【Java】Collection子接口:其一 List 列接口
Collection子接口 其一:List接口List
接口存储结构:元素有序,且可重复,每个元素都有对应的索引
根据索引获取容器元素
实现类有:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
三个实现类的异同?
- 都实现了List接口,存储数据的特点相同、存储有序的、可重复的数据
- ArrayList 是List接口的主要实现类,线程不安全的,但是效率高,底层Object[] elementData存储
- LinkedList 双向链表结构存储,对于插入和删除频繁操作,效率比ArrayList高
- Vector 初代List接口实现类,线程安全,效率低。底层Object[]存储
List的接口常用方法【索引支持】
在指定索引位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
从参数的容器对象的索引位置开始到结尾,添加元素到调用此方法的容器对象
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
按索引获取元素
public E get(int index)
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index);
}
返回元素的索引位置,如果是重复了多个元素,返回第一个的位置
public int indexOf(Object o)
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
返回元素的索引位置,如果多个重复元素,返回最后一个出现的
public int lastIndexOf(Object o)
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
移除参数的索引上的元素,并返回元素
public E remove(int index)
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue;
}
修改指定索引位置的元素
public E set(int index, E element)
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
截取一段,返回指定起始位置到结束位置的元素到一个新的容器上 【返回子集合】
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. (If
* {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
*
* <p>This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* </pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for {@link #indexOf(Object)} and
* {@link #lastIndexOf(Object)}, and all of the algorithms in the
* {@link Collections} class can be applied to a subList.
*
* <p>The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
} static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
List支持的三种遍历方式
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("元素1");
list.add("元素2");
list.add("元素3");
list.add("元素4");
list.add("元素5");
list.add("元素6");
// 第一种 迭代器实现遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 第二种 ForEach
for (Object object : list) {
System.out.println(object);
}
// 第三种 For
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
注意点: remove的重载
如何判断注入的是按元素删除?还是按索引删除?
- 按元素删除,建议使用 new Integer(10) 这样对基本类型数据包装再注入 arrayList.remove(new Integer(5));
- 按索引删除,默认注入数字值即可 arrayList.remove(3);
ArrayList的底层源码查看【未完待续...】
JDK8
底层elementData初始化为0

但是注释依赖没改,仍然称为10初始化容量
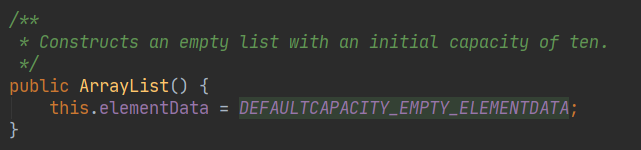
只有在第一次调用add后初始化10的容量,再往后大于10【右移1 除2】增加1.5倍容量

【Java】Collection子接口:其一 List 列接口的更多相关文章
- Java基础-Collection子接口之List接口
Java基础-Collection子接口之List接口 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 我们掌握了Collection接口的使用后,再来看看Collection接口中 ...
- Java基础-Collection子接口之Set接口
Java基础-Collection子接口之Set接口 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 学习Collection接口时,记得Collection中可以存放重复元素,也可 ...
- Collection子接口(List/Set/Queue/SortedSet)
Collection基本的子接口: List:能够存放反复内容 Set:不能存放反复内容,全部反复的内容靠hashCode()和equals()两个方法区分 Queue:队列接口 SortedSet: ...
- Java面向对象之 接口: [修饰符] interface 接口名 {...};子接口:[修饰符] interface 接口名 extends 父接口,父接口2...{...}
1.什么是接口? 类比抽象类,把功能或者特性类似的一类 抽象的更彻底,可以提炼出更加特殊的"抽象类"----接口 2.如何定义接口 语法: [修饰符] interface 接口名 ...
- Java学习关于集合框架的基础接口--Collection接口
集合框架(Collection Framework)是Java最强大的子系统之一,位于java.util 包中.集合框架是一个复杂的接口与和类层次,提供了管理对象组的最新技术.Java集合框架标准 ...
- java Collection接口
Collection 1——————Set子接口:无序,不允许重复. 2——————List子接口:有序,允许重复. Set和List对比: 1.set:检索元素的效率比较低,删除和插入效率比较高,删 ...
- 自顶向下理解Java集合框架(三)Map接口
Map基本概念 数据结构中Map是一种重要的形式.Map接口定义的是查询表,或称查找表,其用于储存所谓的键/值对(key-value pair),其中key是映射表的索引. JDK结构中还存在实现Ma ...
- 数据结构-List接口-LinkedList类-Set接口-HashSet类-Collection总结
一.数据结构:4种--<需补充> 1.堆栈结构: 特点:LIFO(后进先出);栈的入口/出口都在顶端位置;压栈就是存元素/弹栈就是取元素; 代表类:Stack; 其 ...
- Effective Java 第三版——41.使用标记接口定义类型
Tips <Effective Java, Third Edition>一书英文版已经出版,这本书的第二版想必很多人都读过,号称Java四大名著之一,不过第二版2009年出版,到现在已经将 ...
- Java第二十天,Map集合(接口)
Map接口 一.定义 Map集合是双列集合,即一个元素包含两个值(一个key,一个value),Collection集合是单列集合. 定义格式: public interface Map<K,V ...
随机推荐
- 如何实现sm3加密
SM3加密应用 何为sm3加密? SM3是由中国国家密码管理局设计的一种密码杂凑函数,类似于SHA-256和MD5等国际标准的散列算法.SM3算法是中国国家标准<GB/T 32905-2016 ...
- 2024-06-05:用go语言,给定三个正整数 n、x 和 y, 描述一个城市中由 n 个房屋和 n 条街道连接的情况。 城市中存在一条额外的街道连接房屋 x 和房屋 y。 需要计算对于每个街道数(
2024-06-05:用go语言,给定三个正整数 n.x 和 y, 描述一个城市中由 n 个房屋和 n 条街道连接的情况. 城市中存在一条额外的街道连接房屋 x 和房屋 y. 需要计算对于每个街道数( ...
- xv6 内核空间共享
首发公号:Rand_cs 共享内核空间 我们常说,每个进程都有自己的虚拟地址空间,但其中内核部分是共享的. 这就有个问题,如何共享的? 系统启动时创建了一张内核页表,里面记录着内核地址空间与物理地址空 ...
- Linux扩展篇-shell编程(十一)- shell编程工具-VS Code
根据个人多年工作经验,shell没有自己专用的IDE,使用vim开发,对于新手而言不太友好,那如何高效快速书写shell脚本?合适的工具就显得尤为重要,本人比较推荐的就是VS Code.里面有比较成熟 ...
- 玩转Zabbix智能告警:降噪、排班、认领、升级、IM协同
Zabbix作为一款流行的企业级监控工具,可以监控各种网络设备和服务的状态,并提供强大的告警功能,能够在出现异常情况时及时通知管理员.以下是Zabbix的一些特点: 支持多种监控方式,包括SNMP.J ...
- mongodb基于角色的访问控制
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/v4.4/tutorial/enable-authentication/ https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manua ...
- 网易面试:SpringBoot如何开启虚拟线程?
虚拟线程(Virtual Thread)也称协程或纤程,是一种轻量级的线程实现,与传统的线程以及操作系统级别的线程(也称为平台线程)相比,它的创建开销更小.资源利用率更高,是 Java 并发编程领域的 ...
- Primer Premier 6安装使用教程
Primer Premier是一款专业级PCR引物设计工具软件,专为科研及分子生物学实验定制PCR扩增.测序探针及杂交引物.该程序运用尖端演算法评估引物的特异性.二聚体可能性和熔解温度等核心属性,确保 ...
- HDU2062题解 01背包而已
RT,我就不解释了,题目连接http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2602. 初学01背包的人可以做做 #include<iostream> ...
- Django-CBV和跨域请求伪造
1. django模式 def users(request): user_list = ['alex','oldboy'] return HttpResponse(json.dumps((user_l ...
