android开发------编写用户界面之线性布局
一个好的应用程序离不开人性化的用户界面。在学习其他东西之前。理应先学习编写程序的布局(外观)
今天,我们就来学习android的UI布局----LinearLayout。
LinearLayout,即线性布局。从名字我们就可以知道,它的元素是线型排列的。
注意:在以后的部分代码编写当中,我们采用硬编码的方式将字符串值写入android:text等标签中,
不会另外在strings.xml文件中定义字符串值,这个时候eclipse IDE会出现黄色的下划线警告,我们忽略就可以了
主要知识点:
android:layout_width
android:layout_height
android:orientation
android:id
我们先创建一个名叫Layouts的项目,项目名称首字母记得大写,虽然不是必须,但这是一个最佳实践。
我们依然用layouts目录下的activity_main.xml文件作为示范,不多说,直接上代码
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入登录信息"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_gravity="center"/> <EditText
android:id="@+id/userName"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:hint="输入你的用户名"/> <EditText
android:id="@+id/passwd"
android:password="true"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="18dp"
android:hint="输入你的密码" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/btnLogin"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登录"
android:layout_gravity="center" />
</LinearLayout>
看一下运行效果
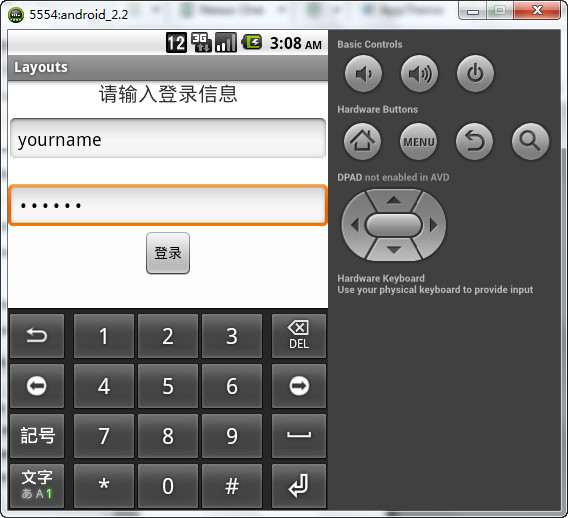
接下来我们解释一下代码的结构和原理
我们编写了一个LinearLayout的布局,需要注意的是,LinearLayout标签必须是一个根元素,它的外面不能出现任何元素。但是里面能嵌套任何布局元素。即,最外层的布局不能有兄弟元素(同级元素)
因此,下面的情况不能出现
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <!-- 其他元素 --> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"> <!-- 其他元素 --> </LinearLayout>
现在知道什么是线性布局了吧
它们一个跟在另一个的后面排列,就像一条线一样。
认识新标签:
<TextView />:我们昨天说过,不再重复
<EditText />:文本框,用于接收用户的输入
<Button />:按钮,当用户点击的时候处理相应的事件
设置元素属性:
我们主要简单说一下下面的几个属性,其他的可以自己研究一下。
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
layout_width: 设置元素长度,值可以是fill_parent(填充父元素,最外层的父元素就是Activity窗体)、wrap_content(根据内容的长度自适应)、或者用单位控制,如10dp,20dp,100dp等等
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
layout_height: 设置元素高度,layout_width的设置同样适用于layout_height
android:orientation="vertical"
orientation:布局的排列方向,值可以是vertical(垂直)和horizontal(水平),如果忽略这个属性,默认是horizontal
android:layout_gravity="center"
layout_gravity:元素的对齐方向,常用的有right,left,center等,有多个值可以选择,这里就自己测试吧,多动手,学得快。
android:id="@+id/idName"
android:id: 为元素添加一个独一无二的身份标识。@符号的作用我们说过了。那么+号的作用又是什么呢?
当我们第一次为一个元素添加一个身份标识的时候,就需要用到+号,这样,程序编译的时候,就会在gen目录下的R.java文件中生成一个资源ID,
以后我们就可以通过这个ID引用这个标签中的内容。
除了添加自己的ID名称之外,我们还可以使用android内置的ID。这个时候+号就不需要了,如:
@android:id/list、@android:id/empty
这样,我们定义的元素就会使用android.R类中预先定义的ID值
上面的使用方法,以后会说到,这里不进一步解释。
那么,第二个文本框中的效果又是怎样实现的呢
很简单,就是android:password="true",这样,我们看到的就是一个个黑点,而不是我们输入的字母和数字等
上面的代码中,android:orientation的值是vertical,现在我们将它换成horizontal,看又是什么情况
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <EditText
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="send message"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送"/> </LinearLayout>
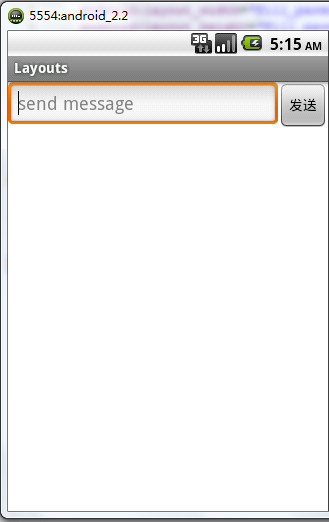
没有错,元素现在向水平方向排列,我们再添加多几个元素看看
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="信息标题:"/> <EditText
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:hint="message title here"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="message content"/> <EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="message title here"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSend"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送"/> </LinearLayout>
运行效果:
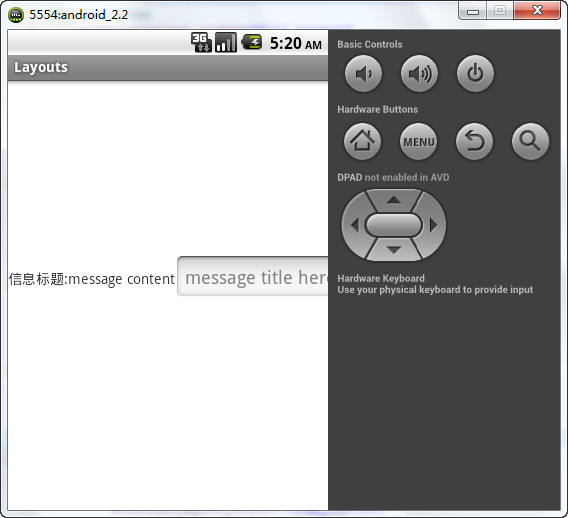
乱套了,为什么
当水平排列的时候,如果元素的长度超过activity本身的长度的时候,元素就会溢出,导致部分元素无法显示。
我们先不管android:layout_weight="1"是什么,也不管为什么要将android:layout_width的值设置为0dp。后面会说。
现在,我们应该对LinearLayout有所了解了。代码最好自己敲一次,这样学习才有意思
那么我就布置一道简单的练习题吧
请用LinearLayout完成下图中的布局

android开发------编写用户界面之线性布局的更多相关文章
- android开发------编写用户界面之线性布局(补充知识)
在前面的文章中 http://www.cnblogs.com/ai-developers/p/android_linearlayout.html 我们看到了布局中有这样一个属性: layout_wei ...
- android开发------编写用户界面之相对布局
今天要说的是RelativeLayout.RelativeLayout相对于LinearLayout的主要不同点在于它需要一个参照物. 我们先来看一下官方对这个布局的解释: RelativeLayou ...
- Android开发之详解五大布局
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-3654213-1-1.html 为了适应各式各样的界面风格,Android系统提供了5种布局,这5种布局分别是: LinearLayo ...
- Android开发之玩转FlexboxLayout布局
在这之前,我曾认真的研究过鸿洋大神的Android 自定义ViewGroup 实战篇 -> 实现FlowLayout,按照大神的思路写出了一个流式布局,所有的东西都是难者不会会者不难,当自己能自 ...
- android 开发 RecyclerView 横排列列表布局
1.写一个一竖的自定义布局: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xml ...
- Android之UI编程(一):线性布局
package com.example.fk_layout; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class L ...
- android开发4:Android布局管理器1(线性布局,相对布局RelativeLayout-案例)
控件类概述 View 可视化控件的基类 属性名称 对应方法 描述 android:background setBackgroundResource(int) 设置背景 android:clickabl ...
- Android开发自学笔记(Android Studio)—4.1布局组件
一.引言 Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.在Android4.0之前,我们通常说 ...
- Android开发1:基本UI界面设计——布局和组件
前言 啦啦啦~本学期要开始学习Android开发啦~ 博主在开始学习前是完完全全的小白,只有在平时完成老师要求的实验的过程中一步一步学习~从此篇博文起,博主将开始发布Android开发有关的博文,希望 ...
随机推荐
- 【JAVA小结】字符串比较是否相等
public class CompareObject1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = new String(&quo ...
- oracle函数--trunc
作用:截取 语法:trunc(date,[fmt]) TRUNC函数,ORA-01898 精度说明符过多 TRUNC(SYSDATE)即可默认当前日期(年月日),---写到这一步就好了 TRUNC ...
- 在DigitalOcean云主机上搭建SVN服务器
最近买了个DigitalOcean主机,顺便搭建个PPTP SVN服务器. 下面是搭建方法: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how- ...
- hdu-5492 Find a path(dp)
题目链接: Find a path Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- java 24 - 9 GUI 之 给窗体换图标、设置启动在屏幕中间、更换皮肤
A.首先更改窗体左上角的图片 步骤一: 创建3个包,分别建立1个类 第一个是窗体的包,窗体类:设置窗体的主要布置和功能 第二个是资源包,图片:把想要改的图案拉进来 第三个是UI界面包,UI界面设计类: ...
- fragment的切换(解决REPLACE的低效)
在项目中切换Fragment,一直都是用replace()方法来替换Fragment.但是这样做有一个问题,每次切换的时候Fragment都会重新实列化,重新加载一次数据,这样做会非常消耗性能用用户的 ...
- javascript里面foreach遍历函数介绍,以及跟jquery里面each的区别
foreach是把数组从头到尾遍历一遍,有三个参数分别是:数组元素,数组索引,数组本身.如果是一个参数,就是数组元素. var data=[1,2,3,4,5,6]; var sum=0; data. ...
- HTML-学习笔记(文本格式化,引用,计算机代码)
HTML 可定义很多供格式化输出的元素,比如粗体和斜体字. <b>定义粗体字体 <p>这是一段<b>粗体字体</b>通过标签定义</p> & ...
- hadoop怎么读?怎么发音
hadoop不是一个英文单词,是作者发明的词,hadoop名称来源作者小孩的一个}h毛填充黄色大象玩具. 它的发音是:[hædu:p]
- mysql--测试前缀索引能否用于order by 或者 group by
创建一个测试用表 mysql> desc two; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field ...
