UVA 1601 双向BFS
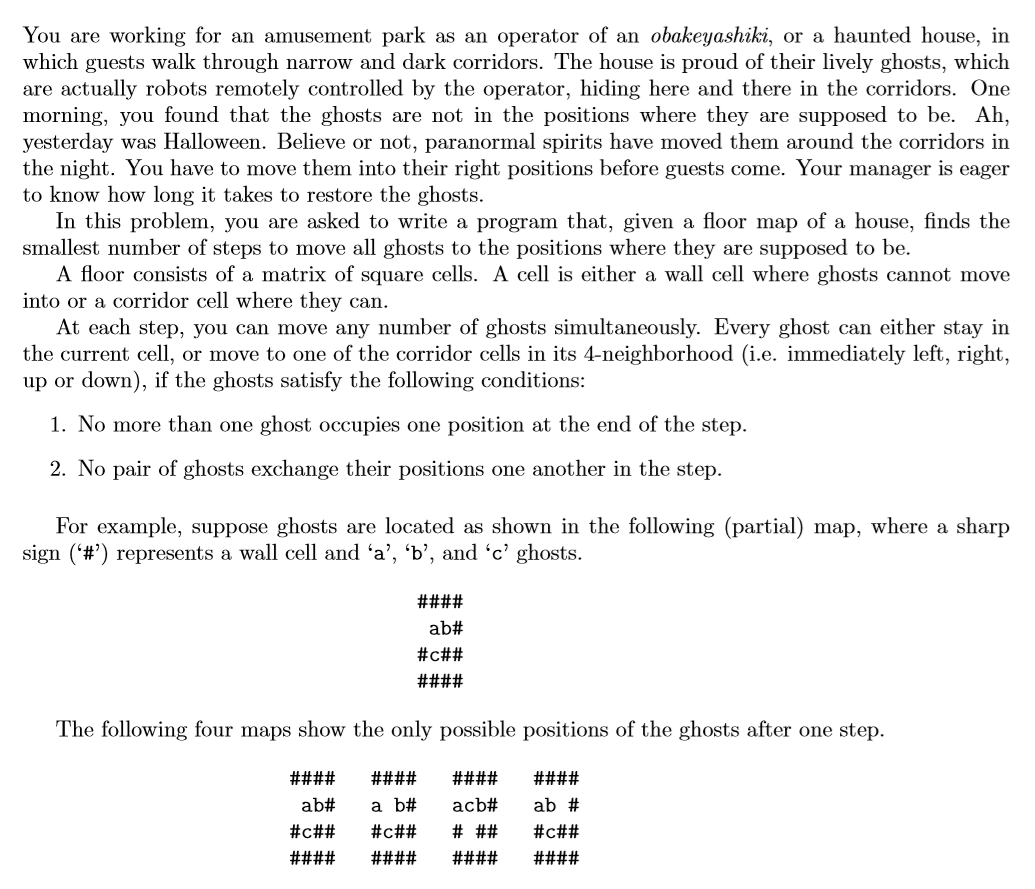


但是我们还不是很清楚每一次的状态怎么储存?我们可以用一个结构体,将每次的位置存起来,但是这个程序中用了一个更好的储存方法:我们知道最大的格数是16*16个,也就是256个,那么我们转换为二进制表示就是8位数,那么我们可以使用24位的二进制表示啊!然后我们再进行解压缩,所以这就是很神奇的地方!
普通BFS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
//const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
const int maxs = ;
const int dx[] = { ,-,,, };
const int dy[] = { ,,,-, }; inline int ID(int a, int b, int c) {
return (a << ) | (b << ) | c;
} int s[], t[]; int deg[maxn]; //记录每个编号为i的空格周围可以走的步数
int G[maxn][]; inline bool conflict(int a, int b, int a2, int b2) {
return a2 == b2 || (a2 == b && b2 == a);
} int d[maxn][maxn][maxn]; int bfs() {
queue<int> q;
memset(d, -, sizeof d);
q.push(ID(s[], s[], s[]));
d[s[]][s[]][s[]] = ;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
int a = (u >> ) & 0xff, b = (u >> ) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; //解码出三个鬼的位置
if (a == t[] && b == t[] && c == t[]) return d[a][b][c];
for (int i = ; i < deg[a]; i++) {
int a2 = G[a][i];
for (int j = ; j < deg[b]; j++) {
int b2 = G[b][j];
if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue;
for (int k = ; k < deg[c]; k++) {
int c2 = G[c][k];
if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2)) continue;
if (conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue;
if (d[a2][b2][c2] != -) continue;
d[a2][b2][c2] = d[a][b][c] + ;
q.push(ID(a2, b2, c2));
}
}
}
}
return -;
} int main() {
int w, h, n; while (scanf("%d%d%d", &w, &h, &n) == && n) {
char maze[][];
for (int i = ; i < h; i++) fgets(maze[i], , stdin); int cnt, x[maxn], y[maxn], id[maxs][maxs];
cnt = ;
for (int i = ; i < h; i++) {
for(int j=;j<w;j++)
if (maze[i][j] != '#') {
x[cnt] = i;
y[cnt] = j;
id[i][j] = cnt;
if (islower(maze[i][j])) s[maze[i][j] - 'a'] = cnt;
else if (isupper(maze[i][j])) t[maze[i][j] - 'A'] = cnt;
cnt++;
}
} for (int i = ; i < cnt; i++) {
deg[i] = ;
for (int dir = ; dir < ; dir++) {
int xx = x[i] + dx[dir], yy = y[i] + dy[dir];
if (maze[xx][yy] != '#') G[i][deg[i]++] = id[xx][yy];
}
} if (n <= ) {
deg[cnt] = ;
G[cnt][] = cnt;
s[] = t[] = cnt++;
}
if (n <= ) {
deg[cnt] = ;
G[cnt][] = cnt;
s[] = t[] = cnt++;
} printf("%d\n", bfs()); }
return ;
}
双向BFS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
//const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
const int maxs = ;
const int dx[] = { ,-,,, };
const int dy[] = { ,,,-, }; inline int ID(int a, int b, int c) {
return (a << ) | (b << ) | c;
} int s[], t[]; int deg[maxn]; //记录每个编号为i的空格周围可以走的步数
int G[maxn][];
char maze[maxn][maxn];
int color[maxn][maxn][maxn]; inline bool conflict(int a, int b, int a2, int b2) {
//两个鬼是exchange位置(违反第2条)
//两个鬼移动到同一个格子(违反第1条)
return a2 == b2 || (a2 == b && b2 == a);
} int d1[maxn][maxn][maxn]; int bfs() {
queue<int> qf;
queue<int> qb; d1[s[]][s[]][s[]] = ;
d1[t[]][t[]][t[]] = ; qf.push(ID(s[], s[], s[]));
qb.push(ID(t[], t[], t[])); while (!qf.empty() || !qb.empty()) {
int fnum = qf.size(), bnum = qb.size();
while (fnum--) {
int u = qf.front(); qf.pop();
int a = (u >> ) & 0xff, b = (u >> ) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; for (int i = ; i < deg[a]; i++) {
int a2 = G[a][i];
for (int j = ; j < deg[b]; j++) {
int b2 = G[b][j];
if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue;
for (int k = ; k < deg[c]; k++) {
int c2 = G[c][k];
if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2) || conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue;
if (color[a2][b2][c2] == ) {
d1[a2][b2][c2] = d1[a][b][c] + ;
color[a2][b2][c2] = ;
qf.push(ID(a2, b2, c2));
}
else if (color[a2][b2][c2] == ) {
return d1[a][b][c] + d1[a2][b2][c2];
}
}
}
}
}
while (bnum--) {
int u = qb.front(); qb.pop();
int a = (u >> ) & 0xff, b = (u >> ) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; for (int i = ; i < deg[a]; i++) {
int a2 = G[a][i];
for (int j = ; j < deg[b]; j++) {
int b2 = G[b][j];
if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue;
for (int k = ; k < deg[c]; k++) {
int c2 = G[c][k];
if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2) || conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue;
if (color[a2][b2][c2] == ) {
d1[a2][b2][c2] = d1[a][b][c] + ;
color[a2][b2][c2] = ;
qb.push(ID(a2, b2, c2));
}
else if (color[a2][b2][c2] == ) {
return d1[a][b][c] + d1[a2][b2][c2];
}
}
}
}
}
}
return -;
} int main() {
int w, h, n;
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &w, &h, &n) == , n) {
for (int i = ; i < h; i++) fgets(maze[i], , stdin);
int cnt = ;
int x[maxn], y[maxn];
int id[maxs][maxs];
for (int i = ; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = ; j < w; j++) {
if (maze[i][j] != '#') {
x[cnt] = i, y[cnt] = j, id[i][j] = cnt;
if (islower(maze[i][j])) s[maze[i][j] - 'a'] = cnt;
else if (isupper(maze[i][j])) t[maze[i][j] - 'A'] = cnt;
cnt++;
}
}
} for (int i = ; i < cnt; i++) {
for (int j = ; j < ; j++) {
int xx = x[i] + dx[j], yy = y[i] + dy[j];
if (maze[xx][yy] != '#') G[i][deg[i]++] = id[xx][yy];
}
} if (n <= ) {
deg[cnt] = ;
G[cnt][] = cnt;
s[] = t[] = cnt++;
}
if (n <= ) {
deg[cnt] = ;
G[cnt][] = cnt;
s[] = t[] = cnt++;
} memset(d1, , sizeof d1);
memset(color, , sizeof color); if (s[] == t[] && s[] == t[] && s[] == t[]) printf("0\n");
else printf("%d\n", bfs());
}
return ;
}
UVA 1601 双向BFS的更多相关文章
- 【UVa】1601 The Morning after Halloween(双向bfs)
题目 题目 分析 双向bfs,对着书打的,我还调了好久. 代码 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<c ...
- UVA - 1601 The Morning after Halloween (双向BFS&单向BFS)
题目: w*h(w,h≤16)网格上有n(n≤3)个小写字母(代表鬼).要求把它们分别移动到对应的大写字母里.每步可以有多个鬼同时移动(均为往上下左右4个方向之一移动),但每步结束之后任何两个鬼不能占 ...
- UVa 1601 || POJ 3523 The Morning after Halloween (BFS || 双向BFS && 降维 && 状压)
题意 :w*h(w,h≤16)网格上有n(n≤3)个小写字母(代表鬼).要求把它们分别移动到对应的大写字母里.每步可以有多个鬼同时移动(均为往上下左右4个方向之一移动),但每步结束之后任何两个鬼不能占 ...
- UVA - 11624 Fire! 双向BFS追击问题
Fire! Joe works in a maze. Unfortunately, portions of the maze have caught on fire, and the owner of ...
- <<操作,&0xff以及|的巧妙运用(以POJ3523---The Morning after Halloween(UVa 1601)为例)
<<表示左移,如a<<1表示将a的二进制左移一位,加一个0,&0xff表示取最后8个字节,如a&0xff表示取a表示的二进制中最后8个数字组成一个新的二进制数, ...
- POJ1915Knight Moves(单向BFS + 双向BFS)
题目链接 单向bfs就是水题 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include & ...
- HDU 3085 Nightmare II 双向bfs 难度:2
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3085 出的很好的双向bfs,卡时间,普通的bfs会超时 题意方面: 1. 可停留 2. ghost无视墙壁 3. ...
- POJ 3170 Knights of Ni (暴力,双向BFS)
题意:一个人要从2先走到4再走到3,计算最少路径. 析:其实这个题很水的,就是要注意,在没有到4之前是不能经过3的,一点要注意.其他的就比较简单了,就是一个双向BFS,先从2搜到4,再从3到搜到4, ...
- [转] 搜索之双向BFS
转自:http://www.cppblog.com/Yuan/archive/2011/02/23/140553.aspx 如果目标也已知的话,用双向BFS能很大程度上提高速度. 单向时,是 b^le ...
随机推荐
- 解决安装PyMySQL一直停在Building wheels for collected package:cryptography, cffi, pycparser的问题
我的运行环境为: 硬件:树莓派3b 系统:ubuntu_meta_16.04.2 因为项目需要,我在树莓派上搭建了基于python编程的Django的web框架,需要从MySQL中读取树莓派以及传感器 ...
- 从零构建以太坊(Ethereum)智能合约到项目实战——第25章 Embark FrameWork
P109 .1-Embark Framework 开发入门篇P110 .2-Embark Framework 去中心化存储 (IPFS)
- mysql mvcc 的理解
mvcc 全称 multiple version concurrency control 多版本并发控制,是数据库领域比较常用的一种非锁并发技术. mysql 的innodb中,在RR.RC级别会使用 ...
- 使用 CocoaPods 遇到的问题记录
1. 在 Terminal 输入 Cocoapods 命令时,有时会一直等待,出现“Performing a deep fetch of the `master` specs repo to impr ...
- centos6.5安装图形操作界面
yum -y install xorg-x11-fonts-Type1 #安装Xwindow yum -y groupinstall "X Window System" #安装GN ...
- Scrapy 使用 LinkExtractor 提取链接和使用 Exporter 导出数据
在爬取一个网站时,想要爬取的数据通常分布到多个页面中,每个页面包含一部分数据以及其他页面的链接,提取链接有使用 Selector 和使用 Linkextractor 两种方法. 1.使用Selecto ...
- SpringMVC:自定义视图及其执行过程
一:自定义视图 1.自定义一个实现View接口的类,添加@Component注解,将其放入SpringIOC容器 package com.zzj.view; import java.io.PrintW ...
- Python用户界面编程PyQt5的四种的布局方式
1.QT是C++编写的跨平台GUI库,GUI是指桌面程序应用. 2.开发基于pyqt5的桌面应用程序必须要使用两个类Qapplication和Qwidget类,都在PyQt5.Qt.widgets里面 ...
- topthink/think-swoole 扩展包的使用 之 WebSocket
嗯~ o(* ̄▽ ̄*)o,没错欢迎收看继续爬坑系列233...话不多说直接开撸 今天的题材是websocket,没有特殊说明的话默认环境都和此系列第一篇文章中申明一致,此后不再赘述. websocke ...
- 认识系统服务 (daemons)
daemon(守护进程:后台程序)与服务: 系统为了某些功能必须要提供一些服务 (不论是系统本身还是网络方面),这个服务就称为 service .但是 service 的提供总是需要程序的运作 ...
