I2C的库函数应用示例
I2C Arduino 简单应用举例
例1 多机通信
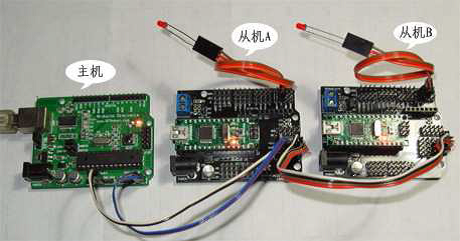
主机代码:(从编译器串口监视器发送数字1,2,3,4来控制从机的LED亮与灭)
1 #include <Wire.h>
2 void setup()
3 {
4 Wire.begin(); //启动I2C 总线,地址缺省表示为主机
5 Serial.begin(9600); //启动串口,设置波特率为9600
6 Serial.println("Ready"); //发送字符
7 }
8
9 void loop()
10 {
11 int val;
12 if(Serial.available() > 0) //判断串口缓冲器是否有数据装入
13 {
14 val=Serial.read(); //读串口
15 if(val==49) //1
16 {
17 Wire.beginTransmission(4); // 与地址4 的从机连接通讯
18 Wire.write(1); // 发送数字 1 开LED
19 Wire.endTransmission(); // 停止发送
20 Serial.println("49 OK"); // 串口上显示 49 OK 表示完成,49 表示为数字 1 的ASCII 码
21 delay(10);
22 }
23 else if(val==50)//2
24 {
25 Wire.beginTransmission(4); // 与地址4 的从机连接通讯
26 Wire. write (0); // 发送数字 0 关LED
27 Wire.endTransmission(); // 停止发送
28 Serial.println("50 OK"); // 串口上显示 50 OK 表示完成
29 delay(10);
30 }
31 else if(val==51) //3
32 {
33 Wire.beginTransmission(5); // 与地址5 的从机连接通讯
34 Wire. write (1); // 发送数字 1 开LED
35 Wire.endTransmission(); // 停止发送
36 Serial.println("51 OK"); // 串口上显示 51 OK 表示完成
37 delay(10);
38 }
39 else if(val==52) //4
40 {
41 Wire.beginTransmission(5); // 与地址5 的从机连接通讯
42 Wire.write (0); // 发送数字 0 关LED
43 Wire.endTransmission(); // 停止发送
44 Serial.println("52 OK"); // 串口上显示 52 OK 表示完成
45 delay(10);
46 }
47 else
48 { Serial.println(val); }
49 }
50 }
从机A代码:(接收到主机发送的1点亮LED,接收到0关掉LED)
1 #include <Wire.h>
2 int LED = 2;
3
4 void setup()
5 {
6 Wire.begin(4); // 设置从机地址为 4
7 pinMode(LED,OUTPUT); // 设置IO 口为输出模式
8 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); //从机接收主机发来的数据
9 }
10
11 void loop()
12 { delay(100); }
13
14 void receiveEvent(int howMany) // 接收从主机发过来的数据
15 {
16 int c = Wire.receive(); // 接收单个字节
17 if(c==1)
18 { digitalWrite(LED,HIGH); // 如果为 1 开LED }
19 else if(c==0)
20 { digitalWrite(LED,LOW); // 如果为 0 关LED }
21 }
从机B代码:(接收到主机发送的1点亮LED,接收到0关掉LED)
1 #include <Wire.h>
2 int LED = 2;
3
4 void setup()
5 {
6 Wire.begin(5); // 设置从机地址为 5
7 pinMode(LED,OUTPUT);
8 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent);
9 }
10
11 void loop()
12 { delay(100);}
13
14 void receiveEvent(int howMany)
15 {
16 int c = Wire.receive();
17 if(c==1)
18 { digitalWrite(LED,HIGH); }
19 else if(c==0)
20 { digitalWrite(LED,LOW); }
21 }
例2 Master Reader/Slave Sender 从发主收信息共享
In some situations, it can be helpful to set up two (or more!) Arduino and Genuino boards to share information with each other(彼此共享信息). In this example, two boards are programmed to communicate with one another in a Master Reader/Slave Sender configuration(配置) via the I2C synchronous serial protocol(I2C同步串行协议).Several functions of Arduino's Wire Library are used to accomplish this. Arduino 1, the Master, is programmed to request, and then read, 6 bytes of data sent from the uniquely addressed Slave Arduino. Once that message is received, it can then be viewed in the Arduino Software (IDE) serial monitor window.
The I2C protocol involves using two lines to send and receive data: a serial clock pin (SCL) that the Arduino or Genuino Master board pulses at a regular interval, and a serial data pin (SDA) over which data is sent between the two devices. As the clock line changes from low to high (known as the rising edge of the clock pulse), a single bit of information - that will form in sequence the address of a specific device and a command or data - is transferred from the board to the I2Cdevice over the SDA line. When this information is sent - bit after bit -, the called upon device executes the request and transmits it's data back - if required - to the board over the same line using the clock signal still generated by the Master on SCL as timing.
Because the I2C protocol allows for each enabled device to have it's own unique address, and as both master and slave devices to take turns communicating over a single line, it is possible for your Arduino or Genuino board to communicate (in turn) with many devices, or other boards, while using just two pins of your microcontroller.
Hardware Required
- 2 Arduino or Genuino Boards
- hook-up wires
Circuit
Connect pin 4 (the data, or SDA, pin) and pin 5 (the clock, or SCL, pin) on the master board to their counterparts on the slave board. Make sure that both boards share a common ground. In order to enable serial communication, the master board must be connected to your computer via USB.
If powering the boards independently is an issue, connect the 5V output of the Master to the VIN pin on the slave.
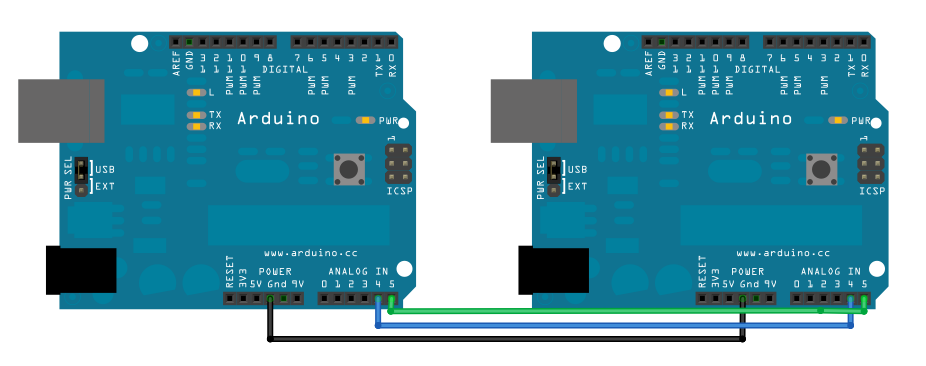
Schematic
Code for Master Reader - Program for Arduino 1
1 #include <Wire.h>
2
3 void setup()
4 {
5 Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
6 Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
7 }
8
9 void loop()
10 {
11 Wire.requestFrom(8, 6); // request 6 bytes from slave device #8
12 while (Wire.available())
13 {
14 char c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
15 Serial.print(c); // print the character
16 }
17 delay(500);
18 }
Code for Slave Sender - Program for Arduino 2
1 #include <Wire.h>
2
3 void setup()
4 {
5 Wire.begin(8); // join i2c bus with address #8
6 Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // register event
7 }
8
9 void loop()
10 { delay(100); }
11
12 void requestEvent()
13 {
14 Wire.write("hello "); // respond with message of 6 bytes as expected by master
15 }
例3 Master Writer/Slave Receiver 主发从收信息共享
Hardware Required,Circuit,Schematic 同例2
Master Writer Code - Program for Arduino 1
1 #include <Wire.h>
2 byte x = 0;
3
4 void setup()
5 { Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master) }
6
7 void loop()
8 {
9 Wire.beginTransmission(8); // transmit to device #8
10 Wire.write("x is "); // sends five bytes
11 Wire.write(x); // sends one byte
12 Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
13 x++;
14 delay(500);
15 }
Slave Receiver Code - Program for Arduino 2
1 #include <Wire.h>
2
3 void setup()
4 {
5 Wire.begin(8); // join i2c bus with address #8
6 Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event
7 Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
8 }
9
10 void loop()
11 { delay(100);}
12
13 void receiveEvent(int howMany)
14 {
15 while (1 < Wire.available())
16 {
17 char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character
18 Serial.print(c); // print the character
19 }
20 int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer
21 Serial.println(x); // print the integer
22 }
I2C的库函数应用示例的更多相关文章
- linux下创建库函数
来源: 在Linux下如何使用自己的库函数-riverok-ChinaUnix博客 http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-21393885-id-88128.html 构建Lin ...
- STM32模拟I2C
之前为了测试, 拿最小板做了一个I2C的主发跟主读, 一开始当然是尝试用硬件I2C, 结果弄了很久, 时间紧迫, 只好用了模拟, 结果发现, 哎, 真特么挺好用的, 现在1片儿顶过去5片儿. 硬件I2 ...
- NHibernate查询示例合集
基本查询 复杂查询示例 /// <summary> /// 获取自定义表单数据中属于部门的部分 /// </summary> /// <param name=&quo ...
- Python---socket库
为方便以后查询和学习,特从常用库函数和示例来总结socket库 1. 术语 family:AF_INET socktype:SOCK_STREAM或SOCK_DGRAM protocol:IPPROT ...
- 程序设计与算法(一)C语言程序设计CAP之字符串
C++中的字符串 字符串有三种形式 用双引号括起来的字符串常量,如果"CHINA"."C++ program" 存放于字符串数组中,以'\0'字符(ASCII吗 ...
- 剑指offer——把字符串转换成整数(c++)
题目描述请你写一个函数StrToInt,实现把字符串转换成整数这个功能.当然,不能使用atoi或者其他类似的库函数. 示例 1:输入: " -42"输出: -42解释: 第一个非空 ...
- Programiz 中文系列教程·翻译完成
原文:Programiz 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 欢迎任何人参与和完善:一个人可以走的很快,但是一群人却可以走的更远. 在线阅读 ApacheCN 学习资源 目录 Programiz C ...
- Programiz C 语言教程·翻译完成
原文:Programiz 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 欢迎任何人参与和完善:一个人可以走的很快,但是一群人却可以走的更远. 在线阅读 ApacheCN 学习资源 目录 C 简介 C 关键字和 ...
- GNU Readline库函数的应用示例
说明 GNU Readline是一个跨平台开源程序库,提供交互式的文本编辑功能.应用程序借助该库函数,允许用户编辑键入的命令行,并提供自动补全和命令历史等功能.Bash(Bourne Again Sh ...
随机推荐
- pymssql 介绍
pymssql包是Python语言用于连接SQL Server数据库的驱动程序(或者称作DB API),它是最终和数据库进行交互的工具.SQLAlchemy包就是利用pymssql包实现和SQL Se ...
- github travis-ci持续部署hexo博客
引言 目前我的博客源码是在coding上的,因为有很方便的持续部署,但是coding目前还不提供push文件的开放API. 因为最近做了一个一键分发平台,将博客分发到简书.CSDN等等的平台,但是我的 ...
- [BUUOJ记录] [极客大挑战 2019]RCE ME
前面考察取反或者异或绕过,后面读Flag那里我用脏方法过了,没看出来考察啥 进入题目给出源码: <?php error_reporting(0); if(isset($_GET['code']) ...
- 最小生成树MST
定义 在一给定的无向联通带权图\(G = (V, E, W)\)中,\((u, v)\) 代表连接顶点 \(u\) 与顶点 \(v\) 的边,而 \(w(u, v)\) 代表此边的权重,若存在 \(T ...
- 想要使用GPU进行加速?那你必须事先了解CUDA和cuDNN
这一期我们来介绍如何在Windows上安装CUDA,使得对图像数据处理的速度大大加快,在正式的下载与安装之前,首先一起学习一下预导知识,让大家知道为什么使用GPU可以加速对图像的处理和计算,以及自己的 ...
- mysql如何查询多样同样的表/sql分表查询、java项目日志表分表的开发思路/按月分表
之前开发的一个监控系统,数据库的日志表是单表,虽然现在数据还不大并且做了查询sql优化,不过以后数据库的日志表数据肯定会越来越庞大,将会导致查询缓慢,所以把日志表改成分表,日志表可以按时间做水平分表, ...
- Mybatis动态SQL配置
使用 if where foreach标签对映射配置文件中sql语句进行动态配置 1.首先在dao接口中设置两个查询方法 package sun.dao; import sun.domain.Quer ...
- 快速生成网络mp4视频缩略图技术
背景 由于网络原因,在下载视频之前我们往往会希望能够先生成一些视频的缩略图,大致浏览视频内容,再确定是否应花时间下载.如何能够快速得到视频多个帧的缩略图的同时尽量少的下载视频的内容,是一个值得研究的问 ...
- visual studio项目多级引用不拷贝dll的问题
最近碰到一个visual studio项目多级引用不拷贝dll的问题,花了很久查了很多资料,特此记录 A项目引用B项目, B项目引用C项目,C项目引用ef及oracle.ef using Oracle ...
- 掌控安全sql注入靶场pass-05
1.判断注入点 1 and 1=1 1 and 1=2 考虑存在布尔盲注 布尔盲注解释 当不能像前面那样直接在网页中显示我们要的数据时就需要用到盲注,来得到数据库之类的名字.基于布尔的盲注就是通过判断 ...
