HashSet源码解读
一:先看其实现了哪些接口和继承了哪些类
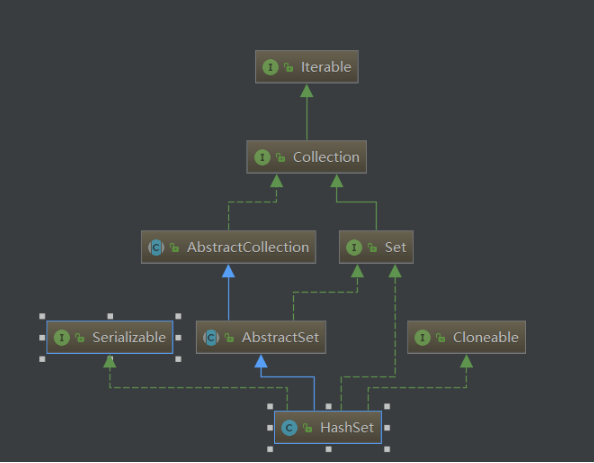
1.实现了Serializable接口,表明它支持序列化。
2.实现了Cloneable接口,表明它支持克隆,可以调用超类的clone()方法进行浅拷贝。
3.继承了AbstractSet抽象类,和ArrayList和LinkedList一样,在他们的抽象父类中,都提供了equals()方法和hashCode()方法。它们自身并不实现这两个方法
4.从JDK源码可以看出,底层并没有使用我们常规认为的利用hashcode()方法求的值进行比较,而是通过调用AbstractCollection的containsAll()方法,如果他们中元素完全相同(与顺序无关),则他们的equals()方法的比较结果就为true。
/**
* Compares the specified object with this set for equality. Returns
* <tt>true</tt> if the given object is also a set, the two sets have
* the same size, and every member of the given set is contained in
* this set. This ensures that the <tt>equals</tt> method works
* properly across different implementations of the <tt>Set</tt>
* interface.<p>
*
* This implementation first checks if the specified object is this
* set; if so it returns <tt>true</tt>. Then, it checks if the
* specified object is a set whose size is identical to the size of
* this set; if not, it returns false. If so, it returns
* <tt>containsAll((Collection) o)</tt>.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this set
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true; if (!(o instanceof Set))
return false;
Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o;
//保证个数相等
if (c.size() != size())
return false;
try {
//调用了AbstractCollection的方法。
return containsAll(c);
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
//只需要逐个判断集合是否包含其中的元素。
for (Object e : c)
if (!contains(e))
return false;
return true;
}
4.实现了Set接口。
二:HashSet概述
1.HashSet是通过HashMap的键来存值,HashMap里面的所有值都为null;
2.学习这个之前先看HashMap;附上网址https://www.cnblogs.com/xhlwjy/p/11246618.html
三:HashSet的属性
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;//用HashMap的Key来存值
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();//用于填充HashMap的value
四:构造方法
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
//这个是初始化一个HashMap
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
} /**
* Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified
* collection. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with default load factor
* (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in
* the specified collection.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
//初始化HashMap,把c集合中的所有元素添加到map中
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
} /**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* the specified initial capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive
*/
//初始化HashMap的容量和加载因子
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
} /**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* the specified initial capacity and default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero
*/
//初始化HashMap的容量
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
} /**
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set. (This package private
* constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet.) The backing
* HashMap instance is a LinkedHashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
* @param dummy ignored (distinguishes this
* constructor from other int, float constructor.)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive
*/
//这个初始化使用的是LinkedHashMap
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
五:添加新元素
//底层仍然利用了HashMap键进行了元素的添加。
//在HashMap的put()方法中,该方法的返回值是对应HashMap中键值对中的值,而值总是PRESENT,
//该PRESENT一直都是private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
//PRESENT只是初始化了,并不能改变,所以PRESENT的值一直为null。
//所以只要插入成功了,put()方法返回的值总是null。
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
这段代码就不分析了,与HashMap的插入差不多,可以先去看HashMap
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
六:删除一个元素
//该方法底层实现了仍然使用了map的remove()方法。
//map的remove()方法的返回的是被删除键对应的值。(在HashSet的底层HashMap中的所有键值对的值都是PRESENT)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
之后的代码就不粘贴出来了,自己可以去源码里面看
七:清空方法
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
八:克隆方法
底层仍然使用了Object的clone()方法,得到的Object对象,并把它强制转化为HashSet<E>,然后把它的底层的HashMap也克隆一份(调用的HashMap的clone()方法),并把它赋值给newSet,最后返回newSet即可。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
九:是否包含某个元素
底层使用了HashMap的containsKey()
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
十:判读是不是空
调用HashMap的方法
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
十一:统计HashSet中包含元素的个数
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
十二:生成迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
十三:序列化
/**
* Save the state of this <tt>HashSet</tt> instance to a stream (that is,
* serialize it).
*
* @serialData The capacity of the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance
* (int), and its load factor (float) are emitted, followed by
* the size of the set (the number of elements it contains)
* (int), followed by all of its elements (each an Object) in
* no particular order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out HashMap capacity and load factor
//容量写入流
s.writeInt(map.capacity());
//加载因子写入流
s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor()); // Write out size
//存放的数量写入流
s.writeInt(map.size()); // Write out all elements in the proper order.
//把每个元素写入流
for (E e : map.keySet())
s.writeObject(e);
}
十四:反序列化
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject(); // Read capacity and verify non-negative.
int capacity = s.readInt();
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal capacity: " +
capacity);
} // Read load factor and verify positive and non NaN.
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
} // Read size and verify non-negative.
int size = s.readInt();
if (size < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal size: " +
size);
}
// Set the capacity according to the size and load factor ensuring that
// the HashMap is at least 25% full but clamping to maximum capacity.
capacity = (int) Math.min(size * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),
HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); //HashMap中构建哈希桶数组是在第一个元素被添加的时候才构建,所以在构建之前检查它,
// 调用HashMap.tableSizeFor来计算实际分配的大小,
// 检查Map.Entry []类,因为它是最接近的公共类型实际创建的内容。 SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess()
.checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class,HashMap.tableSizeFor(capacity)); //创建HashMap。
map = (((HashSet<?>)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor)); // 按写入流中的顺序再把元素依次读取出来放到map中。
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
}
HashSet源码解读的更多相关文章
- JDK容器类List,Set,Queue源码解读
List,Set,Queue都是继承Collection接口的单列集合接口.List常用的实现主要有ArrayList,LinkedList,List中的数据是有序可重复的.Set常用的实现主要是Ha ...
- jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——HashSet的实现
jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——HashSet的实现 一.HashSet概述 HashSet实现Set接口,由哈希表(实际上是一个HashMap实例)支持.主要具有以下的特点: 不保证set的迭代顺 ...
- 【原】Spark中Job的提交源码解读
版权声明:本文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载. Spark程序程序job的运行是通过actions算子触发的,每一个action算子其实是一个runJob方法的运行,详见文章 SparkContex源码 ...
- HttpClient 4.3连接池参数配置及源码解读
目前所在公司使用HttpClient 4.3.3版本发送Rest请求,调用接口.最近出现了调用查询接口服务慢的生产问题,在排查整个调用链可能存在的问题时(从客户端发起Http请求->ESB-&g ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor源码解读
1. 背景与简介 在Java中异步任务的处理,我们通常会使用Executor框架,而ThreadPoolExecutor是JUC为我们提供的线程池实现. 线程池的优点在于规避线程的频繁创建,对线程资源 ...
- jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现
jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现 一. Set架构 如上图: (01) Set 是继承于Collection的接口.它是一个不允许有重复元素的集合.(0 ...
- MyBatis源码解读之延迟加载
1. 目的 本文主要解读MyBatis 延迟加载实现原理 2. 延迟加载如何使用 Setting 参数配置 设置参数 描述 有效值 默认值 lazyLoadingEnabled 延迟加载的全局开关.当 ...
- HttpClient4.3 连接池参数配置及源码解读
目前所在公司使用HttpClient 4.3.3版本发送Rest请求,调用接口.最近出现了调用查询接口服务慢的生产问题,在排查整个调用链可能存在的问题时(从客户端发起Http请求->ESB-&g ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
第七篇 前言 本篇文章主要讲解下载操作的相关知识,SDWebImageDownloaderOperation的主要任务是把一张图片从服务器下载到内存中.下载数据并不难,如何对下载这一系列的任务进行设计 ...
随机推荐
- 推荐一些C#相关的网站、资源和书籍 (转载自http://blog.csdn.net/chinacsharper/article/details/17514923)
一.网站 1.http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-CN/ 微软的官方网站,C#程序员必去的地方.那里有API开发文档,还有各种代码.资源下载. 2.http://social.m ...
- 怎么看待php 面向对象思想
面向对象的程序设计思路是现代程序设计由面向过程演变面向对象的必然趋势,所以面向对象的而设计思路必然有它不同的时代意义,必然有着不同面向过程的不同历史使命,而php 5以后成功添加面向对象的设计思路其实 ...
- 血的教训--如何正确使用线程池submit和execute方法
血的教训之背景:使用线程池对存量数据进行迁移,但是总有一批数据迁移失败,无异常日志打印 凶案起因 听说parallelStream并行流是个好东西,由于日常开发stream串行流的场景比较多,这次 ...
- (Demo分享)利用原生JavaScript-随机数-实现做一个烟花案例
原生js实现放烟花效果,点击鼠标,然后随机向四周扩散,! 思路: 1.首先烟花是五颜六色的,所以我们先写一个随机颜色的函数: 2.创建一个制造烟花的构造函数,第一个参数为元素,第二参数为初始x轴位置, ...
- 【数据结构--二叉树】Java递归实现二叉树遍历
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yaobolove/p/6213936.html 这有一棵树: 1.节点对象 package com.tree.mybinarytree; / ...
- 设计和编写一个异步通用Picker选择器,用于时间日期、城市、商品分类的选择
目录 一.功能规划 二.最底层基础实现 (1)Picker界面和功能实现 (2)不同类型的选择器基础实现 三.数据源层 (1)时间日期 (2)多级同步分类,如:城市 (3)多级异步分类,如:城市 四. ...
- html、javascript、url特殊字符的转义诠释及使用方法详解
html.javascript.url特殊字符转义在实际编程中都是有用到的,有的人对特殊字符转义的使用不是很清楚,下面就对html,javascript,url特殊字符的转义做一下说明和归纳. htm ...
- 第一个SpringBoot
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置.用我 ...
- leadcode的Hot100系列--155. 最小栈
栈:先入后出,后入先出 像电梯一样,先进入电梯的,走到电梯最深处,后进入电梯的,站在电梯门口, 所以电梯打开的时候,后进入的会先走出来,先进入的会后走出来. push,对应入电梯,把数据往里面压 po ...
- 用python的matplotlib和numpy库绘制股票K线均线和成交量的整合效果(含量化验证交易策略代码)
在用python的matplotlib和numpy库绘制股票K线均线的整合效果(含从网络接口爬取数据和验证交易策略代码)一文里,我讲述了通过爬虫接口得到股票数据并绘制出K线均线图形的方式,在本文里,将 ...
