(21)Oracle表查询进阶
转到基本查询
一、多表查询
笛卡尔积:每张表的列数相加,行数相乘。
连接条件:得出笛卡尔积后需要用where条件筛选出正确的数据。连接条件至少需要n张表减1个
1.等值连接
连接条件为等号
select t1.a,t1.b,t1.c,t2.d from table t1,t2 where t1.c=t2.c
2.不等值连接
select t1.a,t1.b,t1.c,t2.d from table t1,t2 where t1.c between t2.e and t2.f --between and 小值在前,大值在后
3.外连接(把对于连接条件不成立的数据包含在最近的结果中)
SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列,相似的数据类型,和相同的顺序。这种条件下能合并表
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2
union 去重,union all不去重
inner join(join)内连接
左外连接:当连接条件不成立时,等号左边的表依然被包含在结果中
left join
右外连接:当连接条件不成立时,等号右边的表依然被包含在结果中
right join
full join
4.自连接
一张表起两个别名,当做两张表来用。
自接连不适合查询大表
5.层次查询
对于树型结构的单表查询
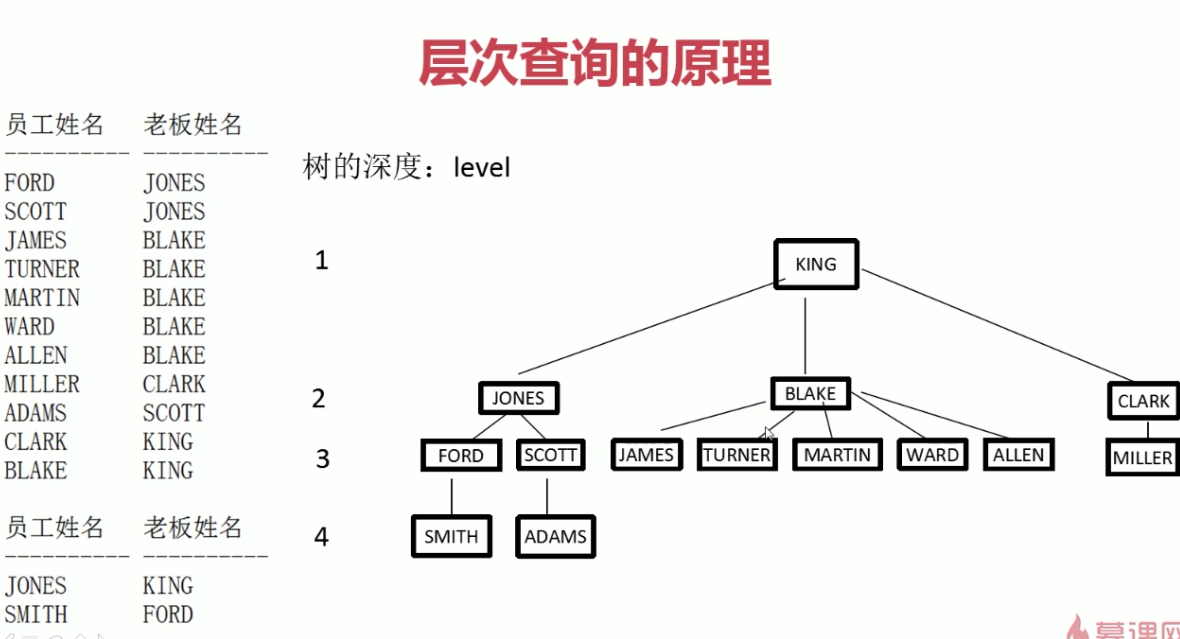
select * from table connect by 上一层字段=本层字段 start with 分支的定点字段=xxx;
如果从根节点开始查询还可以写成 : start with 上层字段 is null
select * from table connect by 上一层字段=本层字段 start with 上层字段 is null;
注意 :上层字段和本层字段是不同的两个列
二、行转列
先建表,插入数据
create table fruits(id int,name varchar(20),place varchar(20),amount int); ---- 创建表
/
insert into fruits values(1, '苹果','河北', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(2, '苹果','浙江', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(3, '苹果','河北', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(4, '橘子','浙江', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(5, '橘子','河北', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(6, '葡萄','浙江', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(7, '芒果','浙江', 1000);
/
insert into fruits values(8, '芒果','浙江', 1000);
/
行转列sql
select * from (select PLACE,NAME,AMOUNT from FRUITS) pivot (sum(AMOUNT) for NAME in('苹果','橘子' as 橙子,'葡萄' 葡萄))
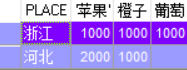
pivot(聚合函数 for 列名 in(类型)
等同于
WITH t AS (SELECT PLACE, NAME, AMOUNT FROM FRUITS)
SELECT *
FROM t PIVOT (SUM (AMOUNT)
FOR NAME
IN ('苹果', '橘子' AS 橙子, '葡萄' 葡萄))
使用 with as 的原因:1优化速度 2方便阅读
三、条件控制
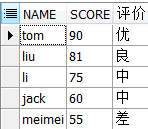
SELECT name,
score,
CASE --如果
WHEN score >= 90 THEN '优' --当...那么...
WHEN (80 <= score AND score < 90) THEN '良'
WHEN (60 <= score AND score < 80) THEN '中'
ELSE '差'
END --结束
AS 评价
FROM student
WHERE 1 = 1
ORDER BY score DESC
四、分组查询
分组函数
1.avg()平均(avg函数会过滤掉空值), sum()求和
select avg(字段名) ,sum(字段名) from table
2.min()最小值,max()最大值
select min(字段名), max(字段名) from table
3.count()统计个数
select count(*) from table
select count(字段名) from table
select count( distinct 字段名) from table --去掉某字段重复数据后,再统计行数
4.nvl() 为空时替换
select count(nvl(字段名,0)) from table --当字段名有数据为空时,会把他替换成第二个参数
5.gourp by
select 需要分组的字段, 分组函数(需要统计的字段) from table group by 需要分组的字段
select a,b,c, max(x) from table group by a,b,c --所有未包含在分组函数的列,都必须在 group by 中表示出来
当执行多个列分组时,先执行 a分组,分组后b如果有重复再执行b分组。
6. having
where 和 having 都是筛选条件,区别是 where 子句中不能使用分组函数
select a,avg(b) from table group by a having avg(b) ;
其他条件下通用
select a,avg(b) from table group a by having a=10;
select a,avg(b) from table where=10 group by a;
在sql的优化角度考虑尽量使用where
7.分组查询的中order by
可以按照: 列,别名,表达式,序号排列
select a,avg(b) from table group by a order by avg(b) ; --按b升序排列
select a,avg(b) as 平均工资 from table group by a order by 平均工资 ;--按别名
select a,avg(b) as from table group by a order by 2; --按序号
8.分组嵌套
平均工资的最大值
select max(avg(b)) from table group by b;
9.group by 增强语句
group by rollup(a,b)
五、子查询
select * from t1 where t1.a>(select t2.b from t2 where ...);
注意问题
.可以写子查询的位置: where ,select ,having,from
.不可以使用子查询的位置 group by
六、排重
select PROD_NORM_CODE,REMARK from T_MD_PROD_NORM GROUP BY PROD_NORM_CODE,REMARK having count(PROD_NORM_CODE)>1
正则表达式 查询所有是数字的
REGEXP_LIKE(列名,'(^[+-]?\d{0,}\.?\d{0,}$)');
剔除改字段下非数字数据,然后转成数字,四舍五入保留三位小数
select round (to_number(列名),3) as 列名 from table1 where REGEXP_LIKE(列名,'(^[+-]?\d{0,}\.?\d{0,}$)');
(21)Oracle表查询进阶的更多相关文章
- oracle 表查询(2)
使用逻辑操作符号 问题:查询工资高于500 或者是岗位为MANAGER 的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J? or job = 'MANAGER') and ename LIKE 'J%' ...
- oracle 表查询(1)
oracle 表基本查询 介绍在我们讲解的过程中我们利用scott 用户存在的几张表(emp,dept)为大家演示如何使用select语句,select 语句在软件编程中非常有用,希望大家好好的掌握. ...
- (六)Oracle 的 oracle表查询关键字
参考:http://www.hechaku.com/Oracle/oracle_tables2.html 1.使用逻辑操作符号问题:查询工资高于500或者是岗位为manager的雇员,同时还要满足他们 ...
- 第五章、Django之多表查询进阶与事务
目录 第五章.Django之多表查询 一.聚合查询 二.分组查询 三.F与Q查询 四.查询优化 五.Django开启事务 六.自定义char字段 七.ORM常用字段 第五章.Django之多表查询 一 ...
- oracle表查询
使用scott用户中存在的emp.dept表等做演示 一.单表查询 查看表结构:desc dept; 查看所有列:select * from dept: 查询指定列:select ename,sal, ...
- oracle 表查询二
1.使用逻辑操作符号问题:查询工资高于500或者是岗位为manager的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J?select * from emp where (sal > 500 or ...
- 七、oracle 表查询二
1.使用逻辑操作符号问题:查询工资高于500或者是岗位为manager的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J?select * from emp where (sal > 500 or ...
- oracle 表查询(二)
1.使用逻辑操作符号问题:查询工资高于500或者是岗位为manager的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J?select * from emp where (sal > 500 or ...
- 七 oracle 表查询二
1.使用逻辑操作符号问题:查询工资高于500或者是岗位为manager的雇员,同时还要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J?select * from emp where (sal > 500 or ...
随机推荐
- Mysql存储过程中的事务回滚
create procedure test(in a int) BEGIN ; ;-- 异常时设置为1 START TRANSACTION; ,); ,); THEN ROLLBACK; ELSE C ...
- Sql日期时间格式转换(转 子夜.)
sql server2000中使用convert来取得datetime数据类型样式(全) 日期数据格式的处理,两个示例: CONVERT(varchar(16), 时间一, 20) 结果:2007-0 ...
- JVM——自定义类加载器
)以上两种情况在实际中的综合运用:比如你的应用需要通过网络来传输 Java 类的字节码,为了安全性,这些字节码经过了加密处理.这个时候你就需要自定义类加载器来从某个网络地址上读取加密后的字节代码,接着 ...
- 【Kubernetes】资源列表
1.Kubernetes资源列表 https://www.cnblogs.com/linuxk/p/10436260.html
- 分治 - 计算几何 - BZOJ2458,[BeiJing2011]最小三角形
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2458 [BeiJing2011]最小三角形 描述 Frisk现在遇到了一个有趣的问题. 平面上有N个 ...
- R语言分析朝阳医院数据
R语言分析朝阳医院数据 本次实践通过分析朝阳医院2016年销售数据,得出“月均消费次数”.“月均消费金额”.“客单价”.“消费趋势”等结果,并据此作出可视化图形. 一.读取数据: library(op ...
- 12个scp传输文件的命令栗子
12个scp传输文件的命令栗子 一直在用scp进行简单的远程复制文件的功能,今天无意间看到一篇介绍scp的文章,便想着学习学习并将其翻译了过来.原文戳这里.翻译不对的地方,敬请指正. 另外我最近搭建了 ...
- 【SDOI2009】HH的项链 线段树
题目描述 HH 有一串由各种漂亮的贝壳组成的项链.HH 相信不同的贝壳会带来好运,所以每次散步完后,他都会随意取出一段贝壳,思考它们所表达的含义.HH 不断地收集新的贝壳,因此,他的项链变得越来越长. ...
- c#委托使用
public class StepArgs : EventArgs { public int m_IMax = 0; public int m_IStep = 0; public string m_S ...
- 分布式存储ceph集群实践
1.环境规划,三台主机 10.213.14.51/24 10.213.14.52/24 10.213.14.53/24 集群网络 172.140.140.11. ...
