-nodemanager-laptop.out
We can check if it's really up and running:
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ jps
9026 NodeManager
7348 NameNode
9766 Jps
8887 ResourceManager
7507 DataNode
The output means that we now have a functional instance of Hadoop running on our VPS (Virtual private server).
Another way to check is using netstat:
hduser@laptop:~$ netstat -plten | grep java
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50020 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1843372 10605/java
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:54310 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1841277 10447/java
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50090 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1841130 10895/java
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50070 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1840196 10447/java
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1841320 10605/java
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50075 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1001 1841646 10605/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8040 :::* LISTEN 1001 1845543 11383/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8042 :::* LISTEN 1001 1845551 11383/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8088 :::* LISTEN 1001 1842110 11252/java
tcp6 0 0 :::49630 :::* LISTEN 1001 1845534 11383/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8030 :::* LISTEN 1001 1842036 11252/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8031 :::* LISTEN 1001 1842005 11252/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8032 :::* LISTEN 1001 1842100 11252/java
tcp6 0 0 :::8033 :::* LISTEN 1001 1842162 11252/java
$ pwd
/usr/local/hadoop/sbin $ ls
distribute-exclude.sh httpfs.sh start-all.sh start-yarn.cmd stop-dfs.cmd yarn-daemon.sh
hadoop-daemon.sh mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start-balancer.sh start-yarn.sh stop-dfs.sh yarn-daemons.sh
hadoop-daemons.sh refresh-namenodes.sh start-dfs.cmd stop-all.cmd stop-secure-dns.sh
hdfs-config.cmd slaves.sh start-dfs.sh stop-all.sh stop-yarn.cmd
hdfs-config.sh start-all.cmd start-secure-dns.sh stop-balancer.sh stop-yarn.sh
We run stop-all.sh or (stop-dfs.sh and stop-yarn.sh) to stop all the daemons running on our machine:
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ pwd
/usr/local/hadoop/sbin
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ ls
distribute-exclude.sh httpfs.sh start-all.cmd start-secure-dns.sh stop-balancer.sh stop-yarn.sh
hadoop-daemon.sh kms.sh start-all.sh start-yarn.cmd stop-dfs.cmd yarn-daemon.sh
hadoop-daemons.sh mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start-balancer.sh start-yarn.sh stop-dfs.sh yarn-daemons.sh
hdfs-config.cmd refresh-namenodes.sh start-dfs.cmd stop-all.cmd stop-secure-dns.sh
hdfs-config.sh slaves.sh start-dfs.sh stop-all.sh stop-yarn.cmd
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ stop-all.sh
This script is Deprecated. Instead use stop-dfs.sh and stop-yarn.sh
15/04/18 15:46:31 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
Stopping namenodes on [localhost]
localhost: stopping namenode
localhost: stopping datanode
Stopping secondary namenodes [0.0.0.0]
0.0.0.0: no secondarynamenode to stop
15/04/18 15:46:59 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
stopping yarn daemons
stopping resourcemanager
localhost: stopping nodemanager
no proxyserver to stop
Let's start the Hadoop again and see its Web UI:
hduser@laptop:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin$ start-all.sh
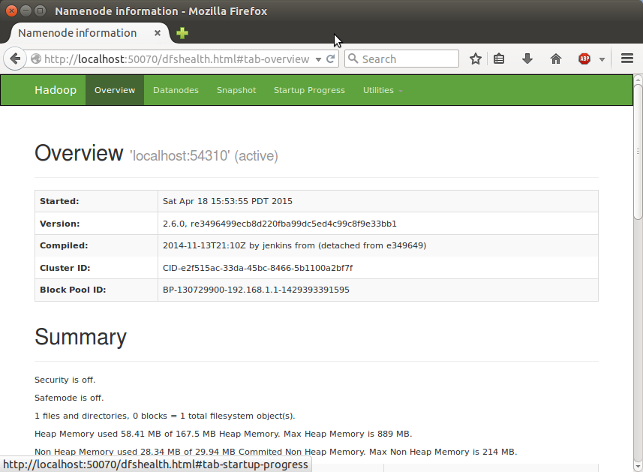
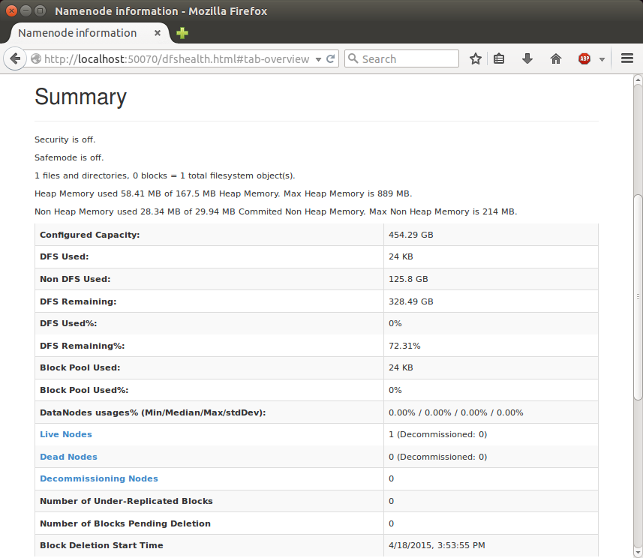
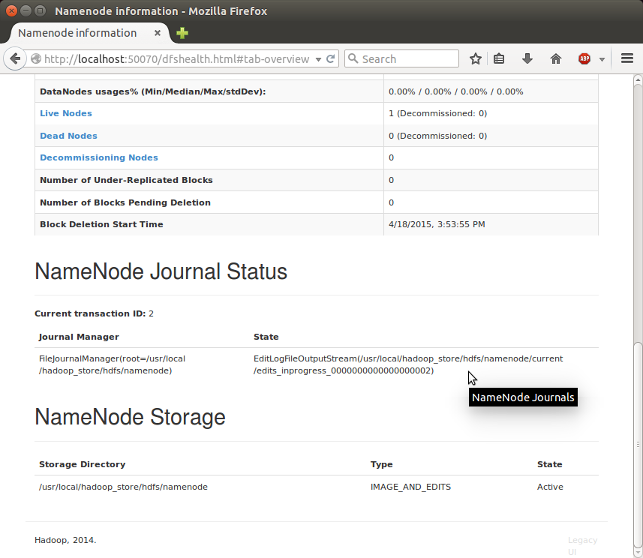
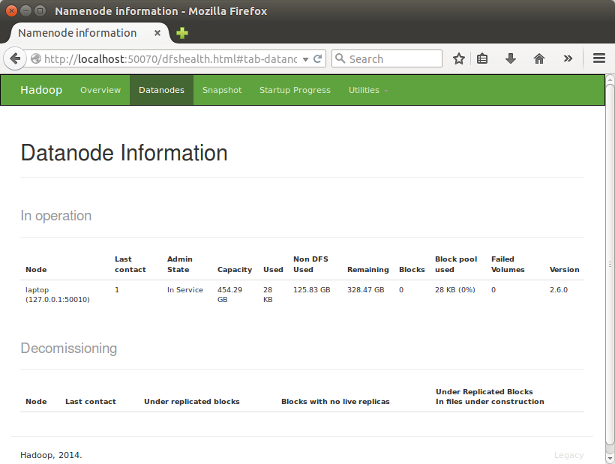
http://localhost:50070/ - web UI of the NameNode daemon
SecondaryNameNode
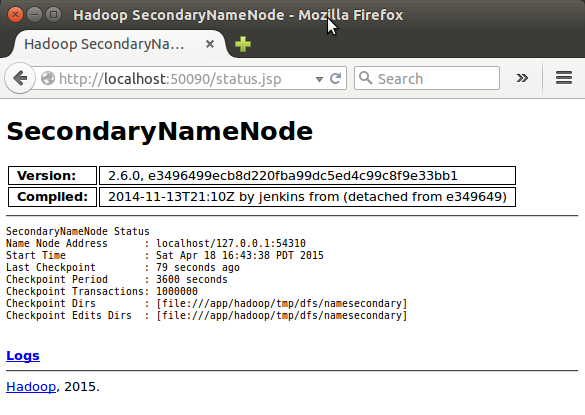
(Note) I had to restart Hadoop to get this Secondary Namenode.
DataNode
原文链接http://www.bogotobogo.com/Hadoop/BigData_hadoop_Install_on_ubuntu_single_node_cluster.php
HADOOP 2.6 INSTALLING ON UBUNTU 14.04 (hadoop 2.6 部署到ubuntu 14.04上面)的更多相关文章
- [转]Ubuntu Tweak 0.8.7 发布:支持 Ubuntu 14.04
原文网址:http://www.oschina.net/news/51054/ubuntu-tweak-0-8-7 这是我开发 Ubuntu Tweak 七年以来第一次没在 Ubuntu 正式发布之前 ...
- Ubuntu 14.04 上使用 Nginx 部署 Laravel
本教程将会涉及以下工具: Ubuntu 14.04 LTS PHP 5.5 MySQL Laravel 5.0 Nginx 参考文章:Ubuntu 14.04 上使用 Nginx 部署 Laravel ...
- Ubuntu上的Hadoop安装教程
Install Hadoop 2.2.0 on Ubuntu Linux 13.04 (Single-Node Cluster) This tutorial explains how to insta ...
- Ubuntu上搭建Hadoop环境(单机模式+伪分布模式)
首先要了解一下Hadoop的运行模式: 单机模式(standalone) 单机模式是Hadoop的默认模式.当首次解压Hadoop的源码包时,Hadoop无法了解硬件安装环境,便保守地选 ...
- Ubuntu上搭建Hadoop环境(单机模式+伪分布模式) (转载)
Hadoop在处理海量数据分析方面具有独天优势.今天花了在自己的Linux上搭建了伪分布模式,期间经历很多曲折,现在将经验总结如下. 首先,了解Hadoop的三种安装模式: 1. 单机模式. 单机模式 ...
- Ubuntu上搭建Hadoop环境(单机模式+伪分布模式)【转】
[转自:]http://blog.csdn.net/hitwengqi/article/details/8008203 最近一直在自学Hadoop,今天花点时间搭建一个开发环境,并整理成文. 首先要了 ...
- 1.如何在虚拟机ubuntu上安装hadoop多节点分布式集群
要想深入的学习hadoop数据分析技术,首要的任务是必须要将hadoop集群环境搭建起来,可以将hadoop简化地想象成一个小软件,通过在各个物理节点上安装这个小软件,然后将其运行起来,就是一个had ...
- ubuntu中安装hadoop集群
hadoop是由java 语言编写的主从结构分布式计算存储架构 准备工作: 操作系统: Ubuntu16.04 软件安装包:jdk-8u171-linux-x64.tar.gz : hadoop-2. ...
- Ubuntu系统之Hadoop搭建
作业来源:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gzcc/GZCC-16SE1/homework/3223 一.在Window中安装Oracle VM VirtualBox 二 ...
随机推荐
- unexpected token: * 和 java.lang.ClassCastException: [Ljava.lang.Object; cannot be cast to 解决办法
一.unexpected token: * 的解决办法 首先要搞清楚sql与hql的区别! sql操作的是数据库表,而hql操作的是对象! sql中“select * from table”,而hq ...
- STL栈的应用之表达式求值
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<stack> using ...
- KineticJS教程(6)
KineticJS教程(6) 作者: ysm 6.拖拽 6.1.拖拽功能 要实现Kinetic对象的拖拽功能很简单,只需要将图形对象的draggable属性设为true就可以了. <script ...
- 开发移动 APP 时,你应注意这 5 个细节
智能手机的普及带动了大批移动应用的诞生,这些应用能够帮助人们解决日常生活所面临的种种问题.Smart Insights 发表的一份报告指出,移动应用占人们使用智能手机总时间的89%,因此,为了确保你所 ...
- 算法笔记_016:凸包问题(Java)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 2.1 蛮力法 1 问题描述 给定一个平面上n个点的集合,它的凸包就是包含所有这些点的最小凸多边形,求取满足此条件的所有点. 另外,形象生动的描述: (1)我们可以把 ...
- 开源微内核seL4
微内核 越大的系统潜在的bug就越多.所以微内核在降低bug方面非常有优势,seL4是世界上最小的内核之中的一个.可是seL4的性能能够与当今性能最好的微内核相比. 作为微内核,seL4为应用程序提供 ...
- STRUTS2配置动态页面
STRUTS2配置动态页面 CreateTime--2017年5月11日09:00:31Author:Marydon 1.struts配置 <?xml version="1.0&q ...
- ie6/7 bug大全
1. ie6/7下ul高度变高 li 加 vertical-align:bottom; 2.ie6不支持min-height a:height:auto !important; height:10 ...
- zookeeper 入门讲解实例 转
转 http://www.blogjava.net/BucketLi/archive/2010/12/21/341268.html zookeeper使用和原理探究(一) zookeeper介绍zo ...
- Overlapped I/O模型深入分析(转)
随笔 - 262 文章 - 0 评论 - 531 博客园 首页 新随笔 联系 管理 订阅 Overlapped I/O模型深入分析(转) 简述: Overlapped I/O也 ...
