Tree - Rooted Trees
Rooted Trees
A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite set of vertices and E is a binary relation on Vrepresented by a set of edges. Fig. 1 illustrates an example of a graph (or graphs).
Fig. 1
A free tree is a connnected, acyclic, undirected graph. A rooted tree is a free tree in which one of the vertices is distinguished from the others. A vertex of a rooted tree is called "node."
Your task is to write a program which reports the following information for each node u of a given rooted tree T:
- node ID of u
- parent of u
- depth of u
- node type (root, internal node or leaf)
- a list of chidlren of u
If the last edge on the path from the root r of a tree T to a node x is (p, x), then p is the parent of x, and xis a child of p. The root is the only node in T with no parent.
A node with no children is an external node or leaf. A nonleaf node is an internal node
The number of children of a node x in a rooted tree T is called the degree of x.
The length of the path from the root r to a node x is the depth of x in T.
Here, the given tree consists of n nodes and evey node has a unique ID from 0 to n-1.
Fig. 2 shows an example of rooted trees where ID of each node is indicated by a number in a circle (node). The example corresponds to the first sample input.
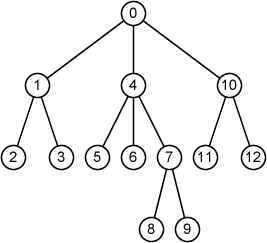
Fig. 2
Input
The first line of the input includes an integer n, the number of nodes of the tree.
In the next n lines, the information of each node u is given in the following format:
id k c1 c2 ... ck
where id is the node ID of u, k is the degree of u, c1 ... ck are node IDs of 1st, ... kth child of u. If the node does not have a child, the k is 0.
Output
Print the information of each node in the following format ordered by IDs:
node id: parent = p , depth = d, type, [c1...ck]
p is ID of its parent. If the node does not have a parent, print -1.
d is depth of the node.
type is a type of nodes represented by a string (root, internal node or leaf). If the root can be considered as a leaf or an internal node, print root.
c1...ck is the list of children as a ordered tree.
Please follow the format presented in a sample output below.
Constraints
- 1 ≤ n ≤ 100000
Sample Input 1
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
Sample Output 1
node 0: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [1, 4, 10]
node 1: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [2, 3]
node 2: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 3: parent = 1, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 4: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [5, 6, 7]
node 5: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 6: parent = 4, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 7: parent = 4, depth = 2, internal node, [8, 9]
node 8: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, []
node 9: parent = 7, depth = 3, leaf, []
node 10: parent = 0, depth = 1, internal node, [11, 12]
node 11: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, []
node 12: parent = 10, depth = 2, leaf, []
Sample Input 2
4
1 3 3 2 0
0 0
3 0
2 0
Sample Output 2
node 0: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
node 1: parent = -1, depth = 0, root, [3, 2, 0]
node 2: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
node 3: parent = 1, depth = 1, leaf, []
Note
You can use a left-child, right-sibling representation to implement a tree which has the following data:
- the parent of u
- the leftmost child of u
- the immediate right sibling of u
Reference
Introduction to Algorithms, Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. The MIT Press.
有根树的存储, 根据数据看出不是二叉树, 故用孩子兄弟表示法存储(左孩子, 右兄弟)
利用递归求树的深度时, 若是左孩子则深度加一, 右孩子(兄弟节点)还是当前深度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100005
#define NIL -1 struct Node {
int parent;
int left;
int right;
}; Node T[MAX];
int n, D[MAX]; void print(int u)
{
int i, c;
cout << "node " << u << ": ";
cout << "parent = " << T[u].parent << ", ";
cout << "depth = " << D[u] << ", "; if(T[u].parent == NIL)
{
cout << "root, ";
}
else if(T[u].left == NIL)
{
cout << "leaf, ";
}
else
{
cout << "internal node, ";
} cout << "["; for(i = 0, c = T[u].left; c != NIL; ++ i, c = T[c].right)
{
if(i) cout << ", ";
cout << c;
} cout << "]" << endl;
} // 递归求深度
void rec(int u, int p)
{
D[u] = p;
if(T[u].right != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].right, p);
}
if(T[u].left != NIL)
{
rec(T[u].left, p + 1);
}
} int main()
{
int i, j, d, v, c, l, r;
cin >> n;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
T[i].parent = T[i].left = T[i].right = NIL;
} for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
cin >> v >> d;
for(j = 0; j < d; ++ j)
{
cin >> c;
if(j == 0)
{
T[v].left = c; // 父节点的左孩子为c
}
else
{
T[l].right = c; // 当前兄弟节点为c
}
l = c; // 记录前一个兄弟节点
T[c].parent = v;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
if(T[i].parent == NIL)
{
r = i;
}
} rec(r, 0); for(i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
print(i);
} return 0;
} /*
13
0 3 1 4 10
1 2 2 3
2 0
3 0
4 3 5 6 7
5 0
6 0
7 2 8 9
8 0
9 0
10 2 11 12
11 0
12 0
*/
Tree - Rooted Trees的更多相关文章
- HDU p1294 Rooted Trees Problem 解题报告
http://www.cnblogs.com/keam37/p/3639294.html keam所有 转载请注明出处 Problem Description Give you two definit ...
- 【Aizu - ALDS1_7_A】Rooted Trees(树的表达)
Rooted Trees Descriptions: A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite set of vertice ...
- 有根树的表达 Aizu - ALDS1_7_A: Rooted Trees
有根树的表达 题目:Rooted Trees Aizu - ALDS1_7_A A graph G = (V, E) is a data structure where V is a finite ...
- 10.3 Implementing pointers and objects and 10.4 Representing rooted trees
Algorithms 10.3 Implementing pointers and objects and 10.4 Representing rooted trees Allocating an ...
- HDU1294 Rooted Trees Problem(整数划分 组合数学 DP)
讲解见http://www.cnblogs.com/IMGavin/p/5621370.html, 4 可重组合 dfs枚举子树的节点个数,相乘再累加 1 #include<iostream& ...
- HDU 1294 Rooted Trees Problem
题目大意:求有n个节点的树有几种? 题解:http://www.cnblogs.com/keam37/p/3639294.html #include <iostream> typedef ...
- [LeetCode] Minimum Height Trees 最小高度树
For a undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result gra ...
- Minimum Height Trees
For a undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result gra ...
- LeetCode Minimum Height Trees
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/ 题目: For a undirected graph with tree cha ...
随机推荐
- ios audio不能自动播放
今天做了一个简单的落地页项目,就是类似于手机微信上经常看到的滑动效果.因为公司要求需要自己开发,所以我就用swiper+swiper.animate开发,开发速度很快,只不过最后音乐哪里出现了一点小b ...
- IntelliJ IDEA 安装配置
之前一直用的eclipse,以前公司的老大推荐过用这个,但是由于项目都比较赶,没及时学习. 后面这个公司的同时都用的idea,所以就换了 其实并没有那么难主要是刚刚切换时候快捷键不熟悉,打包什么的,有 ...
- 关于使用flying-saucer-pdf,实现xhtml2pdf
@author Guoguo 2013.11.24 关于flying-saucer-pdf 是一个XML/CSS渲染器,flying-saucer-pdf工具以XML标准文件作为输入,CSS进行排版. ...
- 关于iframe中使用fixed定位的一些问题
先来看看position: fixed:的定义:生成绝对定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位: 但是在iframe中使用fixed定位,实际上是相对于iframe窗口进行定位,原因在于iframe类似 ...
- flask 服务器详解
#!/usr/local/bin/python # coding=utf-8 from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') ...
- 按需引入antd
使用create-react-app创建项目的时候,官网推荐使用 babel-plugin-import 对antd 按需引入文件.但是配置文件在项目里没有. 可以直接在package.json里加上 ...
- IsWindow,findwindow
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/ahuo/archive/2007/12/05/983354.html IsWindow 函数功能:该函数确定给定的窗口句柄是否识别一个已存在的窗口 ...
- Python3.5 使用Sqlite3
-------------------- 修雨轩陈@cnblog Python3.5 使用Sqlite3 python3.5 安装的时候会有很多可选参数,这些参数是默认不提供的,可是当我们想通过pip ...
- 在IDEA中设置方法自动注释(带参数和返回值)
第一部分 设置 打开设置面板 新建 在线模板 新建自动添加规则,注意 这里触发的字符 不能随便写 必须为 * Template text 区域 看上去有点乱,但是是为了显示时的对齐,该区域的内容如下( ...
- yii2.0表单自带验证码
Yii2.0的自带的验证依赖于GD2或者ImageMagick扩展. 使用步骤如下: 第一步,控制器: 在任意controller里面重写方法
