Roles on a Machine Learning Project (机器学习项目中的角色)
原文 :https://medium.com/machine-learning-in-practice/roles-on-a-machine-learning-project-216903a6dc12


Machine learning is a technical process, but it starts and ends with people. The first step to structuring your machine learning project is to consider the people you need to make it happen.
角色1 数据科学家 Data Scientists
Data scientists are the “x factor” in a machine learning project, representing the main difference between an ML project and other kinds of software development. They create (or select) and train algorithms, building the models for machine learning. Data scientists may specialize in certain kinds of problems or data sets. Some are more research-driven and academically minded, while others are more results and task focused. While both kinds can contribute, it’s preferable for team leaders have a results orientation, rather than a tendency to linger on questions.
Data scientists can grab data, throw together an algorithm, and show that it works. But when they hack together a demo, they may take shortcuts. They may create their solution under idealized assumptions about the data inputs and algorithmic outputs. Integrating and scaling a data scientist’s work into production requires building pipelines for data to go to the right place. In other words, it requires . . .
角色2 软件工程师 Software Engineers
Engineers are the people that typically put the “In Practice” into “Machine Learning in Practice.” They ensure the technology is built in a robust way so that it can be packaged and deployed into production in mission-critical systems. Engineers help with software development, best practices, and data wrangling/pre-processing. They might set the infrastructure, get the data pipeline in place, and ensure the data scientists have everything they need to focus on the models.
A machine learning algorithm often ends up as a single function in a working piece of software. Software engineers think about how to maintain the software over time, making the algorithm robust for the real world. Data scientists are often not classically trained programmers, and so they may not have the best practices when it comes to creating reusable code.
Engineers also help ensure the entire effort is not beholden to the one expert who worked on the project. They make sure the software does appropriate levels of logging, that it can be monitored, that there is proper documentation, and that other software best practices are followed. This allows data scientists to build the best algorithm possible. Without engineers, data scientists may be stuck just doing cool demos.
A “unicorn” developer is one that can do both leading data science and implement software best practices. It’s rare to find one person that can handle all of these responsibilities.
Note that while it is preferable to involve engineers from the beginning of a project, the full engineering need may be difficult to know during early planning stages. Engineers are most necessary during the later deployment stage (see below), at which point the project may have evolved significantly.
角色3: 数据工程师 Data Engineer
This role is focused on wrangling/pre-processing data to prepare it for machine learning.
Text data, for example, may come in as a PDF, a .docx file, a .txt file, or a string from a database. A data engineer may need to convert the text to the proper format for a given programming language. After the text is loaded, more pre-processing might be required due to language, length, word frequency, and word variation.
It’s an iterative process: if an algorithm isn’t working, a data engineer will try finessing the data in a different way. After a project goes into production, data engineers may work together with software engineers and data scientists to assess and optimize the data feeding back into the model.
The need for this role will vary with projects and team size. In cases where a lot of pre-processing is required and senior data scientists are better focused elsewhere, more junior data experts could take on this role. In other cases, data scientists may take on the data prep themselves.
Project Roles During Project Phases
Data Processing Phase
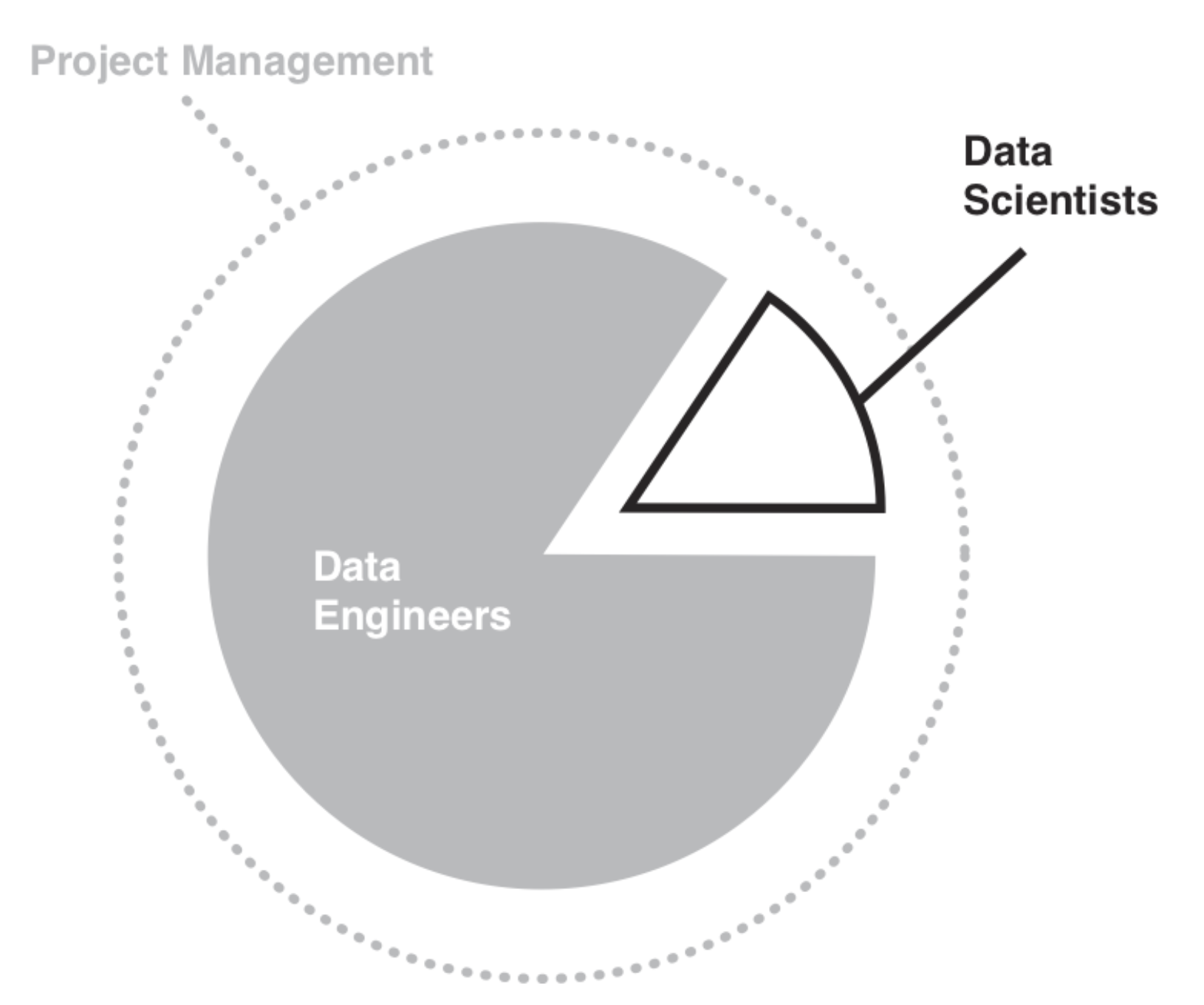
Data Engineers wrangle the data while Data Scientists offer guidance (and do data engineering as needed).
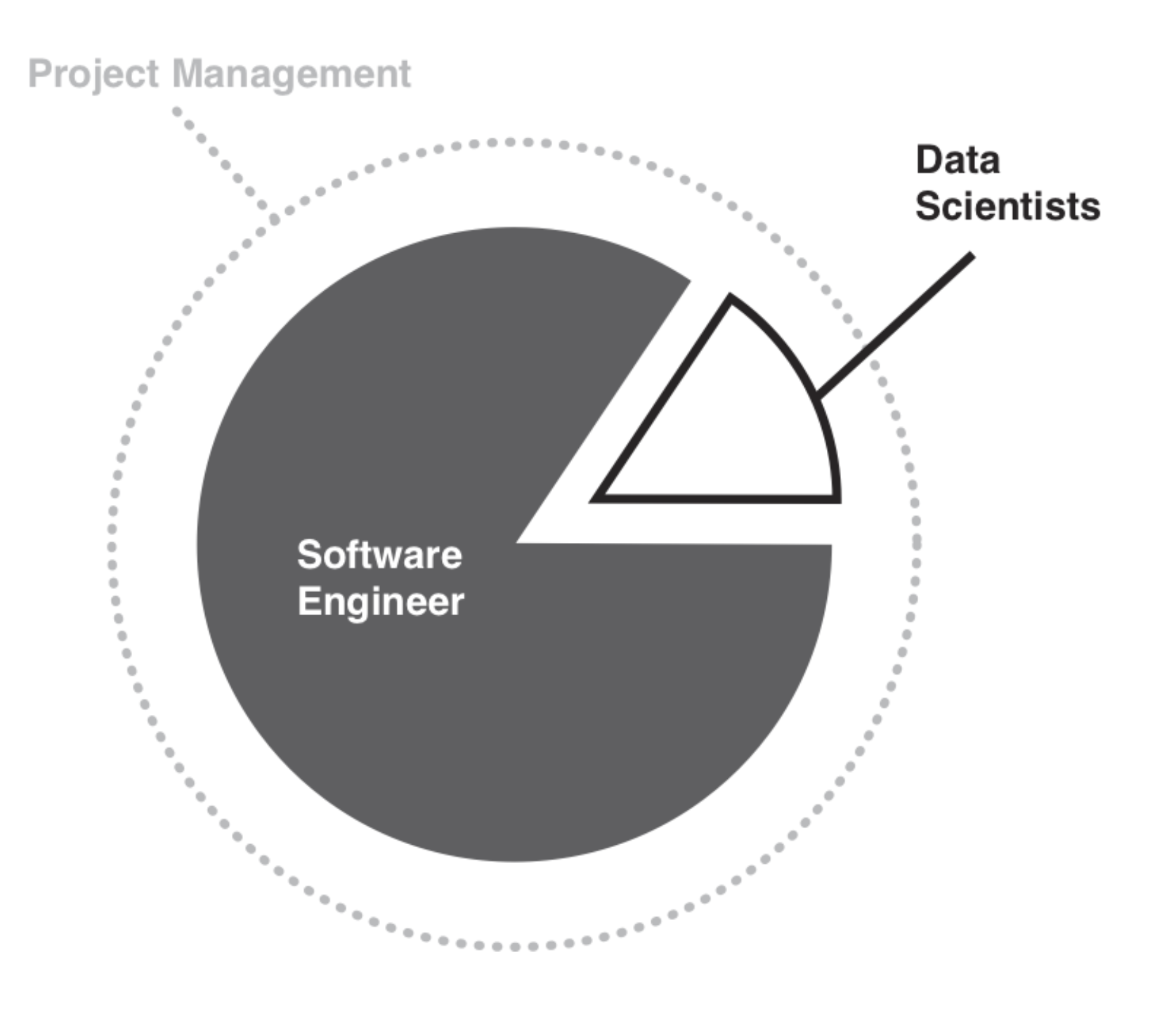
Algorithm Development Phase
Data Scientists create algorithms while Software Engineers offer help and guidance.
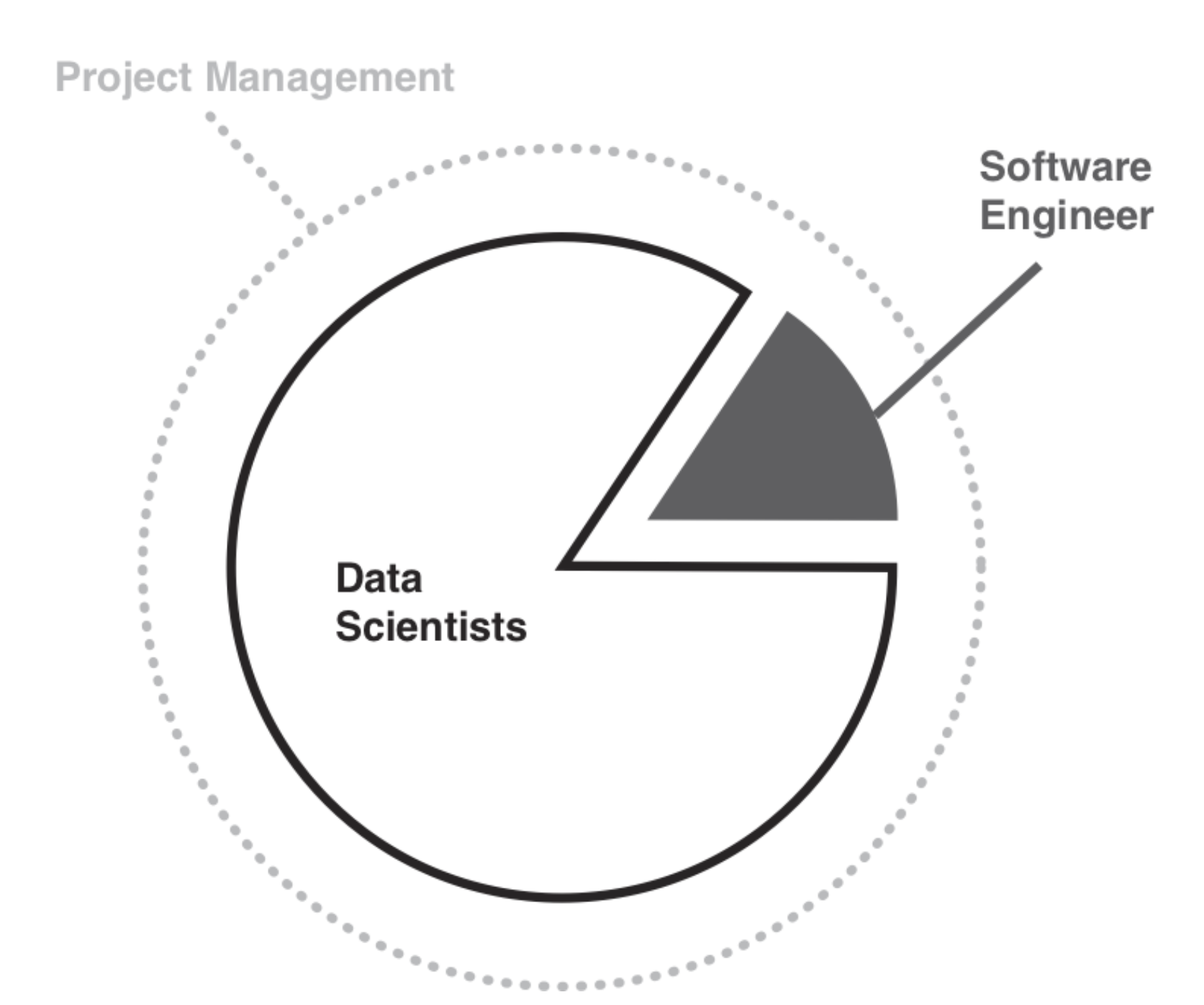
Solution Deployment Phase
Software Engineers implement the solution while Data Scientists tweak algorithms as needed.
Leadership Roles
Beyond the core technical team, more roles are crucial for achieving business impact in a machine learning:
- The Business Owner
The Business Owner is responsible for focusing the team on the core business problem to be solved and for providing business support via the budget. Business owners may also need to communicate the unique attributes of machine learning projects to the leaders above them, including the potential ebb and flow of project timelines. The business owner’s biggest challenge is often understanding what is actually possible with machine learning. Making promises without a firm understanding can hurt a project. - The Technical Lead
The Technical Lead is responsible for the overall architecture of the solution. They know how to put all the necessary data sources and infrastructure elements together to complete a project. While this person should have some technical understanding, they may not be a machine learning authority. - The Project Manager
The Project Manager structures and guides the project, interfaces with stakeholders, adheres to standard procedures, keep projects on time and on budget, reuses lessons and technologies from past projects, and appropriately documents the endeavor and business results.
A given ML project may see different individuals in each of these positions. But it’s also possible for one person to hold multiple roles (a technical team member may take on project management tasks, a data scientist may do data engineering). Also, a machine learning team may have members from different companies: business owners will likely be internal employees, but data scientists and engineers may come from external partners.
Roles on a Machine Learning Project (机器学习项目中的角色)的更多相关文章
- 【Machine Learning】机器学习及其基础概念简介
机器学习及其基础概念简介 作者:白宁超 2016年12月23日21:24:51 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本系列文章是作者结 ...
- Teaching Your Computer To Play Super Mario Bros. – A Fork of the Google DeepMind Atari Machine Learning Project
Teaching Your Computer To Play Super Mario Bros. – A Fork of the Google DeepMind Atari Machine Learn ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 17—Large Scale Machine Learning 大规模机器学习
Lecture17 Large Scale Machine Learning大规模机器学习 17.1 大型数据集的学习 Learning With Large Datasets 如果有一个低方差的模型 ...
- 第二章——机器学习项目完整案例(End-to-End Machine Learning Project)
本章通过一个例子,介绍机器学习的整个流程. 2.1 使用真实数据集练手(Working with Real Data) 国外一些获取数据的网站: Popular open data repositor ...
- 人工智能(Machine Learning)—— 机器学习
https://blog.csdn.net/luyao_cxy/article/details/82383091 转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27297393/articl ...
- 【Machine Learning】机器学习の特征
绘制了一张导图,有不对的地方欢迎指正: 下载地址 机器学习中,特征是很关键的.其中包括,特征的提取和特征的选择.他们是降维的两种方法,但又有所不同: 特征抽取(Feature Extraction): ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 课后习题链接汇总
大家好,我是Mac Jiang,非常高兴您能在百忙之中阅读我的博客!这个专题我主要讲的是Coursera-台湾大学-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)的课后习题解 ...
- 壁虎书2 End-to-End Machine Learning Project
the main steps: 1. look at the big picture 2. get the data 3. discover and visualize the data to gai ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 作业三 课后习题解答
今天和大家分享coursera-NTU-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)-作业三的习题解答.笔者在做这些题目时遇到非常多困难,当我在网上寻找答案时却找不到,而林 ...
随机推荐
- 如何获取主键返回值(MySQL、Oracle)
添加用户.返回主键 --场景:在执行新增用户sql后,service层返回新增用户的主键值(与mybatis一起使用) insert into user(username, sex, birthday ...
- JVM年轻代,老年代,永久代详解
前言 最近被问到了这个问题,解释的不是很清晰,有一些概念略微模糊,在此进行整理和记录,分享给大家.本篇文章主要讲解内存区域的年轻代,老年代和永久代,略微提及一些垃圾回收算法,下面是正文. 堆整体 堆主 ...
- java简单序列化和反序列化
一.序列流 1.什么是序列流 序列流可以把多个字节输入流整合成一个, 从序列流中读取数据时, 将从被整合的第一个流开始读, 读完一个之后继续读第二个, 以此类推. 2.使用方式 整合两个: Seque ...
- RabbitMQ 在Ubuntu18.04上的安装
1.安装erlang由于rabbitMq需要erlang语言的支持,在安装rabbitMq之前需要安装erlang sudo apt-get install erlang2.安装Rabbitmq更新源 ...
- Servlet(四)----HTTP、Response、servletContent
## HTTP协议: 1.请求消息:客户端发送给服务器端的数据 * 数据格式: 1.请求行 2.请求头 3.请求空行 4.请求体 2.响应消息:服务器端发送给客户端的数据 * 数据格式: ...
- 洛谷 P5176 公约数 题解
原题链接 我天哪 大大的庆祝一下: 数论黑题 \(T1\) 达成! 激动地不行 记住套路:乱推 \(\gcd\),欧拉筛模板,然后乱换元,乱换式子,完了整除分块,欧拉筛和前缀和就解决了! \[\sum ...
- Python 趣题
如何优雅判断list为空 list_temp = [] if list_temp: # 存在值即为真 else: # list_temp是空的 在Python中,False,0,'',[],{},() ...
- MySQL逻辑分层介绍
上一篇文章主要介绍了MySQL在Ubuntu18.04系统上的安装,以及安装过程中可能会遇到的一些问题的解决方案. 在这篇文章里,开始介绍MySQL数据库的逻辑分层.通过本文的介绍,可以大致了解到My ...
- effective-java学习笔记---优先使用泛型方法30
泛型类型比需要在客户端代码中强制转换的类型更安全,更易于使用. 当你设计新的类型时,确保它们可以在没有这种强制转换的情况下使用. 这通常意味着使类型泛型化. 如果你有任何现有的类型,应该是泛型的但实际 ...
- 模块 schedule 定时任务
schedule模块实现定时任务 2018-08-29 15:01:51 更多 一.官方示例 import schedule import time def job(): print("I' ...
