第2课第5节_Java面向对象编程_异常_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记
java的异常处理的原则如下:


1、我们先写一个没有对异常处理的程序,在进行除法运算的时候,除数是非零的话,运行时没有问题的,但是除数为零的时候,运行就会有问题,程序也不能往下执行(只打印了Begin of div)
public class Div{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println("Begin of div");
int r = div(m,n);
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n){
int r = m / n;
return r;
}
}
编译运行:

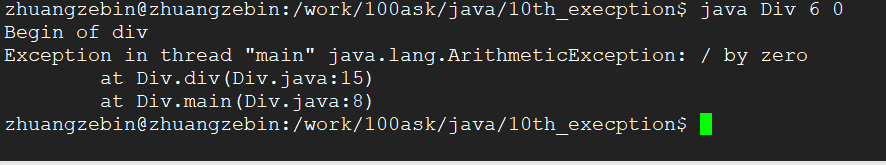
2、我们先写一个有对异常进行处理程序(自己处理异常),根据下面的运行结果,程序可以捕获到异常并且可以正常的执行.
public class Div2{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println("Begin of div");
int r = div(m,n);
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n){
int r = 0;
try {
r = m / n ;
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(e);
}finally{
System.out.println("This is finally of div");
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行:
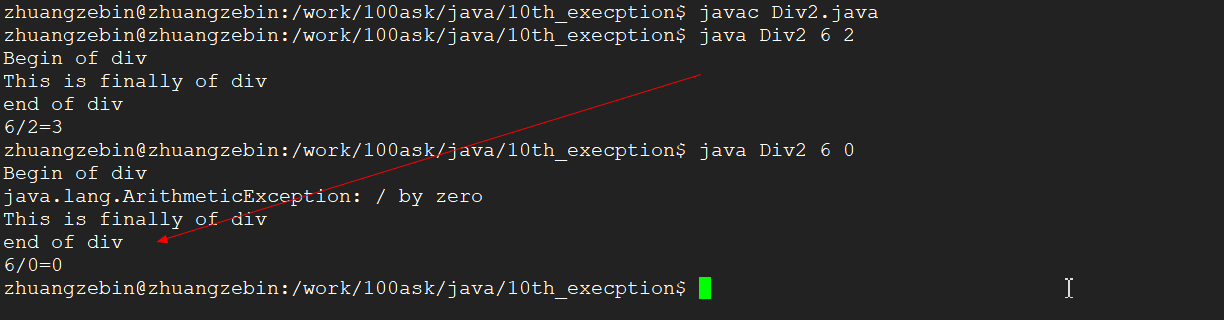
3、我们写一个程序将异常抛出的类,这个抛出的异常是由main进行处理.
public class Div4{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
int r = 0;
r = m / n ;
return r;
}
}
编译运行:
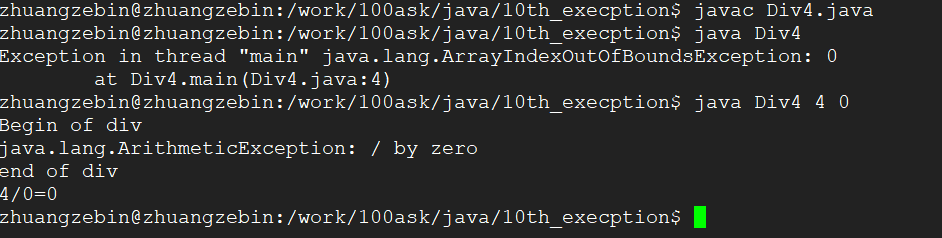
4、如果在类的方法中如果处理了异常,那样在main方法中就不会对异常进行处理.
public class Div5{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
int r = 0;
try{
r = m / n ;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("div :"+e);
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行:

5、如果在类的方法中如果处理了异常,同时在类方法中把异常抛出,那样main方法也可以捕获到异常.
public class Div6{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
int r = 0;
try{
r = m / n ;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("div :"+e);
throw e;
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行:
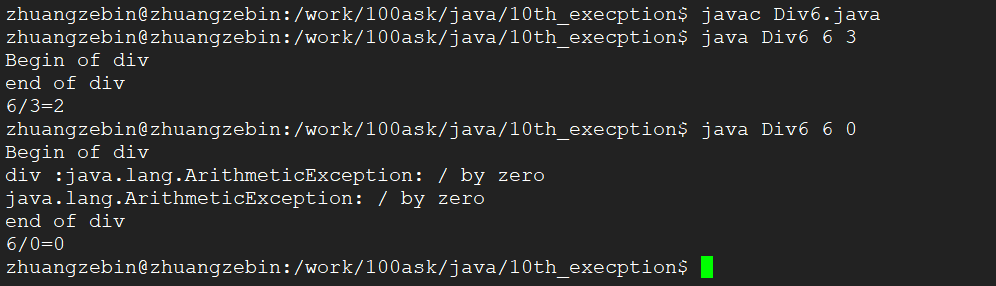
6、现在我们上面第5个例子的代码,只有对这种算术运行的异常进行处理,如果我传入的参数个数不对,还有参数的格式也不对,程序是处理不了的。
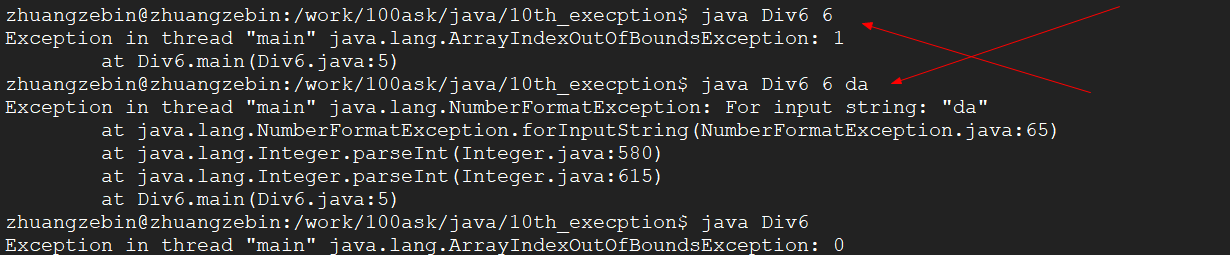
为了修复上述的问题,我们添加对传入参数格式不对,还有传入参数个数不对这两种异常的处理。
public class Div7{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
int r = 0;
try{
r = m / n ;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("div :"+e);
throw e;
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行结果
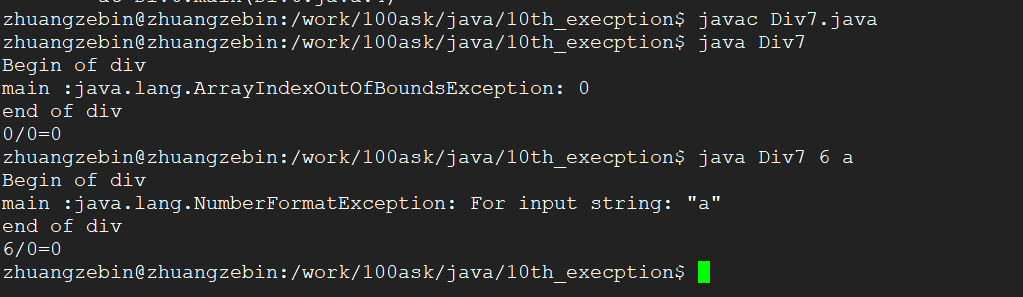
7、在第6个例子继续优化,上面的程序目前只能对算术运算、参数格式还有参数个数不对的异常进行处理,其他的情况是无法处理的到的,我们可以添加对这些异常的父类RuntimeException来捕获异常.
public class Div8{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){ //去掉了参数个数的异常,仍然可以捕获到
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (RuntimeException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
int r = 0;
try{
r = m / n ;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("div :"+e);
throw e;
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行结果
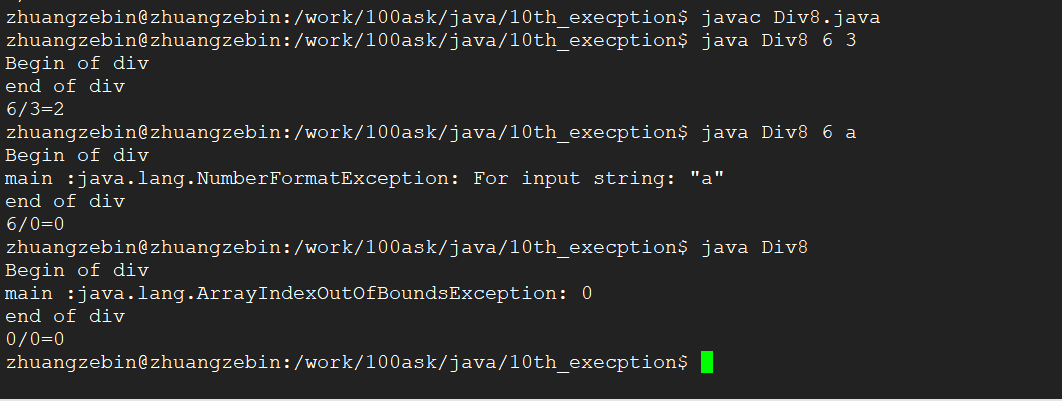
8、对于“不可查异常”, 系统也会抛出它,写不写throws效果一样
public class Div9{
public static void main(String args[]){
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
int r = 0;
System.out.println("Begin of div");
try {
m = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
n = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
r = div(m,n);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}catch (RuntimeException e){
System.out.println("main :" + e);
}
System.out.println("end of div");
System.out.println(m+"/"+n+"="+r);
}
//public static int div(int m,int n) throws ArithmeticException{
public static int div(int m,int n){
int r = 0;
try{
r = m / n ;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("div :"+e);
throw e;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally of div");
}
return r;
}
}
编译运行:

相关代码存放在github,可以下载https://github.com/zzb2760715357/100ask

第2课第5节_Java面向对象编程_异常_P【学习笔记】的更多相关文章
- 第2课第3节_Java面向对象编程_继承性_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 面向对象程序的三大特性之继承性:继承性的主要作用就是复用代码.继承性也有一定的限制,如图一 图一 1.我们在第2课第2节_Java面向对象编程_封装性_P 中 ...
- 第2课第4节_Java面向对象编程_多态性_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 面向对象程序的三大特性之继承性: 1.向上转换:只能定义被子类覆写的方法,不能调用在子类中定义的方法. class Father { private int ...
- 第2课第7节_Java面向对象编程_内部类_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 1.什么是内部类:在类的内部定义一个类,内部类可以访问类的私有属性 class Outer{ ; class Inner{ public void print ...
- 第2课第2节_Java面向对象编程_封装性_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 面向对象程序的三大特性之封装性:把属性和方法封装在一个整体,同时添加权限访问. 1.封装性的简单程序如下,看一下第19行,如果我们不对age变量进行权限的管控 ...
- 第2课第1节_Java面向对象编程_类的引入_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 1. 面向对象编程的引入,我们先写一个简单的程序输出张三,李四的名字.代码如下,假如,现在我们要在名字前面添加籍贯广东,那样岂不是每个printf语句都得修改添 ...
- 第2课第6节_Java面向对象编程_包和权限_P【学习笔记】
摘要:韦东山android视频学习笔记 1.使用package定义编译的时候存放的位置 package a.b.c.d; public class Package { public static v ...
- 类和对象:面向对象编程 - 零基础入门学习Python037
类和对象:面向对象编程 让编程改变世界 Change the world by program 经过上节课的热身,相信大家对类和对象已经有了初步的认识,但似乎还是懵懵懂懂:好像面向对象编程很厉害,但不 ...
- .net 4.0 面向对象编程漫谈基础篇读书笔记
话说笔者接触.net 已有些年头,做过的项目也有不少,有几百万的,也有几十万的,有C/S的,也有B/S的.感觉几年下来,用过的框架不少,但是.net的精髓一直没有掌握.就像学武之人懂得各种招式,但内功 ...
- Python 进阶_OOP 面向对象编程_组合与继承
#目录 前言 组合 派生 通过继承来覆盖重载方法 最常用的重载场景实例方法的重载 从标准类中派生类方法的重载 前言 我们定义一个类是希望能够把类当成模块来使用,并把类嵌入到我们的应用代码中,与其他的数 ...
随机推荐
- scrapy xpath去除空格
content = response.xpath("normalize-space('//img/@src')")
- mysql-connector-java与mysql版本的对应关系
记录下mysql-connector-java与mysql版本的对应关系,已方便以后参考,这是最新版本对应, 时间:2019年9月27日 官网文档地址: https://dev.mysql.com/d ...
- MySQL Percona Toolkit--pt-osc与online DDL选择
pt-osc和online ddl选择 1.如果表存在触发器,不能使用pt-osc.2.如果新增唯一索引,不建议使用pt-osc,以免数据丢失.3.修改索引.外键.列名时,优先选择使用ALGORITH ...
- MySQL Execution Plan--IN子查询对UPDATE语句影响
问题描述 在系统中发现一条执行时间为为44652.060734秒(12.5小时)的慢SQL,SQL语句为: UPDATE ob_internal_task SET OPERATE_STATUS WHE ...
- Spring AOP无法拦截内部方法调用
当在同一个类中,A方法调用B方法时,AOP无法工作的问题 假设一个接口里面有两个方法: package demo.long; public interface CustomerService { pu ...
- Python_soket
1.socket建立连接,服务端,客户端代码如下: import socket #服务端,AF_INET:IPV4地址,SOCK_STREAM:TCP协议 sk=socket.socket(socke ...
- win2008r2 32位odbc安装笔记
这ORACLE也太难用了,想简单点了事只用个ODBC CLIENT都是件麻烦事,总结了一下,安装流程如下: 1.去官网或其它地方下载: 64位: instantclient-basic-windows ...
- 高精度NTC测温的硬件电路以及软件设计
什么是NTC NTC是热敏电阻,其电阻值对温度变化敏感,在不同的温度下,可以呈现不同的电阻值. 热敏电阻有两类,一类是负温度系数电阻(NTC),温度增加时,电阻值降低,另一类是正温度系数电阻(PTC) ...
- 【Miscalculation UVALive - 6833 】【模拟】
题目分析 题目讲的是给你一个串,里面是加法.乘法混合运算(个人赛中误看成是加减乘除混合运算),有两种算法,一种是乘法优先运算,另一种是依次从左向右运算(不管它是否乘在前还是加在前). 个人赛中试着模拟 ...
- 35 Top Open Source Companies
https://www.datamation.com/open-source/35-top-open-source-companies-1.html If you think of open sour ...
