剑指offer——已知二叉树的先序和中序排列,重构二叉树
这是剑指offer中关于二叉树重构的一道题。题目原型为:
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
一、二叉树的数据结构
做题之前,我们先熟悉下二叉树的数据结构。其一,定义:二叉树是一个连通的无环图,并且每一个顶点的度不大于3。有根二叉树还要满足根结点的度不大于2。有了根结点之后,每个顶点定义了唯一的父结点,和最多2个子结点。然而,没有足够的信息来区分左结点和右结点。如果不考虑连通性,允许图中有多个连通分量,这样的结构叫做森林。(定义来自百度百科)
由定义可知,二叉树含有许多节点,而不同节点之间通过子父关系来连接。一般来说,二叉树的节点由结构体来定义,如下所示:
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
~TreeNode() {
cout << "TreeNode with value " << val << " has been destroyed." <<endl;
}
};
该结构体定义了节点的int型变量(当然也可以是其它类型),以及指向左右孩子的指针。在TreeNode中,我们还定义了构造函数和析构函数,其实可有可无,对本题来说没有多大意义。
二、二叉树的建立
二叉树的建立过程,就是不断扩展节点的过程。建立根节点,由根节点建立左右子节点,再递归的建立子节点的子节点。我们下面看看代码的实现过程:
void BiTree::createBiTree(struct TreeNode* &root) {
int val;
//cout << "Please input the tree node:" << endl;
cin >> val;
if ( == val) {
root = NULL;
}
else {
//root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root = new TreeNode();
if (root == NULL)
return;
root->val = val;
cout << "Please input the left child of " << val << ": ";
createBiTree(root->left);
cout << "Please input the right child of" << val << ": ";
createBiTree(root->right);
}
}
这里,我是把创建二叉树的方法createBiTree()作为了BiTree的成员函数(简单说明一下)。
1、首先,我们看参数 struct TreeNode* &root, 这是结构体指针的引用。为什么要传递引用呢,就是希望函数体外的指针变量能指向函数体内所新建的根节点。若只是指针传递,那么函数体内新建的节点和函数体外的指针变量是没有指向关系的。
2、然后就是新建节点,
//root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root = new TreeNode(1);
这两条语句的效果相同。如果创建成功,那么递归调用本方法,创建后续节点。 三、二叉树的遍历
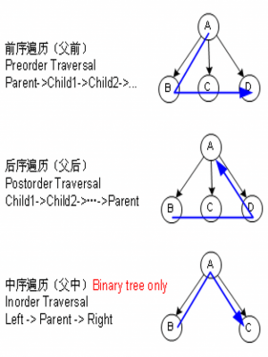
二叉树有三种遍历方法:先序,中序,后序。即父前(父-左-右),父中(左-父-右),父后(左-右-父)。
1、先序遍历
// 这里参数传递指针,或指针的引用都可以
void BiTree::preOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
cout << root->val << ' ';
preTrav.push_back(root->val);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
其中,preTraa.push_back(root->val);我只是把先序遍历的结果存在了vector 中,方便重构二叉树时作为输入。下同。
2,、中序遍历
void BiTree::inOrder(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->val << ' ';
inTrav.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
3、后序遍历,就不贴代码了。
另外,值得说明一下的是。这里的遍历方法都是通过递归来实现的,还有遍历的非递归算法(日后再详细去探讨,这里先着重看这个题目,也不知日后是否会想起这个任务。。。囧)
三、已知先序遍历,中序遍历,重构二叉树
我们观察先序遍历和中序遍历的结果。先序遍历的第一个节点肯定是根节点,然后在中序遍历中找到此根节点,我们可以看到,中序遍历中根节点以左是二叉树的左子树,根节点以右是二叉树的右子树。然后,左右子女树又可以单独的看成一个独立的二叉树,然后再对其划分,如此递归,便可重构二叉树的结构。下面上代码:
struct TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre, vector<int> in){
//TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
/* 注意上面这一条语句不能放在函数体的第一句。
* 因为此时还不能确定pre这个vector是否为空,如果不为空,那么访问pre[0]就是非法内存访问。此时若debug,会有
* Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.的错误信息。其中,SIG是signal的缩写,SEGV是segmentation violation(段违例)的缩写。详见维基百科
* 所以,此条语句放在return NULL;语句之后为宜,因为这个时候已经确定vector in不为空。但是好像没判断pre是否为空呢,这就可以了??
*/
vector<int> left_pre, left_in, right_pre, right_in;
int pos = ;
int length = in.size();
if (length == )
return NULL;
TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[]);
for (int i = ; i < length; ++i) {
if (pre[] == in[i]) {
pos = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = ; i < pos + ; ++i) {
left_pre.push_back(pre[i]);
left_in.push_back(in[i-]);
}
for (int i = pos + ; i < length; ++i) {
right_pre.push_back(pre[i]);
right_in.push_back(in[i]);
}
head->left = reConstructBinaryTree(left_pre, left_in);
head->right = reConstructBinaryTree(right_pre, right_in);
return head;
}
其实,关于这个重构函数,笔者还有一个问题,就如函数中注释中所诉。还请广大博友解答下(新手博客,都没人看,好忧伤~_~!)
四、重构验证
首先,贴上验证程序。验证程序综合了上述建立二叉树,遍历二叉树以及重构二叉树的相关实现。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std; // Definition for binary tree
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
~TreeNode() {
cout << "TreeNode with value " << val << " has been destroyed." <<endl;
}
}; class BiTree {
public:
int flag;
vector<int> preTrav, inTrav; BiTree(int _flag) : flag(_flag){
cout << "Instance of Bitree with flag " << flag << " has been constructed." << endl;
}
~BiTree() {
cout << "Instance of Bitree with flag " << flag << " has been destroyed." << endl;
} /* createBiTree()注意这里传递的是指针的引用,因为函数体内部在不断的new,需要让传进来的根节点指向内部新开辟的空间,
* 不过这样的话,在main函数内,定义的mytree结构体的空间就浪费了,怎么去优化呢?
* struct TreeNode* tree = nullptr;此条语句解决上诉问题
*/
void createBiTree(struct TreeNode*&);
void preOrder(struct TreeNode*&); //这里传递指针或指针的引用都可以
void inOrder(struct TreeNode*);
};
// Create the binary tree
void BiTree::createBiTree(struct TreeNode* &root) {
int val;
//cout << "Please input the tree node:" << endl;
cin >> val;
if ( == val) {
root = NULL;
}
else {
//root = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root = new TreeNode();
if (root == NULL)
return;
root->val = val; cout << "Please input the left child of " << val << ": ";
createBiTree(root->left); cout << "Please input the right child of" << val << ": ";
createBiTree(root->right);
}
} // pre order of binary tree
void BiTree::preOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
cout << root->val << ' ';
preTrav.push_back(root->val);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
} // in order of binary tree
void BiTree::inOrder(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->val << ' ';
inTrav.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
// 在类外部定义一个中序遍历,作调试用
void inOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->val << ' ';
inOrder(root->right);
} // Solution of reconstruct binary tree
class Soultion {
public:
int flag;
Soultion(int _flag) : flag(_flag) {
cout << "Instance of Solution with flag " << flag << " has been constructed." << endl;
}
~Soultion() {
cout << "Instance of Solution with flag " << flag << " has been destroyed." << endl;
} struct TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre, vector<int> in){
//TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
/* 注意上面这一条语句不能放在函数体的第一句。
* 因为此时还不能确定pre这个vector是否为空,如果不为空,那么访问pre[0]就是非法内存访问。此时若debug,会有
* Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.的错误信息。其中,SIG是signal的缩写,SEGV是segmentation violation(段违例)的缩写。详见维基百科
* 所以,此条语句放在return NULL;语句之后为宜,因为这个时候已经确定vector in不为空。但是好像没判断pre是否为空呢,这就可以了??
*/
vector<int> left_pre, left_in, right_pre, right_in; int pos = ;
int length = in.size(); if (length == )
return NULL; TreeNode* head = new TreeNode(pre[]); for (int i = ; i < length; ++i) {
if (pre[] == in[i]) {
pos = i;
break;
}
} for (int i = ; i < pos + ; ++i) {
left_pre.push_back(pre[i]);
left_in.push_back(in[i-]);
} for (int i = pos + ; i < length; ++i) {
right_pre.push_back(pre[i]);
right_in.push_back(in[i]);
} head->left = reConstructBinaryTree(left_pre, left_in);
head->right = reConstructBinaryTree(right_pre, right_in); return head; }
// 在solution类中也定义个中序遍历,作调试用
void inOrder(struct TreeNode* &root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->val << ' ';
inOrder(root->right);
} }; int main() {
//struct TreeNode myTree(1);
//struct TreeNode* tree = &myTree;
struct TreeNode* tree = nullptr; BiTree myBiTree();
cout << "Please input the head tree node: ";
myBiTree.createBiTree(tree); cout << "Preorder of binary tree." << endl;
myBiTree.preOrder(tree); cout << endl << "Inorder of binary tree." << endl;
myBiTree.inOrder(tree);
cout << endl; Soultion mySolution();
cout << endl
<< "refactor the binary tree based on preorder and inorder\n"
<< "and print it with preorder"
<< endl;
myBiTree.inOrder(mySolution.reConstructBinaryTree(myBiTree.preTrav, myBiTree.inTrav));
cout << endl; delete tree;
//struct TreeNode* refactor = mySolution.reConstructBinaryTree(myBiTree.preTrav, myBiTree.inTrav);
//myBiTree.inOrder(refactor);
//mySolution.inOrder(refactor); //inOrder(refactor);
return ;
}
下面我们看看程序结果。
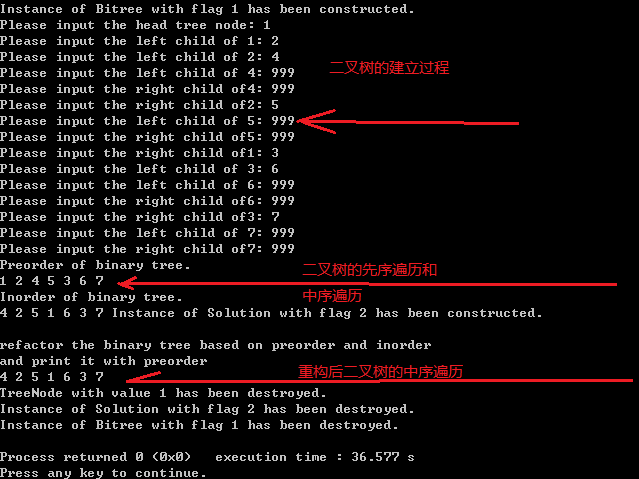
从结果中我们可以看见,重构后二叉树的中序遍历和我们输入的二叉树的中序遍历相同。我们还可以输出重构后的先序遍历,来确定我们的重构是正确的。
二叉树的重构暂且先探讨这。二叉树还有其它很多特性需要没我们去研究,择日再说。
剑指offer——已知二叉树的先序和中序排列,重构二叉树的更多相关文章
- 剑指Offer(二十二):从上往下打印二叉树
剑指Offer(二十二):从上往下打印二叉树 搜索微信公众号:'AI-ming3526'或者'计算机视觉这件小事' 获取更多算法.机器学习干货 csdn:https://blog.csdn.net/b ...
- 剑指Offer - 九度1367 - 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
剑指Offer - 九度1367 - 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列2013-11-23 03:16 题目描述: 输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果.如果是则输出Yes,否则输出 ...
- 剑指Offer - 九度1349 - 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
剑指Offer - 九度1349 - 数字在排序数组中出现的次数2013-11-23 00:47 题目描述: 统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数. 输入: 每个测试案例包括两行: 第一行有1个整数n, ...
- 剑指Offer(二十八):数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
剑指Offer(二十八):数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 搜索微信公众号:'AI-ming3526'或者'计算机视觉这件小事' 获取更多算法.机器学习干货 csdn:https://blog.csdn. ...
- 剑指Offer(三十五):数组中的逆序对
剑指Offer(三十五):数组中的逆序对 搜索微信公众号:'AI-ming3526'或者'计算机视觉这件小事' 获取更多算法.机器学习干货 csdn:https://blog.csdn.net/bai ...
- 剑指Offer(一):二维数组中的查找
一.前言 刷题平台:牛客网 二.题目 在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整 ...
- 《剑指offer》面试题32----从1到n整数中1出现的次数
题目:输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数.例如输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含1的数字有1,10,11和12,1一共出现了5次. 解法一:不考虑时间效率的解法(略) ps ...
- 一起来刷《剑指Offer》-- 题目一:找出数组中重复的数字(Python多种方法实现)
数组中重复的数字 最近在复习算法和数据结构(基于Python实现),然后看了Python的各种"序列"--比如列表List.元组Tuple和字符串String,后期会写一篇博客介绍 ...
- 剑指offer——面试题32.1:分行从上到下打印二叉树
void BFSLayer(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot) { if(pRoot==nullptr) return; queue<BinaryTreeNode*> pNode ...
随机推荐
- ios读取文件
// 创建文件管理器 NSFileManager *fm=[NSFileManager defaultManager]; //获取路径 NSArray *paths=NSSearchPathForDi ...
- 【MVC】过滤器
APS.NET MVC中(以下简称“MVC”)的每一个请求,都会分配给相应的控制器和对应的行为方法去处理,而在这些处理的前前后后如果想再加一些额外的逻辑处理.这时候就用到了过滤器. MVC支持的过滤器 ...
- PSR-2 Coding Style Guide
本文主要是对PSR-2 的简单翻译. 英文源址 http://www.php-fig.org/psr/psr-2/ PSR2继承和扩展PSR1--基本编码规范 本手册的目的是使用一系列共同遵守的编码格 ...
- MUD教程--巫师入门教程3
1. 指令格式为:edit <档名>,只加文件名,默认为当前目录,加here,表示编辑你当前所处的房间, 回车后即进入线上编辑系统. 2. 如果这是一个已经有的档案,你可以使用 z 或 Z ...
- Linux突然断电后文件丢失的问题
原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.http://yuyongid.blog.51cto.com/10626891/168504 ...
- mysql 插入前 锁表问题
$dbh = DBI->connect("dbi:mysql:database=$db_name;host=$ip;port=3306",$user,$passwd,{ Ra ...
- egret随笔-egret浅入浅出
•不知道有多人跟笔者一样,喜欢学各种技术,但是都不精,但也有一两项算是精的. 自从踏上了egret游戏开发的道路,就不得不学习各种技术了,因为,要精通egret,首先必须要会TypeScript,其次 ...
- 高效 Java Web 开发框架 JessMA v3.2.3 beta-2 发布
JessMA(原名:Portal-Basic)是一套功能完备的高性能 Full-Stack Web 应用开发框架,内置可扩展的 MVC Web 基础架构和 DAO 数据库访问组件(内部已提供了 Hib ...
- Zookeeper介绍
Zookeeper是一个分布式的开源系统,目的是为分布式应用提供协调一致性服务. 分布式应用可以在Zookeeper提供的简单原语集之上构造更高层次的服务.比如统一命名服务.状态同步服务.集群管理.分 ...
- LA - 5031 - Graph and Queries
题意:一个N个点(编号从1开始),M条边的无向图(编号从1开始),有3种操作: D X:把编号为X的边删了: Q X K:查询编号为X的结点所在连通分量第K大的元素: C X V:将编号为X的结点的权 ...