ViewBinding 与 Kotlin 委托双剑合璧
请点赞关注,你的支持对我意义重大。
Hi,我是小彭。本文已收录到 GitHub · Android-NoteBook 中。这里有 Android 进阶成长知识体系,有志同道合的朋友,关注公众号 [彭旭锐] 带你建立核心竞争力。
前言
大家好,我是小彭。
过去两年,我们在掘金平台上发表过一些文章,小彭也收到了大家的意见和鼓励。最近,我会陆续搬运到公众号上。
ViewBinding 是 Android Gradle Plugin 3.6 中新增的特性,用于更加轻量地实现视图绑定(即视图与变量的绑定),可以理解为轻量版本的 DataBinding。 在这篇文章里,我将总结 ViewBinding 使用方法 & 原理,示例程序 AndroidFamilyDemo · KotlinDelegate 有用请记得给 Star ,给小彭一点创作的动力。
前置知识:
- Kotlin | 委托机制 & 原理 & 应用
- Kotlin | 扩展函数(终于知道为什么 with 用 this,let 用 it)
- Java | 关于泛型能问的都在这里了(含Kotlin)
- Android | Fragment 核心原理 & 面试题 (AndroidX 版本)
学习路线图
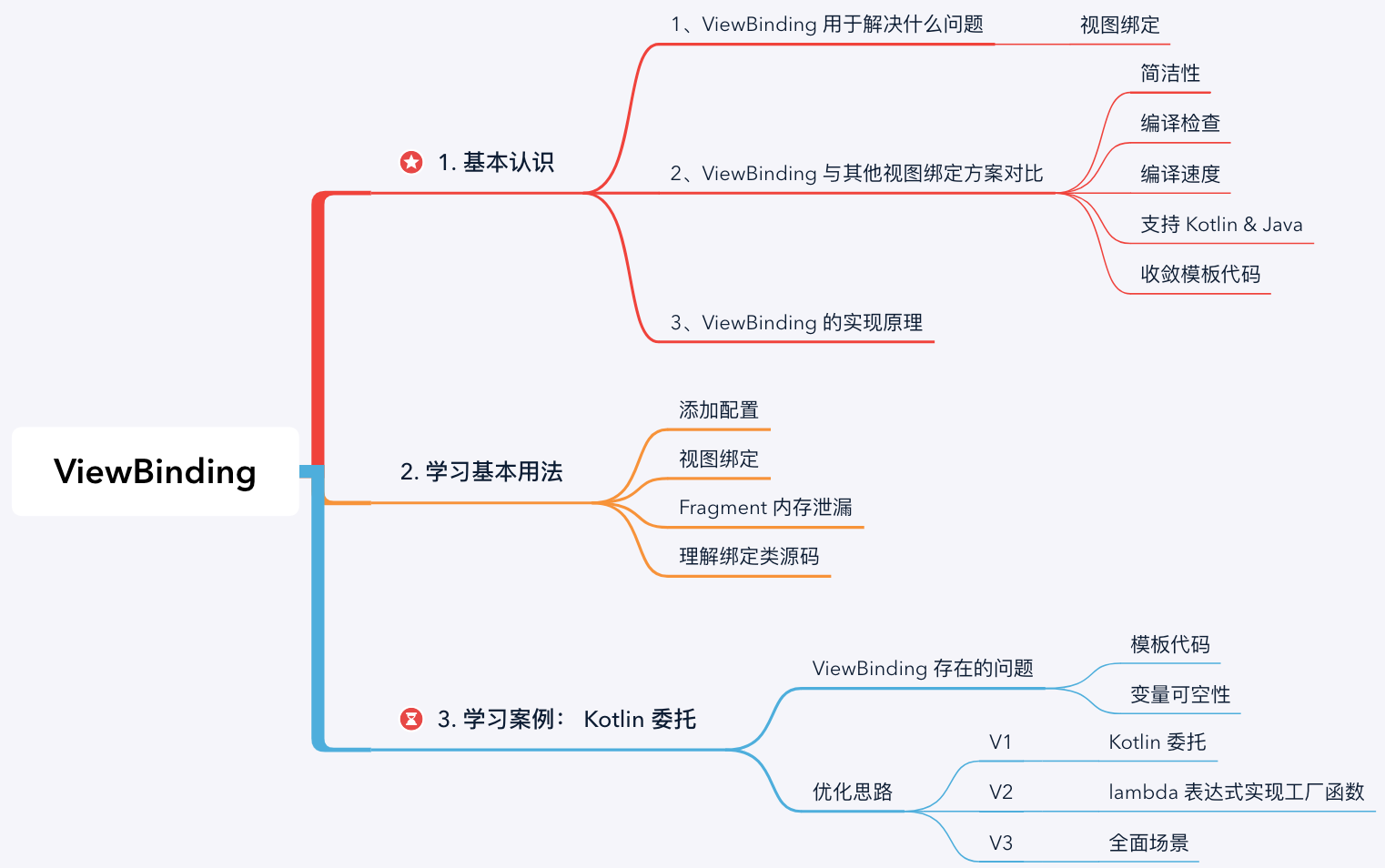
1. 认识 ViewBinding
1.1 ViewBinding 用于解决什么问题?
ViewBinding 是 Android Gradle Plugin 3.6 中新增的特性,用于更加轻量地实现视图绑定(即视图与变量的绑定),可以理解为轻量版本的 DataBinding。
1.2 ViewBinding 与其他视图绑定方案对比
在 ViewBinding 之前,业界已经有过几种视图绑定方案了,想必你也用过。那么,ViewBinding 作为后起之秀就一定比前者香吗?我从多个维度对比它们的区别:
| 角度 | findViewById | ButterKnife | Kotlin Synthetics | DataBinding | ViewBinding | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 简洁性 | ||||||
| 编译期检查 | ||||||
| 编译速度 | ||||||
| 支持 Kotlin & Java | ||||||
| 收敛模板代码 |
- 1、简洁性: findViewById 和 ButterKnife 需要在代码中声明很多变量,其他几种方案代码简洁读较好;
- 2、编译检查: 编译期间主要有两个方面的检查:类型检查 + 只能访问当前布局中的 id。findViewById、ButterKnife 和 Kotlin Synthetics 在这方面表现较差;
- 3、编译速度: findViewById 的编译速度是最快的,而 ButterKnife 和 DataBinding 中存在注解处理,编译速度略逊色于 Kotlin Synthetics 和 ViewBinding;
- 4、支持 Kotlin & Java: Kotlin Synthetics 只支持 Kotlin 语言;
- 5、收敛模板代码: 基本上每种方案都带有一定量的模板代码,只有 Kotlin Synthetics 的模板代码是较少的。
可以看到,并没有一种绝对优势的方法,但越往后整体的效果是有提升的。另外,是什么呢?
1.3 ViewBinding 的实现原理
AGP 插件会为每个 XML 布局文件创建一个绑定类文件 xxxBinding ,绑定类中会持有布局文件中所有带 android:id 属性的 View 引用。例如,有布局文件为 fragment_test.xml ,则插件会生成绑定类 FragmentTestBinding.java 。
那么,所有 XML 布局文件都生成 Java 类,会不会导致包体积瞬间增大?不会的, 未使用的类会在混淆时被压缩。
2. ViewBinding 的基本用法
这一节我们来介绍 ViewBinding 的使用方法,内容不多。
提示: ViewBinding 要求在 Android Gradle Plugin 版本在至少在 3.6 以上。
2.1 添加配置
视图绑定功能按模块级别启用,启用的模块需要在模块级 build.gralde 中添加配置。例如:
build.gradle
android {
...
viewBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
对于不需要生成绑定类的布局文件,可以在根节点声明 tools:viewBindingIgnore="true" 。例如:
<LinearLayout
...
tools:viewBindingIgnore="true" >
...
</LinearLayout>
2.2 视图绑定
绑定类中提供了 3 个视图绑定 API:
// 绑定到视图 view 上
fun <T> bind(view : View) : T
// 使用 inflater 解析布局,再绑定到 View 上
fun <T> inflate(inflater : LayoutInflater) : T
// 使用 inflater 解析布局,再绑定到 View 上
fun <T> inflate(inflater : LayoutInflater, parent : ViewGroup?, attachToParent : Boolean) : T
- 1、在 Activity 中使用
MainActivity.kt
class TestActivity: AppCompatActivity(R.layout.activity_test) {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityTestBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityTestBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
binding.tvDisplay.text = "Hello World."
}
}
- 2、在 Fragment 中使用
TestFragment.kt
class TestFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_test) {
private var _binding: FragmentTestBinding? = null
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onViewCreated(root: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
_binding = FragmentTestBinding.bind(root)
binding.tvDisplay.text = "Hello World."
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
// 置空
_binding = null
}
}
2.3 避免内存泄露
这里有一个隐藏的内存泄露问题,你需要理解清楚(严格来说这并不是 ViewBinding 的问题,即使你采用其它视图绑定方案也要考虑这个问题)。
问题:为什么 Fragment#onDestroyView() 里需要置空绑定类对象,而 Activity 里不需要?
答:Activity 实例和 Activity 视图的生命周期是同步的,而 Fragment 实例和 Fragment 视图的生命周期并不是完全同步的,因此需要在 Fragment 视图销毁时,手动回收绑定类对象,否则造成内存泄露。例如:detach Fragment,或者 remove Fragment 并且事务进入返回栈,此时 Fragment 视图销毁但 Fragment 实例存在。关于 Fragment 生命周期和事务在我之前的一篇文章里讨论过:Android | Fragment 核心原理 & 面试题 (AndroidX 版本)
总之,在视图销毁但是控制类对象实例还存活的时机,你就需要手动回收绑定类对象,否则造成内存泄露。
2.4 ViewBinding 绑定类源码
反编译如下:
ActivityTestBinding.java
public final class ActivityTestBinding implements ViewBinding {
private final ConstraintLayout rootView;
public final TextView tvDisplay;
private ActivityTestBinding (ConstraintLayout paramConstraintLayout1, TextView paramTextView)
this.rootView = paramConstraintLayout1;
this.tvDisplay = paramTextView;
}
public static ActivityTestBinding bind(View paramView) {
TextView localTextView = (TextView)paramView.findViewById(2131165363);
if (localTextView != null) {
return new ActivityMainBinding((ConstraintLayout)paramView, localTextView);
}else {
paramView = "tvDisplay";
}
throw new NullPointerException("Missing required view with ID: ".concat(paramView));
}
public static ActivityMainBinding inflate(LayoutInflater paramLayoutInflater) {
return inflate(paramLayoutInflater, null, false);
}
public static ActivityMainBinding inflate(LayoutInflater paramLayoutInflater, ViewGroup paramViewGroup, boolean paramBoolean) {
paramLayoutInflater = paramLayoutInflater.inflate(2131361821, paramViewGroup, false);
if (paramBoolean) {
paramViewGroup.addView(paramLayoutInflater);
}
return bind(paramLayoutInflater);
}
public ConstraintLayout getRoot() {
return this.rootView;
}
}
3. ViewBinding 与 Kotlin 委托双剑合璧
到这里,ViewBinding 的使用教程已经说完了。但是回过头看,有没有发现一些局限性呢?
- 1、创建和回收 ViewBinding 对象需要重复编写样板代码,特别是在 Fragment 中使用的案例;
- 2、binding 属性是可空的,也是可变的,使用起来不方便。
那么,有没有可优化的方案呢?我们想起了 Kotlin 属性委托,关于 Kotlin 委托机制在我之前的一篇文章里讨论过:Kotlin | 委托机制 & 原理。如果你还不太了解 Kotlin 委托,下面的内容对你会有些难度。下面,我将带你一步步封装 ViewBinding 属性委托工具。首先,我们梳理一下我们要委托的内容与需求,以及相应的解决办法:
| 需求 | 解决办法 |
|---|---|
| 需要委托 ViewBinding#bind() 的调用 | 反射 |
| 需要委托 binding = null 的调用 | 监听 Fragment 视图生命周期 |
| 期望 binding 属性声明为非空不可变变量 | ReadOnlyProperty<F, V> |
3.1 ViewBinding + Kotlin 委托 1.0
我们现在较复杂的 Fragment 中尝试使用 Kotlin 委托优化:
FragmentViewBindingPropertyV1.kt
private const val TAG = "ViewBindingProperty"
public inline fun <reified V : ViewBinding> viewBindingV1() = viewBindingV1(V::class.java)
public inline fun <reified T : ViewBinding> viewBindingV1(clazz: Class<T>): FragmentViewBindingPropertyV1<Fragment, T> {
val bindMethod = clazz.getMethod("bind", View::class.java)
return FragmentViewBindingPropertyV1 {
bindMethod(null, it.requireView()) as T
}
}
/**
* @param viewBinder 创建绑定类对象
*/
class FragmentViewBindingPropertyV1<in F : Fragment, out V : ViewBinding>(
private val viewBinder: (F) -> V
) : ReadOnlyProperty<F, V> {
private var viewBinding: V? = null
@MainThread
override fun getValue(thisRef: F, property: KProperty<*>): V {
// 已经绑定,直接返回
viewBinding?.let { return it }
// Use viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle other than lifecycle
val lifecycle = thisRef.viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle
val viewBinding = viewBinder(thisRef)
if (lifecycle.currentState == Lifecycle.State.DESTROYED) {
Log.w(
TAG, "Access to viewBinding after Lifecycle is destroyed or hasn't created yet. " +
"The instance of viewBinding will be not cached."
)
// We can access to ViewBinding after Fragment.onDestroyView(), but don't save it to prevent memory leak
} else {
lifecycle.addObserver(ClearOnDestroyLifecycleObserver())
this.viewBinding = viewBinding
}
return viewBinding
}
@MainThread
fun clear() {
viewBinding = null
}
private inner class ClearOnDestroyLifecycleObserver : LifecycleObserver {
private val mainHandler = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())
@MainThread
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY)
fun onDestroy(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
owner.lifecycle.removeObserver(this)
mainHandler.post { clear() }
}
}
}
使用示例:
class TestFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_test) {
private val binding : FragmentTestBinding by viewBindingV1()
override fun onViewCreated(root: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
binding.tvDisplay.text = "Hello World."
}
}
干净清爽!前面提出的三个需求也都实现了,现在我为你解答细节:
- 问题 1、为什么可以使用 V::class.java,不是泛型擦除了吗? 利用了 Kotlin 内敛函数 + 实化类型参数,编译后函数体整体被复制到调用处,V::class.java 其实是 FragmentTestBinding::class.java。具体分析见:Java | 关于泛型能问的都在这里了(含Kotlin)
- 问题 2、ReadOnlyProperty<F, V> 是什么? ReadOnlyProperty 是不可变属性代理,通过 getValue(...) 方法实现委托行为。第一个类型参数 F 是属性所有者,第二个参数 V 是属性类型,因为我们在 Fragment 中定义属性,属性类型为 ViewBinding,所谓定义类型参数为 <in F : Fragment, out V : ViewBinding>;
- 问题 3、解释下 getValue(...) 方法? 直接看注释:
FragmentViewBindingPropertyV1.kt
@MainThread
override fun getValue(thisRef: F, property: KProperty<*>): V {
// 1、viewBinding 不为空说明已经绑定,直接返回
viewBinding?.let { return it }
// 2、Fragment 视图的生命周期
val lifecycle = thisRef.viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycle
// 3、实例化绑定类对象
val viewBinding = viewBinder(thisRef)
if (lifecycle.currentState == Lifecycle.State.DESTROYED) {
// 4.1 如果视图生命周期为 DESTROYED,说明视图被销毁,此时不缓存绑定类对象(避免内存泄漏)
} else {
// 4.2 定义视图生命周期监听者
lifecycle.addObserver(ClearOnDestroyLifecycleObserver())
// 4.3 缓存绑定类对象
this.viewBinding = viewBinding
}
return viewBinding
}
- 问题 4、为什么 onDestroy() 要采用 Handler#post(Message) 完成? 因为 Fragment#viewLifecycleOwner 通知生命周期事件 ON_DESTROY 的时机在 Fragment#onDestroyView 之前。如果不使用 post 的方式,那么业务方要是在 onDestroyView 中访问了 binding,则会二次执行 getValue() 这是不必要的。
3.2 ViewBinding + Kotlin 委托 2.0
V1.0 版本使用了反射,真的一定要反射吗?反射调用 bind 函数的目的就是获得一个 ViewBinding 绑定类对象,或许我们可以试试把创建对象的行为交给外部去定义,类似这样用一个 lambda 表达式实现工厂函数:
FragmentViewBindingPropertyV2.kt
inline fun <F : Fragment, V : ViewBinding> viewBindingV2(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
// 类似于创建工厂
crossinline viewProvider: (F) -> View = Fragment::requireView
) = FragmentViewBindingPropertyV2 { fragment: F ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(fragment))
}
class FragmentViewBindingPropertyV2<in F : Fragment, out V : ViewBinding>(
private val viewBinder: (F) -> V
) : ReadOnlyProperty<F, V> {
// 以下源码相同 ...
}
使用示例:
class TestFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_test) {
private val binding by viewBindingV2(FragmentTestBinding::bind)
override fun onViewCreated(root: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
binding.tvDisplay.text = "Hello World."
}
}
干净清爽!不使用反射也可以实现,现在我为你解答细节:
- 问题 5、(View) -> V 是什么? Kotlin 高阶函数,可以把 lambda 表达式直接作为参数传递,其中 View 是函数参数,而 T 是函数返回值。lambda 表达式本质上是 「可以作为值传递的代码块」。在老版本 Java 中,传递代码块需要使用匿名内部类实现,而使用 lambda 表达式甚至连函数声明都不需要,可以直接传递代码块作为函数值;
- 问题 6、Fragment::requireView 是什么? 把函数 requireView() 作为参数传递。Fragment#requireView() 会返回 Fragment 的根节点,但要注意在 onCreateView() 之前调用 requireView() 会抛出异常;
- 问题 7、FragmentTestBinding::bind 是什么? 把函数 bind() 作为参数传递,bind 函数的参数为 View,返回值为 ViewBinding,与函数声明 (View) -> V 匹配。
3.3 ViewBinding + Kotlin 委托最终版
V2.0 版本已经完成了针对 Fragment 的属性代理,但是实际场景中只会在 Fragment 中使用 ViewBinding 吗?显然并不是,我们还有其他一些场景:
- Activity
- Fragment
- DialogFragment
- ViewGroup
- RecyclerView.ViewHolder
所以,我们有必要将委托工具适当封装得更通用些,完整代码和演示工程你可以直接下载查看: AndroidFamilyDemo · KotlinDelegate
ViewBindingProperty.kt
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ViewBindingProperty for Activity
// -------------------------------------------------------
@JvmName("viewBindingActivity")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> ComponentActivity.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
crossinline viewProvider: (ComponentActivity) -> View = ::findRootView
): ViewBindingProperty<ComponentActivity, V> = ActivityViewBindingProperty { activity: ComponentActivity ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(activity))
}
@JvmName("viewBindingActivity")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> ComponentActivity.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
@IdRes viewBindingRootId: Int
): ViewBindingProperty<ComponentActivity, V> = ActivityViewBindingProperty { activity: ComponentActivity ->
viewBinder(activity.requireViewByIdCompat(viewBindingRootId))
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ViewBindingProperty for Fragment / DialogFragment
// -------------------------------------------------------
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
@JvmName("viewBindingFragment")
inline fun <F : Fragment, V : ViewBinding> Fragment.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
crossinline viewProvider: (F) -> View = Fragment::requireView
): ViewBindingProperty<F, V> = when (this) {
is DialogFragment -> DialogFragmentViewBindingProperty { fragment: F ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(fragment))
} as ViewBindingProperty<F, V>
else -> FragmentViewBindingProperty { fragment: F ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(fragment))
}
}
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
@JvmName("viewBindingFragment")
inline fun <F : Fragment, V : ViewBinding> Fragment.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
@IdRes viewBindingRootId: Int
): ViewBindingProperty<F, V> = when (this) {
is DialogFragment -> viewBinding(viewBinder) { fragment: DialogFragment ->
fragment.getRootView(viewBindingRootId)
} as ViewBindingProperty<F, V>
else -> viewBinding(viewBinder) { fragment: F ->
fragment.requireView().requireViewByIdCompat(viewBindingRootId)
}
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ViewBindingProperty for ViewGroup
// -------------------------------------------------------
@JvmName("viewBindingViewGroup")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> ViewGroup.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
crossinline viewProvider: (ViewGroup) -> View = { this }
): ViewBindingProperty<ViewGroup, V> = LazyViewBindingProperty { viewGroup: ViewGroup ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(viewGroup))
}
@JvmName("viewBindingViewGroup")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> ViewGroup.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
@IdRes viewBindingRootId: Int
): ViewBindingProperty<ViewGroup, V> = LazyViewBindingProperty { viewGroup: ViewGroup ->
viewBinder(viewGroup.requireViewByIdCompat(viewBindingRootId))
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ViewBindingProperty for RecyclerView#ViewHolder
// -------------------------------------------------------
@JvmName("viewBindingViewHolder")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> RecyclerView.ViewHolder.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
crossinline viewProvider: (RecyclerView.ViewHolder) -> View = RecyclerView.ViewHolder::itemView
): ViewBindingProperty<RecyclerView.ViewHolder, V> = LazyViewBindingProperty { holder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder ->
viewBinder(viewProvider(holder))
}
@JvmName("viewBindingViewHolder")
inline fun <V : ViewBinding> RecyclerView.ViewHolder.viewBinding(
crossinline viewBinder: (View) -> V,
@IdRes viewBindingRootId: Int
): ViewBindingProperty<RecyclerView.ViewHolder, V> = LazyViewBindingProperty { holder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder ->
viewBinder(holder.itemView.requireViewByIdCompat(viewBindingRootId))
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ViewBindingProperty
// -------------------------------------------------------
private const val TAG = "ViewBindingProperty"
interface ViewBindingProperty<in R : Any, out V : ViewBinding> : ReadOnlyProperty<R, V> {
@MainThread
fun clear()
}
class LazyViewBindingProperty<in R : Any, out V : ViewBinding>(
private val viewBinder: (R) -> V
) : ViewBindingProperty<R, V> {
private var viewBinding: V? = null
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
@MainThread
override fun getValue(thisRef: R, property: KProperty<*>): V {
// Already bound
viewBinding?.let { return it }
return viewBinder(thisRef).also {
this.viewBinding = it
}
}
@MainThread
override fun clear() {
viewBinding = null
}
}
abstract class LifecycleViewBindingProperty<in R : Any, out V : ViewBinding>(
private val viewBinder: (R) -> V
) : ViewBindingProperty<R, V> {
private var viewBinding: V? = null
protected abstract fun getLifecycleOwner(thisRef: R): LifecycleOwner
@MainThread
override fun getValue(thisRef: R, property: KProperty<*>): V {
// Already bound
viewBinding?.let { return it }
val lifecycle = getLifecycleOwner(thisRef).lifecycle
val viewBinding = viewBinder(thisRef)
if (lifecycle.currentState == Lifecycle.State.DESTROYED) {
Log.w(
TAG, "Access to viewBinding after Lifecycle is destroyed or hasn't created yet. " +
"The instance of viewBinding will be not cached."
)
// We can access to ViewBinding after Fragment.onDestroyView(), but don't save it to prevent memory leak
} else {
lifecycle.addObserver(ClearOnDestroyLifecycleObserver(this))
this.viewBinding = viewBinding
}
return viewBinding
}
@MainThread
override fun clear() {
viewBinding = null
}
private class ClearOnDestroyLifecycleObserver(
private val property: LifecycleViewBindingProperty<*, *>
) : LifecycleObserver {
private companion object {
private val mainHandler = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())
}
@MainThread
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY)
fun onDestroy(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
mainHandler.post { property.clear() }
}
}
}
class FragmentViewBindingProperty<in F : Fragment, out V : ViewBinding>(
viewBinder: (F) -> V
) : LifecycleViewBindingProperty<F, V>(viewBinder) {
override fun getLifecycleOwner(thisRef: F): LifecycleOwner {
try {
return thisRef.viewLifecycleOwner
} catch (ignored: IllegalStateException) {
error("Fragment doesn't have view associated with it or the view has been destroyed")
}
}
}
class DialogFragmentViewBindingProperty<in F : DialogFragment, out V : ViewBinding>(
viewBinder: (F) -> V
) : LifecycleViewBindingProperty<F, V>(viewBinder) {
override fun getLifecycleOwner(thisRef: F): LifecycleOwner {
return if (thisRef.showsDialog) {
thisRef
} else {
try {
thisRef.viewLifecycleOwner
} catch (ignored: IllegalStateException) {
error("Fragment doesn't have view associated with it or the view has been destroyed")
}
}
}
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// Utils
// -------------------------------------------------------
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY)
class ActivityViewBindingProperty<in A : ComponentActivity, out V : ViewBinding>(
viewBinder: (A) -> V
) : LifecycleViewBindingProperty<A, V>(viewBinder) {
override fun getLifecycleOwner(thisRef: A): LifecycleOwner {
return thisRef
}
}
fun <V : View> View.requireViewByIdCompat(@IdRes id: Int): V {
return ViewCompat.requireViewById(this, id)
}
fun <V : View> Activity.requireViewByIdCompat(@IdRes id: Int): V {
return ActivityCompat.requireViewById(this, id)
}
/**
* Utility to find root view for ViewBinding in Activity
*/
fun findRootView(activity: Activity): View {
val contentView = activity.findViewById<ViewGroup>(android.R.id.content)
checkNotNull(contentView) { "Activity has no content view" }
return when (contentView.childCount) {
1 -> contentView.getChildAt(0)
0 -> error("Content view has no children. Provide root view explicitly")
else -> error("More than one child view found in Activity content view")
}
}
fun DialogFragment.getRootView(viewBindingRootId: Int): View {
val dialog = checkNotNull(dialog) {
"DialogFragment doesn't have dialog. Use viewBinding delegate after onCreateDialog"
}
val window = checkNotNull(dialog.window) { "Fragment's Dialog has no window" }
return with(window.decorView) {
if (viewBindingRootId != 0) requireViewByIdCompat(
viewBindingRootId
) else this
}
}
4. 总结
ViewBinding 是一个轻量级的视图绑定方案,Android Gradle 插件会为每个 XML 布局文件创建一个绑定类。在 Fragment 中使用 ViewBinding 需要注意在 Fragment#onDestroyView() 里置空绑定类对象避免内存泄漏。但这会带来很多重复编写样板代码,使用属性委托可以收敛模板代码,保证调用方代码干净清爽。
| 角度 | findViewById | ButterKnife | Kotlin Synthetics | DataBinding | ViewBinding | ViewBindingProperty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 简洁性 | ||||||
| 编译期检查 | ||||||
| 编译速度 | ||||||
| 支持 Kotlin & Java | ||||||
| 收敛模板代码 |
参考资料
- View Binding 视图绑定 —— 官方文档
- View Binding 与 Kotlin 委托属性的巧妙结合,告别垃圾代码! —— Kirill Rozov 著,依然范特稀西 译
- 谁才是 ButterKnife 的终结者? —— fundroid 著
- 深入研究 ViewBinding 在 include, merge, adapter, fragment, activity 中使用 —— Flywith24 著
ViewBinding 与 Kotlin 委托双剑合璧的更多相关文章
- MarkDown、Vim双剑合璧
作为一名软件攻城狮(是的,我从来都以攻城狮自居! 我坚信如今的每一天,都在朝攻城狮迈进.虽然被菜鸟的肉身皮囊裹着,我依然还是怀着攻城狮的内心! 我非常讨厌别人喊我程序猿.虽然这是不争的事实!).... ...
- Spring Cloud & Alibaba 实战 | 第十二篇: 微服务整合Sentinel的流控、熔断降级,赋能拥有降级功能的Feign新技能熔断,实现熔断降级双剑合璧(JMeter模拟测试)
目录 一. Sentinel概念 1. 什么是Sentinel? 2. Sentinel功能特性 3. Sentinel VS Hystrix 二. Docker部署Sentinel Dashboar ...
- kotlin 委托
委托模式是软件设计模式中的一项基本技巧.在委托模式中,有两个对象参与处理同一个请求,接受请求的对象将请求委托给另一个对象来处理. Kotlin 直接支持委托模式,更加优雅,简洁.Kotlin 通过关键 ...
- [转帖]双剑合璧:CPU+GPU异构计算完全解析
引用自:http://tech.sina.com.cn/mobile/n/2011-06-20/18371792199.shtml 这篇文章写的深入浅出,把异构计算的思想和行业趋势描述的非常清楚,难得 ...
- kotlin委托属性
fun main(arg: Array<String>) { val myClass1 = myClass1() myClass1.name="mycalsss1" v ...
- Kotlin 委托(2)变量委托是什么、自定义变量委托
1.委托是什么? 1.1 官网示例 在每个变量委托的实现的背后,Kotlin 编译器都会生成辅助对象并委托给它. 假设委托如下, class C { var prop: Type by MyDeleg ...
- Kotlin 委托(1)类委托、变量委托注意事项
1.官方文档 英文: https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/delegation.html https://kotlinlang.org/docs/referen ...
- kotlin 委托类的初始化函数
import java.beans.AppletInitializer import kotlin.reflect.KProperty fun main(arg: Array<String> ...
- ASP.NET Core和Angular 2双剑合璧
(此文章同时发表在本人微信公众号"dotNET每日精华文章",欢迎右边二维码来关注.) 题记:两个还没有正式发布的东西一起用,是什么效果? 效果当然会很好了(我猜的),那么如何在A ...
随机推荐
- Python实现简繁体转换,真的玩得花
大家好鸭, 我是小熊猫 直接开搞!!! 1.opencc-python 首先介绍opencc中的Python实现库,它具有安装简单,翻译准确,使用方便等优点.对于我们日常的需求完全能够胜任. 1.1安 ...
- Git下载(快速快速快速下载!!)
在安装Git环境的时候,需要下载Git的安装包,但是官网的下载网速实在是太慢的(几十M的安装包,下载速度只有几十K) (所以可以在镜像中下载,速度超快) Git镜像下载链接-------------- ...
- NC16746 神奇盘子
NC16746 神奇盘子 题目 题目描述 有一个神奇的盘子,形状为圆形.盘子上面爬着一个大象(视作一个点).由于现实的扭曲,当大象在盘子某个直径的一端的时候,可以瞬间传送至直径的另一端.现在大象想去盘 ...
- [开源] .Net ORM 访问 Firebird 数据库
前言 Firebird 是一个跨平台的关系数据库系统,目前能够运行在 Windows.linux 和各种 Unix 操作系统上,提供了大部分 SQL-99 标准的功能.它既能作为多用户环境下的数据库服 ...
- linux Error downloading packages free 0 * needed 71 k
linux Error downloading packages free 0 * needed 71 k 原因:硬盘空间不足 查看磁盘大小 /]# df -hl 从/主目录开始搜索, ...
- 5-2 SpringCloud | 微服务
服务器端项目演进 服务器初期状态 最早的服务器就是安装部署了一些静态页面 功能非常单一,只能做信息的呈现和输出 服务器动态页面 后来因为业务和技术的发展,页面连接了数据库,页面中大部分数据来自于数据库 ...
- Java之struts2框架学习
Java之struts2框架学习 About Struts2 Struts也是一款MVC框架 , Struts2是Struts的下一代产品,是在Struts1和WebWork的技术基础上进行了合并的全 ...
- OpenCV视频防抖技术解析
视频防抖有很多种技术,各有优劣,主流的目前分为三种:EIS电子防抖EIS电子防抖是通过软件算法实现防抖的.其技术运作原理是通过加速度传感器和陀螺仪模块侦测手机抖动的幅度,从而来动态调节整ISO.快门以 ...
- Nginx搭建简易文件服务器
Nginx搭建简易文件服务器 1.安装nginx,此处略过 2.修改nginx配置文件 详细如下 # 此处为部分文件是否有权限,使用root,则不会出现403权限问题 user root; worke ...
- 清北学堂 2020 国庆J2考前综合强化 Day4
目录 1. 题目 T1 写字符串 题目描述 Sol T2 神奇的数 题目描述 Sol T3 珠子染色 题目描述 Sol T4 病毒扩散 题目描述 Sol 算法 -- 图论 1. 题目 T1 写字符串 ...
