hmac的python实现
Hash-based message authentication code,利用哈希算法,以一个密钥和一个消息为输入,生成一个消息摘要作为输出
可以查看python的内置模块hmac.py的源码来学习hmac的用法
举例:
一、
import hmac
import hashlib
mac = hmac.new('secret_key','message_be_crypted',hashlib.md5)#第一个参数是密钥key,第二个参数是待加密的字符串,第三个参数是hash函数
print mac.digest()#打印出字符串的ascii格式
5 print mac.hexdigest()#打印出加密后字符串的十六进制格式 >>> mac=hmac.new('secret_key','ssssddddddd',hashlib.sha1)
>>> mac.digest()
'g\x98\xfeZ\x1a\x99\xccm\x82\x8f\xa7\xa6\x13\xc6\x96\x0c\\;\xd5b' #ascii码格式,里面包含十六进制格式
>>> mac.hexdigest()
'6798fe5a1a99cc6d828fa7a613c6960c5c3bd562' #把上面的ascii码转换为十六机制格式:\x98-->98;g-->十进制的103-->十六进制的0x67-->67
>>> >>> ord('g')
103
>>> hex(103)
'0x67'
>>>
二、
1 import hmac
2 import hashlib
3 mac = hmac.new('secret_key',digestmod=hashlib.md5)
4 mac.update('message_be_crypted')
5 print mac.digest()
6 print mac.hexdigest() >>> mac=hmac.new('secret_key',digestmod=hashlib.sha1)
>>> mac.update('ssssddddddd')
>>> mac.digest()
'g\x98\xfeZ\x1a\x99\xccm\x82\x8f\xa7\xa6\x13\xc6\x96\x0c\\;\xd5b' #ascii码格式,里面包含十六进制格式
>>> mac.hexdigest()
'6798fe5a1a99cc6d828fa7a613c6960c5c3bd562' #把上面的ascii码转换为十六机制格式:\x98-->98;g-->十进制的103-->十六进制的0x67-->67
>>> >>> ord('g')
103
>>> hex(103)
'0x67'
>>>
三、hmac.py源码:支持的hash(散列)函数为==>'md5', 'sha1', 'sha224', 'sha256', 'sha384', 'sha512'
"""HMAC (Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication) Python module. Implements the HMAC algorithm as described by RFC 2104.
""" import warnings as _warnings from operator import _compare_digest as compare_digest trans_5C = "".join ([chr (x ^ 0x5C) for x in xrange(256)])
trans_36 = "".join ([chr (x ^ 0x36) for x in xrange(256)]) # The size of the digests returned by HMAC depends on the underlying
# hashing module used. Use digest_size from the instance of HMAC instead.
digest_size = None # A unique object passed by HMAC.copy() to the HMAC constructor, in order
# that the latter return very quickly. HMAC("") in contrast is quite
# expensive.
_secret_backdoor_key = [] class HMAC:
"""RFC 2104 HMAC class. Also complies with RFC 4231. This supports the API for Cryptographic Hash Functions (PEP 247).
"""
blocksize = 64 # 512-bit HMAC; can be changed in subclasses. def __init__(self, key, msg = None, digestmod = None):
"""Create a new HMAC object. key: key for the keyed hash object.
msg: Initial input for the hash, if provided.
digestmod: A module supporting PEP 247. *OR*
A hashlib constructor returning a new hash object.
Defaults to hashlib.md5.
""" if key is _secret_backdoor_key: # cheap
return if digestmod is None:
import hashlib
digestmod = hashlib.md5 if hasattr(digestmod, '__call__'):
self.digest_cons = digestmod
else:
self.digest_cons = lambda d='': digestmod.new(d) self.outer = self.digest_cons()
self.inner = self.digest_cons()
self.digest_size = self.inner.digest_size if hasattr(self.inner, 'block_size'):
blocksize = self.inner.block_size
if blocksize < 16:
# Very low blocksize, most likely a legacy value like
# Lib/sha.py and Lib/md5.py have.
_warnings.warn('block_size of %d seems too small; using our '
'default of %d.' % (blocksize, self.blocksize),
RuntimeWarning, 2)
blocksize = self.blocksize
else:
_warnings.warn('No block_size attribute on given digest object; '
'Assuming %d.' % (self.blocksize),
RuntimeWarning, 2)
blocksize = self.blocksize if len(key) > blocksize:
key = self.digest_cons(key).digest() key = key + chr(0) * (blocksize - len(key))
self.outer.update(key.translate(trans_5C))
self.inner.update(key.translate(trans_36))
if msg is not None:
self.update(msg) ## def clear(self):
## raise NotImplementedError, "clear() method not available in HMAC." def update(self, msg):
"""Update this hashing object with the string msg.
"""
self.inner.update(msg) def copy(self):
"""Return a separate copy of this hashing object. An update to this copy won't affect the original object.
"""
other = self.__class__(_secret_backdoor_key)
other.digest_cons = self.digest_cons
other.digest_size = self.digest_size
other.inner = self.inner.copy()
other.outer = self.outer.copy()
return other def _current(self):
"""Return a hash object for the current state. To be used only internally with digest() and hexdigest().
"""
h = self.outer.copy()
h.update(self.inner.digest())
return h def digest(self):
"""Return the hash value of this hashing object. This returns a string containing 8-bit data. The object is
not altered in any way by this function; you can continue
updating the object after calling this function.
"""
h = self._current()
return h.digest() def hexdigest(self):
"""Like digest(), but returns a string of hexadecimal digits instead.
"""
h = self._current()
return h.hexdigest() def new(key, msg = None, digestmod = None):
"""Create a new hashing object and return it. key: The starting key for the hash.
msg: if available, will immediately be hashed into the object's starting
state. You can now feed arbitrary strings into the object using its update()
method, and can ask for the hash value at any time by calling its digest()
method.
"""
return HMAC(key, msg, digestmod)
hmac.py
四、方法:
HMAC(K,m) = H((K ⊕ opad) ∥ H((K ⊕ ipad) ∥ m))
【opad重复0x36,ipad重复0x5C】
通过两次hash两个不同的key来生成。 还没有发现有任何的方法来产生碰撞。

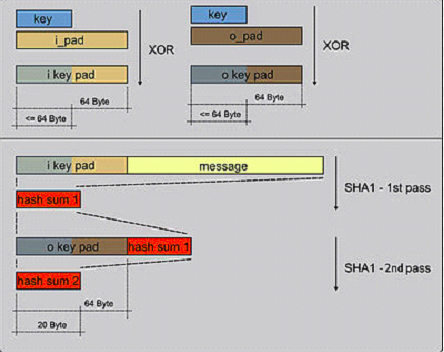
步骤:
First-Hash: H(Ko XOR Ipad || (data to auth))
Second-Hash: H(Ko XOR Opad || First-Hash)
1. 字符含义
H 代表所采用的HASH算法(如SHA-256)
K 代表认证密码
B 代表H中所处理的块大小,这个大小是处理块大小,而不是输出hash的大小 【SHA-1和SHA-256 B = 64,SHA-384和SHA-512 B = 128 】
Ko 代表HASH算法的密文 【在密钥K后面添加0来创建一个字长为B的字符串。(例如,如果K的字长是20字节,B=64字节,则K后会加入44个零字节0x00)
Opad 用0x5a重复B次
Ipad 用0x36重复B次
2. Ko与ipad做异或运算。
3. 将数据流text填充至第2步的结果字符串中
4. 用H作用于第3步生成的数据流。
5. Ko与opad做异或运算。
6. 再将第4步的结果填充进第5步的结果中。
7. 用H作用于第6步生成的数据流,输出最终结果
五、应用场景:
HMAC的一个典型应用是用在“挑战/响应”(Challenge/Response)身份认证中
1. 客户端向服务器发出一个验证请求
2. 服务器接到此请求后生成一个随机数并通过网络传输给客户端(此为挑战)
3. 客户端将收到的随机数提供给ePass,由ePass使用该随机数与存储在ePass中的密钥进行HMAC-MD5运算并得到一个结果作为认证证据传给服务器(此为响应)。
4. 与此同时,服务器也使用该随机数与存储在服务器数据库中的该客户密钥进行HMAC-MD5运算,如果服务器的运算结果与客户端传回的响应结果相同,则认为客户端是一个合法用户
六、安全性:
HMAC算法更象是一种加密算法,它引入了密钥,其安全性已经不完全依赖于所使用的HASH算法
1. 使用的密钥是双方事先约定的,第三方不可能知道。能够得到的信息只有作为“挑战”的随机数和作为“响应”的HMAC结果,无法根据这两个数据推算出密钥。由于不知道密钥,所以无法仿造出一致的响应。
2. HMAC与一般的加密重要的区别在于它具有“瞬时”性,即认证只在当时有效
六、MAC与HMAC:HMAC是MAC的hash方式实现
消息认证码可以使用单向散列函数和对称密码等技术来实现

参考:
1、http://www.jianshu.com/p/8d7c8f59ea21
2、http://www.ftsafe.com.cn/service/kbase/infomation-2
hmac的python实现的更多相关文章
- Python的平凡之路(5)
一.模块介绍 定义: 模块--用来从逻辑上组织python代码(变量,函数,类,逻辑:实现一个功能),本质就是.py结尾的python文件(文件名test.py,模块名test) 包—用来从逻辑上组织 ...
- python成长之路第三篇(4)_作用域,递归,模块,内置模块(os,ConfigParser,hashlib),with文件操作
打个广告欢迎加入linux,python资源分享群群号:478616847 目录: 1.作用域 2.递归 3.模块介绍 4.内置模块-OS 5.内置模块-ConfigParser 6.内置模块-has ...
- python之路第五篇之模块和加密算法(进阶篇:续)
模块 Python中,如果要引用一些内置的函数,该怎么处理呢?在Python中有一个概念叫做模块(module) 简单地说,模块就是一个保存了Python代码的文件. 模块分类: 1)内置模块 2)自 ...
- hashlib hmac configparser subprocess xlrd xlwt
hashlib模块:加密 import hashlib # 基本使用 cipher = hashlib.md5('需要加密的数据的二进制形式'.encode('utf-8')) print(ciphe ...
- python之hashlib
简介: 用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供SHA1,SHA224,SHA256,SHA384,SHA512,MD5算法.在python3中已经废弃了md5和sha模块,简单说明 ...
- Day6 Python常用的模块
一.logging模块 一.日志级别 critical=50 error=40 waring=30 info=20 debug=10 notset=0 二.默认的日志级别是waring(30),默认的 ...
- Python常用模块(logging&re&时间&random&os&sys&shutil&序列化&configparser&&hashlib)
一. logging(日志模块) 二 .re模块 三. 时间模块 四. random模块 五. os模块 六. sys模块 七. shutil模块 八. 序列化模块(json&pickle&a ...
- Python学习day17-常用的一些模块
figure:last-child { margin-bottom: 0.5rem; } #write ol, #write ul { position: relative; } img { max- ...
- python常用模块集合
python常用模块集合 Python自定义模块 python collections模块/系列 Python 常用模块-json/pickle序列化/反序列化 python 常用模块os系统接口 p ...
随机推荐
- iOS大神班笔记01-项目中常见的文件
1.Info.plist文件:项目配置文件 主要作用:保存应用的信息,软件名称等等,相当于身份 证.程序加载首先加载配置文件,读取软件名称等信息. Bundle display name:项目名称 B ...
- ZOJ 1081 Points Within | 判断点在多边形内
题目: 给个n个点的多边形,n个点按顺序给出,给个点m,判断m在不在多边形内部 题解: 网上有两种方法,这里写一种:射线法 大体的思想是:以这个点为端点,做一条平行与x轴的射线(代码中射线指向x轴正方 ...
- Iterator pattern 及其在java API中的运用
1.问题: 当我们看到java中的Collection,List,Set,Map等集合类时都可以用Iterator进行遍历元素时,我们是否感到很神奇.我们不禁要问java是如何实现这一目标的.这就是我 ...
- Nodejs express框架 浅析
http://www.expressjs.com.cn/ 1. 中间件 ①挂载中间件的函数:app.use var http = require('http'); var express = requ ...
- 快速激活最新JetBrains公司系列产品包括最新的phpstorm10
快速激活最新JetBrains公司系列产品包括最新的phpstorm10 IntelliJ IDEA开源社区 提供了如下通用激活方法: 注册时选择License server 然后输入框填写:http ...
- C/S模式和BS模式是什么?
C/S是Client/Server,即客户端/服务器:B/S是Browser/Server,即浏览器/服务器的意思. C/S (Client/Server)结构,即大家熟知的客户机和服务器结构.它 ...
- BEE网站
http://www.bee-framework.com/ http://syxiaqj.github.io/2014/02/28/bee-learning-1/#0-tsina-1-24637-39 ...
- 几种常见的YUV格式--yuv422:yuv420【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/u012288815/article/details/51799477 关于yuv 格式 YUV 格式通常有两大类:打包(packed)格式和平面(pl ...
- v4l2读取摄像头程序流程解析【转】
转自:https://my.oschina.net/u/1024767/blog/210801 v4l2 操作实际上就是 open() 设备, close() 设备,以及中间过程的 ioctl() 操 ...
- js5秒后自动关闭本页面及5秒钟后自动跳转指定页面的方法
5秒钟后自动关闭 <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <title>倒计时自动关闭/跳转页面</title> < ...
