(转)Windows管道(Pipe)重定向stdout,stderr,stdin
参考:
http://qiusuoge.com/11496.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/BoyXiao/archive/2011/01/01/1923828.html
stdin是标准输入,stdout是标准输出,stderr是标准错误输出。大多数的命令行程序从stdin输入,输出到stdout或 stderr,有时我们需要重定向stdout,stderr,stdin。比如:将输出写入文件,又或者我们要将命令行程序输出结果显示到 Windows对话框中。
相关阅读
在Windows编程中,重定向需要用到管道(Pipe)的概念。管道是一种用于在进程间共享数据的机制。一个管道类似于一个管子的两端,一端是写入的,一端是读出的。由一个进程从写入端写入、另一个进程从读出端读出,从而实现通信,就向一个“管道”一样。
重定向的原理是:
首先声明两个概念:主程序(重定向的操纵者)、子进程(被重定向的子进程)
如果要重定位stdout的话,先生成一个管道, 管道的写入端交给子进程去写,主程序从管道的读出端读数据,然后可以把数据写成文件、显示等等。重定向stderr和stdout是相同的。
同理,要重定向stdin的话,生成一个管道, 管道的写入端由主程序写,子进程从管道的读出端读数据。
其中需要用到几个Windows API : CreatePipe, DuplicateHandle, CreateProcess, ReadFile, WriteFile 等,函数详解可参见MSDN.
一、编程实现原理 ( C语言)
view plaincopy to clipboard
#include <windows.h>
//定义句柄: 构成stdin管道的两端句柄
HANDLE hStdInRead; //子进程用的stdin的读入端
HANDLE hStdInWrite; //主程序用的stdin的读入端
//定义句柄: 构成stdout管道的两端句柄
HANDLE hStdOutRead; ///主程序用的stdout的读入端
HANDLE hStdOutWrite; ///子进程用的stdout的写入端
//定义句柄: 构成stderr管道的句柄,由于stderr一般等于stdout,我们没有定义hStdErrRead,直接用hStdOutRead即可
HANDLE hStdErrWrite; ///子进程用的stderr的写入端
//定义一个用于产生子进程的STARTUPINFO结构体 (定义见CreateProcess,函数说明)
STARTUPINFO siStartInfo;
//定义一个用于产生子进程的PROCESS_INFORMATION结构体 (定义见CreateProcess,函数说明)
PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo;
//产生一个用于stdin的管道,得到两个HANDLE: hStdInRead用于子进程读出数据,hStdInWrite用于主程序写入数据
//其中saAttr是一个STARTUPINFO结构体,定义见CreatePipe函数说明
if (!CreatePipe(&hStdInRead, &hStdInWrite,&saAttr, 0))
return;
//产生一个用于stdout的管道,得到两个HANDLE: hStdInRead用于主程序读出数据,hStdInWrite用于子程序写入数据
if (!CreatePipe(&hStdOutRead, &hStdOutWrite,&saAttr, 0))
return;
//由于stderr一般就是stdout, 直接复制句柄hStdOutWrite,得到 hStdErrWrite
if (!DuplicateHandle(GetCurrentProcess(), hStdOutWrite,
GetCurrentProcess(), &hStdErrWrite, 0, TRUE,
DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS))
return;
//对STARTUPINFO结构体赋值,对stdin,stdout,stderr的Handle设置为刚才得到的管道HANDLE
ZeroMemory( &siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO) );
siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW;
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput = hStdOutWrite; //意思是:子进程的stdout输出到hStdOutWrite
siStartInfo.hStdError = hStdErrWrite; //意思是:子进程的stderr输出到hStdErrWrite
siStartInfo.hStdInput = hStdInRead;
// 产生子进程,具体参数说明见CreateProcess函数
bSuccess = CreateProcess(NULL,
CommandLine, // 子进程的命令行
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
0, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION
//如果失败,退出
if (!bSuccess ) return;
//然后,就可以读写管道了
//写入stdin,具体代码在一个WriteToPipe函数中
WriteToPipe();
//不断子检测进程有否结束
while (GetExitCodeProcess(piProcInfo.hProcess,&process_exit_code))
{
//读stdout,stderr
ReadFromPipe();
//如果子进程结束,退出循环
if (process_exit_code!=STILL_ACTIVE) break;
}
[html] view plaincopy
#include <windows.h>
//定义句柄: 构成stdin管道的两端句柄
HANDLE hStdInRead; //子进程用的stdin的读入端
HANDLE hStdInWrite; //主程序用的stdin的读入端
//定义句柄: 构成stdout管道的两端句柄
HANDLE hStdOutRead; ///主程序用的stdout的读入端
HANDLE hStdOutWrite; ///子进程用的stdout的写入端
//定义句柄: 构成stderr管道的句柄,由于stderr一般等于stdout,我们没有定义hStdErrRead,直接用hStdOutRead即可
HANDLE hStdErrWrite; ///子进程用的stderr的写入端
//定义一个用于产生子进程的STARTUPINFO结构体 (定义见CreateProcess,函数说明)
STARTUPINFO siStartInfo;
//定义一个用于产生子进程的PROCESS_INFORMATION结构体 (定义见CreateProcess,函数说明)
PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo;
//产生一个用于stdin的管道,得到两个HANDLE: hStdInRead用于子进程读出数据,hStdInWrite用于主程序写入数据
//其中saAttr是一个STARTUPINFO结构体,定义见CreatePipe函数说明
if (!CreatePipe(&hStdInRead, &hStdInWrite,&saAttr, 0))
return;
//产生一个用于stdout的管道,得到两个HANDLE: hStdInRead用于主程序读出数据,hStdInWrite用于子程序写入数据
if (!CreatePipe(&hStdOutRead, &hStdOutWrite,&saAttr, 0))
return;
//由于stderr一般就是stdout, 直接复制句柄hStdOutWrite,得到 hStdErrWrite
if (!DuplicateHandle(GetCurrentProcess(), hStdOutWrite,
GetCurrentProcess(), &hStdErrWrite, 0, TRUE,
DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS))
return;
//对STARTUPINFO结构体赋值,对stdin,stdout,stderr的Handle设置为刚才得到的管道HANDLE
ZeroMemory( &siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO) );
siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW;
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput = hStdOutWrite; //意思是:子进程的stdout输出到hStdOutWrite
siStartInfo.hStdError = hStdErrWrite; //意思是:子进程的stderr输出到hStdErrWrite
siStartInfo.hStdInput = hStdInRead;
// 产生子进程,具体参数说明见CreateProcess函数
bSuccess = CreateProcess(NULL,
CommandLine, // 子进程的命令行
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
0, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION
//如果失败,退出
if (!bSuccess ) return;
//然后,就可以读写管道了
//写入stdin,具体代码在一个WriteToPipe函数中
WriteToPipe();
//不断子检测进程有否结束
while (GetExitCodeProcess(piProcInfo.hProcess,&process_exit_code))
{
//读stdout,stderr
ReadFromPipe();
//如果子进程结束,退出循环
if (process_exit_code!=STILL_ACTIVE) break;
}
具体看一下WriteToPipe(), ReadFromPipe函数:
view plaincopy to clipboard
//写入stdin
BOOL WriteToPipe()
{
DWORD dwWritten;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
//用WriteFile,从hStdInWrite写入数据,数据在in_buffer中,长度为dwSize
bSuccess = WriteFile( hStdInWrite, in_buffer, dwSize, &dwWritten, NULL);
return bSuccess;
}
[html] view plaincopy
//写入stdin
BOOL WriteToPipe()
{
DWORD dwWritten;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
//用WriteFile,从hStdInWrite写入数据,数据在in_buffer中,长度为dwSize
bSuccess = WriteFile( hStdInWrite, in_buffer, dwSize, &dwWritten, NULL);
return bSuccess;
}
view plaincopy to clipboard
// 读出stdout
BOOL ReadFromPipe()
{
char out_buffer[4096];
DWORD dwRead;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
//用WriteFile,从hStdOutRead读出子进程stdout输出的数据,数据结果在out_buffer中,长度为dwRead
bSuccess = ReadFile( hStdOutRead, out_buffer, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if ((bSuccess) && (dwRead!=0)) //如果成功了,且长度>0
{
// 此处加入你自己的代码
// 比如:将数据写入文件或显示到窗口中
}
return bSuccess;
}
[html] view plaincopy
// 读出stdout
BOOL ReadFromPipe()
{
char out_buffer[4096];
DWORD dwRead;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
//用WriteFile,从hStdOutRead读出子进程stdout输出的数据,数据结果在out_buffer中,长度为dwRead
bSuccess = ReadFile( hStdOutRead, out_buffer, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if ((bSuccess) && (dwRead!=0)) //如果成功了,且长度>0
{
// 此处加入你自己的代码
// 比如:将数据写入文件或显示到窗口中
}
return bSuccess;
}
OK,到此原理写完了。为简化说明原理,上述代码省略了出错处理、结束处理(如:CloseHandle等),具体可以参见我的源码。
二、封装、实用的代码
上述过程有些麻烦,实际使用中,我封装成几个函数:
首先定义三个回调函数 (就是函数指针类型)
//当stdin输入时,调用此函数。将要写的数据写入buf中,*p_size写为数据长度即可。
typedef void FuncIn(char *buf,int *p_size);
//当stdout,stderr输出时,调用此函数。可读取的数据在buf中,数据长度为size。
typedef void FuncOut(char *buf,int size);
//当子进程持续过程中,周期性调用此函数,设置p_abort可中断子进程。
typedef void FuncProcessing(int *p_abort);
然后定义了四个函数
//执行一个命令行,重定向stdin, stdout,stderr。
//OnStdOut是回调函数指针,当有输出时,OnStdOut被调用。
//OnStdIn是回调函数指针,当输入时,OnStdIn被调用。
int ExecCommandEx(char *szCommandLine,char *CurrentDirectory,char *Environment,unsigned short ShowWindow,
FuncOut *OnStdOut,FuncProcessing *OnProcessing,FuncIn *OnStdIn);
//执行一个命令行,重定向stdout,stderr。
//OnLineOut是回调函数指针,当有一行输出时,OnLineOut被调用。
int ExecCommandOutput(char *szCommandLine,char *Environment,unsigned short ShowWindow,
FuncOut *OnLineOut,FuncProcessing *OnProcessing);
//执行一个命令行,等待子进程结束,返回子进程的程序退出代码。不处理重定向。
int ExecCommandWait(char *szCommandLine,unsigned short ShowWindow,FuncProcessing *OnProcessing);
//执行一个命令行,不等待子进程结束,即返回。不处理重定向。功能相当于 Windows API WinExec.
int ExecCommandNoWait(char *szCommandLine,unsigned short ShowWindow);
还定义了一个存储数据的EXEC_INFO结构体及操作它的函数。
全部代码为C语言,在JExecution.c, JExecution.h两个文件中。只用到了Windows API,没有用MFC及其他库。
三、使用方法
有了JExecution.c,使用就很方便了。比如:
view plaincopy to clipboard
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "JExecution.h"
//定义一个处理输出的回调函数
void OnLineOut(char *buf,int size)
{
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int n;
char *command;
command = "cmd.exe /r dir/w "; //这个命令的意思就是调用DOS,执行dir命令,显示当前目前下的文件
n=ExecCommandOutput(command,NULL,SW_HIDE,OnLineOut,NULL);
printf("<Return:>%d",n);
}
[html] view plaincopy
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "JExecution.h"
//定义一个处理输出的回调函数
void OnLineOut(char *buf,int size)
{
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int n;
char *command;
command = "cmd.exe /r dir/w "; //这个命令的意思就是调用DOS,执行dir命令,显示当前目前下的文件
n=ExecCommandOutput(command,NULL,SW_HIDE,OnLineOut,NULL);
printf("<Return:>%d",n);
}
我用C++ Builder 6写了一个示范程序。示范将stdout重定向,输出到窗口中。
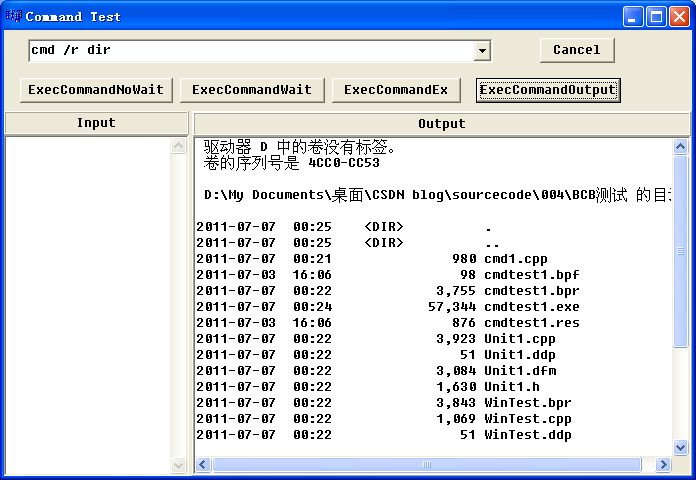
四、小结
Windows管道虽然有些麻烦,却可以产生好的效果。
比如:我们常用的IDE就是把调用命令行的编译程序,将其stdout重定向,将结果信息显示在窗口中。
又比如,我们把上述的程序改一下,把dir命令的结果通过网络发送出去,嗯,Hacker.
(转)Windows管道(Pipe)重定向stdout,stderr,stdin的更多相关文章
- file descriptor 0 1 2 一切皆文件 stdout stderr stdin /dev/null 沉默是金 pipes 禁止输出 屏蔽 stdout 和 stderr 输入输出重定向 重定向文件描述符
movie.mpeg.001 movie.mpeg.002 movie.mpeg.003 ... movie.mpeg.099 $cat movie.mpeg.0*>movie.mpeg ...
- 【python】使用unix管道pipe处理stdout实时数据
现在有个实时抓包处理的程序,大概的流程是 使用tshark抓包->实时上传,如果写log的话是可以的,但是log文件切割需要定时执行. 由于log中有些内容需要实时处理,延迟时间会导致数据误差, ...
- file descriptor 0 1 2 一切皆文件 stdout stderr stdin /dev/null 沉默是金 pipes
$>emtry_or_create_a_file.f $ll>>append_a_file.f standard output input error $ls -l /usr/bin ...
- 【原创】Linux基础之重定向stdout/stderr
启动进程后查看日志(stdout和stderr) 1 nohup+tail # nohup $cmd > /path/to/file 2>&1 & # tail -f /p ...
- shell基础知识之 stdin,stdout,stderr和文件描述符
stdin,stdout,stderr stdin=0 stdout=1 stderr=2 使用tee来传递内容,把stdout 作为stdin 传到下个命令 root@172-18-21-195:/ ...
- Linux Shell 文件描述符 及 stdin stdout stderr 重定向
Abstract: 1) Linux Shell 命令的标准输入.标准输出.标准错误,及其重定位: 2)Linux Shell 操作自定义文件描述符: 文件描述符是与文件相关联的一些整数,他们保持与已 ...
- WorkerMan源码分析(resetStd方法,PHP中STDIN, STDOUT, STDERR的重定向)
WorkerMan中work.php中 resetStd 方法中代码如下 public static function resetStd() { if (!static::$daemonize || ...
- STDOUT/STDERR重定向到ALOG中
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/kangear/article/details/24534707 说下背景:如今众多Andr ...
- stdin stdout stderr 标准I/O流
Unix中一切皆文件,磁盘等设备在操作系统来看都是文件. 对文件进行操作时,需要打开这个文件,并获得文件描述符(file descriptor, fd) 而每个进程生来就有三个文件描述符绑定在它身上, ...
随机推荐
- 关于MTK平台SIM-ME Lock的配置方案
针对一些运营商的锁网需求,MTK平台已经对其有很好的支持.绝大多数的海外需求可以通过直接配置相关文件来完成.这里简单描述一下配置方法,不做原理分析. 相关数据结构分析: Modem中与SML锁网配置相 ...
- 星语硬件检测专家 V4.3 官方版
软件名称: 星语硬件检测专家 软件语言: 简体中文 授权方式: 免费软件 运行环境: Win 32位/64位 软件大小: 15.8MB 图片预览: 软件简介: 星语硬件检测专家是一款功能非常强大的硬件 ...
- 实验六 多线程编程 1.随便选择两个城市作为预选旅游目标。实现两个独立的线程分别显示10次城市名,每次显示后休眠一段随机时间(1000ms以内),哪个先显示完毕,就决定去哪个城市。分别用Runnable接口和Thread类实现。
//继承Thread类 package zuoye; //继承Thread类 public class City extends Thread{ private String name; public ...
- Android 中OKHttp请求数据get和post
1:在Android Studio 的 build.gradle下 添加 然后再同步一下 compile 'com.squareup.okhttp:okhttp:2.4.0'compile 'com ...
- php+ajax的三级联动下拉菜单
封装一个三级联动,就可以在任何页面进行引用了 先写个页面引用一下这个js <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" conte ...
- linux同步windows的时间
找了很多的资料,都没有windows做时间服务,linux同步windows的时间的,最后自己找了一些软件,终于搞定了,写出来给大家共享,以免大家多走弯路 首先在http://www.meinberg ...
- Java静态语句块、语句块、构造方法执行顺序
package com.imooc.practice; class Parent{ public Parent(){ System.out.println("Parent构造方法执行!&qu ...
- petstore-jdbc
拖了好多天,终于决定开始写作业了,搞了大半天的把软件安好. jdk(安装与环境配置) Tomcat(安装与环境配置) mysql(安装,同时配置图形化操作界面) eclipse for Javaee ...
- 矩阵快速幂——将运算推广到矩阵上HDU 1575
/* 本题的思路比较简单,就是将递推公式写出来,然后表达成为一个矩阵的形式 最后通过计算就可以得到一个符合题目要求的矩阵, 然后就是将矩阵上面所有的对角线元素相加 得到的结果即为所求的目标 */ #i ...
- lua学习
在lua中,一切都是变量,除了关键字. 1.注释: 单行注释: 连续两个减号“--”表示注释的开始,一直延续到行末.相当于C语言中的“//” 多行注释:由“--[[”表示注释开始, “]]”表示注释结 ...
