C++ 11 snippets , 2
<1>auto ,initializer_list<T>,auto指向函数指针的简易,和typdef 定义的类型执行函数指针有多复杂。
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <string>
using namespace std; template <typename T>
T sum(initializer_list<T> rh)
{
T val;
for(auto p= rh.begin();p!=rh.end();p++)
{
val+= *p;
}
return val;
} int main()
{
// use init list
cout << sum({,,,,}) <<endl;
cout << sum({1.0,2.0,3.1,4.0,5.0}) <<endl; //
cout << "use auto to point the function sum" <<endl;
auto dadd_func = sum<double>;
auto iadd_func = sum<int>;
auto tadd_func = sum<string>;
cout << dadd_func({,,,}) <<endl;
cout << iadd_func({,,,,}) <<endl;
cout << tadd_func({"houdini","maya","json"}) <<endl; cout << "\nuse the typedef to pointer\n";
typedef int (*td_int_sum)(initializer_list<int> rh);
typedef string (*td_str_sum)(initializer_list<string> rh);
td_int_sum int_add = sum<int>;
td_str_sum str_add = sum<string>;
cout << int_add({,,,,,}) <<endl;
cout << str_add({"s1","s2","s5"}) << endl; return ;
}
<2>funcional,std::generate,std::count_if
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional> using namespace std; double square(double x){return x*x;} int main()
{
vector <int> vars(); generate(vars.begin(),vars.end(),std::rand);
for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){cout << v <<endl;}); // lambda can transfer local variable
int sum = ;
for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[&sum](int v){sum+=v;});
cout << "the sum is " << sum <<endl; // <100 num
cout << "get <100 numbers" <<endl;
cout << count_if(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){ return v<;}) <<endl; // functional
function<double(double)> ef1 = square;
cout << ef1() <<endl; // function<void(int var)> ef2 = [](int val){cout << val <<endl;};
ef2(); // return ;
}
<3> remove_if,vector,min_element,max_element
include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std; void cppRemove_if()
{
cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n";
int myInts[]{,,,,,,,}; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
int *pbegin = myInts;
int *pend = myInts + sizeof(myInts)/ sizeof(int);
pend = remove_if(pbegin,pend,
[](const int &val)->bool{return val% == ;});//2 4 5 8 ? ? ? ?
for (int* p=pbegin; p!=pend; ++p)
cout << ' ' << *p;
cout << "\n";
cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n"; } int main()
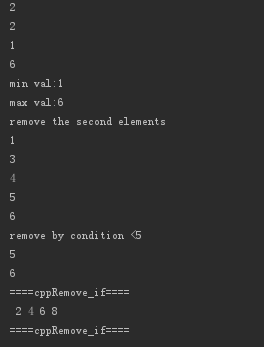
{ vector<int> va{,,,,,}; // find, if not find elements,will return last *iter;
auto va_find2 = find(va.begin(),va.end(),);
auto va_find2e = find_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){return x==;});
cout << *va_find2 <<endl;
cout << *va_find2e <<endl; cout << *min_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl;
cout << *max_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl; auto min_max = minmax_element(va.begin(),va.end());
cout << "min val:" <<*(min_max.first)<<endl;
cout << "max val:" <<*(min_max.second)<<endl; cout << "remove the second elements \n";
va.erase(va.begin()+,va.begin()+);
for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;}); cout << "remove by condition <5 \n";
va.erase(remove_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](int x){return x <;}),va.end());
for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;}); cppRemove_if();
return ;
}
<4>binary_search,sort更加详细的用法:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std; template <typename T1>
void ShowIntArray(const T1 begin, const T1 end)
{
for_each(begin,end,[](const int &x){cout << x <<" "; });
cout << "\n";
}
template <typename T>
void ShowSTLArray(const T&cont)
{
auto iter = cont.begin();
auto end = cont.end();
for(;iter!=end;iter++)
{
cout << *iter <<" ";
}
cout <<endl;
}; void cpp_sort()
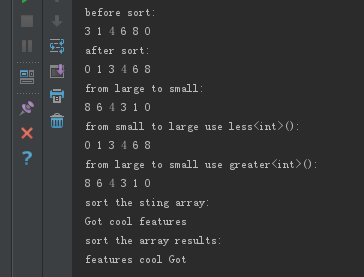
{
int a[]= {,,,,,};
int *begin = a;
int *end = a + ; cout << "before sort:\n";
ShowIntArray(begin, end); sort(begin,end);
cout << "after sort:\n";
ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from large to small:\n";
sort(begin,end,[](const int &x,const int &y){return x>y;});
ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from small to large use less<int>():\n";
sort(begin,end,less<int>());
ShowIntArray(begin, end); cout << "from large to small use greater<int>():\n";
sort(begin,end,greater<int>());
ShowIntArray(begin, end); vector<string> vecStr{"Got","cool","features"};
cout << "sort the sting array:\n";
ShowSTLArray(vecStr);
auto strCmp = [](string &a,string &b)
{
return a.length() > b.length();
};
cout << "sort the array results:\n";
sort(vecStr.begin(),vecStr.end(),strCmp);
ShowSTLArray(vecStr); } void cpp_binary_search()
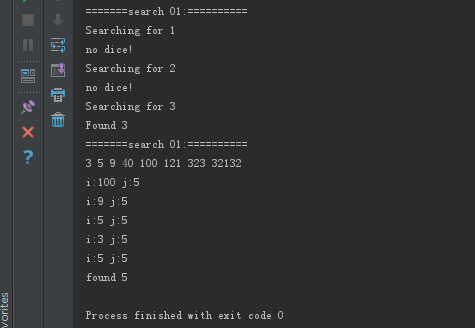
{ cout << "=======search 01:==========\n";
std::vector<int> haystack {, , , , };
std::vector<int> needles {, , };
sort(haystack.begin(),haystack.end());
for (auto needle : needles)
{
cout << "Searching for " << needle << '\n';
if (binary_search(haystack.begin(), haystack.end(), needle))
{ cout << "Found " << needle << '\n';
}
else
{
cout << "no dice!\n";
}
}
cout << "=======search 01:==========\n"; std::vector<int> haystack2 {, , , , ,,,};
sort(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),[](int &x,int &y){return x<y;});
ShowSTLArray(haystack2); auto func =[](int i,int j)->bool{cout<< "i:" << i; cout << " j:"<<j;cout<<"\n";return (i<j);};
if (binary_search(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),,func))
{
cout << "found 5" <<endl;
} } int main()
{
//cpp_sort();
cpp_binary_search();
return ;
}
binarySearch结果:
Sort结果:
<5> 线程大法
(1) hello world thread:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>
using namespace std; void thread_task()
{
cout << "thread hello world\n";
} int main()
{
shared_ptr<thread> t(new thread(thread_task));
t->join(); return ;
}
(2)带参数的函数(bind方法,直接使用thread构造也可以)
void thread_parm(const int &n,const string& name)
{
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
cout << name <<":thread loop in " << i <<endl;
}
} void withParam()
{
thread t0(thread_parm,,"houdini");
thread t1(bind(thread_parm,,"maya"));
t0.join();
t1.join();
} int main()
{
withParam();
return ;
}
(3)成员对象函数执行在线程中(也可以作用到智能指针对象)
class HelloObject
{
public:
void sayHello(const string& name,int n)
{
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
cout << name << " thread: " << i <<endl;
}
}
}; void objectFunction()
{
HelloObject obj;
thread t(&HelloObject::sayHello,&obj,"Json",);
t.join(); // work with shared_ptr
shared_ptr<HelloObject> objPtr(new HelloObject());
thread tptr(&HelloObject::sayHello,objPtr,"Houdini",);
tptr.join();
} int main()
{
objectFunction();
return ;
}
(4)传递引用,头文件functional,std::ref()
class FuncObj
{
public:
void operator()()const
{
cout << this <<endl;
}
};
void passRef()
{
auto obj = FuncObj();
obj(); //pass by value
cout << "thread will pass by value\n";
thread t1(obj);
t1.join(); //pass by ref
cout << "thread will pass by ref\n";
thread t2(ref(obj));
t2.join(); } int main()
{
passRef();
return ;
}
结果:
0x22fdff
thread will pass by value
0x7c6150
thread will pass by ref
0x22fdff
普通的函数也可以
void increment(int &value)
{
value++ ;
cout << "value :" << value <<endl; }
void passRef2()
{
int a = ;
thread t(increment,ref(a));
t.join();
} int main()
{
passRef2();
return ;
}
(5)基本功能:
匿名函数:get_id() 区分线程
void lambdaTest()
{
vector <thread> threads;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
threads.emplace_back(thread([](){cout << "thread id " << this_thread::get_id() << endl;}));
} for(auto &t : threads)
{
t.join();
}
} int main()
{
lambdaTest();
return ;
}
总线程数:
cout << thread::hardware_concurrency() <<endl;
(6)异常与线程
标准处理方法
struct Counter2
{
int value;
Counter2():value(){}
void increment()
{
++value;
}
void decrement()
{
if(value == )
{
throw string("value cannot be less than 0");
} --value;
}
}; struct Wrapper
{
Counter2 ct;
mutex m; void increment()
{ }
void decrement()
{
m.lock();
try
{
ct.decrement();
}
catch (const string &e)
{
m.unlock();
cout << e <<endl;
throw e;
} m.unlock();
}
}; void exceptionLock()
{
Wrapper wap;
wap.ct.value = ; vector<thread> threads;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
threads.emplace_back(thread([&wap](){
wap.decrement(); }));
}
for(auto &t:threads)
{
t.join();
}
cout << wap.ct.value << endl;
}
(7)模仿Inter TBB parallel_for
串行时间:87
并行时间:19
struct BlockRange
{
BlockRange():begin(),end()
{ }
int begin;
int end;
}; class ApplyFoo
{
public:
ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data)
{
}
void operator()(const BlockRange &range)const
{
for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++)
{
(*mData)[i] += ;
}
}
private:
vector<int> *mData;
}; template <typename T>
void parallel_for(const T &body,int size,int begin)
{
auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency();
auto nValuesSize = size;
auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads;
if(nValuesSize < nThreads)
{
BlockRange range;
range.begin = begin;
range.end = nValuesSize;
body(range);
return;
}
// building blocks
vector<BlockRange> blocks;
int index = begin;
while(index <= nValuesSize)
{
BlockRange range;
range.begin = index;
range.end = index+ perBlockSize;
blocks.push_back(range);
index += (perBlockSize) ;
}
// fix last block end size;
blocks[blocks.size()-].end = nValuesSize;
// thread pool to run
typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr;
vector<thread_ptr> pools;
for(BlockRange&r:blocks)
{
pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r));
}
for(auto &t:pools)
{
t->join();
} } void parallel()
{
vector<int> values();
fill(values.begin(),values.end(),); double start,end,cost;
start=clock();
parallel_for(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),);
end= clock();
cost = end -start;
cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl; }
void serial()
{
vector<int> values();
fill(values.begin(),values.end(),); double start,end,cost;
start=clock();
for(int i=;i<values.size();i++)
{
values[i] += ;
}
end= clock();
cost = end -start;
cout << "serial for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
} int main()
{ parallel();
serial();
return ;
}
并行accumulation:
10亿个元素相加:简直他妈的快飞起来了。
串行时间:13063
并行时间:1023
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; struct BlockRange
{
BlockRange():begin(),end(),id()
{ }
int begin;
int end;
int id;
}; class ApplyFoo
{
public:
ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data)
{
}
void operator()(const BlockRange &range,vector<int> *des)const
{
auto value = int();
for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++)
{
value +=(*mData)[i];
}
(*des)[range.id] = value;
}
private:
vector<int> *mData; }; template <typename retType,typename T>
retType parallel_add(const T &body,int size,int begin)
{
vector<retType> partial_accum;
auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency();
auto nValuesSize = size;
auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads;
if(nValuesSize < nThreads)
{
partial_accum.resize();
BlockRange range;
range.begin = begin;
range.end = nValuesSize;
range.id = ;
body(range,&partial_accum);
return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType());
}
// building blocks
vector<BlockRange> blocks;
int index = begin;
int blockId = ;
while(index <= nValuesSize)
{
BlockRange range;
range.begin = index;
range.end = index+ perBlockSize;
range.id = blockId;
blocks.push_back(range);
index += (perBlockSize) ;
blockId += ;
}
partial_accum.resize(blocks.size()); // fix last block end size;
blocks[blocks.size()-].end = nValuesSize;
// thread pool to run
typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr;
vector<thread_ptr> pools; for(BlockRange&r:blocks)
{
pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r,&partial_accum));
}
for(auto &t:pools)
{
t->join();
} return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType()); } void parallel()
{
vector<int> values();
fill(values.begin(),values.end(),); double start,end,cost;
start=clock();
cout << "get the result :" <<parallel_add<int>(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),) <<endl;
end= clock();
cost = end -start;
cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
} void serial()
{
vector<int> values();
fill(values.begin(),values.end(),); double start,end,cost;
start=clock();
cout << "get the result :" <<accumulate(values.begin(),values.end(),) <<endl;
end= clock();
cost = end -start;
cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
} int main()
{ parallel();
//serial();
return ;
}
<n> boost bind
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp> #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void dprint(int x,int y)
{
cout << x << " " <<y <<endl;
} class Bind_test
{
public:
void setData(int x,int y)
{
_x = x;
_y = y;
}
void printData()
{
cout << _x << " " <<_y <<endl;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y; }; void increnum(int &dg)
{
dg++;
} int main()
{
boost::bind(&dprint,,)(); // 5,5
boost::bind(&dprint,,_1)(); // 3, 5
boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_1)(); // 2, 2
boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_2)(,); // 1, 2
boost::bind(&dprint,_2,_1)(,); // 2, 1 ->函数参数对掉 cout << "\nbind the class function\n";
boost::shared_ptr<Bind_test> bclass(new Bind_test);
boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass,,)();
bclass->printData(); Bind_test *bclass_02 = new Bind_test;
boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass_02,,)();
bclass_02->printData(); // 2 ,3
delete bclass_02; Bind_test bclass_03;
boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,,)();
bclass_03.printData(); // 4 ,5
boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_1)();
bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,9
boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_2)(,);
bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,10 int dgNum = ;
boost::bind(&increnum,boost::ref(dgNum))(); // 类似C++11 Thread 里要传递引用std::ref(x)
cout << dgNum <<endl; cin.get();
return ;
}
额外的:
static_assert 编译时候assertions

下面将输出:hello \n no
cout << R"(hello \n no)" <<endl;
。
C++ 11 snippets , 2的更多相关文章
- C++ 11 snippets , 1
1->创建7个Thread,跑个非常大的循环.观察CPU void func(string &name) { ;i<0xFFFFFFFF;i++) { //cout << ...
- Visual Studio 2010 中的 Web 开发
概述 Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 为 ASP.NET Web 应用程序的开发提供非常多新的功能.这些新功能旨在帮助开发者高速方便地创建和部署质量高且功能全的 Web 应用 ...
- [OpenCV] Install OpenCV 3.4 with DNN
目标定位 一.开始全面支持 Tensorflow OpenCV3.4 新功能 当前最新进展OpenCV 3.4 dev:https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/ma ...
- 地区sql
/*Navicat MySQL Data Transfer Source Server : localhostSource Server Version : 50136Source Host : lo ...
- 25+ Useful Selenium Web driver Code Snippets For GUI Testing Automation
本文总结了使用Selenium Web driver 做页面自动化测试的一些 tips, tricks, snippets. 1. Chrome Driver 如何安装 extensions 两种方式 ...
- Java 9 揭秘(11. Java Shell)
Tips 做一个终身学习的人. 在本章节中,主要介绍以下内容: 什么是Java shell JShell工具和JShell API是什么 如何配置JShell工具 如何使用JShell工具对Java代 ...
- 11月26号host
127.0.0.1 localhost255.255.255.255 broadcasthost::1 localhostfe80::1%lo0 localhost # Google start216 ...
- 11月16host文件
#################################################################################################### ...
- c++ telescoping constructor is NOT supported until c++11
Telescoping constructor: see Effective Java 2nd Edition Item 2 If you want to use telescoping constr ...
随机推荐
- 干货分享:互联网运营 学习SEO从零开始 SEO深度解析学习笔记
最近在自学SEO,互联网运营,把做的笔记干货分享给大家啊! 希望能帮到大家,如有好的建议可以关注我[磨人的小妖精]或留言,大家一起探讨. 之前还写过一篇文章互联网运营+SEO:推荐必看的5本书籍,学习 ...
- python自动化开发-[第二十四天]-高性能相关与初识scrapy
今日内容概要 1.高性能相关 2.scrapy初识 上节回顾: 1. Http协议 Http协议:GET / http1.1/r/n...../r/r/r/na=1 TCP协议:sendall(&qu ...
- oracle中的insert all into,在mysql中的写法
oracle中的insert all into表示插入多条数据,mysql中可以采用: INSERT INTO表名(字段1,字段2..) values <foreach collection=& ...
- 时间偏移sql
mysql:select date_sub(str_to_date('2018/8/21','%Y/%m/%d') ,interval 90 day) ; oracle:select to_date( ...
- 网络设备监控-Catic添加H3C的监控图解
网络设备监控-Catic添加H3C的监控图解 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 首先,我要声明满足2个条件才能作本篇笔记的操作:第一:你得有台cacti服务器,第二 ...
- 2.抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
常规的对象创建方法: //创建一个Road对象 Road road =new Road(); new 的问题: 实现依赖,不能应对“具体实例化类型”的变化.解决思路: 封装变化点-----哪里变 ...
- https笔记【转】
图解HTTPS 我们都知道HTTPS能够加密信息,以免敏感信息被第三方获取.所以很多银行网站或电子邮箱等等安全级别较高的服务都会采用HTTPS协议. HTTPS简介 HTTPS其实是有两部分组成:HT ...
- 伯克利SocketAPI(一) socket的C语言接口/最简单的服务器和对应的客户端C语言实现
1. 头文件 2. API函数 3. 最简单的服务器和对应的客户端C语言实现 3.1 server #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/sock ...
- Python复习笔记(六)网络编程(udp/tcp)
一.网络-udp(用户数据报协议) 用户数据报协议 类似写信,不安全,数据有可能丢 1.1 ip地址 注意: IP地址127.0.0.1 ~ 127.255.255.255 用于回路测试 私有ip地址 ...
- 使用JAVA数组实现顺序栈
1,首先总结一下线性表(分为顺序表和链接表,[即顺序存储结构和链式存储结构的区别])和栈(顺序栈和链接栈)还有队列(顺序队列和链接队列)的JAVA类库中的实现: java.util.ArrayList ...
