『TensorFlow』读书笔记_AlexNet
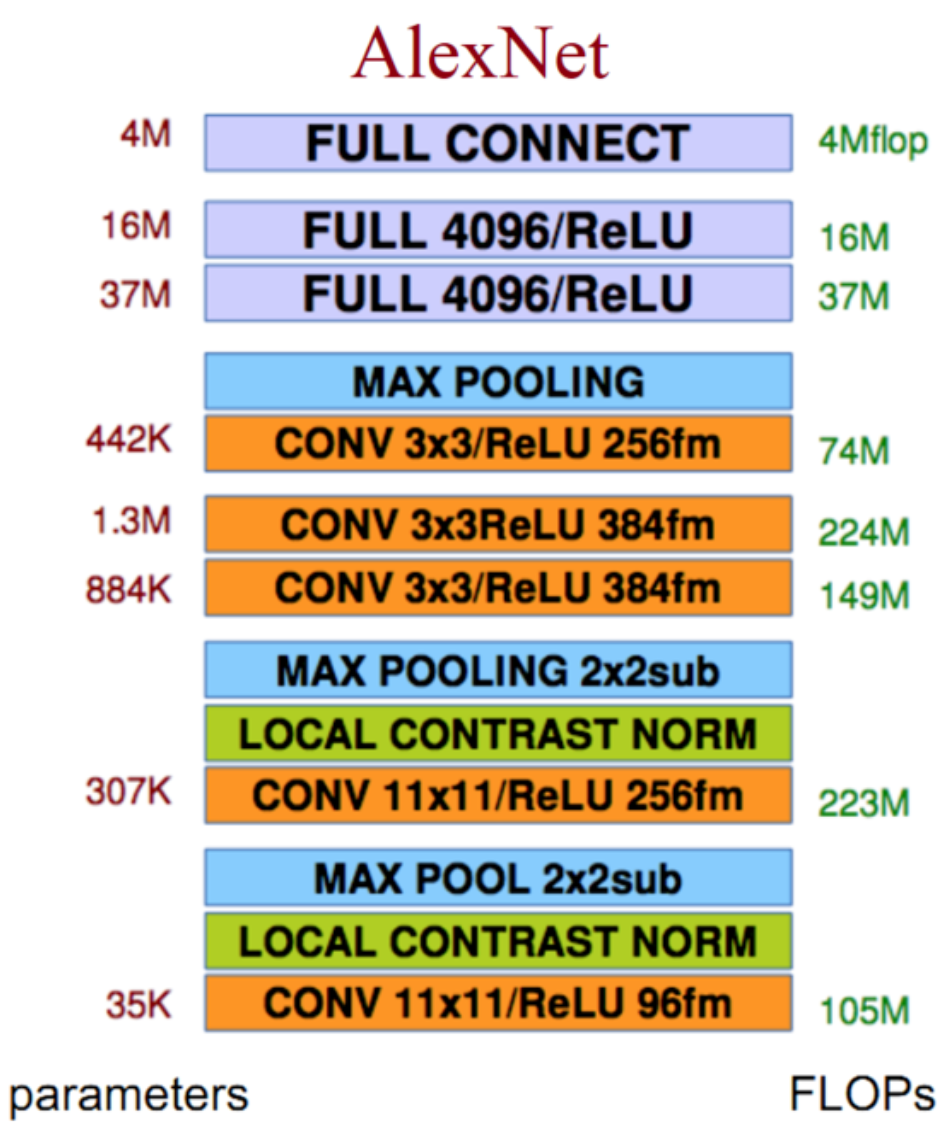
网络结构
创新点
Relu激活函数:效果好于sigmoid,且解决了梯度弥散问题
Dropout层:Alexnet验证了dropout层的效果
重叠的最大池化:此前以平均池化为主,最大池化避免了平均池化的模糊效果;而重叠的池化步长和池化窗口大小设置增加了特征的丰富性
LRN层:局部响应归一化层,这个层能够使得响应大的神经元变得相对更大,其他的收到抑制,理论上增加了泛化能力,不过实际上在大大增加了训练时间的同时并没有对效果有明显的提升,故除了AlexNet外基本没有使用;提出原因在于Relu函数输出不想之前的tanh和sigmoid有一个有限值域,所以LRN加以限制,似乎作用并不明显
代码实现
# Author : Hellcat
# Time : 2017/12/8 import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from datetime import datetime batch_size = 32
num_batches = 100 def print_activations(t):
'''
查看tensor信息
:param t: tensor对象
:return: 隶属节点的名称,张量本身尺寸
'''
print(t.op.name, ' ', t.get_shape().as_list()) def inference(images):
parameters = [] with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11,11,3,64],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-4),
name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel,[1,4,4,1],padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.,shape=[64],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
print_activations(conv1)
parameters += [kernel,biases]
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1,4,bias=1.,alpha=0.001/9,beta=0.75,name='lrn1')
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
padding='VALID',name='pool1')
print_activations(pool1) with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,64,192],
dtype=tf.float32,stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.,shape=[192],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
print_activations(conv2)
parameters += [kernel,biases]
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2,4,bias=1.,alpha=0.001/9,beta=0.75,name='lrn2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
padding='VALID',name='pool2')
print_activations(pool2) with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,192,384],
dtype=tf.float32,stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.,shape=[384],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
parameters += [kernel,biases]
print_activations(conv3) with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,384,256],
dtype=tf.float32,stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.,shape=[256],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
parameters += [kernel,biases]
print_activations(conv4) with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,256,256],
dtype=tf.float32,stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.,shape=[256],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
parameters += [kernel,biases]
print_activations(conv5)
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1,3,3,1],
strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='VALID',name='pool5')
print_activations(pool5) with tf.name_scope('fcl1') as scope:
reshape = tf.reshape(pool5,[batch_size,-1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([dim,4096],stddev=0.001),dtype=tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[4096]),dtype=tf.float32)
fcl1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(reshape,weights),biases))
fcl1 = tf.nn.dropout(fcl1,keep_prob=0.75)
parameters += [weights,biases]
print_activations(fcl1) with tf.name_scope('fcl2') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096,4096],stddev=0.001),dtype=tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[4096]),dtype=tf.float32)
fcl2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(fcl1,weights),biases))
fcl2 = tf.nn.dropout(fcl2,keep_prob=0.75)
parameters += [weights,biases]
print_activations(fcl2) with tf.name_scope('fcl3') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096,10],stddev=0.001),dtype=tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[10]),dtype=tf.float32)
fcl3 = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(fcl2,weights),biases)
parameters += [weights,biases]
print_activations(fcl3) return fcl3, parameters def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
'''
网路运行时间测试函数
:param session: 会话对象
:param target: 运行目标节点
:param info_string:提示字符
:return: None
'''
num_steps_burn_in = 10 # 预热轮数
total_duration = 0.0 # 总时间
total_duration_squared = 0.0 # 总时间平方和
for i in range(num_steps_burn_in + num_batches):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time # 本轮时间
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(),i-num_steps_burn_in,duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration**2 mn = total_duration/num_batches # 平均耗时
vr = total_duration_squared/num_batches - mn**2
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s:%s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd)) def run_benchmark():
with tf.Graph().as_default():
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size,image_size,image_size,3],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1))
target_layer,parameters = inference(images) init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init) time_tensorflow_run(sess,target_layer,'Forward')
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(target_layer) # 模拟目标函数
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters) # 梯度求解
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad,'Forward-backward') # 反向传播
# 参数更新并未计入时耗中 if __name__=='__main__':
run_benchmark()
输出结果
conv1 [32, 56, 56, 64]
conv1/pool1 [32, 27, 27, 64]
conv2 [32, 27, 27, 192]
conv2/pool2 [32, 13, 13, 192]
conv3 [32, 13, 13, 384]
conv4 [32, 13, 13, 256]
conv5 [32, 13, 13, 256]
conv5/pool5 [32, 6, 6, 256]
fcl1/Relu [32, 4096]
fcl2/Relu [32, 4096]
fcl3/BiasAdd [32, 10]
2017-12-11 15:54:04.515831: I C:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\rel-win\M\windows\PY\35\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:137] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX AVX2
2017-12-11 15:54:25.862993: step 0, duration = 1.664
2017-12-11 15:54:42.982326: step 10, duration = 1.522
2017-12-11 15:54:59.837156: step 20, duration = 1.514
2017-12-11 15:55:14.968393: step 30, duration = 1.482
2017-12-11 15:55:29.901042: step 40, duration = 1.488
2017-12-11 15:55:44.832427: step 50, duration = 1.481
2017-12-11 15:55:59.978011: step 60, duration = 1.533
2017-12-11 15:56:15.705833: step 70, duration = 1.557
2017-12-11 15:56:32.164702: step 80, duration = 2.052
2017-12-11 15:56:49.980907: step 90, duration = 1.985
2017-12-11 15:57:06.628665:Forward across 100 steps, 0.163 +/- 0.492 sec / batch
2017-12-11 15:58:31.174363: step 0, duration = 7.852
2017-12-11 15:59:49.693544: step 10, duration = 7.901
2017-12-11 16:01:16.828232: step 20, duration = 8.463
2017-12-11 16:02:40.500340: step 30, duration = 6.796
2017-12-11 16:03:45.091418: step 40, duration = 6.690
2017-12-11 16:04:50.500747: step 50, duration = 5.797
2017-12-11 16:05:48.492420: step 60, duration = 5.754
2017-12-11 16:06:46.093358: step 70, duration = 5.737
2017-12-11 16:07:43.135421: step 80, duration = 5.704
2017-12-11 16:08:40.122760: step 90, duration = 5.626
2017-12-11 16:09:30.885931:Forward-backward across 100 steps, 0.663 +/- 2.016 sec / batch
『TensorFlow』读书笔记_AlexNet的更多相关文章
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_降噪自编码器
『TensorFlow』降噪自编码器设计 之前学习过的代码,又敲了一遍,新的收获也还是有的,因为这次注释写的比较详尽,所以再次记录一下,具体的相关知识查阅之前写的文章即可(见上面链接). # Aut ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_VGGNet
VGGNet网络介绍 VGG系列结构图, 『cs231n』卷积神经网络工程实践技巧_下 1,全部使用3*3的卷积核和2*2的池化核,通过不断加深网络结构来提升性能. 所有卷积层都是同样大小的filte ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_ResNet_V2
『PyTorch × TensorFlow』第十七弹_ResNet快速实现 要点 神经网络逐层加深有Degradiation问题,准确率先上升到饱和,再加深会下降,这不是过拟合,是测试集和训练集同时下 ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_SoftMax分类器
开坑之前 今年3.4月份的时候就买了这本书,同时还买了另外一本更为浅显的书,当时读不懂这本,所以一度以为这本书很一般,前些日子看见知乎有人推荐它,也就拿出来翻翻看,发现写的的确蛮好,只是稍微深一点,当 ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_多层感知机
多层感知机 输入->线性变换->Relu激活->线性变换->Softmax分类 多层感知机将mnist的结果提升到了98%左右的水平 知识点 过拟合:采用dropout解决,本 ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_简单卷积神经网络
如果你可视化CNN的各层级结构,你会发现里面的每一层神经元的激活态都对应了一种特定的信息,越是底层的,就越接近画面的纹理信息,如同物品的材质. 越是上层的,就越接近实际内容(能说出来是个什么东西的那些 ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_进阶卷积神经网络_分类cifar10_上
完整项目见:Github 完整项目中最终使用了ResNet进行分类,而卷积版本较本篇中结构为了提升训练效果也略有改动 本节主要介绍进阶的卷积神经网络设计相关,数据读入以及增强在下一节再与介绍 网络相关 ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_进阶卷积神经网络_分类cifar10_下
数据读取部分实现 文中采用了tensorflow的从文件直接读取数据的方式,逻辑流程如下, 实现如下, # Author : Hellcat # Time : 2017/12/9 import os ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_Inception_V3_下
极为庞大的网络结构,不过下一节的ResNet也不小 线性的组成,结构大体如下: 常规卷积部分->Inception模块组1->Inception模块组2->Inception模块组3 ...
随机推荐
- EFM32G232F64时钟树
1.为了熟悉MCU的时钟树,先看看EFM32G232F64的CMU(ClockManagementUnit) 时钟管理单元(CMU)用于管控晶振(时钟源)和各个时钟节点.出于降低功耗和启动时间的目的, ...
- linear-gradient常用实现效果
之前也研究过css3的这个属性,感觉没什么大用,一般的开发不会用到,毕竟调出来的渐变不专业,不如找一个好看的图片,其实很多时候还是有用的,偷来三个例子. 一.控制虚线 一般写虚线都用dashed,但有 ...
- Cocos2d-js3.3 模态对话框的实现
首先,先了解一下什么是模态对话框,百度百科的给出了下面一个定义: 模态对话框(Modal Dialogue Box,又叫做模式对话框),是指在用户想要对对话框以外的应用程序进行操作时,必须首先对该对话 ...
- vue 之iview
iView-admin2.0:https://admin.iviewui.com/ 组件:https://www.iviewui.com/docs/guide/install
- python 判断两个ip是不是处于同一网段
a_ip:10.10.15.100b_ip:10.10.15.101c_ip:10.10.10.100netmask:255.255.255.0 def numtobinary(num): binar ...
- Feign 与 Hystrix
Feign 与 Hystrix Feign是一个声明式的web服务客户端,它使得web服务调用非常的简单,当我们使用Feign时,Spring Cloud 整合了Ribbon和Eureka,从而为我们 ...
- Array类型和方法
var ft = new Array(); var ft = new Array(20); var ft = new Array("1","2","3 ...
- JavaScript判断对象有没有定义
if ( typeof(callbackfun) != "undefined" ) { callbackfun(); }
- docker overlay
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangshouzhuang/article/details/52822125
- javax.el.PropertyNotFoundException: Property 'know_id' not found on type java.lang.String
今天通过Servlet明明查出来了结果,在跳转到页面时报这个异常.根据经验仔细核对了字段书写时,未发现错误. 耐心仔细检查之后发现el表达式的List集合写错了 <c:forEach items ...
