[数据结构]P1.1 链表结构
* 注: 本文/本系列谢绝转载,如有转载,本人有权利追究相应责任。 2019年4月8日
Stan Zhang 2019年4月8日 格物致知,经世致用。
[面试题]1.为什么要用链表?
数组具有的缺陷: 数组是长度固定类型固定的,并且它取值快,插入和删除慢。
链表正弥补了这样的不足,它是长度都可以灵活扩展的,另外它是插入和删除快,但是取值非常慢。
查找也比较慢,这是这种线性结构的通病,需要通过散列的思路进行解决,当然一个例外是
有下标的有序线性结构可以使用二分查找提高查找效率。
因此没有最好的,只有最合适的数据结构。
2.链表的分类.
A.单链表:
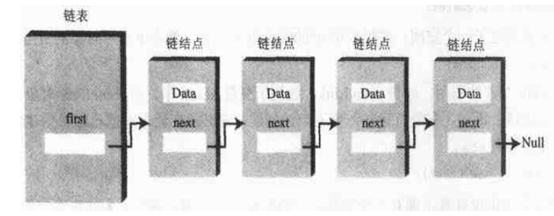
B:双端链表
C:有序链表 : 没有什么突出的优点,只是为了迎合扩展性(长度扩展)以及业务
故名思意,有序链表的序列是有序的。
先比较一下有序数组,有序数组牺牲插入效率来提升查找效率,配合二分查找(利用数组索引)可以LogN级别定位元素。
但是有序链表中有序并不能提升其查找效率(它没有数组的索引)。
List本生就是按照添加的顺序有序的,再引入一个排序标准没有必要,因此Java当中没有SortedList.
而Set本身没有顺序规则,可以设置一个排序,因此当需要使用有序的集合时,我们可以使用SortedSet.
D:双向链表
3.实现
A.单链表
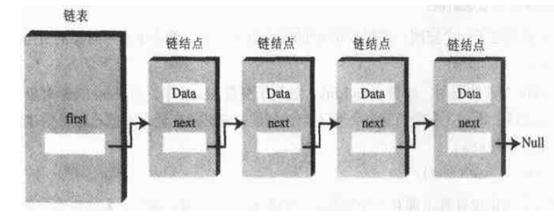
单链表的特点是头部插入快,其他无论是查找、尾部插入还是删除,效率都是N级别的。
Java代码的实现:
package ds1.linked.table.singleDirection; /**
* 单向链表
* 单向链表的表中会存留一个链表的起始端 Node first,这导致从尾部插入数据非常麻烦需要花费O(N)的时间
*/
public class SingleDirectionList {
static class Node {
Node next;
String data;
Node(String data){
this.data = data;
}
} static class LinkedList{
Node first; // 保存第一个节点 public LinkedList(){
} public LinkedList(Node first) {
this.first = first;
} public void foreachPrint(){
if(first == null){
System.out.println("[]");
}else{
System.out.print("[" + this.first.data);
Node current = first.next;
while(current != null){
System.out.print("," + current.data);
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
} /**
* 插入节点的时间复杂度: O(1)
* @param node
*/
public void addNode(Node node){
if(first == null){
this.first = node;
}else{
node.next = this.first;
this.first = node;
}
} /**
* 删除节点的时间复杂度: O(N)
* @param node
*/
public void removeNode(Node node){
if(this.first == null){
return;
} if(this.first.equals(node)){
this.first = this.first.next;
node.next = null;
return;
}
Node current = this.first;
Node before = current;
while(current.next != null){
if(current.equals(node)){
before.next = current.next;
node.next = null;
break;
}
before = current;
current = current.next;
}
} /**
* 查找节点的时间复杂度: O(N)
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node findNodeByData(String data){
Node result = null;
Node current = this.first;
while(current != null){
if(current.data != null && current.data.equals(data)){
result = current;
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
} } public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
Node node1 = new Node("node1");
Node node2 = new Node("node2");
Node node3 = new Node("node3");
Node node4 = new Node("node4");
Node node5 = new Node("node5");
Node node6 = new Node("node6");
Node node7 = new Node("node7");
linkedList.addNode(node1);
linkedList.addNode(node2);
linkedList.addNode(node3);
linkedList.addNode(node4);
linkedList.addNode(node5);
linkedList.addNode(node6);
linkedList.addNode(node7);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
Node tmpNode4 = linkedList.findNodeByData("node4");
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNode(tmpNode4);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
}
}
结果:
[node7,node6,node5,node4,node3,node2,node1]
[node7,node6,node5,node4,node3,node2,node1]
[node7,node6,node5,node3,node2,node1]
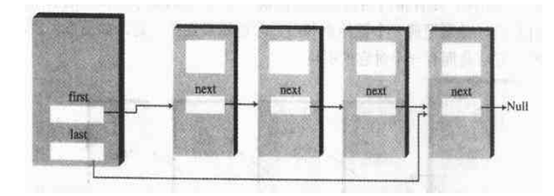
B.双端链表

双端链表具有两个端点指针,分别指向收尾指针。它具有首位快速插入,首部快速删除的能力。但是因为还是单向的,因此尾部删除性能不佳。
Java代码:
package ds1.linked.table.twoHead; import ds1.linked.table.singleDirection.SingleDirectionList; /**
* 双端列表
* 有两个端点
*/
public class TwoHeadLinkedList {
static class Node{
Node next;
String data; public Node(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
} static class LinkedList{
Node first;
Node tail; public LinkedList(){
} public LinkedList(Node node){
this();
addNodeToHead(node);
} /**
* 从首部添加一个节点
* 常数时间
* @param node
*/
public void addNodeToHead(Node node){
if(this.first == null){
this.first = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
node.next = this.first;
this.first = node;
}
} /**
* 删除头节点
* 常数时间
*/
public void removeHead(){
if(this.first != null){
if(this.first == this.tail){
this.tail = null;
}
this.first = this.first.next;
}
} /**
* 添加尾部节点
* 常数时间
* @param node
*/
public void addNodeTail(Node node){
if(this.tail != null){
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
this.first = this.tail = node;
}
} /**
* 删除尾部节点
* 线性时间
*/
public void removeTailNode(){
if(this.first == null){
return;
}
if(this.first == this.tail){
this.first = this.tail = null;
return;
} Node current = this.first;
Node before = current;
while(current.next != null){
before = current;
current = current.next;
}
before.next = null;
this.tail = before;
} /**
* 查找一个节点
* 时间复杂度: 线性时间
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node findByData(String data){
Node result = null;
if(this.first == null){
return result;
}
Node current = this.first;
while(current != null){
if(current.data != null && current.data.equals(data)){
result = current;
break;
}
current = current.next;
} return result;
} /**
* 删除一个节点
* 时间复杂度:线性时间
* @param node
*/
public void removeNode(Node node){
if(this.first == null){
return;
} if(this.first.equals(node)){
this.first = node.next;
} Node current = this.first;
Node before = current;
while(current != null){
if(current == node){
before.next = current.next;
break;
}
before = current;
current = current.next;
} if(this.tail == node){
this.tail = before;
}
} public void foreachPrint(){
if(first == null){
System.out.println("[]");
}else{
System.out.print("[" + this.first.data);
Node current = first.next;
while(current != null){
System.out.print("," + current.data);
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
} } public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
Node node1 = new Node("node1");
Node node2 = new Node("node2");
Node node3 = new Node("node3");
Node node4 = new Node("node4");
Node node5 = new Node("node5");
Node node6 = new Node("node6");
Node node7 = new Node("node7");
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node1);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node2);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeTail(node3);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node4);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeTail(node5);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node6);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeTail(node7);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
Node tmpNode4 = linkedList.findByData("node4");
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNode(tmpNode4);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
} }
结果:
[node1]
[node2,node1]
[node2,node1,node3]
[node4,node2,node1,node3]
[node4,node2,node1,node3,node5]
[node6,node4,node2,node1,node3,node5]
[node6,node4,node2,node1,node3,node5,node7]
[node6,node4,node2,node1,node3,node5,node7]
[node6,node2,node1,node3,node5,node7]
C:有序链表 : 没有什么突出的优点,只是为了迎合扩展性(长度扩展/类型扩展)以及业务
package ds1.linked.table.orderedList;
public class OrderedList {
static class Node{
Node next;
long data;
public Node(long data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
static class LinkedList{
Node first;
LinkedList(){
}
public void foreachPrint(){
if(first == null){
System.out.println("[]");
}else{
System.out.print("[" + this.first.data);
Node current = first.next;
while(current != null){
System.out.print("," + current.data);
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
/**
* 插入过程,线性时间
* @param node
*/
public void insert(Node node){
if(this.first == null){
this.first = node;
return;
}
if(this.first.data > node.data){
node.next = this.first;
this.first = node;
return;
}
Node current = this.first;
Node before = current;
while(current != null){
if(current.data > node.data){
node.next = current;
before.next = node;
break;
}
before = current;
current = current.next;
}
if(current == null){
before.next = node;
}
}
/**
* 查找过程: 不能利用二分查找,还是线性时间
* @param data
*/
public Node findByValue(long data){
Node result = null;
Node current = this.first;
while (current != null){
if(current.data == data){
result = current;
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return result;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insert(new Node(100));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.insert(new Node(200));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.insert(new Node(122));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.insert(new Node(39));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.insert(new Node(103));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.insert(new Node(145));
linkedList.foreachPrint();
}
}
结果:
[]
[,]
[,,]
[,,,]
[,,,,]
[,,,,,]
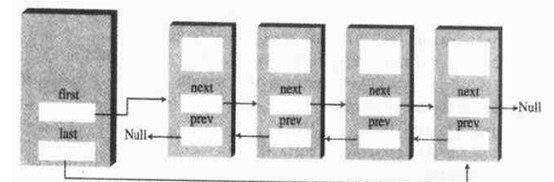
D:双向链表

双向链表很好的利用了双端和双向的优势,使得双端的插入删除操作变为常数级别。
package ds1.linked.table.twoHeadTwoDirection; /**
* 双向链表
* 有双端点双向,也就意味着两头的插入删除效率都是线性的。
*/
public class TwoHeadTwoDirectionList {
static class Node {
Node next;
Node before;
String data;
Node(String data){
this.data = data;
}
} static class LinkedList{
Node first; // 保存第一个节点
Node tail; // 保留最后一个节点 public LinkedList(){
} public LinkedList(Node first) {
this.first = this.tail = first;
} public void foreachPrint(){
if(first == null){
System.out.println("[]");
}else{
System.out.print("[" + this.first.data);
Node current = first.next;
while(current != null){
System.out.print("," + current.data);
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
} /**
* 插入头节点的时间复杂度:线性
* @param node
*/
public void addNodeToHead(Node node){
if(first == null){
this.first = this.tail = node;
}else{
node.next = this.first;
this.first = node;
}
} /**
* 删除头节点的时间复杂度:线性时间
*/
public void removeNodeFromHead(){
if(this.first != null){
Node tmp = this.first.next;
this.first.next = null;
this.first = tmp;
}
} /**
* 尾部新增一个节点
* 线性时间
* @param node
*/
public void addNodeToTail(Node node){
if(this.tail == null){
this.tail = node;
}else{
node.before = this.tail;
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
} /**
* 从尾部删除节点
* 线性时间
*/
public void removeNodeFromTail(){
if(this.tail != null){
Node tmp = this.tail;
this.tail = this.tail.before;
this.tail.next = null;
tmp.before = null;
}
} /**
* 删除节点的时间复杂度: O(N)
* @param node
*/
public void removeNode(Node node){
if(this.first == null){
return;
} if(this.first.equals(node)){
this.first = this.first.next;
node.next = null;
return;
}
Node current = this.first;
Node before = current;
while(current.next != null){
if(current.equals(node)){
before.next = current.next;
before.next.before = before;
node.next = null;
node.before = null;
break;
}
before = current;
current = current.next;
}
} /**
* 查找节点的时间复杂度: O(N)
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node findNodeByData(String data){
Node result = null;
Node current = this.first;
while(current != null){
if(current.data != null && current.data.equals(data)){
result = current;
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
} } public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
Node node1 = new Node("node1");
Node node2 = new Node("node2");
Node node3 = new Node("node3");
Node node4 = new Node("node4");
Node node5 = new Node("node5");
Node node6 = new Node("node6");
Node node7 = new Node("node7");
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node1);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node2);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToTail(node3);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node4);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToTail(node5);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToTail(node6);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.addNodeToHead(node7);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
Node tmpNode4 = linkedList.findNodeByData("node4");
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNode(tmpNode4);
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNodeFromHead();
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNodeFromTail();
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNodeFromTail();
linkedList.foreachPrint();
linkedList.removeNodeFromHead();
linkedList.foreachPrint();
}
}
结果:
[node1]
[node2,node1]
[node2,node1,node3]
[node4,node2,node1,node3]
[node4,node2,node1,node3,node5]
[node4,node2,node1,node3,node5,node6]
[node7,node4,node2,node1,node3,node5,node6]
[node7,node4,node2,node1,node3,node5,node6]
[node7,node2,node1,node3,node5,node6]
[node2,node1,node3,node5,node6]
[node2,node1,node3,node5]
[node2,node1,node3]
[node1,node3]
[数据结构]P1.1 链表结构的更多相关文章
- 数据结构:单链表结构字符串(python版)改进
此篇文章的replace实现了字符串类的多次匹配,但依然有些不足. 因为python字符串对象为不变对象,所以replace方法并不修改原先的字符串,而是返回修改后的字符串. 而此字符串对象时用单链表 ...
- 数据结构:单链表结构字符串(python版)添加了三个新功能
#!/urs/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #异常类 class stringTypeError(TypeError): pass #节点类 class ...
- 数据结构:单链表结构字符串(python版)
#!/urs/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #异常类 class stringTypeError(TypeError): pass #节点类 class ...
- 【C&数据结构】---关于链表结构的前序插入和后序插入
刷LeetCode题目,需要用到链表的知识,忽然发现自己对于链表的插入已经忘得差不多了,以前总觉得理解了记住了,但是发现真的好记性不如烂笔头,每一次得学习没有总结输出,基本等于没有学习.连复盘得机会都 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第4章:数据和链表结构
数据结构是表示一个集合中包含的数据的一个对象 数组数据结构 数组是一个数据结构 支持按照位置对某一项的随机访问,且这种访问的时间是常数 在创建数组时,给定了用于存储数据的位置的一个数目,并且数组的长度 ...
- 《Java数据结构》链表结构(单向链表,双向链表)
单向链表(单链表)是链表的一种,其特点是链表的链接方向是单向的,对链表的访问要通过顺序读取从头部开始:链表是使用指针进行构造的列表:又称为结点列表,因为链表是由一个个结点组装起来的:其中每个结点都有指 ...
- python数据结构与算法——链表
具体的数据结构可以参考下面的这两篇博客: python 数据结构之单链表的实现: http://www.cnblogs.com/yupeng/p/3413763.html python 数据结构之双向 ...
- [pjsip]Pjlib中的链表结构
Pjlib的链表结构跟常见的链表结构有所区别,如下图所示: 图1:一般链表结构 图2:pjlib中的链表结构 可以看到一般的双向链表是链表节点包含数据域,而pjlib中是数据域包含链表节点.一般的链表 ...
- 数据结构与算法 —— 链表linked list(01)
链表(维基百科) 链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的指针(Pointer).由于不必须按顺序存储, ...
随机推荐
- [No0000197]Windows用户都应该知道的运行命令
通过"运行"命令,运行Windows丰富工具的方法.如果您知道工具或任务的相应"运行"命令,那么您就知道访问所述工具或任务的最快方法. 以下是我们最喜欢的Run ...
- Spark入门到精通--(第二节)Scala编程详解基础语法
Scala是什么? Scala是以实现scaleable language为初衷设计出来的一门语言.官方中,称它是object-oriented language和functional languag ...
- echart 判断数据是否为空
formatter 判断数据是否为空
- mysql报错Ignoring the redo log due to missing MLOG_CHECKPOINT between
mysql报错Ignoring the redo log due to missing MLOG_CHECKPOINT between mysql版本:5.7.19 系统版本:centos7.3 由于 ...
- nginx cookie 丢失问题
- Django配置相关及其它
配置 模板 TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [ os.pat ...
- JDBC-DAO层数据访问工具类的实现
private static PreparedStatement pst; private static ResultSet rst; public static <T> int inse ...
- LCA Tarjan方法
LCA Tarjan方法 不得不说,高中生好厉害,OI大佬,感觉上个大学好憋屈啊! 说多了都是眼泪 链接拿去:http://www.cnblogs.com/JVxie/p/4854719.html
- HP Jack介绍
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/Peter-Chen/p/3999212.html 目前市场上耳机分为4环耳机(图1所示,iphone型)和3环耳机(图2所示).4环耳机称为he ...
- K均值
K-means算法的工作流程 首先,随机确定k个初始点的质心:然后将数据集中的每一个点分配到一个簇中,即为每一个点找到距其最近的质心,并将其分配给该质心所对应的簇:该步完成后,每一个簇的质心更新为该簇 ...
