[C++ Primer Plus] 第7章、函数(二)课后习题
一、复习题
6.为什么不对基本数据类型的函数参数使用const?

8.编写一个函数,将字符串中所有c1替换成c2,并返回替换次数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; int replace(char *str, char c1, char c2) {
int n = ;
while (*str)
{
if (*str == c1) {
*str = c2;
n++;
}
str++;
}
return n;
} void main()
{
char str[] = "i love china,i love cpp";
cout << str << endl;
int n=replace(str, 'l', 'L');
cout << str << endl<<n<<endl;
system("pause");
}


typedef int zheng;//给int取个小名,可以用zheng代替int
zheng a = ;
struct app {
char name[];
int credit[];
};
void f1(app *a);
const char * f2(const app *a1, const app *a2);
typedef void(*p_f1) (app *);
typedef const char * (*p_f2) (const app *, const app *);
void main()
{
p_f1 p1 = f1;//void(*p1)(app *) = f1;
p_f2 p2 = f2;//const char *(*p1)(const app*, const app*) = f2;
p_f1 ap[];//void(*ap[5])(app *);
p_f2 ap2[];p_f2 *pa = ap2;//p_f2 (*pa)[10];
//或者 const char *(*pa[10])(const app*, const app*);
}
二、编程练习
1.编写一个程序,不断要求用户输入两个数,直到其中一个为0。对于每两个数,程序将使用一个函数来计算它们的调和平均数,并将结果返回给main(),而后者将报告结果。调和平均数指的是倒数平均值的倒数,计算公式如下:
调和平均数 = 2.0 * x * y / (x + y)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; double fun(double a, double b) {
if (a == -b) {
cout << "调和平均数的分母不能为0" << endl;
return ;
}
return 2.0*a*b / (a + b);
} void main()
{
cout << "请输入两个数(输入0结束):";
double a, b, ave;
while (cin >> a >> b&&a&&b)
{
ave = fun(a, b);
if (ave == )
cout << "请重新输入两个数(输入0结束):";
else {
cout << "调和平均数为:" << ave << endl;
cout << "请输入两个数(输入0结束):";
}
}
system("pause");
}

2.编写一个程序,要求用户输入最多10个高尔夫成绩,并将其存储在一个数组中。程序允许用户提早结束输入,并在 一行上显示所有成绩,然后报告平均成绩。请使用3个数组处理函数来分别进行输入、显示和计算平均成绩。请使用3个数组 处理函数来分别进行输入、显示和计算平均成绩。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; int input(double *arr) {
cout << "请输入高尔夫成绩:" << endl;
int n;
for (n = ; n < ; n++)
{
cout << "请输入第" << n+ << "次的成绩(q结束输入):";
if (!(cin >> arr[n]))
break;
}
return n;
} void show(double *arr,int n) {
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
} double ave(double *arr,int n) {
if (n == )
return ;
double sum=0.0;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
return sum / n;
} void main()
{
double arr[];
int n=input(arr);
show(arr,n);
cout <<endl<< "平均成绩为" << ave(arr,n) << endl;
system("pause");
}

3.下面是一个结构声明:
struct box
{
char maker[40];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
};
a.编写一个函数,按值传递box结构,并显示每个成员的值
b.编写一个函数,传递box结构的地址,并将volume成员设置为其他三维长度的乘积。
c.编写一个使用这两个函数的简单程序。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; struct box
{
char maker[];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
}; void set(box *b) {
b->volume = b->height*b->length*b->width;
} void show(box b) {
cout << "maker:" << b.maker << endl;
cout << "height:" << b.height << endl;
cout << "width:" << b.width << endl;
cout << "length:" << b.length << endl;
cout << "volume:" << b.volume << endl;
} void main()
{
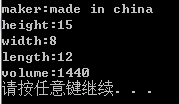
box b = {"made in china",,,};
set(&b);
show(b);
system("pause");
}
4.许多州的彩票发行机构都使用如程序清单7.4所示的简单彩票玩法的变体。在这些玩法中,玩家从一组被称为域号码 (field number)的号码中选择几个。例如,可以从域号码1~47中选择5个号码:还可以从第二个区间(如1~27)选择一个号码 (称为特选号码)。要赢得头奖,必须正确猜中所有的号码。中头奖的几率是选中所有域号码的几率与选中特选号码几率的乘积。 例如,在这个例子中,中头奖的几率是从47个号码中正确选取5个号码的几率与从27个号码中选择1个号码的几率的乘积。请修改程序清单7.4,以计算中得这种彩票头奖的几率。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
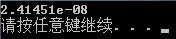
long double ans = 1.0;
for (double i = 0.0; i < 5.0; i++)
ans *=( - i)/( - i);
ans *=1.0/ 27.0;
cout << ans << endl;
system("pause");
}
5.定义一个递归函数,接受一个整型参数,并返回该参数的阶乘。前面讲过,3的阶乘写作3!,等于3 * 2!,以此类推:而0!被定义为1.通用的计算公式是,如果n大于零 , 则n! = n * (n - 1)!。在程序中对该函数进行测试,程序使用循环让用户输入不同的值,程序将报告这些值的阶乘。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; long long recursion(int n) {
if (n == || n == )
return ;
return n*recursion(n - );
} void main()
{
int n;
long long factorial;
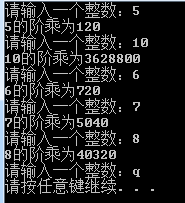
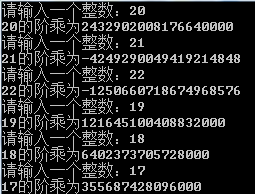
cout << "请输入一个整数:";
while (cin>>n)
{
factorial = recursion(n);
cout << n << "的阶乘为" << factorial << endl;
cout << "请输入一个整数:";
}
system("pause");
}
6.编写一个程序,它使用下列函数:
Fill_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数。它提示用户输入double值,并将这些值存储到数组中。当数组被填满或 用户输入了非数字时,输入将停止,并返回实际输入了多少个数字。 Show_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并显示该数组的内容。 Reverse_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并将存储在数组中的值的顺序反转。 程序将使用这些函数来填充数组,然后显示数组;反转数组,然后显示数组;反转数组中除第一个和最后一个元素之外的所有元素, 然后显示数组。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; void Fill_array(double arr[], int n) {
cout << "请输入一个double值:";
int i = ;
while (n&&cin >> arr[i]) //&&左右表达式换顺序会有截然不同的结果
{
i++, n--;
if(n!=)
cout << "请zai输入一个double值:";
}
cout << "实际输入了"<<i<<"个数字"<<endl;
}
void Show_array(double arr[], int n) {
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void Reverse_array(double arr[], int n) {
for (int i = ; i < n-; i++)
{
if (i >= n / )
break;
int t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[n - - i];
arr[n - - i] = t;
}
} void main()
{
double arr[];
Fill_array(arr, );
Show_array(arr, );
Reverse_array(arr, );
Show_array(arr, );
system("pause");
}

7.修改程序清单7.7中的3个数组处理函数,使之使用两个指针参数来表示区间。file_array()函数不返回实际读取了多少个数字,而是返回一个指针,该指针指向最后被填充的位置:其他的函数可以将该指针作为第二个参数,以标识数据结尾。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; double *fill_array(double *a)
{
int i = ;
while (cin >> a[i++]) {
if (i == )
break;
}
return &a[i];
} void show_array(double *a, double *b)
{
while (a != b) {
cout << *a << "\t";
++a;
}
cout << endl;
} void revalue(double r, double *a, double *b)
{
while (a != b) {
(*a) *= r;
++a;
}
} void main()
{
double a[];
double *e = fill_array(a);
show_array(a, e);
revalue(0.5, a, e);
show_array(a, e);
system("pause");
}
8.在不使用array类的情况下完成程序清单7.15所做的工作。编写两个这样的版本:
a.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用double数组存储开支。
b.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用一个结构,该结构只有一个成员——一个用于存储开支的double数组。这种设计与使用array类的基本设计类似。
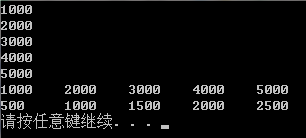
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const char *Sname[] = { "Spring","Summer","Fall","Winter" }; void fill(double *p) {
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << "Enter " << Sname[i] << " expenses:";
cin >> p[i];
}
}
void show(double *p) {
double sum = 0.0;
cout << "EXPENSES" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << Sname[i] << ": $" << p[i] << endl;
sum += p[i];
}
cout << "Sum expenses: $" << sum << endl;
} void main()
{
double expense[];
fill(expense);
show(expense);
system("pause");
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const char *Sname[] = { "Spring","Summer","Fall","Winter" };
struct EXPENSES {
double expense[];
}; void fill(EXPENSES *p) {
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << "Enter " << Sname[i] << " expenses:";
cin >> (*p).expense[i];
}
}
void show(EXPENSES *p) {
double sum = 0.0;
cout << "EXPENSES" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << Sname[i] << ": $" << (*p).expense[i] << endl;
sum += (*p).expense[i];
}
cout << "Sum expenses: $" << sum << endl;
} void main()
{
EXPENSES e;
fill(&e);
show(&e);
system("pause");
}
9.这个练习让您编写处理数组和结构的函数。下面是程序的框架,请提供其中描述的函数,以完成该程序。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int SLEN = ;
struct student {
char fullname[SLEN];
char hobby[SLEN];
int ooplevel;
};
int getinfo(student pa[], int n);
void display1(student st);
void display2(const student * ps);
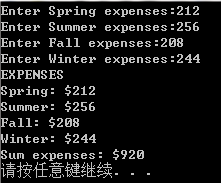
void display3(const student pa[], int n); void main()
{
cout << "Enter class size: ";
int class_size;
cin >> class_size;
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue; student * ptr_stu = new student[class_size];//用了new记得要delete 创建一个student数组
int entered = getinfo(ptr_stu, class_size);//输入信息
for (int i = ; i < entered; ++i)
{
display1(ptr_stu[i]);//传入元素,可以用.表示法
display2(&ptr_stu[i]);//传入地址,只能用->表示法
}
display3(ptr_stu, entered);
delete[] ptr_stu;
cout << "Done\n";
system("pause");
} int getinfo(student pa[], int n)
{
for (int i = ; i<n; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the fullname:";
cin >> pa[i].fullname;
cout << "Please enter the hobby:";
cin >> pa[i].hobby;
cout << "Please enter the ooplevel:";
cin >> pa[i].ooplevel;
}
cout << "Enter end!"<<endl;
return n;
} void display1(student st)
{
cout << "display1:FullName:" << st.fullname << "\nhobby:" << st.hobby
<< "\nooplevel:" << st.ooplevel << endl;
} void display2(const student *ps)
{
cout << "dispaly2:FullName:" << ps->fullname << "\nhobby:" << ps->hobby
<< "\nooplevel:" << ps->ooplevel << endl; }
void display3(const student pa[], int n)
{
cout << "dispaly3:" << endl;
for (int i = ; i<n; i++)
cout << i << ":FullName:" << pa[i].fullname << "\nhobby:" << pa[i].hobby
<< "\nooplevel:" << pa[i].ooplevel << endl;
}
10.设计一个名为calculate()的函数,它接受两个double值和一个指向函数的指针,而被指向的函数接受两个double参数,并返回一个double值、calculate()函数的类型也是double,并返回被指向的函数使用calculate()的两个double参数计算得到的值。例如,假如add()函数的定义如下:
{
return x + y;
}
则下述代码中的函数调用:
double q = calculate(2.5,10.4,add);
将导致calculate()把2.5和10.4传递给add()函数,并返回add()的返回值(12.9).请编写一个程序,它调用上述两个函数和至少另一个与add()类似的数。如果读者爱冒险,可以尝试创建一个指针数组,其中的指针指向add()样式的函数,并编写一个循环,使用这些指针连续让calculate()调用这些函数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; double calculate(double x, double y, double(*pf)(double, double))//pf表示函数指针
{
return (*pf)(x, y);//pf表示函数指针,是一个地址,*pf表示调用函数
}
double add(double x, double y)
{
return x + y;
}
double sub(double x, double y)
{
return x - y;
}
double mean(double x, double y)
{
return (x + y) / 2.0;
} void main()
{
double(*pf[])(double, double) = { add, sub, mean };//函数指针数组,分别指向三个不同函数
const char(*pch[]) = { "sum", "difference", "mean" };
double a, b;
cout << "Enter pairs of numbers (q to quit):";
int i;
while (cin >> a >> b)
{
for (i = ; i<; i++)
cout << calculate(a, b, pf[i]) << " = " << pch[i] << "\n";
cout << "Enter pairs of numbers (q to quit):";
}
system("pause");
}

[C++ Primer Plus] 第7章、函数(二)课后习题的更多相关文章
- C++ Primer 5th 第6章 函数
正如第一章所说:C++的函数是一个能够完成一个功能的模块或者说是一段命名了的代码块. 如下图所示,函数可以重载,是一段实现某些功能命名了的代码. 一个完整的函数的构成有四部分: 1.返回类型 2.函数 ...
- 《C++primer》v5 第6章 函数 读书笔记 习题答案
6.1 实参是在函数调用处填写的参数.形参是在函数体使用的参数. 实参是形参的初始值. 具体参见:http://blog.163.com/zhengguo_li/blog/static/7030148 ...
- C++ Primer高速学习 第一章 获得二:输入和输出 (IO)
什么是输入输出.即Input-Output,缩写是非常装B的IO?请看经典民间解释: C++语言的输入输出是指信息从外部输入设备(如键盘.磁盘等)向计算机内部(内存)输入(即Input)和从内存向外单 ...
- C Primer Plus 第9章 函数 编程练习
复习题: 8. int choice(int a,int b,int c){ int max; max = a; if (b > max) max = b; if (c > max) ma ...
- 《Python核心编程》 第四章 Python对象- 课后习题
练习 4-1. Python对象.与所有Python对象有关的三个属性是什么?请简单的描述一下. 答:身份.类型和值: 身份:每一个对象都有一个唯一的身份标识自己,可以用id()得到. 类型:对象的 ...
- C语言程序设计·谭浩强(第四版)第二章课后习题的答案,算法——程序的灵魂
C语言程序小练习 1.用C语言设计程序算出1-1/2+1/3-14+1/5...+1/99-1/100的值 #include<stdio.h> int main() { ; double ...
- c++ primer plus 第6版 部分二 5- 8章
---恢复内容开始--- c++ primer plus 第6版 部分二 5- 章 第五章 计算机除了存储外 还可以对数据进行分析.合并.重组.抽取.修改.推断.合成.以及其他操作 1.for ...
- 《C++ Primer》 第四版 第7章 函数
<C++ Primer> 第四版 第7章 函数 思维导图笔记 超级具体.很具体,图片版,有利于复习查看 http://download.csdn.net/detail/onlyshi/94 ...
- <<C++ Primer>> 第 6 章 函数
术语表 第 6 章 函数 二义性调用(ambiguous call): 是一种编译时发生的错误,造成二义性调用的原因时在函数匹配时两个或多个函数提供的匹配一样好,编译器找不到唯一的最佳匹配. 实 ...
- C++ primer plus读书笔记——第8章 函数探幽
第8章 函数探幽 1. 对于内联函数,编译器将使用相应的函数代码替换函数调用,程序无需跳到一个位置执行代码,再调回来.因此,内联函数的运行速度比常规函数稍快,但代价是需要占用更多内存. 2. 要使用内 ...
随机推荐
- linux系统下Nagios+rrdtool+Pnp4nagios监控环境的搭建
环境中的软件版本>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>nagios版本:3.5.1rrdtoo ...
- 第六天 py 加法练习
其实就是while的用法! 该看第65 啦
- UCloud 的安全秘钥 (计蒜客初赛第五场)(待解决)
20.7% 1200ms 262144K 每个 UCloud 用户会构造一个由数字序列组成的秘钥,用于对服务器进行各种操作.作为一家安全可信的云计算平台,秘钥的安全性至关重要.因此,UCloud 每年 ...
- 8、路由 router
路由:router 用户功能 /user ----> index.html /user/login ----> login.html /user/reg ----> reg.html ...
- 【微信小程序——开发步骤1】
知识点: view,image,text编写文本框架 使用弹性盒子动态布局 使用rpx调试分辨率 在wxml中查看默认样式属性 步骤: 1.以如图页面实例说明如何写出微信文本内容 先对页面写出整体 ...
- react-redux简单实用
首先了解一个过程,redux 肯定是通过在组件中出发一个方法(事件),我们可以实现一个简单的例子播放和停止播放(写到这今日心情不好,下次继续) redux需要安装 以下依赖:cnpm install ...
- 学习完HTML后的5大测试题----9.18
考试题目 第一题: 布局出该效果 提示:使用DIV的border样式,调整边框粗细出现该效果,保留上边框,其它三个方向的边框需设置:border-left:100px solid transpar ...
- PHP(一般标签介绍,标签特性,实体名称,绝对路径与相对路径)
h1:为标题 h1~h6 标题会逐渐变小 需更换标签里面的数字 如: <h1>这是标题123</h1>---标题 <h2>这是标题123</h2>-- ...
- Ubuntu 16.04 Java8 安装
添加ppa apt-get update apt install software-properties-common add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java ...
- Codeforces 1089E - Easy Chess - [DFS+特判][2018-2019 ICPC, NEERC, Northern Eurasia Finals Problem E]
题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1089/problem/E Elma is learning chess figures. She learned that ...
