大聊Python----装饰器
什么是装饰器?
装饰器其实和函数没啥区别,都是用def去定义的,其本质就是函数,而功能就是装饰其他的函数,说白了就是为其他函数提供附加功能
装饰器有什么作用?
比如你是一个公司的员工,你所写的程序里有100个函数,但是你所写的程序都已经上线运行了,突然有一天你的产品经理来找你,让你在咱们的APP上新增一段功能!那你说该怎么做这件事情?问题是你的程序都已经在运行了 ,不能修改你程序的源代码,否则会出现意想不到的效果!所以你想新增一项功能,但是不能修改你的源代码!那该怎么办呢?
装饰器对待被修饰的函数是完全透明的状态!也就是函数感觉不到装饰器的存在,装饰器没有动函数的源代码,也不影响函数的运行。
先看一下代码:
import time def timmer(func): # 装饰器
def warpper(*args,**kwargs):
start_time = time.time() # 开始的时间
func()
stop_time = time.time() # 结束的时间
print('the fun run time is %s'%(stop_time - start_time))
return warpper @timmer # 被装饰的函数
def test1():
time.sleep(3) # 延时3秒
print("in the test1") test1()
结果展示:
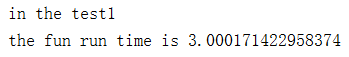
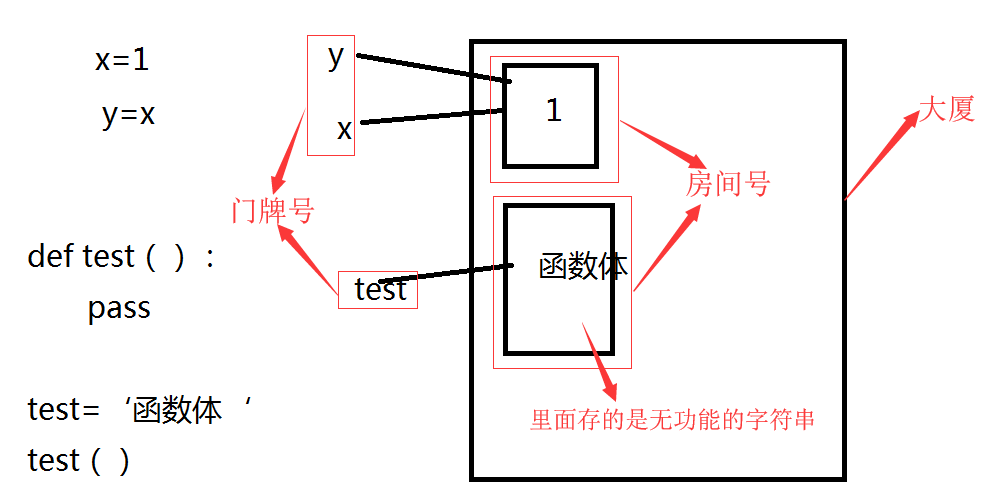
实现装饰器知识储备
1、函数即“变量”
机制:
函数调用顺序:其他高级语言类似,Python 不允许在函数未声明之前,对其进行引用或者调用
错误示范:
def foo():
print 'in the foo'
bar()
foo()
报错:
in the foo
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#13>", line 1, in <module>
foo()
File "<pyshell#12>", line 3, in foo
bar()
NameError: global name 'bar' is not defined
def foo():
print 'foo'
bar()
foo()
def bar():
print 'bar'
报错:NameError: global name 'bar' is not defined
正确示范:(注意,python为解释执行,函数foo在调用前已经声明了bar和foo,所以bar和foo无顺序之分)
def bar():
print 'in the bar'
def foo():
print 'in the foo'
bar()
foo()
def foo():
print 'in the foo'
bar()
def bar():
print 'in the bar'
foo()
2、高阶函数
a、就是把函数名当做实参传给另外一个函数(在不修改被装饰函数源代码的情况下为其增添功能)
示例:
import time def bar():
time.sleep(3)
print("in the bar")
def test1(func):
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run rime is %s"%(stop_time - start_time)) test1(bar)
结果:

b、返回值中包含函数名(不修改函数的调用方式)
示例:
import time def bar():
time.sleep(3)
print("in the bar")
def test2(func):
print(func)
return func bar = test2(bar)
print(bar) # run bar
效果:
<function bar at 0x00000000007C48C8>
<function bar at 0x00000000007C48C8>
3、嵌套函数
局部作用域和全局作用域的访问顺序
x=0
def grandpa():
# x=1
def dad():
x=2
def son():
x=3
print(x)
son()
dad()
grandpa()
显示效果为:
3

高阶函数 + 嵌套函数 ==》 装饰器
先看个例子
import time
def timer(func):
def deco():
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func's run time is %s "%(stop_time - start_time))
return deco @timer
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print("the test1 is running!") @timer
def test2():
time.sleep(3)
print("the test2 is running!") test1()
test2()

结果显示:
the test1 is running!
the func's run time is 3.000171422958374
the test2 is running!
the func's run time is 3.000171661376953
若想给test2传递参数,如下例,该怎么做呢?
import time
def timer(func):
def deco():
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func's run time is %s "%(stop_time - start_time))
return deco @timer
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print("the test1 is running!") @timer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(3)
print("the test2 is running!",name) test1()
test2("alex")
通过执行,会出现下面的错误

意思是说,deco()缺少了一个元素!
那该怎么解决这个问题呢?
咱们先来捋顺下思路!
通过@timer可知test2() =timer(test2) = deco ,test2(name) = deco(name)
所以可以看出要给deco传递实参,所以做了下面
def timer(func):
def deco(name):
start_time = time.time()
func(name)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func's run time is %s "%(stop_time - start_time))
return deco
通过执行,会看到下面的结果!
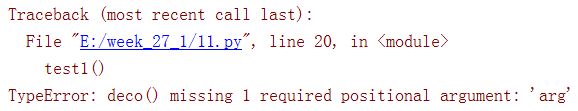
这回好了,test2不出错了,反而test1报错了,那个该怎么办呢?
看下test1出错的原因是test1的deco缺少了一个实参,那么问题来了,test1该怎么处理呢?
其实很简单,使用*args,和**kwargs尽可以完美的解决这个问题!
现在来看看经过改正的程序
import time
def timer(func):
def deco(*args,**kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
func(*args,**kwargs)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func's run time is %s "%(stop_time - start_time))
return deco @timer
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print("the test1 is running!") @timer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(3)
print("the test2 is running!",name) test1()
test2("alex")
结果显示:
the test1 is running!
the func's run time is 3.000171661376953
the test2 is running! alex
the func's run time is 3.000171422958374
装饰器之高潮
进入高潮之前,我们先来点前戏
先看下面的代码
import time
user , passwd = "sutaoyu" , "sutaoyu01" def auth(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
username = input("Username").strip()
password = input("Password").strip()
if user == username and passwd == password:
print("\033[32;1mUser has passed authentication\033[0m")
func(*args,**kwargs)
else:
exit("\033[31;1mInvalid username and password\033[0m")
return wrapper @auth
def index():
print("welcome to index Page!") @auth
def home():
print("welcome to index Home!") @auth
def bbs():
print("welcome to index BBS!") index()
home()
bbs()
其输出的结果为:
输入正确时:

输入错误时:

现在当我们把前面的代码稍微改一下,装饰器代码不动,只改变下面两个地方
def index():
print("welcome to index Page!")
return "Page" print(index())
此时看输出的结果:
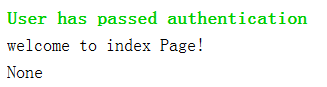
会发现无结果并为None,那是因为什么呢?
因为装饰器里的wrapper没有返回值所以,我们给他提供返回值即可!
def auth(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
username = input("Username:").strip()
password = input("Password:").strip()
if user == username and passwd == password:
print("\033[32;1mUser has passed authentication\033[0m")
return func(*args,**kwargs)
else:
exit("\033[31;1mInvalid username and password\033[0m")
return wrapper
运行下程序,看看结果
可以看出,问题已经解决!
现在高潮部分即将来临:
我能不能让我的home在认证的时候用本地的认证,但是bbs认证的时候用远程的ldap?
答案是肯定的!
先看下代码!
import time
user , passwd = "" , "" def auth(auth_type):
print("auth_typr:",auth_type)
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
print("wrapper func args:",*args,**kwargs)
if auth_type == "local":
username = input("Username:").strip()
password = input("Password:").strip()
if user == username and passwd == password:
print("\033[32;1mUser has passed authentication\033[0m")
func(*args,**kwargs)
else:
exit("\033[31;1mInvalid username and password\033[0m")
elif auth_type == "ldap":
print("搞毛啊!!!!!")
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper # @auth
def index():
print("welcome to Index page!")
return "Page" @auth(auth_type = "local")
def home():
print("welcome to Home page!") @auth(auth_type = "ldap")
def bbs():
print("welcome to BBS page!") index()
home()
bbs()
运行的结果为:

可以看出,我们的认真已经成功!
大聊Python----装饰器的更多相关文章
- Python装饰器总结,带你几步跨越此坑!
欢迎添加华为云小助手微信(微信号:HWCloud002 或 HWCloud003),输入关键字"加群",加入华为云线上技术讨论群:输入关键字"最新活动",获取华 ...
- Python装饰器由浅入深
装饰器的功能在很多语言中都有,名字也不尽相同,其实它体现的是一种设计模式,强调的是开放封闭原则,更多的用于后期功能升级而不是编写新的代码.装饰器不光能装饰函数,也能装饰其他的对象,比如类,但通常,我们 ...
- Python装饰器与面向切面编程
今天来讨论一下装饰器.装饰器是一个很著名的设计模式,经常被用于有切面需求的场景,较为经典的有插入日志.性能测试.事务处理等.装饰器是解决这类问题的绝佳设计,有了装饰器,我们就可以抽离出大量函数中与函数 ...
- 一篇关于Python装饰器的博文
这是一篇关于python装饰器的博文 在学习python的过程中处处受阻,之前的学习中Python的装饰器学习了好几遍也没能真正的弄懂.这一次抓住视频猛啃了一波,就连python大佬讲解装饰器起来也需 ...
- python 装饰器 一篇就能讲清楚
装饰器一直是我们学习python难以理解并且纠结的问题,想要弄明白装饰器,必须理解一下函数式编程概念,并且对python中函数调用语法中的特性有所了解,使用装饰器非常简单,但是写装饰器却很复杂.为了讲 ...
- Python装饰器模式学习总结
装饰器模式,重点在于装饰.装饰的核心仍旧是被装饰对象. 类比于Java编程的时候的包装模式,是同样的道理.虽然概念上稍有不同但是原理上还是比较相近的.下面我就来谈一谈我对Python的装饰器的学习的一 ...
- 转发对python装饰器的理解
[Python] 对 Python 装饰器的理解的一些心得分享出来给大家参考 原文 http://blog.csdn.net/sxw3718401/article/details/3951958 ...
- 利用世界杯,读懂 Python 装饰器
Python 装饰器是在面试过程高频被问到的问题,装饰器也是一个非常好用的特性, 熟练掌握装饰器会让你的编程思路更加宽广,程序也更加 pythonic. 今天就结合最近的世界杯带大家理解下装饰器. 德 ...
- 理解 Python 装饰器看这一篇就够了
讲 Python 装饰器前,我想先举个例子,虽有点污,但跟装饰器这个话题很贴切. 每个人都有的内裤主要功能是用来遮羞,但是到了冬天它没法为我们防风御寒,咋办?我们想到的一个办法就是把内裤改造一下,让它 ...
- Python高级特性: 12步轻松搞定Python装饰器
12步轻松搞定Python装饰器 通过 Python 装饰器实现DRY(不重复代码)原则: http://python.jobbole.com/84151/ 基本上一开始很难搞定python的装 ...
随机推荐
- jetty之maven配置
<!-- jetty 插件配置 --><plugin> <groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId> <artifac ...
- PHP关于传众多参数还是传上下文对象的性能测试
在开发微信公众平台平台的过程中,有这么几个参数总是需要传来传去,$userOpenId,$message,$time. 在整个程序的运行过程中,为了函数方便的处理,将这三个变量一直放在参数列表里.关于 ...
- JDK1.8 之Lambda
Lambda 理解的了很久才有一点小感觉. 语法 lambda表达式的特点,它的语法如下面. parameter -> expression body 下面是一个lambda表达式的重要特征. ...
- Sql Server统计报表案例
场景:查询人员指定年月工作量信息 USE [Test] GO SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO ALTER procedure [dbo ...
- 第91天:CSS3 属性选择器、伪类选择器和伪元素选择器
一.属性选择器 其特点是通过属性来选择元素,具体有以下5种形式: 1.E[attr] 表示存在attr属性即可: div[class] 2.E[attr=val] 表示属性值完全等于val: ...
- 【数据库_Mysql】MySQL—修改表时给表添加联合主键约束
添加语法如下: “ALTER TABLE table_name ADD CONSTRAINT pk_table_name PRIMARY KEY(列名1,列名2):” [示例1]假设订房信息表(O ...
- linux系统启动自动激活网卡的解决方法
linux每次启动的时候网卡都需要激活才能上网,实在是很麻烦. 上网找了找资料,最后是这样解决的: # vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 ...
- 使用Ajax内容签名,减少流量浪费
前端UI界面用Ajax获取数据内容的时候,一般是直接获取内容数据并填充,不管内容有无变化,不管数据量多大,都是直接重新加载数据,例如定时刷新公告等. 今天在浏览器控制台调试的时候,发现动态刷新内容,其 ...
- 《剑指offer》— JavaScript(13)调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面 题目描述 输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的 ...
- ACE服务端编程3:ACE跨平台之分配堆内存
ACE服务端编程系列的第三篇,探究ACE解决不同编译器之间分配堆内存的差异. 在ACE的官方示例中会看到大量的ACE_NEW_RETURN,ACE_NEW这样的宏,这是ACE为了消除不同编译器编译的代 ...
