Redis 内存管理与事件处理
1 Redis内存管理
void *zmalloc(size_t size) {
// 多申请的一部分内存用于存储当前分配了多少自己的内存
void *ptr = malloc(size+PREFIX_SIZE);
if (!ptr) zmalloc_oom_handler(size);
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOC_SIZE
update_zmalloc_stat_alloc(zmalloc_size(ptr));
return ptr;
#else
*((size_t*)ptr) = size;
// 内存分配统计
update_zmalloc_stat_alloc(size+PREFIX_SIZE);
return (char*)ptr+PREFIX_SIZE;
#endif
}
内存布局图示:
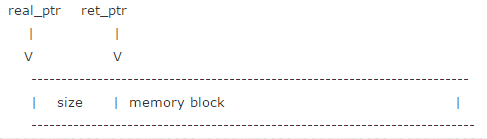
2 事件处理
- 设置信号回调函数。
- 创建事件循环机制,即调用epoll_create。
- 创建服务监听端口,创建定时事件,并将这些事件添加到事件机制中。
void initServer(void) {
int j;
// 设置信号对应的处理函数
signal(SIGHUP, SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
setupSignalHandlers();
...
createSharedObjects();
adjustOpenFilesLimit();
// 创建事件循环机制,及调用epoll_create创建epollfd用于事件监听
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+CONFIG_FDSET_INCR);
server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum);
/* Open the TCP listening socket for the user commands. */
// 创建监听服务端口,socket/bind/listen
if (server.port != &&
listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == C_ERR)
exit();
...
/* Create the Redis databases, and initialize other internal state. */
for (j = ; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&keyptrDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].blocking_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].ready_keys = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].watched_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].eviction_pool = evictionPoolAlloc();
server.db[j].id = j;
server.db[j].avg_ttl = ;
}
...
/* Create the serverCron() time event, that's our main way to process
* background operations. 创建定时事件 */
if(aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, , serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic("Can't create the serverCron time event.");
exit();
}
/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix
* domain sockets. */
for (j = ; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
serverPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
// 将事件加入到事件机制中,调用链为 aeCreateFileEvent/aeApiAddEvent/epoll_ctl
if (server.sofd > && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) serverPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event.");
/* Open the AOF file if needed. */
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON) {
server.aof_fd = open(server.aof_filename,
O_WRONLY|O_APPEND|O_CREAT,);
if (server.aof_fd == -) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Can't open the append-only file: %s",
strerror(errno));
exit();
}
}
...
}
static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
int retval, numevents = ;
retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize,
tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec* + tvp->tv_usec/) : -);
if (retval > ) {
int j;
numevents = retval;
for (j = ; j < numevents; j++) {
int mask = ;
struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j;
if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd;
eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask;
}
}
return numevents;
}
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = ; j < numevents; j++) {
// 从eventLoop->events数组中查找对应的回调函数
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = ;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
rfired = ;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
...
}
3 如何添加自定义命令
From 5304020683078273c1bc6cc9666dab95efa18607 Mon Sep ::
From: luoxn28 <luoxn28@.com>
Date: Fri, Jun :: -
Subject: [PATCH] add own command: random num ---
src/server.c | ++-
src/server.h | +
src/t_string.c | ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
files changed, insertions(+), deletion(-) diff --git a/src/server.c b/src/server.c
index 609f396..e040104
--- a/src/server.c
+++ b/src/server.c
@@ -, +, @@ struct redisCommand redisCommandTable[] = {
{"pfdebug",pfdebugCommand,-,"w",,NULL,,,,,},
{"post",securityWarningCommand,-,"lt",,NULL,,,,,},
{"host:",securityWarningCommand,-,"lt",,NULL,,,,,},
- {"latency",latencyCommand,-,"aslt",,NULL,,,,,}
+ {"latency",latencyCommand,-,"aslt",,NULL,,,,,},
+ {"random",randomCommand,,"rF",,NULL,,,,,}
}; struct evictionPoolEntry *evictionPoolAlloc(void);
diff --git a/src/server.h b/src/server.h
index 3fa7c3a..427ac92
--- a/src/server.h
+++ b/src/server.h
@@ -, +, @@ void setnxCommand(client *c);
void setexCommand(client *c);
void psetexCommand(client *c);
void getCommand(client *c);
+void randomCommand(client *c);
void delCommand(client *c);
void existsCommand(client *c);
void setbitCommand(client *c);
diff --git a/src/t_string.c b/src/t_string.c
index 8c737c4..df4022d
--- a/src/t_string.c
+++ b/src/t_string.c
@@ -, +, @@ void getCommand(client *c) {
getGenericCommand(c);
} +static bool checkRandomNum(char *num)
+{
+ char *c = num;
+
+ while (*c != '\0') {
+ if (!(('' <= *c) && (*c <= ''))) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ c++;
+ }
+
+ return true;
+}
+
+/**
+ * command: random n
+ * return a random num < n, if n <= 0, return 0
+ * @author: luoxiangnan
+ */
+void randomCommand(client *c)
+{
+ char buff[] = {};
+ int num = ;
+ robj *o = NULL;
+
+ if (!checkRandomNum(c->argv[]->ptr)) {
+ o = createObject(OBJ_STRING, sdsnewlen("sorry, it's not a num :(",
+ strlen("sorry, it's not a num :(")));
+ addReplyBulk(c, o);
+ return;
+ }
+
+ sscanf(c->argv[]->ptr, "%d", &num);
+ if (num > ) {
+ num = random() % num;
+ } else {
+ num = ;
+ }
+
+ sprintf(buff, "%s %d", "redis: ", num);
+ o = createObject(OBJ_STRING, sdsnewlen(buff, strlen(buff)));
+ addReplyBulk(c, o);
+}
+
void getsetCommand(client *c) {
if (getGenericCommand(c) == C_ERR) return;
c->argv[] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[]);
--
1.8.3.1
Redis 内存管理与事件处理的更多相关文章
- Redis 内存管理 源码分析
要想了解redis底层的内存管理是如何进行的,直接看源码绝对是一个很好的选择 下面是我添加了详细注释的源码,需要注意的是,为了便于源码分析,我把redis为了弥补平台差异的那部分代码删了,只需要知道有 ...
- Redis内存管理(二)
上一遍详细的写明了Redis为内存管理所做的初始化工作,这篇文章写具体的函数实现. 1.zmalloc_size,返回内存池大小函数,因为库不同,所以这个函数在内部有很多的宏定义,通过具体使用的库来确 ...
- Redis内存管理(一)
Redis数据库的内存管理函数有关的文件为:zmalloc.h和zmalloc.c. Redis作者在编写内存管理模块时考虑到了查看系统内是否安装了TCMalloc或者Jemalloc模块,这两个是已 ...
- TCMalloc优化MySQL、Nginx、Redis内存管理
TCMalloc(Thread-Caching Malloc)与标准glibc库的malloc实现一样的功能,但是TCMalloc在效率和速度效率都比标准malloc高很多.TCMalloc是 goo ...
- redis内存管理
Redis主要通过控制内存上线和回收策略来实现内存管理. 1. 设置内存上限 redis使用maxmemory参数限制最大可用内存.限制的目的主要有: 用户缓存场景,当超出内存上限maxmemory时 ...
- Redis内存管理的基石zmallc.c源代码解读(一)
当我第一次阅读了这个文件的源代码的时候.我笑了,忽然想起前几周阿里电话二面的时候,问到了自己定义内存管理函数并处理8字节对齐问题. 当时无言以对,在面试官无数次的提示下才答了出来,结果显而易见,挂掉了 ...
- 详解 Redis 内存管理机制和实现
Redis是一个基于内存的键值数据库,其内存管理是非常重要的.本文内存管理的内容包括:过期键的懒性删除和过期删除以及内存溢出控制策略. 最大内存限制 Redis使用 maxmemory 参数限制最大可 ...
- redis内存管理代码的目光
zmalloc.h /* zmalloc - total amount of allocated memory aware version of malloc() * * Copyright (c) ...
- redis 内存管理与数据淘汰机制(转载)
原文地址:http://www.jianshu.com/p/2f14bc570563?from=jiantop.com 最大内存设置 默认情况下,在32位OS中,Redis最大使用3GB的内存,在64 ...
随机推荐
- Archive for required library:xxxxx/spring-beans-3.2.4.RELEASE.jar in project XXXXX cannot be read or is not a valid ZIP file
今天在导入maven项目的时候在problems视图中报错: Archive for required library:xxxxx/spring-beans-3.2.4.RELEASE.jar in ...
- Scala基础 - 下划线使用指南
下划线这个符号几乎贯穿了任何一本Scala编程书籍,并且在不同的场景下具有不同的含义,绕晕了不少初学者.正因如此,下划线这个特殊符号无形中增加Scala的入门难度.本文希望帮助初学者踏平这个小山坡. ...
- 深入理解Struts2----类型转换
之前的一系列文章主要介绍了有关Struts2的一些基本用法和部分的简单原理,但是始终没有介绍有关拦截器的相关内容,从本篇开始我们将从另一个角度去深入理解框架的使用,核心还是拦截器,但本篇首先 ...
- MyBatis3入门
这里对mybatis的入门介绍以官方最新MyBatis3.4.1为准,具体文档及jar包请访问:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases. 以前经常都 ...
- object-fit 解决图片指定大小被压缩问题
object-fit 解决图片指定大小被压缩问题 第一次遇到这个属性,是在给video 写 poster的时候,选取的作为poster的img的尺寸有点小,导致video播放器两边有留白.在控制台查看 ...
- Opencv在linux下安装
Opencv in Linux These steps have been tested for Ubuntu 10.04 but should work with other distros as ...
- MySQL优化总结,百万级数据库优化方案
1.对查询进行优化,应尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 where 及 order by 涉及的列上建立索引. 2.应尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行 null 值判断,否则将导致引擎放弃使用索 ...
- day5_ 导入模块和包
######################模块导入模块做的事1.产生新的名称空间2.以新建的名称空间为全局名称空间,执行文件的代码3.拿到一个模块名spam,指向spam.py产生的名称空间 imp ...
- css3 linear-gradient渐变效果及兼容性处理
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- Java之JSON数据
特别注意:使用JSON前需要导包 操作步骤地址:http://blog.csdn.net/baidu_37107022/article/details/70876993 1.定义 JSON(JavaS ...
