Spring框架使用@Autowired自动装配引发的讨论
问题描述
有同事在开发新功能测试时,报了个错,大致就是,在使用 @Autowired 注入时,某个类有两个bean,一个叫a,一个叫b,Spring不知道该使用哪个bean注入。
一般这种情况应该声明注入哪个bean,他没有声明,他不知道这个类有两个bean,他说他和别人写的一样,别的都不报错。
OK,那来分析下吧。
问题分析
前提:@Autowired是根据类型(byType)进行自动装配的。
- 当找不到一个匹配的 Bean 时,Spring 容器将抛出 BeanCreationException 异常,并指出必须至少拥有一个匹配的 Bean。
- 如果当Spring上下文中存在不止一个候选Bean时,就会抛出BeanCreationException异常;
- 如果Spring上下文中不存在候选Bean,也会抛出BeanCreationException异常。
- 容器中有该类型的候选Bean
- 容器中只含有一个该类型的候选Bean
问题探究
public class Student{
private String name;
//getter and setter...
}
然后我们在 Spring 容器中创建多个 Student 的实例,如下:
我们通过 XML 配置文件的方式在 Spring 的配置文件里实现一个类型多个 bean。
如下,创建了两个 Student 的 bean ,id 分别为 student 和 student02,对应的bean 的name 属性 分别为小红和小明。
<bean id="student" class="com.autowiredtest.entity.Student">
<property name="name" value="小红"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student02" class="com.autowiredtest.entity.Student">
<property name="name" value="小明"/>
</bean>
我们也可以通过使用 配置类+注解 的方式实现一个类型多个 bean:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
public class StudentConfiguration{
@Bean
Student student03(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("小华");
return student;
}
@Bean
Student student04(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("小玲");
return student;
}
}
@Controller
public class AutowiredTestController{
@Autowired
private Student student; @RequestMapping("/AutowiredTest")
@ResponseBody
public String loanSign(){
String docSignUrl = "ok";
System.out.println("--------------要打印了------------");
System.out.println(student.getName());
System.out.println("--------------打印结束------------");
return docSignUrl;
}
}
(这里就是用一个简单的spring mvc的小demo来验证这个问题。)

是不是很奇怪?和上面说的不符合啊!这里 Student 类有4个实例,分别为 student、student02、student03和student04。
非但没有在调用时抛出 BeanCreationException 异常,反而正常运行,输出【小红】,说明注入的是 id 为 student 的 bean。
大胆的猜想:多个 bean 时,是根据 Student 的变量名自动匹配 bean id!
即 :当@Autowired private Student student; 时
我们的 Student 变量名是 student ,那么在 Spring 为其注入时,如果有多个 bean 的话就默认去容器中找 bean id 为 student 得那个 bean。
验证一下
把 Student 的变量名改为 student02,@Autowired private Student student02
重启,并访问http://localhost:8080/AutowiredTest,控制台输出:
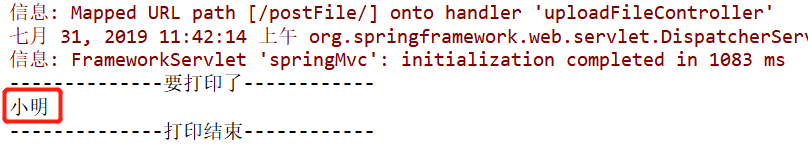
同样,改为 student03、student04控制台相应输出小华、小玲。
所以我们的大胆猜想是正确的!这里使用的 Spring 版本为 4.2.0.RELEASE。
本文永久链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ibigboy/p/11236729.html
大胆的猜想,和上面说的不一致,那是不是版本兼容了这个问题?
验证一下
把版本改低一点。首先,把 Spring 版本改为2.5(@Autowired第一次出现在该版本),这时候 @ResponseBody @Configuration 以及 @Bean都不能用了(更高版本才能用)。
这时候启动项目,不报错,访问http://localhost:8080/AutowiredTest,报错:
控制台错误信息:
严重: Context initialization failed
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'autowiredTestController': Autowiring of fields failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Could not autowire field: private com.autowiredtest.entity.Student com.autowiredtest.controller.AutowiredTestController.student02; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No unique bean of type [com.autowiredtest.entity.Student] is defined: expected single matching bean but found : [student, student02]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory$.run(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory$.getObject(AbstractBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.createWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.initServletBean(FrameworkServlet.java:)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean.init(HttpServletBean.java:)
at javax.servlet.GenericServlet.init(GenericServlet.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.initServlet(StandardWrapper.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.loadServlet(StandardWrapper.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.allocate(StandardWrapper.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve.invoke(AccessLogValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:)
at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:)
at org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor.process(AbstractHttp11Processor.java:)
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$AbstractConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AprEndpoint$SocketProcessor.doRun(AprEndpoint.java:)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AprEndpoint$SocketProcessor.run(AprEndpoint.java:)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:)
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Could not autowire field: private com.autowiredtest.entity.Student com.autowiredtest.controller.AutowiredTestController.student02; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No unique bean of type [com.autowiredtest.entity.Student] is defined: expected single matching bean but found : [student, student02]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.injectFields(InjectionMetadata.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:)
... more
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No unique bean of type [com.autowiredtest.entity.Student] is defined: expected single matching bean but found : [student, student02]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.resolveDependency(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:)
... more
控制台错误输出图:
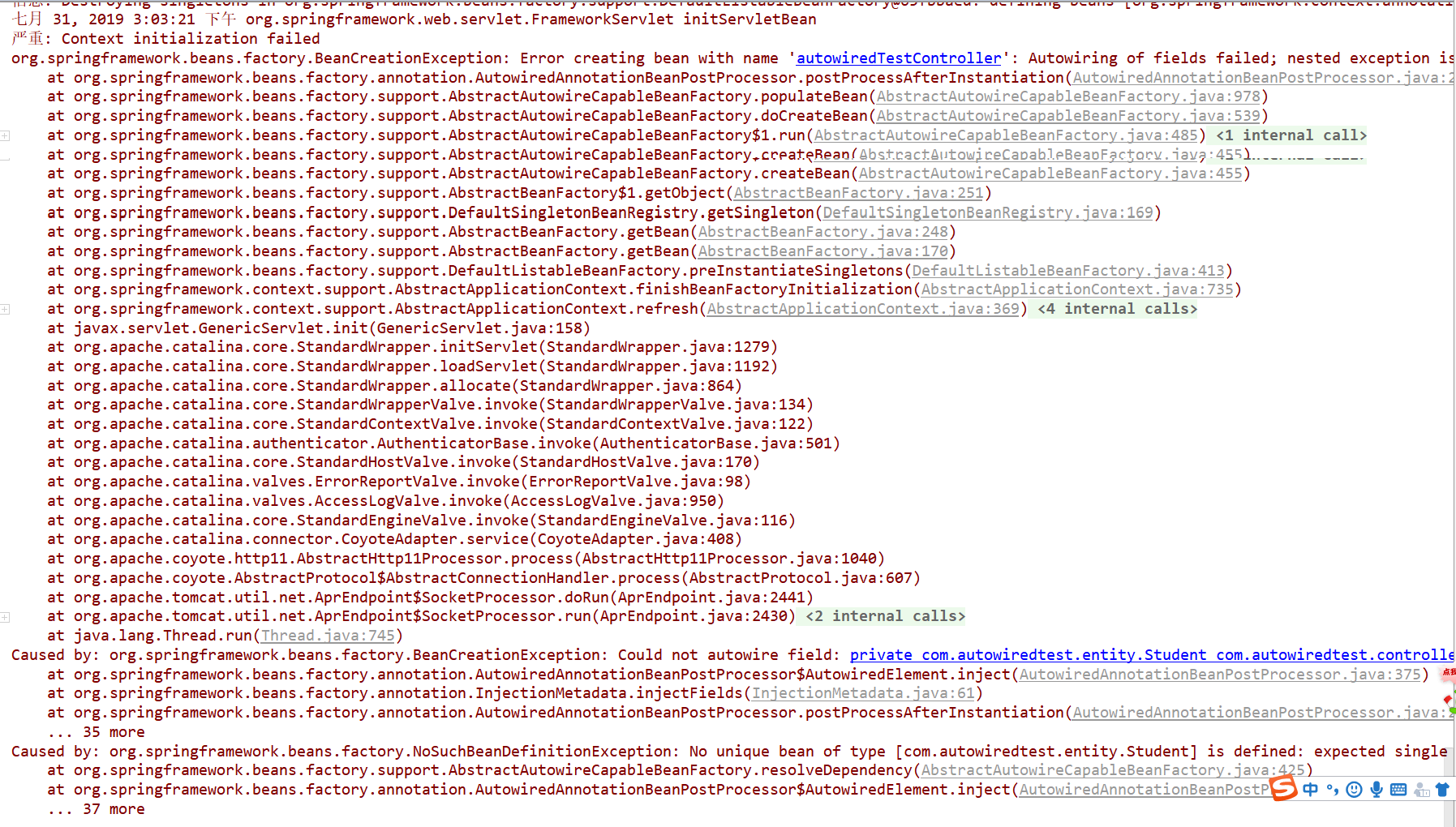
关键的异常信息:


这时候报了预期的错了。
我们再增大版本号,去测试一下到底是哪个版本号开始兼容了这个问题。
这是版本的发布情况,采用二分法逼近。
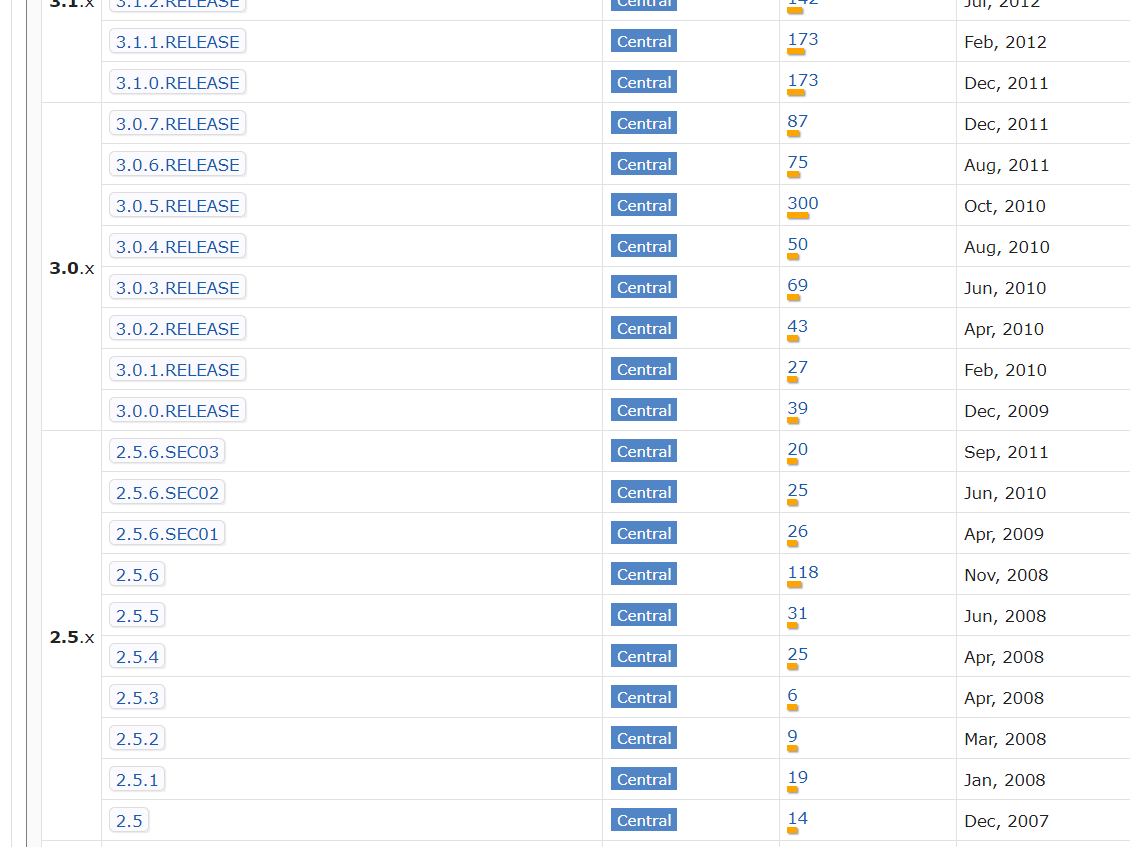
先从当前用的版本 4.2.0.RELEASE 换到 3.2.18.RELEASE(Spring 3.x的最后一个版本)也是没问题的,3.0.0.RELEASE也没问题,2.5.5报错,2.5.6报错,2.5.6.SEC03报错。
因此可以断定,从 Spring 3.x 开始兼容了这个问题,更加人性化。
所以上述关于 @Autowired 的使用规则要发生变化了:
- 容器中有该类型的候选Bean
- 容器中可以含有多个该类型的候选Bean(Spring 3.x以后)
- Spring 3.x 之前Spring容器中只能有一个Bean,否则抛出 BeanCreationException 异常
- Spring 3.x以后,可以有多个Bean使用 @Autowired 时变量名一定要和该类型多个Bean 的其中一个相同
(即上文中的@Autowired private Student student;,student 就是多个Bean中其中一个bean的id) - 若违反第4条规则,会抛出 BeanCreationException 异常
假如我们想自定义变量名呢?
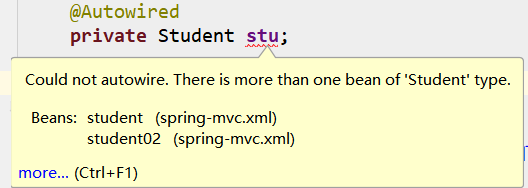
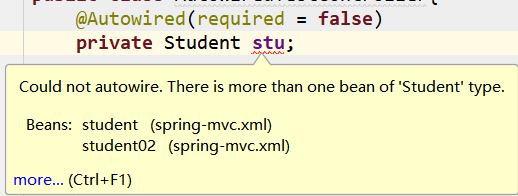
idea 直接告诉你,现在有两个 bean ,一个叫 student 另一个叫 student02,你现在写的变量名不是这俩种的任一个,你写的不对,给你报错!
而对于另外一些 IDE 则是没这么智能,如 eclipse。那就只有等到测试的时候才能发现了。
回到正题,怎么自定义变量名呢?
有2种方法:
@Autowired
@Qualifier("student")
private Student stu;
这样 Spring 会找到 id 为 student 的 bean 进行装配。
@Autowired(required = false)
public Student stu
但是idea可不惯着你,依旧给你报错提示,虽然这时候可以忽略它继续启动,但访问时还是会报 BeanCreationException:
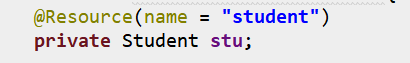
这个和 @Autowired 和 @Qualifier 的作用一样,可以理解为是二者的合并吧。
总结
附:为什么@Autowired 和 @Qualifier注解不合成一个?
//对成员变量使用 @Qualifier 注释
public class Boss {
@Autowired
private Car car; @Autowired
@Qualifier("office")
private Office office;
…
}
//对构造函数变量使用 @Qualifier 注释
public class Boss {
private Car car;
private Office office; @Autowired
public Boss(Car car , @Qualifier("office")Office office){
this.car = car;
this.office = office ;
}
}
Spring框架使用@Autowired自动装配引发的讨论的更多相关文章
- Spring(二)-生命周期 + 自动装配(xml) +自动装配(注解)
1.生命周期 **Spring容器的 bean **的生命周期: 1.1 默认生命周期 1.1.1 生命周期 调用构造方法,创建实例对象: set方法,给实例对象赋值: init 初始化方法 初始化对 ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记99:Spring学习---Spring Bean配置:自动装配,配置bean之间的关系(继承/依赖),bean的作用域(singleton,prototype,web环境作用域),使用外部属性文件
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- spring(4)——自动装配
set注入和构造注入有时在做配置时比较麻烦.所以框架为了提高开发效率,提供自动装配功能,简化配置.spring框架式默认不支持自动装配的,要想使用自动装配需要修改spring配置文件中<bean ...
- Spring实战之处理自动装配的歧义性
仅有一个bean匹配所需的结果时,自动装配才是有效的.如果不仅有一个bean能够匹配结果的话,这种歧义性会阻碍Spring自动装配属性.构造器参数或方法参数.为了阐述自动装配的歧义性,假设我们使用@A ...
- 模仿 spring IOC Annotation版自动装配
spring 有两大核心 IOC和AOP. IOC (inversion of control) 译为 控制反转,也可以称为 依赖注入 ; AOP(Aspect Oriented Programmi ...
- Spring入门(八):自动装配的歧义性
1. 什么是自动装配的歧义性? 在Spring中,装配bean有以下3种方式: 自动装配 Java配置 xml配置 在这3种方式中,自动装配为我们带来了很大的便利,大大的降低了我们需要手动装配bean ...
- Spring注解开发系列Ⅴ --- 自动装配&Profile
自动装配: spring利用依赖注入和DI完成对IOC容器中各个组件的依赖关系赋值.自动装配的优点有: 自动装配可以大大地减少属性和构造器参数的指派. 自动装配也可以在解析对象时更新配置. 自动装配的 ...
- Spring学习总结(2)-自动装配
上面说过,IOC的注入有两个地方需要提供依赖关系,一是类的定义中,二是在spring的配置中需要去描述.自动装配则把第二个取消了,即我们仅仅需要在类中提供依赖,继而把对象交给容器管理即可完成注入.在实 ...
- Spring基于的注解自动装配和依赖注入(***)
#自动装配的小Demo: package com.gyf.annotation; //DAO层 public interface UserDao { public void save(); } pac ...
随机推荐
- centos 5.5版本中添加ext4格式
1.我在使用centos 5.5版本做练习的时候发现默认是不支持ext4文件格式. 在添加硬盘后,用fdisk -l 查看到信息如下: 分区完后,使用命令:mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb会 ...
- Hadoop —— 单机环境搭建
一.前置条件 Hadoop的运行依赖JDK,需要预先安装,安装步骤见: Linux下JDK的安装 二.配置免密登录 Hadoop组件之间需要基于SSH进行通讯. 2.1 配置映射 配置ip地址和主机名 ...
- 【Zookeeper02】ZK的作用以及使用
上一篇介绍了ZK的安装以及集群的搭建,这只能算是个软件安装过程,具体是做什么的.怎么用也没有做解释,这一篇中博主就自己的私人理解简单写一下: 1.是什么: a.Zookeeper是一个分布式协调服务, ...
- tomcat实现
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u014795347/article/details/52328221?locationNum=2&fps=1 以下代码纯属本人复制,而且 ...
- phpstorm+xdebug手机app调试
1.安装过程网上搜一下全都是,这里省略. 2.由于debug调试需要去判断cookie中XDEBUG_SESSION,然后去调试.由于app接口请求没法去传,而且就算去传递也很麻烦,还要让app去改动 ...
- 小白开学Asp.Net Core 《五》
小白开学Asp.Net Core<五> —— 使用.Net Core MVC Filter 一.简介 今天在项目(https:/ ...
- 常用的方法论-NPS
- 004-python-列表、元组、字典
1. 什么是列表 列表是一个可变的数据类型 列表由[]来表示, 每一项元素使用逗号隔开. 列表什么都能装. 能装对象的对象. 列表可以装大量的数据 2. 列表的索引和切片 列表和字符串一样. 也有索引 ...
- Codeforces Gym101201B:Buggy Robot(BFS + DP)
题目链接 题意 给出一个n*m的地图,还有一个操作序列,你原本是要按照序列执行操作的,但是你可以修改操作:删除某些操作或者增加某些操作,问从'R'到'E'最少需要多少次修改操作. 思路 和上次比赛做的 ...
- HDU XXXX:求[L,R]的素数数量(数位DP)
Problem G Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 131072/131072K (Java/Other) Total S ...
