数据结构算法及应用——二叉树
一、二叉树性质
特性1 包含n (n> 0 )个元素的二叉树边数为n-1
特性2 二叉树的高度(height)或深度(depth)是指该二叉树的层数(有几层元素,而不是有层的元素间隔)
特性3 若二叉树的高度为h,h≥0,则该二叉树最少有h个元素,最多有(2^h – 1)个元素。
特性4 包含n 个元素的二叉树的高度最大为n,最小[log2 (n+1)]
二、满二叉树:
当高度为h 的二叉树恰好有2^h - 1个元素时,称其为满二叉树.
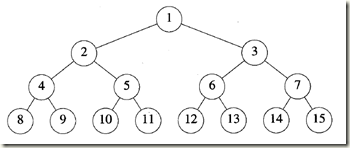
三、完全二叉树
假设对高度为h 的满二叉树中的元素按从第上到下,从左到右的顺序从1到2^h- 1进行编号(如图8 - 6所示)。假设从满二叉树中删除k个元素,其编号为2^h -i, 1≤i≤k,所得到的二叉树被称为完全二叉树.
注意满二叉树是完全二叉树的一个特例,并且,注意有n个元素的完全二叉树的深度为[log2 (n+1)]
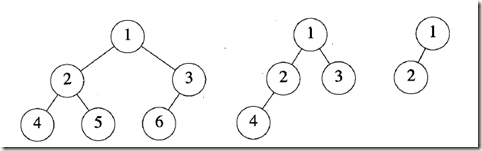
特性5 设完全二叉树中一元素的序号为i, 1≤i≤n。则有以下关系成立:
1) 当i = 1时,该元素为二叉树的根。若i > 1,则该元素父节点的编号为 下取整【i/2】
2) 当2i >n时,该元素无左孩子。否则,其左孩子的编号为2i。
3) 若2i + 1 >n,该元素无右孩子。否则,其右孩子编号为2i + 1。
四、二叉树的遍历
• 前序遍历。
• 中序遍历。
• 后序遍历。
• 逐层遍历。
在进行前序遍历时,每个节点是在其左右子树被访问之前进行访问的;
在中序遍历时,首先访问左子树,然后访问子树的根节点,最后访问右子树。
在后序遍历时,当左右子树均访问完之后才访问子树的根节点。
五、源码
1.InterfaceBinaryTree 类
#pragma once
/*
T为BinaryTreeNode<U>类型的数据
*/
template<class T>
class InterfaceBinaryTree {
//如果二叉树为空,则返回true ,否则返回false
virtual bool IsEmpty() const=0; //返回二叉树的大小
virtual int Size()const = 0; //前序遍历
virtual void PreOrder(void (*)(T *))const=0; //参数是一个指向 void Func(T*)类型的函数指针 //中序遍历
virtual void InOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0; //后序遍历
virtual void PostOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0; //逐层遍历
virtual void LevelOrder(void(*)(T *))const=0;
};
2.BinaryTreeNode类
#pragma once
template<class T>
class BinaryTreeNode{
public:
template<class T> friend class BinaryTree; BinaryTreeNode() {
leftChild = rightChild = 0;
}
BinaryTreeNode(const T &data) {
this->data = data;
leftChild = rightChild = 0;
}
BinaryTreeNode(const T &data, BinaryTreeNode<T> *leftSubTree, BinaryTreeNode<T> *rightSubTree) {
this->data = data;
leftChild = leftSubTree;
rightChild = rightSubTree;
} private:
T data;
BinaryTreeNode<T> *leftChild;
BinaryTreeNode<T> *rightChild; };
3.BinaryTree类
#pragma once
#include"BinaryTreeNode.h"
#include"InterfaceBinaryTree.h"
#include"MyException.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class BinaryTree:public InterfaceBinaryTree<BinaryTreeNode<T>> {
public:
BinaryTree() { root = 0; }
~BinaryTree() {};
//如果二叉树为空,则返回true ,否则返回false
bool IsEmpty() const {
return (root == 0) ? true : false;
}
//取根节点的数据域放入x;如果操作失败,则返回false,否则返回true
bool Root(T &x)const;
//创建一个二叉树,root作为根节点, left作为左子树,right作为右子树
void MakeTree(const T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right);
//拆分二叉树
void BreakTree(T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right); void PreOrderOutput() const {
PreOrder(output);
}
void InOrderOutput()const {
InOrder(output);
}
void PostOrderOutput()const {
PostOrder(output);
} //前序遍历
void PreOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _preOrder(root);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _inOrder(root);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _postOrder(root);
}
//逐层遍历
void LevelOrder(void(*theVisit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*))const {
visit = theVisit; _levelOrder(root);
} void Delete() {
PostOrder(free);
root = 0;
}
int Height()const {
return height(root);
}
int Size()const {
count = 0;
InOrder(addCount);
return count;
}
protected:
static void _preOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _inOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root);
static void _levelOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root); static void(*visit)(BinaryTreeNode<T> *); //函数指针,用于遍历时的函数访问
static void output(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
cout << t->data << " ";
}
static void free(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
delete t;
}
static void addCount(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
count++;
}
static int height(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t); private:
BinaryTreeNode<T> *root;
static int count; }; //访问函数的函数指针
template<class T>
void(*BinaryTree<T>::visit)(BinaryTreeNode<T>*);
template<class T>
int BinaryTree<T>::count = 0; //前序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_preOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
_preOrder(root->leftChild);
_preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
//中序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_inOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
_inOrder(root->leftChild);
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
_inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
//后序遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) {
if (root != 0) {
_postOrder(root->leftChild);
_postOrder(root->rightChild);
BinaryTree<T>::visit(root);
}
}
//逐层遍历
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::_levelOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> *root) { } //取根节点的数据域放入x;如果操作失败,则返回false,否则返回true
template<class T>
bool BinaryTree<T>::Root(T &x)const {
if (root == 0) {
return false;
}
x = root->data;
return true;
}
/*生成一个二叉树,新建一个BinaryTreeNode节点,使其值为element,左子树为left,右子树为right*/
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::MakeTree(const T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right) {
root = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element, left.root, right.root);
left.root = right.root = 0;
}
/*将一个二叉树拆分成左子树和右子树两部分,根节点的值保存到element*/
template<class T>
void BinaryTree<T>::BreakTree(T &element, BinaryTree<T> &left, BinaryTree<T> &right) {
if (root == 0)
throw BadInput();
element = root->data;
left.root = root->leftChild;
right.root = root->rightChild;
delete root; //删除原来根节点的内存
root = 0;
}
/*求二叉树的高度*/
template<class T>
int BinaryTree<T>::height(BinaryTreeNode<T> *t) {
if (t == 0)
return 0;
int leftHeight = height(t->leftChild); //左子树的高度
int rightHeight = height(t->rightChild); //右子树的高度 //返回左右子树中的最大值加一
if (leftHeight > rightHeight)
return ++leftHeight;
else
return ++rightHeight;
}
4.MyException类
#pragma once
#pragma once
// exception classes for various error types #include<iostream>
#include <string> using namespace std; class NoMem {
public:
NoMem() {
this->message = "内存不足";
}
NoMem(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
} private:
string message; };
class OutOfBounds {
public:
OutOfBounds() {
this->message = "输入超过了数组的界";
}
OutOfBounds(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
} private:
string message; };
class BadInput {
public:
BadInput() {
this->message = "输入有误";
}
BadInput(string msg) {
this->message = msg;
}
void OutputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;
}
private:
string message;
};
数据结构算法及应用——二叉树的更多相关文章
- 数据结构算法集---C++语言实现
//数据结构算法集---C++语言实现 //各种类都使用模版设计,可以对各种数据类型操作(整形,字符,浮点) /////////////////////////// // // // 堆栈数据结构 s ...
- 数据结构+算法面试100题~~~摘自CSDN
数据结构+算法面试100题~~~摘自CSDN,作者July 1.把二元查找树转变成排序的双向链表(树) 题目:输入一棵二元查找树,将该二元查找树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只调 ...
- 小小c#算法题 - 11 - 二叉树的构造及先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
在上一篇文章 小小c#算法题 - 10 - 求树的深度中,用到了树的数据结构,树型结构是一类重要的非线性数据结构,树是以分支关系定义的层次结构,是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集.但在那篇文章中,只 ...
- C语言版数据结构算法
C语言版数据结构算法 C语言数据结构具体算法 https://pan.baidu.com/s/19oLoEVqV1I4UxW7D7SlwnQ C语言数据结构演示软件 https://pan.baidu ...
- 【数据结构与算法】多种语言(VB、C、C#、JavaScript)系列数据结构算法经典案例教程合集目录
目录 1. 专栏简介 2. 专栏地址 3. 专栏目录 1. 专栏简介 2. 专栏地址 「 刘一哥与GIS的故事 」之<数据结构与算法> 3. 专栏目录 [经典回放]多种语言系列数据结构算法 ...
- 初转java随感(一)程序=数据结构+算法
大学刚学编程的时候,有一句很经典的话程序=数据结构+算法 今天有了进一步认识. 场景: 1.当前局面 (1)有现成的封装好的分页组件 返回结果是page.类型为:Page.包括 page 分页信息,d ...
- python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历)
python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历.中序遍历和后序遍历) 树 树是\(n\)(\(n\ge 0\))个结点的有限集.在任意一棵非空树中,有且只有一个根结点. 二叉树是有限个元素的集合,该集合或 ...
- day40 数据结构-算法(二)
什么是数据结构? 简单来说,数据结构就是设计数据以何种方式组织并存储在计算机中. 比如:列表.集合与字典等都是一种数据结构. N.Wirth: “程序=数据结构+算法” 列表 列表:在其他编程语言中称 ...
- 前端要不要学数据结构&算法
我们都知道前端开发工程师更多偏向 DOM 渲染和 DOM 交互操作,随之 Node 的推广前端工程师也可以完成服务端开发.对于服务端开发而言大家都觉得数据结构和算法是基础,非学不可.所以正在进行 No ...
随机推荐
- 网站发布在另外一个网站下面配置伪静态之后图片样式和JS丢失
<script src="<%=ResolveClientUrl("~/content/js/jquery-1.7.1.min.js") %>" ...
- visual studio 未将对象引用设置到对象的实例
我今天在win10上安装了Visual Studio 2015,结果新建项目后在模板中选择一项后就会弹出一个对话框: 查了许多种方法后,下面这个方法解决了我这个问题: 著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系 ...
- sql建立跨服务器链接
select srvname,* from master.dbo.sysservers //创建linkServer exec sp_addlinkedserver 'srv_lnk',' ...
- Realm
还在为数据库不能获取最新数据而犯愁?信我,你只是需要一个活着的数据库——Realm 写在前面: 又到一年一度七夕虐狗节,看着大家忍受着各种朋友圈和QQ空间还有现实生活中的轮番轰炸,我实在不忍心再在这里 ...
- 可以ping通,浏览器打不开网页 - 解决办法
网络故障表现为: 1.电脑显示网络连接正常,DNS配置和hosts配置均正常 2.cmd可以ping通网址,域名 3.所有浏览器无法打开网页,有道云笔记置灰,微信二维码刷新失败 解决办法: 管理员权限 ...
- 在fedora 20下使用ssh server
在红帽和centos下,一般安装完后会自带ssh,然后可以通过/etc/init.d/sshd start的方式运行,但是在Fedora 20下,系统改用了另外一套服务开启机制. 首先安装ssh se ...
- [原创]零基础R语言教程---第二课---R语言入门
这节教程简单描述了R语言中常用的数据类型, 向量,字符串,矩阵,列表,数据框,以及附带了一个小例子 对于这节课所附带的例子需要做下列补充: 1.这个例子面向于对整列的数据进行预测 2.如果你需要求单行 ...
- PHPDocumentor安装与使用
phpDocuemtor官网:http://www.phpdoc.org/ 通过pear安装,进入dos的php目录,输入pear install -a PhpDocumentor.如果想使用web接 ...
- C3P0连接池详细配置
C3P0连接池详细配置 转自http://msq.javaeye.com/blog/60387 <c3p0-config> <default-config> <!--当连 ...
- VS如何关闭 ReSharper 提示
IDE->工具->选项->click "suspend now" button
