SciTech-Mathmatics - Matrix Analysis(矩阵分析)-重要结论 + 特征值分解 + Matrix视为 Linear Space的 变换 与 运算 + 任两个Vectors可通过Matrix变换互相转化 + 方阵(满秩)不改变向量维数
SciTech-Mathmatics - Matrix Analysis:矩阵分析
Matrix Analysis 重要结论
\(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)(矩阵变换) 亦为 \(\large \text{ Linear Transformation }\)(线性变换).
- 要严格区分 Transformation(变换) 与 Function(函数):
Functions(函数) 与 Transformation(变换) - Matrix
视为"Linear Space"的"Transformation(变换)与Operation(运算)"; - 同LinearSpace(线性空间)的"任意两个非零Vectors可
通过"Matrix变换"互相转化; - "方阵(满秩)"
不改变变换前后的两非零Vectors的"Dimensions(维数)" - "非方阵"
变换改变(升或降)前后两非零Vectors的"Dimensions(维数)"
Linear Space + Vector + Matrix 视角

\(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{K^n}\)上, 任一 \(\large \text{ Vector } \bf{ V_{a_{ n \times 1 }} }\) 通过 \(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)后的 \(\large \text{ Vector } \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} }\) 仍在同一 \(\large \bf{K^n}\)
\(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{K^n}\)上, 任何两个 \(\large \text{ Vector } \bf{ V_{a_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 } \text{ 与 } \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 }\) 都能通过一组合适的 \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation } A_{n \times n}\) (基本线性变换) 实现互相转化, 即 \(\large \exists A_{n \times n} \in \bf{K^n} , \ 使\ A_{n \times n} \bf{ V_{a_{n \times 1}} } = \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} }\) 。
例如在 \(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{R^2}(2D空间)\)上的 \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\)(基本线性变换)只有 \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) 与 \(\large \bf{\text{ Scale(伸缩)} }\) 两种(后文有独立章节).任一\(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\) 都能
分解为一组 \(\large \text{Fundamental Linear Transformation }\)(基本线性变换).两大类 \(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)(矩阵变换)
- 方阵(满秩) 这种特殊的 \(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)
不改变变换前后两个Vector的“Dimensions(维数)”。
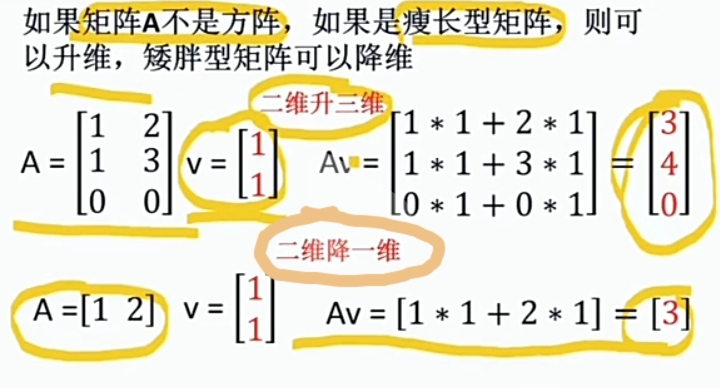
![]()
- 非方阵 种类 \(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\) 升或降 Vector的Dimensions(维数)
![]()
- 方阵(满秩) 这种特殊的 \(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)
方阵 的 Matrix Transformation
注意:
"非方阵"变换改变(升或降)前后两非零Vectors的"Dimensions(维数)".
\(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\)(基本的 线性变换):
- \(\large \bf{ \text{Scale(伸缩)} }\) : \(\large Av = \lambda v = \lambda \bf{I} v\)
\(\large (\bf{ \lambda I } - A) V = 0 \bf{\text{ 是 Eigenvalue Decomposition 的核心公式 } }\) - \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) : \(\large A^x v = \lambda v\)
\(\large Vector\ V \text{ 作 } x \text{ 次 } Matrix \ Transformation\ A \text{ 就可能 } 与\ V\ \bf{方向重合}\)
如$ x \text{ 依序取 } (1,2,\cdots, n)$ 时 $\large (\lambda \bf{I} - A^x) v $ 就可能趋近或等于 0。
\(\large \text{Possible Transformation }\)(可能的 线性变换):
\(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{K^n}\)上, \(\large \bf{\text{ 方阵 A } }\) 对 任何一个 \(\large \text{ Vector } \bf{V}\), \(\large \bf{ 只有 } \text{ 三种线性变换的可能 }\):
- \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\):
\(\large \bf{ \text{Scale(伸缩)} }\) : \(\large Av = \lambda v = \lambda \bf{I} v\) 或 \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) - \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(伸缩) } }\) 并且 \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\)
\(\large \bf{ K^{n} } \text{ 的通用 } \bf{Scale} 及 Example(\bf{R^{2}})\)
\(\large \bf{K^{n}} \text{ 特征值分解 } 的 \bf{推导}\):
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \because & A_{scale} V = \bf{ \lambda I } V = \bf{ \lambda } V \\ \therefore & \begin{cases} (\bf{ \lambda I } - A) V = 0, \ \text{ the } Characteristic\ Polynomial \text{ for matrix } A \\ |\bf{ \lambda I } - A| = 0 \end{cases} \end{array}\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \\ \bf{注} & V = \begin{bmatrix} v_1 \\ \vdots \\ v_n \end{bmatrix} \bf{ \neq 0 } , where\ v_i \in K, \ i \in [1, n]. \\ & 即\ \bf{ V }\ 是 \text{非零} 的 \text{ 列向量 } \end{array}\)
\(\large \bf{K^{n}} \text{ 特征值分解 } 的 \bf{策略}\):
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} 1. & |\bf{ \lambda I } - A|=0 \Leftarrow \text{ 可先解出 } A \text{ 的所有 } Eigenvalues, \end{array}\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} 2. & (\bf{ \lambda I } - A) V = 0 \Leftarrow \text{ 一一代入 }Eigenvalue \text{ 得其所有 } Eigenvectors \end{array}\)
\(\large \bf{R^{2}} 的Example :\) 求 \(\large \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ -1 & 4 \end{bmatrix}\) 全部 特征值和特征向量
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \because & 0 = |\bf{ \lambda I } - A| = \begin{vmatrix} \lambda - 1 & 0-2 \\ 0-(-1) & \lambda - 4 \end{vmatrix} \\ & \ = \lambda^{2} -5\lambda + 6 = (\lambda-2)(\lambda -3) = 0 \\ \therefore & \bf{ \lambda = 2 \ or \ \lambda = 3 } \end{array}\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} let & V= \begin{bmatrix} v_1 \\ v_2 \end{bmatrix} \bf{ \neq 0 }, \{v_i | v_i \in K, i \in \{1,2\}\}, \ 因为\text{ V 是非零列向量. } \end{array}\)
\(\large for \ Eigenvalue\ \lambda = 2 :\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \because & (\bf{ \lambda I } - A) V = (\bf{ 2 I } - A) V = \begin{bmatrix} \lambda - 1 & 0-2 \\ 0-(-1) & \lambda - 4 \end{bmatrix} V \\ & = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -2 \\ 1 & -2 \end{bmatrix} V = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -2 \\ 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} v_1 \\ v_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} v_1 - 2v_2 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} = 0 \\ & \Rightarrow v_1 - 2v_2 = 0 , or \ v_1 = 2v_2, \text{ where } v_2 \text{ is a freedom variable } \\ & let \ V_{base} = \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ \therefore & \text{All Eigenvectors for } \lambda = 2 \text{ are } \\ & \bf{ \{ V | V=k V_{base}, k \in K, k \neq 0, V_{base} = \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \} } \end{array}\)
\(\large for \ Eigenvalue\ \lambda = 3, \ Similarly:\)
\(\large \begin{array}{ll} \because & (\bf{ \lambda I } - A) V = (\bf{ 3 I } - A) V = \begin{bmatrix} \lambda - 1 & 0-2 \\ 0-(-1) & \lambda - 4 \end{bmatrix} V \\ & = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -2 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix} V = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 \\ 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} v_1 \\ v_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} v_1 - v_2 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} = 0 \\ & \Rightarrow v_1 - v_2 = 0 , or \ v_1 = v_2, \text{ where } v_2 \text{ is a freedom variable } \\ & let \ V_{base} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ \therefore & \text{All Eigenvectors for } \lambda = 3 \text{ are } \\ & \bf{ \{ V | V=k V_{base}, k \in K, k \neq 0 , V_{base} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \} } \end{array}\)
\(\large \bf{R^{2}} \text{ 的 } \bf{Fundamental\ Transformation }\)
$\large \ \bf{Scale(伸缩)} 及 \bf{Rotation(旋转)} $
例如在 \(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{R^2}(2D空间)\)上, 任意一个\(\large \text{ Matrix Transformation }\)(矩阵线性变换)`都可分解为一组两种 \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\)(基本线性变换):
\(\large \bf{\text{向量 }} \Leftrightarrow \bf{\text{ 坐标 : } } let \ V = \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} r \ cos \alpha \\ r \ sin \alpha \end{bmatrix}\)
\(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\)
\(\large A_{rotate} = \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta & -sin \theta \\ sin \theta & cos \theta \end{bmatrix}\),
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\ \because & cos (\alpha + \theta) =& cos \alpha \ cos \theta - \ sin \alpha \ sin \theta \\ & sin(\alpha + \theta) =& sin \alpha \ cos \theta + \ cos \alpha \ sin \theta \end{array}\)
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \therefore & A_{rotate} V =& \begin{bmatrix} r \ cos (\alpha + \theta) \\ r \ sin(\alpha + \theta) \end{bmatrix} =& \begin{bmatrix} cos \theta & -sin \theta \\ sin \theta & cos \theta \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} r \ cos \alpha \\ r \ sin \alpha \end{bmatrix} \end{array}\)\(\large \bf{\text{ Scale(伸缩)} }\)
\(\large A_{scale} = \bf{ \lambda } \begin{bmatrix} cos 0 & -sin 0 \\ sin 0 & cos 0 \end{bmatrix} = \bf{ \lambda I } = \bf{ \lambda } \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)
Matrix Analysis(矩阵分析学)
合成任意的目标 "Matrix Transformation(矩阵变换)"
目标函数\(\large \bf{ M_{n \times n} }\) 用Mathematical Analysis(数学分析)思想: 合成任意的目标 "Function(函数) 或Transformation(变换)". 以下都在 \(\large \text{Linear Space } \bf{K^n}\)上,
- 因为 同LinearSpace(线性空间)的"任意两个非零Vectors可
通过"Matrix变换"互相转化;- 设任意两个非零 \(\large \text{ Vectors } \bf{ V_{a_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 } \text{ 与 } \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 }\),
then, 存在目标 Matrix Transformation(矩阵变换) \(\large \bf{M_{n \times n}}\) 使得 \(\large \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} = M_{n \times n} V_{ a_{n \times 1} } }\) - but, \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\)(基本线性变换) 只有三种:
\(\large \bf{ \text{Scale(伸缩)} }\), \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) 和 \(\large \bf{\text{ Scale }} \text{ and } \bf{ \text{ Rotation } }\) - 因此, 有必要用 \(\large \text{Fundamental Transformation }\) 合成任意的存在目标 Matrix Transformation(矩阵变换) \(\large \bf{M_{n \times n}}\).
即,合成任意的\(\large \bf{ \text{Scale(伸缩)} }\), \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) 和 \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(伸缩) } }\) 并且 \(\large \bf{\text{ Rotation(旋转) } }\) - 分析函数式“合成”:
既然,目标 Matrix Transformation(矩阵变换) \(\large \bf{ M_{n \times n} }\) 使得 \(\large \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} = M_{n \times n} V_{a_{n \times 1}} }\)
设 \(\large \bf{ A, \ shape 为(n \times n) }\) 代表一个 "基本矩阵(函数 或 变换)",
则, 目标 Matrix Transformation(矩阵变换) \(\large \bf{ M, \ shape 为 (n \times n) }\) 可用 $ \bf{A} $ 的 Operations(运算) 合成(Approximation):
例如,用“幂函数”(Operation为Multiplication)形式:
假设,$\large \bf{M} = A^x $, 那e么 \(\large V_{b} = \bf{M} V_{a} = \bf{A^x} V_{a}\)
![]()
- 设任意两个非零 \(\large \text{ Vectors } \bf{ V_{a_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 } \text{ 与 } \bf{ V_{b_{n \times 1}} \neq 0 }\),
\(\large 图示 \bf{R^{2}} 的 \bf{Scale(伸缩)} ( \bf{特征值分解} )\)



SciTech-Mathmatics - Matrix Analysis(矩阵分析)-重要结论 + 特征值分解 + Matrix视为 Linear Space的 变换 与 运算 + 任两个Vectors可通过Matrix变换互相转化 + 方阵(满秩)不改变向量维数的更多相关文章
- 数学基础系列(六)----特征值分解和奇异值分解(SVD)
一.介绍 特征值和奇异值在大部分人的印象中,往往是停留在纯粹的数学计算中.而且线性代数或者矩阵论里面,也很少讲任何跟特征值与奇异值有关的应用背景. 奇异值分解是一个有着很明显的物理意义的一种方法,它可 ...
- /编写一个函数,要求从给定的向量A中删除元素值在x到y之间的所有元素(向量要求各个元素之间不能有间断), 函数原型为int del(int A ,int n , int x , int y),其中n为输入向量的维数,返回值为删除元素后的维数
/** * @author:(LiberHome) * @date:Created in 2019/2/28 19:39 * @description: * @version:$ */ /* 编写一个 ...
- PCA样本数量少于矩阵维数
%test pcaA=[3,7,1,4,1;5,5,2,1,3;4,2,4,5,3];S=cov(A);T=cov(A');[ds,vs]=eig(S)[dt,vt]=eig(T) 样本数量少于矩阵维 ...
- Tensorflow描述张量的维度:阶,形状以及维数
张量 TensorFlow用张量这种数据结构来表示所有的数据.你可以把一个张量想象成一个n维的数组或列表.一个张量有一个静态类型和动态类型的维数.张量可以在图中的节点之间流通. 阶 在TensorFl ...
- 分类问题中的“维数灾难” - robotMax
分类问题中的“维数灾难” - robotMax 在看机器学习的论文时,经常会看到有作者提到“curse of dimensionality”,中文译为“维数灾难”,这到底是一个什么样的“灾难”?本文将 ...
- tensorflow中张量(tensor)的属性——维数(阶)、形状和数据类型
tensorflow的命名来源于本身的运行原理,tensor(张量)意味着N维数组,flow(流)意味着基于数据流图的计算,所以tensorflow字面理解为张量从流图的一端流动到另一端的计算过程. ...
- HOG参数简介及Hog特征维数的计算(转)
HOG构造函数 CV_WRAP HOGDescriptor() :winSize(64,128), blockSize(16,16), blockStride(8,8), cellSize( ...
- [Bhatia.Matrix Analysis.Solutions to Exercises and Problems]ExI.4.1
Let $x,y,z$ be linearly independent vectors in $\scrH$. Find a necessary and sufficient condition th ...
- [Bhatia.Matrix Analysis.Solutions to Exercises and Problems]Contents
I find it may cost me so much time in doing such solutions to exercises and problems....I am sorry t ...
- LR特征维数特别大实时计算问题
美团 https://tech.meituan.com/machinelearning-data-feature-process.html 维数灾难 待续...
随机推荐
- 安卓逆向学习及APK抓包(二)--Google Pixel一代手机的ROOT刷入面具
PS:本文仅作参考勿跟操作,root需谨慎,本次测试用的N手Pixel,因参考本文将真机刷成板砖造成的损失与本人无关 1 Google Pixel介绍 1.1手机 google Pixel 在手机选择 ...
- 亚马逊aws_access_key_id和aws_secret_access_key利用
00X01 信息泄露 敏感信息泄露,例如环境变量.例如,为了配置AWS CLI,需要设置以下环境变量: $ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AKISIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE ...
- MCP Server On FC 之旅1: MCP 协议的深度解析与云上适配最佳实践
在人工智能技术高速发展的今天,数据孤岛.工具碎片化.上下文割裂问题已成为制约大模型发挥潜力的关键瓶颈.Model Context Protocol(MCP)作为 Anthropic 于 2024 年推 ...
- 使用 Joplin + Git + Gitee 实现笔记的多端同步
1-远程仓库环境准备 1.1-注册 Gitee 账号 由于使用 Git 作为版本控制工具,所以只要是 Git 支持的托管平台都是可以的.比如 Github.Gitlab.这里使用 Gitee 主要是考 ...
- 深入解析Tortoise-ORM关系型字段与异步查询
title: 深入解析Tortoise-ORM关系型字段与异步查询 date: 2025/05/01 00:12:39 updated: 2025/05/01 00:12:39 author: cmd ...
- 制作netease-cloud-music-gtk的debian包
要创建一个deb包,只需要有一个基于 debian 的操作系统即可.(不管你用的是什么 Linux 发行版,你可以使用虚拟机或者 systemd-nspawn 来创建构建 DEB 包的环境) 下载上游 ...
- LinqHelper拓展
public static class LinqHelper { //NHibernate.Hql.Ast.HqlBooleanExpression public static Expression& ...
- K8s新手系列之Endponit
概述 官方文档:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/reference/kubernetes-api/service-resources/endpoints-v1/ En ...
- Pandas 清除 Excel 特殊字符
清除 Excel 特殊字符 主要是为了做一个笔记, 用 遍历 DataFrame 用正则匹配特殊字符并替换. 是上个月初的项目了, 其中有个将 Excel 传入数据库的时候, 发现有特殊字符, 很奇怪 ...
- C语言:高级语言怎样抽象执行逻辑
平时我们做编程的时候,底层 CPU 如何执行指令已经被封装好了,因此你很少会想到把底层和语言编译联系在一起.但从我自己学习各种编程语言的经历看,从这样一个全新视角重新剖析 C 语言,有助于加深你对它的 ...