Struts2学习笔记四 OGNL
OGNL,全称为Object-Graph Navigation Language(对象图表达语言),它是一个功能强大的表达式语言,用来获取和设置Java对象的属性,调用java对象的方法,同时能够自动实现必要的类型转换。它旨在提供一个更高的更抽象的层次来对Java对象图进行导航。如果把表达式看作是一个带有语义的字符串,那么OGNL无疑成为了这个语义字符串与Java对象之间沟通的桥梁。
OGNL:对象视图导航语言. ${user.addr.name} 这种写法就叫对象视图导航.
OGNL不仅仅可以视图导航.支持比EL表达式更加丰富的功能.
OGNL的作用
Struts默认的表达式语言就是OGNL,它具有以下特点:
- 支持对象方法调用。
- 支持类静态方法调用和值访问,表达式的格式为@[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名|值名],例如:@java.lang.String@format('foo%s','bar')。
- 支持赋值操作和表达式串联。例如:price=100,discount=0.8,calculatePrice(),在方法中进行乘法计算会返回80.
- 访问OGNL上下文(OGNL context)和ActionContext。
- 操作集合对象。
OGNL的要素
1、表达式
表达式是整个OGNL的核心,OGNL会根据表达式去对象中取值。所有OGNL操作都是针对表达式解析后进行的。它表明了此次OGNL操作要“做什么”。表达式就是一个带有语法含义的字符串,这个字符串规定了操作的类型和操作的内容。OGNL支持大量的表达式语法,不仅支持这种“链式”对象访问路径,还支持在表达式中进行简单的计算。
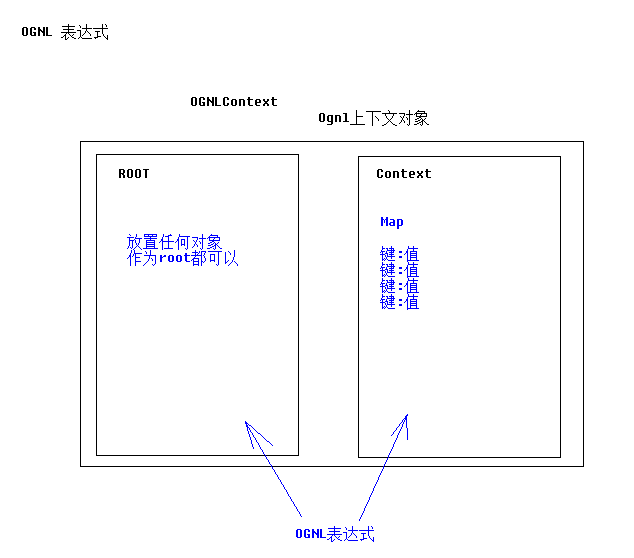
2、根(root)对象
Root对象可以理解为OGNL的操作对象,表达式规定了“做什么”,而Root对象则规定了“对谁操作”。OGNL称为对象图导航语言,所谓对象图,即以任意一个对象为根,通过OGNL可以访问与这个对象关联的其他对象。
3、上下文(context)对象
实际上OGNL的取值还需要一个上下文环境。设置了Root对象,OGNL可以对Root对象进行取值或写值等操作,Root对象所在环境就是OGNL的上下文环境。上下文环境规定了OGNL的操作“在哪里进行”。上下文环境Context是一个Map类型的对象,在表达式中访问Context中的对象,需要使用"#"号加上对象名称,即“#对象名称”的形式。
OGNL的入门
struts2 的包中已经包含了,所以不需要导入额外的jar包。
OGNL取值
@Test
//基本语法演示
//取出context中的属性值
public void fun3() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL
//取出root中user对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
//取出context中键为user1对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
System.out.println(age);
}
对于使用上下文的OGNL,若不指定从哪一个对象中查找"name"属性,则OGNL直接从根对象(root)查找,若指定查找对象(使用'#'号指定,如#user1),则从指定的对象中查找,若指定对象不在上下文中则会抛出异常,即使用#user1.name形式指定查找对象则必须要保证指定对象在上下文环境中。
OGNL为属性赋值
@Test
//基本语法演示
//为属性赋值
public void fun4() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL
//将root中的user对象的name属性赋值
Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
//把user1的name改为xq,并取值,如果多个取值放在一起,只会返回最后一个表达式的值
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='xq',#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
OGNL调用方法
@Test
//基本语法演示
//调用方法
public void fun5() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL //调用root中user对象的setName方法
Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot()); String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
OGNL调用静态方法
@Test
//基本语法演示
//调用静态方法
public void fun6() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.String@format('hello %s!','world')", oc, oc.getRoot());
//Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(pi);
}
创建list对象
@Test
//基本语法演示
//ognl创建对象-list|map
public void fun7() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL //创建list对象
Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
//创建Map对象(#表示要创建一个map)
Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size2);
System.out.println(name3);
System.out.println(age);
}
OGNL与Struts2结合
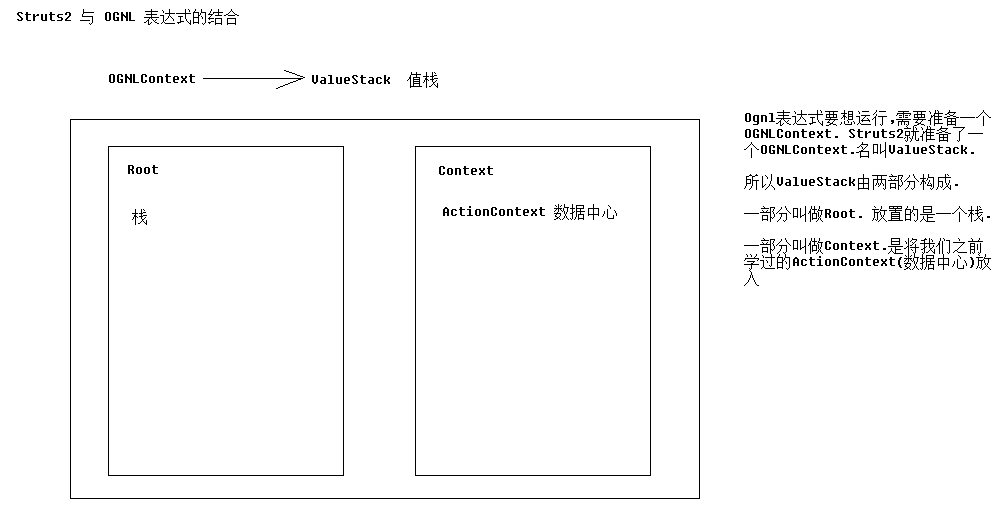
什么是值栈?
具体参考这里,ValueStack是Struts的一个接口,OGNLValueStack是ValueStack的实现类,客户端发起一个请求Struts2架构会创建一个action实例,同时创建一个OgnlValueStack值栈实例,OgnlValueStack贯穿整个Action的生命周期,Struts2中使用OGNL将请求Action的参数封装为对象存储到值栈中,并通过OGNL表达式读取值栈中的对象属性值。
CompoundRoot root;
transient Map<String, Object> context;
Context:即OgnlContext上下文,它是一个map结构,上下文中存储了一些引用,parameters、request、session、application等,上下文的Root为CompoundRoot。
OgnlContext中的一些引用:
- parameters:该Map中包含当前请求的请求参数。
- request:该Map中包含当前request对象中的所有属性。
- session:该Map中包含当前session对象中的所有属性。
- application:该Map中包含当前application对象中的所有属性。
- attr:该map按如下顺序来检索某个属性:request,session,application
CompoundRoot:存储了action实例,它作为OgnlContext的Root对象。action实例位于栈顶,当读取action的属性值时会先从栈顶对象中找对应的属性,如果找不到则继续找栈中的其他对象,如果找到则停止查找。
CompoundRoot继承了ArrayList实现压栈和出栈功能,拥有栈的特点,先进后出,最后压进栈的数据在栈顶。我们把它称为对象栈。
Struts2对原OGNL做出的改进就是Root使用CompoundRoot(自定义栈),使用OgnlValueStack的findValue方法可以在CompoundRoot中从栈顶向栈底找查找的对象的属性值。
ActionContext和ValueStack的关系
PrepareOperations源码:
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Integer counter = Integer.valueOf(1);
Integer oldCounter = (Integer)request.getAttribute("__cleanup_recursion_counter");
if(oldCounter != null) {
counter = Integer.valueOf(oldCounter.intValue() + 1);
}
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext ctx;
if(oldContext != null) {
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
ValueStack stack = ((ValueStackFactory)this.dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class)).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(this.dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, (ActionMapping)null));
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute("__cleanup_recursion_counter", counter);
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
从上源码可以看出:
在创建ActionContext的时候,创建ValueStack的对象,将ValueStack对象给ActionContext。
ActionContext中有一个ValueStack的引用。ValueStack中也有一个ActionContext的引用。
ActionContext获取Servlet API的时候,就依赖值栈。
获取值栈对象
1、通过ActionContext对象获取值栈
ValueStack stack1= ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
2、通过request域获取值栈
ValueStack stack2= (ValueStack)ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
查看值栈中两部分内容(使用DEBUG标签)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 调试标签 -->
<s:debug></s:debug>
</body>
</html>
struts2与ognl结合体现—参数接收
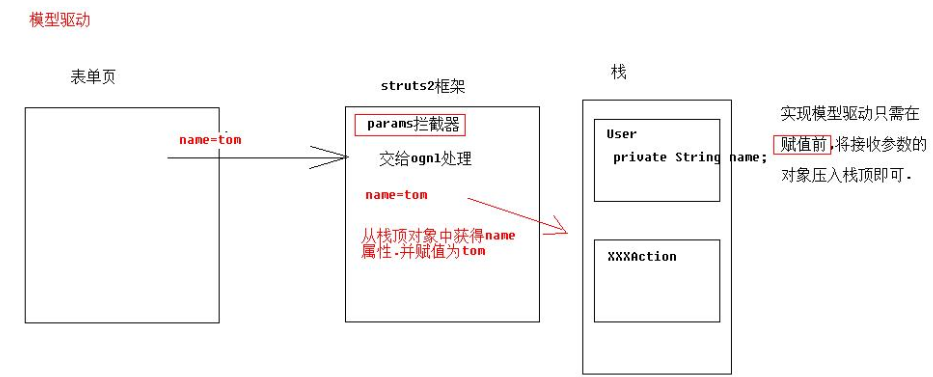
必须在params拦截器之前,把对象压入栈顶。可以使用parpre拦截器,只需在action中实现Preparable接口即可。具体参考这里。
public class Demo2Action implements Preparable {
private User u = new User();
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(u);
return SUCCESS;
}
@Override
public void prepare() throws Exception {
//压入栈顶
//1获得值栈
ValueStack vs = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
//2将u压入栈顶
vs.push(u);
}
}
struts2与ognl结合体现—配置文件
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Demo3Action extends ActionSupport {
private String name;
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
name = "jerry";
return SUCCESS;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
<action name="Demo3Action" class="cn.itheima.d_config.Demo3Action" method="execute" >
<result name="success" type="redirectAction" >
<param name="actionName">Demo1Action</param>
<param name="namespace">/</param>
<!-- 如果添加的参数struts"看不懂".就会作为参数附加重定向的路径之后.
如果参数是动态的.可以使用${}包裹ognl表达式.动态取值
-->
<param name="name">${name}</param>
</result>
</action>
扩展:request对象的getAttribute方法,查找顺序

Struts2学习笔记四 OGNL的更多相关文章
- struts2学习笔记四
一.contextMap中的数据操作 root根:List 元素1 元素2 元素3 元素4 元素5 contextMap:Map key value application Map key value ...
- Struts2学习笔记(OGNL表达式)
Struts 2支持以下几种表达式语言: OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language),可以方便地操作对象属性的开源表达式语言: JSTL(JSP Standard T ...
- Struts2学习笔记四:深入拦截器
一:拦截器的工作原理 拦截器的执行过程可以类比filter过滤器,ActionInvocation实例执行过程中,先执行action实例上引用的拦截器们,然后才执行action实例处理请求,返回res ...
- Struts2学习笔记(四)——result结果类型
当Action类的方法处理请求后,会返回一个字符串(逻辑视图名),框架根据这个结果码选择对应的result,向用户输出,所以需要在struts.xml提供<result>元素定义结果页面, ...
- Struts2 学习笔记(概述)
Struts2 学习笔记 2015年3月7日11:02:55 MVC思想 Strust2的MVC对应关系如下: 在MVC三个模块当中,struts2对应关系如下: Model: 负责封装应用的状态,并 ...
- C#可扩展编程之MEF学习笔记(四):见证奇迹的时刻
前面三篇讲了MEF的基础和基本到导入导出方法,下面就是见证MEF真正魅力所在的时刻.如果没有看过前面的文章,请到我的博客首页查看. 前面我们都是在一个项目中写了一个类来测试的,但实际开发中,我们往往要 ...
- IOS学习笔记(四)之UITextField和UITextView控件学习
IOS学习笔记(四)之UITextField和UITextView控件学习(博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/developer_jiangqq) Author:hmjiangqq ...
- java之jvm学习笔记四(安全管理器)
java之jvm学习笔记四(安全管理器) 前面已经简述了java的安全模型的两个组成部分(类装载器,class文件校验器),接下来学习的是java安全模型的另外一个重要组成部分安全管理器. 安全管理器 ...
- Struts2学习笔记⑧
今天是Struts2学习笔记的最后一篇文章了.用什么做结尾呢,这两天其实还学了很多东西,没有记录下,今天就查漏补缺一下. 文件上传与下载.FreeMarker以及昨天没做完的例子 文件上传与下载 文件 ...
随机推荐
- Linux查看非root运行的进程
Linux查看非root运行的进程 youhaidong@youhaidong-ThinkPad-Edge-E545:~$ ps -U root -u root -N PID TTY TIME CMD ...
- Linux之23个重要命令
作为工作几年的Linux运维老司机,总结了Linux命令行的常用的一些用法,希望对您有所收获. 1. 搜索 在vi和vim中如果打开一个很大的文件,不容易找到对应的内容,可以使用自带的搜索关键字进行搜 ...
- C# 程序员最常犯的 10 个错误(转)
关于C#关于本文常见错误 #1:把引用当做值来用,或者反过来常见错误 #2:误会未初始化变量的默认值常见错误 #3:使用不恰当或未指定的方法比较字符串常见错误 #4:使用迭代式 (而不是声明式)的语句 ...
- 【Luogu1337】平衡点(模拟退火)
[Luogu1337]平衡点(模拟退火) 题面 洛谷 题解 和BZOJ3680吊打XXX是一样的.. 但是数据很强呀.. 疯狂调参 各种WA... 很无奈呀.... #include<iostr ...
- awk多分隔符功能及wc命令案列及企业级应用
打印最后一行行号: cat -n /etc/services|tail -1 awk '{print NR $0}' oldboy.txt|tail -1 awk '{print NR $0}' /e ...
- Spring Boot Security 基于角色的访问控制
@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //如果配置为需要登录 if (needLogin) ...
- 今年暑假不AC【贪心】
Problem Description "今年暑假不AC?""是的.""那你干什么呢?""看世界杯呀,笨蛋!"" ...
- Python爬虫获取异步加载站点pexels并下载图片(Python爬虫实战3)
1. 异步加载爬虫 对于静态页面爬虫很容易获取到站点的数据内容,然而静态页面需要全量加载站点的所有数据,对于网站的访问和带宽是巨大的挑战,对于高并发和大访问访问量的站点来说,需要使用AJAX相关的技术 ...
- redis学习系列——redis持久化
1.写操作的流程 2.RDB快照-redis的第一个持久化策略 第一种是以快照的形式持久化到本地磁盘(RDB文件). 持久化策略是: 1.配置(save N M)在N秒内,redis至少发生M次修改, ...
- openlayers渲染mapbox gl的vector tile
准备条件 https://openlayers.org/en/v4.6.5/build/ol.js https://cdn.polyfill.io/v2/polyfill.min.js DEMO &l ...
