DEXSeq
1)Introduction
DEXSeq是一种在多个比较RNA-seq实验中,检验差异外显子使用情况的方法。 通过差异外显子使用(DEU),我们指的是由实验条件引起的外显子相对使用的变化。 外显子的相对使用定义为:
number of transcripts from the gene that contain this exon / number of all transcripts from the gene
大致思想:. For each exon (or part of an exon) and each sample, we count how many reads map to this exon and how many reads map to any of the other exons of the same gene. We consider the ratio of these two counts, and how it changes across conditions, to infer changes in the relative exon usage
2)安装
if("DEXSeq" %in% rownames(installed.packages()) == FALSE) {source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R");biocLite("DEXSeq")}
suppressMessages(library(DEXSeq))
ls('package:DEXSeq')
pythonScriptsDir = system.file( "python_scripts", package="DEXSeq" )
list.files(pythonScriptsDir)
## [1] "dexseq_count.py" "dexseq_prepare_annotation.py" #查看是否含有这两个脚本
python dexseq_prepare_annotation.py Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP5.72.gtf Dmel.BDGP5.25.62.DEXSeq.chr.gff #GTF转化为GFF with collapsed exon counting bins.
python dexseq_count.py Dmel.BDGP5.25.62.DEXSeq.chr.gff untreated1.sam untreated1fb.txt #count
3) 用自带实验数据集(数据预处理)
suppressMessages(library(pasilla))
inDir = system.file("extdata", package="pasilla")
countFiles = list.files(inDir, pattern="fb.txt$", full.names=TRUE) #countfile(如果不是自带数据集,可以由dexseq_count.py脚本生成)
basename(countFiles)
flattenedFile = list.files(inDir, pattern="gff$", full.names=TRUE)
basename(flattenedFile) #gff文件(如果不是自带数据集,可以由dexseq_prepare_annotation.py脚本生成)
########构造数据框sampleTable,包含sample名字,实验,文库类型等信息#######################
sampleTable = data.frame(
row.names = c( "treated1", "treated2", "treated3",
"untreated1", "untreated2", "untreated3", "untreated4" ),
condition = c("knockdown", "knockdown", "knockdown",
"control", "control", "control", "control" ),
libType = c( "single-end", "paired-end", "paired-end",
"single-end", "single-end", "paired-end", "paired-end" ) )
sampleTable ##############构建 DEXSeqDataSet object#############################
dxd = DEXSeqDataSetFromHTSeq(
countFiles,
sampleData=sampleTable,
design= ~ sample + exon + condition:exon,
flattenedfile=flattenedFile ) #四个参数
4)Standard analysis work-flow
########以下是简单的实验设计#####
genesForSubset = read.table(file.path(inDir, "geneIDsinsubset.txt"),stringsAsFactors=FALSE)[[1]] #基因子集ID
dxd = dxd[geneIDs( dxd ) %in% genesForSubset,] #取子集,减少运行量
head(colData(dxd))
head( counts(dxd), 5 )
split( seq_len(ncol(dxd)), colData(dxd)$exon )
sampleAnnotation( dxd )
############# dispersion estimates and the size factors#############
dxd = estimateSizeFactors( dxd ) ##Normalisation
dxd = estimateDispersions( dxd )
plotDispEsts( dxd ) #图1 #################Testing for differential exon usage############
dxd = testForDEU( dxd )
dxd = estimateExonFoldChanges( dxd, fitExpToVar="condition")
dxr1 = DEXSeqResults( dxd )
dxr1
mcols(dxr1)$description
table ( dxr1$padj < 0.1 )
table ( tapply( dxr1$padj < 0.1, dxr1$groupID, any ) )
plotMA( dxr1, cex=0.8 ) #图2

To see how the power to detect differential exon usage depends on the number of reads that map to an exon, a so-called MA plot is useful, which plots the logarithm of fold change versus average normalized count per exon and marks by red colour the exons which are considered significant; here, the exons with an adjusted p values of less than 0.1

############以下是更复杂的实验设计##################
formulaFullModel = ~ sample + exon + libType:exon + condition:exon
formulaReducedModel = ~ sample + exon + libType:exon
dxd = estimateDispersions( dxd, formula = formulaFullModel )
dxd = testForDEU( dxd,
reducedModel = formulaReducedModel,
fullModel = formulaFullModel )
dxr2 = DEXSeqResults( dxd )
table( dxr2$padj < 0.1 )
table( before = dxr1$padj < 0.1, now = dxr2$padj < 0.1 )##和简单的实验设计比较
5)Visualization
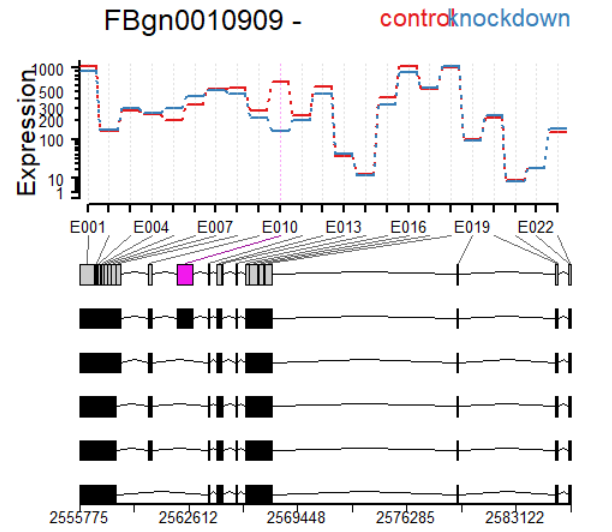
plotDEXSeq( dxr2, "FBgn0010909", legend=TRUE, cex.axis=1.2, cex=1.3,
lwd=2 )
plotDEXSeq( dxr2, "FBgn0010909", displayTranscripts=TRUE, legend=TRUE,
cex.axis=1.2, cex=1.3, lwd=2 )
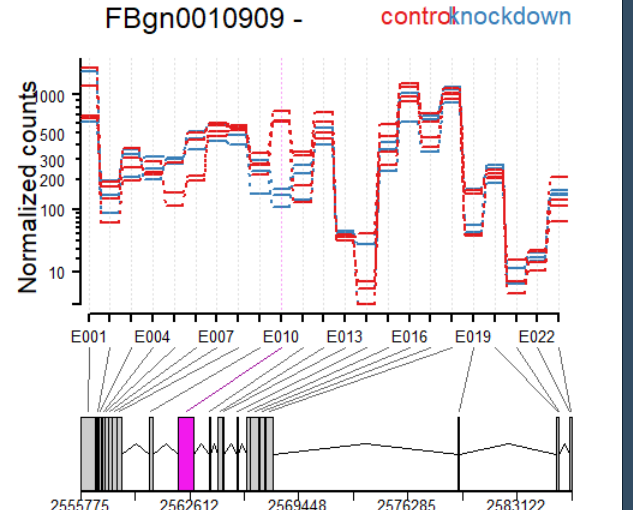
plotDEXSeq( dxr2, "FBgn0010909", expression=FALSE, norCounts=TRUE,
legend=TRUE, cex.axis=1.2, cex=1.3, lwd=2 )
plotDEXSeq( dxr2, "FBgn0010909", expression=FALSE, splicing=TRUE,
legend=TRUE, cex.axis=1.2, cex=1.3, lwd=2 )
DEXSeqHTML( dxr2, FDR=0.1, color=c("#FF000080", "#0000FF80") )


DEXSeq的更多相关文章
- 【转录组入门】6:reads计数
作业要求: 实现这个功能的软件也很多,还是烦请大家先自己搜索几个教程,入门请统一用htseq-count,对每个样本都会输出一个表达量文件. 需要用脚本合并所有的样本为表达矩阵.参考:生信编程直播第四 ...
- Bulk RNA-Seq转录组学习
与之对应的是single cell RNA-Seq,后面也会有类似文章. 参考:https://github.com/xuzhougeng/Learn-Bioinformatics/ 作业:RNA-s ...
- Bioconductor应用领域之基因芯片
引用自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU4NjU4ODQ2MQ==&mid=2247484662&idx=1&sn=194668553f9 ...
随机推荐
- Delphi调用网页美化SQL
百度搜索在线美化SQL语句的网站,为了加快解析速度,这里已下载到本地. 然后delphi用webbrowse载入本地的网页,然后把sql传进去,美化后取出来. 效果如下图 点击下载源码
- jquery粘贴操作
今天忘记记录一个点了,关于input字体默认浅色,聚焦变深的问题. 图一,默认浅色 图二,聚焦出现下拉框“最近搜索”记录,点击“程序员” 图三,input值变为“程序员”,颜色没有变深(复制粘贴也不变 ...
- Python 示例 饮水记录
因为每天都需要喝水 这是非常重要的 目录结构: ├─bin│ │ start.py│ ││ └─__pycache__│ start.cpython-36.pyc│├─core│ │ src.py│ ...
- ubuntu14.04 login loop issue
无法进入图形界面的所有问题几乎都碰到了,可惜尝试所有办法,还是各种broken packages 等,无法重装 ubuntu-desktop 成功. 耽误了2天,果断决定重装系统算了..尽管很多软件, ...
- 阿里云上部署tomcat启动后,通过http不能访问
原因是因为阿里为了安全设置了安全组策略,必须我们授权的端口,其他计算机才能通过http访问 设置流程: 点击安全组 再点击:配置规则 然后点击:添加安全组规则 开始配置:划红线的必写,授权对象:0.0 ...
- 解决Sublime 3提示 Sublime Text Error while loading PyV8 binary
转自:http://blog.initm.com/sublime-text/ 今天打开sublime遇到一个提示 如上图Sublime Text Error while loading PyV8 b ...
- iOS Xcode 调试技巧
一 NSLog调试 官方文档:Logs an error message to the Apple System Log facility. 即NSLog不是作为普通的debug log的,而是err ...
- bat脚本自动备份文件资源
1:xcopy命令进行文件拷贝 2:脚本内容: <span style="font-size:18px;">@echo off color 0D MODE con: ...
- for /f命令之—Delims和Tokens用法&总结
在For命令语踞饽参数F中,最难理解的就是Delims和Tokens两个选项,本文简单的做一个比较和总拮.“For /f”常用来解析文本,读取字符串.分工上,delims负责切分字符串,而tokens ...
- 如何在Windows中使用netsh命令进行端口转发
自Windows XP开始,Windows中就内置网络端口转发的功能.任何传入到本地端口的TCP连接(IPv4或IPv6)都可以被重定向到另一个本地端口,或远程计算机上的端口,并且系统不需要有一个专门 ...
