ASP.NET Core技术研究-探秘Host主机启动过程
当我们将原有ASP.NET 应用程序升级迁移到ASP.NET Core之后,我们发现代码工程中多了两个类Program类和Startup类。
接下来我们详细探秘一下通用主机Host的启动过程。
一、Program类的Main函数入口
Program类最重要的功能就是启动主机,这里有一个主机的概念,是ASP.NET Core全新引入的。
主机负责应用程序启动和生存期管理。 同时,主机也是封装应用程序资源的对象:
- 依赖注入 (DI)
- Logging
- Configuration
- IHostedService 实现
启动主机时,它在 DI 容器中找到 IHostedService 的每个实现,然后调用 IHostedService.StartAsync。 在 web 应用中,其中一个 IHostedService 的实现是启动 HTTP 服务器实现的 web 服务。这里的HTTP服务器默认是Kestrel。
即:ASP.NET Core主机启动时,会启动一个HTTP服务器,默认是Kestrel。启动后监听并响应某个端口的HTTP请求。
我们继续看Program类的代码:

从上述代码可以看到,Main函数中首先调用CreateHostBuilder方法,返回一个IHostBuilder。然后调用IHostBuilder.Build()方法完成
二、Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args): 构造IHostBuilder的默认实现HostBuilder
在CreateHostBuilder方法内部,首先调用了Host.CreateDefaultBuilder构造了一个HostBuilder,这个我们先看下源码,看看到底Host类内部做了什么操作:
https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/Host.cs
public static IHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args)
{
var builder = new HostBuilder(); builder.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
builder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config =>
{
config.AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix: "DOTNET_");
if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
}); builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) =>
{
var env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment; config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true); if (env.IsDevelopment() && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(env.ApplicationName))
{
var appAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(env.ApplicationName));
if (appAssembly != null)
{
config.AddUserSecrets(appAssembly, optional: true);
}
} config.AddEnvironmentVariables(); if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
})
.ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
var isWindows = RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows); // IMPORTANT: This needs to be added *before* configuration is loaded, this lets
// the defaults be overridden by the configuration.
if (isWindows)
{
// Default the EventLogLoggerProvider to warning or above
logging.AddFilter<EventLogLoggerProvider>(level => level >= LogLevel.Warning);
} logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddDebug();
logging.AddEventSourceLogger(); if (isWindows)
{
// Add the EventLogLoggerProvider on windows machines
logging.AddEventLog();
}
})
.UseDefaultServiceProvider((context, options) =>
{
var isDevelopment = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment();
options.ValidateScopes = isDevelopment;
options.ValidateOnBuild = isDevelopment;
}); return builder;
}
从上述代码中,可以看到CreateDefaultBuilder内部构造了一个HostBuilder,同时设置了:
- 将内容根目录(contentRootPath)设置为由 GetCurrentDirectory 返回的路径。
- 通过以下源加载主机配置
- 环境变量(DOTNET_前缀)配置
- 命令行参数配置
- 通过以下对象加载应用配置
- appsettings.json
- appsettings.{Environment}.json
- 密钥管理器 当应用在 Development 环境中运行时
- 环境变量
- 命令行参数
- 添加日志记录提供程序
- 控制台
- 调试
- EventSource
- EventLog( Windows环境下)
- 当环境为“开发”时,启用范围验证和依赖关系验证。
以上构造完成了HostBuilder,针对ASP.NET Core应用,代码继续调用了HostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法。
三、IHostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults:通过GenericWebHostBuilder对HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core的运行时设置
构造完成HostBuilder之后,针对ASP.NET Core应用,继续调用了HostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法。这是一个ASP.NET Core的一个扩展方法:
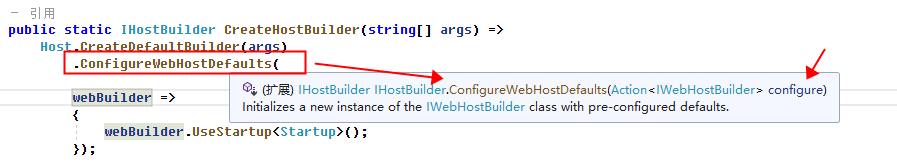
我们继续看ConfigureWebHostDefaults扩展方法内部做了哪些事情:
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore; namespace Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
{
/// <summary>
/// Extension methods for configuring the IWebHostBuilder.
/// </summary>
public static class GenericHostBuilderExtensions
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="IWebHostBuilder"/> class with pre-configured defaults.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// The following defaults are applied to the <see cref="IWebHostBuilder"/>:
/// use Kestrel as the web server and configure it using the application's configuration providers,
/// adds the HostFiltering middleware,
/// adds the ForwardedHeaders middleware if ASPNETCORE_FORWARDEDHEADERS_ENABLED=true,
/// and enable IIS integration.
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IHostBuilder" /> instance to configure</param>
/// <param name="configure">The configure callback</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IHostBuilder"/> for chaining.</returns>
public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHostDefaults(this IHostBuilder builder, Action<IWebHostBuilder> configure)
{
return builder.ConfigureWebHost(webHostBuilder =>
{
WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder); configure(webHostBuilder);
});
}
}
}
© 2020 GitHub, Inc.
首先,通过类GenericHostWebHostBuilderExtensions,对IHostBuilder扩展一个方法:ConfigureWebHost:builder.ConfigureWebHost
在这个扩展方法中实现了对IWebHostBuilder的依赖注入:即将GenericWebHostBuilder实例传入方法ConfigureWebHostDefaults内部
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; namespace Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
{
public static class GenericHostWebHostBuilderExtensions
{
public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHost(this IHostBuilder builder, Action<IWebHostBuilder> configure)
{
var webhostBuilder = new GenericWebHostBuilder(builder);
configure(webhostBuilder);
builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) => services.AddHostedService<GenericWebHostService>());
return builder;
}
}
}
通过GenericWebHostBuilder的构造函数GenericWebHostBuilder(buillder),将已有的HostBuilder增加了ASP.NET Core运行时设置。
。。。
先看到这,让我们回到ConfigureWebHostDefaults:
将上面两段代码合并一下进行理解:ConfigureWebHostDefaults做了两件事情:
1. 扩展IHostBuilder增加ConfigureWebHost,引入IWebHostBuilder的实现GenericWebHostBuilder,将已有的HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core运行时的设置。
2. ConfigureWebHost代码中的configure(webhostBuilder):对注入的IWebHostBuilder,调用 WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder),启用各类设置,如下代码解读:
internal static void ConfigureWebDefaults(IWebHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((ctx, cb) =>
{
if (ctx.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
StaticWebAssetsLoader.UseStaticWebAssets(ctx.HostingEnvironment, ctx.Configuration);
}
});
builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) =>
{
options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"));
})
.ConfigureServices((hostingContext, services) =>
{
// Fallback
services.PostConfigure<HostFilteringOptions>(options =>
{
if (options.AllowedHosts == null || options.AllowedHosts.Count == 0)
{
// "AllowedHosts": "localhost;127.0.0.1;[::1]"
var hosts = hostingContext.Configuration["AllowedHosts"]?.Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
// Fall back to "*" to disable.
options.AllowedHosts = (hosts?.Length > 0 ? hosts : new[] { "*" });
}
});
// Change notification
services.AddSingleton<IOptionsChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>>(
new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>(hostingContext.Configuration)); services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, HostFilteringStartupFilter>(); if (string.Equals("true", hostingContext.Configuration["ForwardedHeaders_Enabled"], StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
// Only loopback proxies are allowed by default. Clear that restriction because forwarders are
// being enabled by explicit configuration.
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
}); services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, ForwardedHeadersStartupFilter>();
} services.AddRouting();
})
.UseIIS()
.UseIISIntegration();
}
内部实现了:
- 前缀为 ASPNETCORE_ 的环境变量加载主机配置。
- 将Kestrel作为默认的Web服务器
- 添加HostFiltering中间件(主机筛选中间件)
- 如果ASPNETCORE_FORWARDEDHEADERS_ENABLED=true,添加转接头中间件ForwardedHeaders
- 启用IIS集成
3. 返回ConfigureWebHostDefaults代码中的configure(webHostBuilder):执行Program类中的webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
第三章节中,以上过程完成了IHostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults,通过GenericWebHostBuilder对HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core的运行时设置。
接下来继续Build和Run的过程。
四、CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
CreateHostBuilder返回的IHostBuilder,我们通过代码Debug,看一下具体的类型:Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.HostBuilder,这样进一步验证了前三个章节的代码。
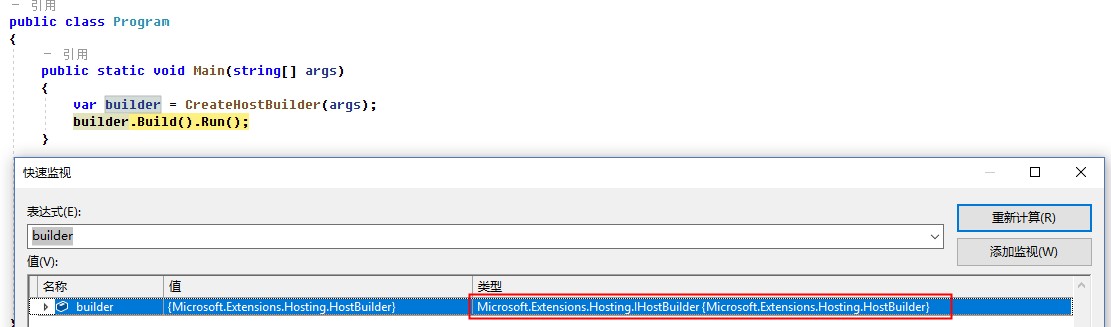
1. Build的过程
先看下Build的源码:https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/HostBuilder.cs

Build的过程主要完成了:
- BuildHostConfiguration: 构造配置系统,初始化 IConfiguration _hostConfiguration;
- CreateHostingEnvironment:构建主机HostingEnvironment环境信息,包含ApplicationName、EnvironmentName、ContentRootPath等
- CreateHostBuilderContext:创建主机Build上下文HostBuilderContext,上下文中包含:HostingEnvironment和Configuration
- BuildAppConfiguration:构建应用程序配置
- CreateServiceProvider:创建依赖注入服务提供程序, 即依赖注入容器
2. Run的过程
我们先通过Debug,看一下Host的信息:Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.Internal.Host
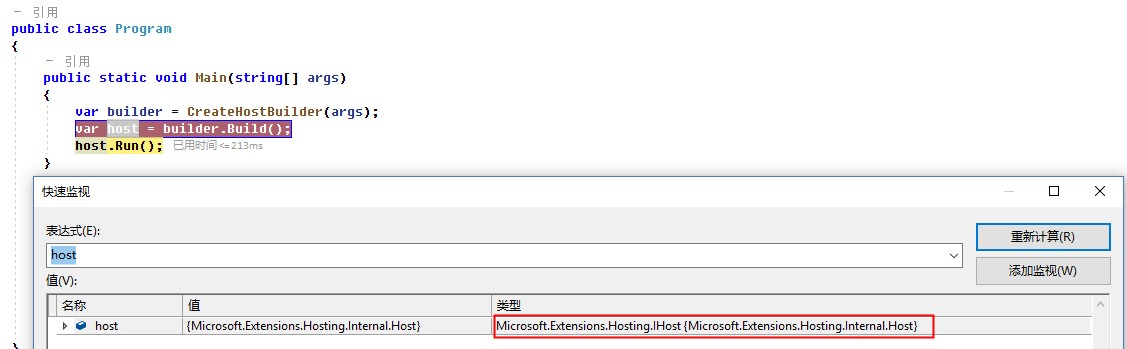
这个Run方法也是一个扩展方法:HostingAbstractionsHostExtensions.Run

其实内部转调的还是Host.StartAsync方法,在内部启动了DI依赖注入容器中所有注册的服务。
代码链接:https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/Internal/Host.cs

整个Host主机的启动过程还是非常复杂的,我们只是简单的在代码层面研究了一遍,感觉只是有了个大致的轮廓,具体怎么执行的,是不是如上面代码的解释,还需要深入继续研究。
接下来下一篇文章准备把源码单步调试看看。加深对ASP.NET Core底层技术原理的理解,只有理解了底层技术实现,我们在应用层才能更好、正确的使用。
周国庆
2020/4/6
ASP.NET Core技术研究-探秘Host主机启动过程的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET Core技术研究-探秘依赖注入框架
ASP.NET Core在底层内置了一个依赖注入框架,通过依赖注入的方式注册服务.提供服务.依赖注入不仅服务于ASP.NET Core自身,同时也是应用程序的服务提供者. 毫不夸张的说,ASP.NET ...
- ASP.NET Core技术研究-全面认识Web服务器Kestrel
因为IIS不支持跨平台的原因,我们在升级到ASP.NET Core后,会接触到一个新的Web服务器Kestrel.相信大家刚接触这个Kestrel时,会有各种各样的疑问. 今天我们全面认识一下ASP. ...
- .NET Core技术研究-主机
前一段时间,和大家分享了 ASP.NET Core技术研究-探秘Host主机启动过程 但是没有深入说明主机的设计.今天整理了一下主机的一些知识,结合先前的博文,完整地介绍一下.NET Core的主机的 ...
- .NET Core技术研究系列-索引篇
随着.NET Core相关技术研究的深入,现在将这一系列的文章,整理到一个索引页中,方便大家翻阅查找,同时,后续也会不断补充进来. .NET Core技术研究-WebApi迁移ASP.NET Core ...
- 简读《ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战》之3:配置
特别说明:1.本系列内容主要基于杨中科老师的书籍<ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战>及配套的B站视频视频教程,同时会增加极少部分的小知识点2.本系列教程主要目的是提炼知识点,追求 ...
- 快读《ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战》EFCore2.5:集合查询原理揭秘(IQueryable和IEnumerable)
本节内容,涉及4.6(P116-P130).主要NuGet包:如前述章节 一.LINQ和EFCore的集合查询扩展方法的区别 1.LINQ和EFCore中的集合查询扩展方法,虽然命名和使用完全一样,都 ...
- 快读《ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战》WebApi3.1:WebApi最佳实践
本节内容,涉及到6.1-6.6(P155-182),以WebApi说明为主.主要NuGet包:无 一.创建WebApi的最佳实践,综合了RPC和Restful两种风格的特点 1 //定义Person类 ...
- 《ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战》精简集-目录
本系列是杨中科2022年最新作品<ASP.NET Core技术内幕与项目实战>及B站配套视频(强插点赞)的精简集,是一个读书笔记.总结和提炼了主要知识点,遵守代码优先原则,以利于快速复习和 ...
- ASP.NET Core Identity 实战(4)授权过程
这篇文章我们将一起来学习 Asp.Net Core 中的(注:这样描述不准确,稍后你会明白)授权过程 前情提要 在之前的文章里,我们有提到认证和授权是两个分开的过程,而且认证过程不属于Identity ...
随机推荐
- JZOJ 5286. 【NOIP2017提高A组模拟8.16】花花的森林 (Standard IO)
5286. [NOIP2017提高A组模拟8.16]花花的森林 (Standard IO) Time Limits: 1000 ms Memory Limits: 131072 KB Descript ...
- 使用tf serving-gpu时,没有安装NVIDIA时报的错?
当部署tf serving-gpu时,出现上述的错误,有两种情况: 1.服务器中已经安装NVIDIA驱动了,只是版本比较低了,需要升级一下比较新的nvidia驱动: 2.就是服务器中没有安装NVIDI ...
- 前端开发--vue开发部分报错指南
前期开发过程中 [Vue warn]: Error in render: "TypeError: Cannot read property '0' of undefined". 解 ...
- 第二章、 Vue 起步
2-2.编写hello world 首先创建vue实例,然后实例接收一些配置项,el表示实例负责管理的区域,data表示区域内的数据 两秒后内容变为bye world 其中app表示实例对象,$dat ...
- 简说python之安装
Python是跨平台程序语言,做为世界流行的语言之一,它可以平滑地部署在Windows,Linux,Mac等平台之上,并有很多第三方模块的函数可供使用. 学习Python,首先需要把Python的编译 ...
- 波兰政府在继韩国之后也增加了对 Linux 的使用
导读 前段时间, 韩国政府起草了一项战略,准备采用基于 Linux 的开源操作系统全面取代 Windows 7,以摆脱对其的依赖. 目前,波兰的社会保险公司 ZUS( Zakład Ubezpiecz ...
- mysql schema设计中应避免的陷阱
谨记红字: 1. 表中谨防太多列: MySQL 的存储引擎API 工作时需要在服务器层和存储引擎层之间通过行缓冲格式拷贝数据,然后在服务器层将缓冲内容解码成各个列.从行缓冲中将编码过的列转换成行数据结 ...
- 03-Vue数据请求
1. vue-resource vue-resource jsonp请求 <body> <div id="app"> <!-- v-model 监听表 ...
- 关于Idea中不能使用Scanner在console
遇到了麻烦,在Idea中使用@Test运行程序时,scanner在控制台无法输入,然后来回折腾... 创建了一个新的类里面含有main方法,可以完美运行scanner: 重新回来,发现还是不行, 创建 ...
- oracle--触发器(转)
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/indexman/article/details/8023740/ 触发器是许多关系数据库系统都提供的一项技术.在oracle系统里,触发器类似过程和函 ...
