SPSC Queue
在多线程编程中,一个著名的问题是生产者-消费者问题 (Producer Consumer Problem, PC Problem)。
对于这类问题,通过信号量加锁 (https://www.cnblogs.com/sinkinben/p/14087750.html) 来设计 RingBuffer 是十分容易实现的,但欠缺性能。
考虑一个特殊的场景,生产者和消费者均只有一个 (Single Producer Single Consumer, SPSC),在这种情况下,我们可以设计一个无锁队列来解决 PC 问题。
0. Background
考虑以下场景:在一个计算密集型 (Computing Intensive) 和延迟敏感的 for 循环当中,每次循环结束,需要打印当前的迭代次数以及计算结果。
void matrix_compute()
{
for (i = 0 to n)
{
// code of computing
...
// print i and result of computing
std::cout << ...
}
}
在这种情况下,如果使用简单的 std::cout 输出,由于 I/O 的性质,将会造成严重的延迟 (Latency)。
一个直观的解决办法是:将 Log 封装为一个字符串,传递给其他线程,让其他线程打印该字符串,实现异步的 Logging 。
1. Lock-free SPSC Queue
此处使用一个 RingBuffer 来实现队列。
由于是 SPSC 型的队列,队列头部 head 只会被 Consumer 写入,队列尾部 tail 只会被 Producer 写入,所以 SPSC Queue 可以是无锁的,但需要保证写入的原子性。
template <class T> class spsc_queue
{
private:
std::vector<T> m_buffer;
std::atomic<size_t> m_head;
std::atomic<size_t> m_tail;
public:
spsc_queue(size_t capacity) : m_buffer(capacity + 1), m_head(0), m_tail(0) {}
inline bool enqueue(const T &item);
inline bool dequeue(T &item);
};
对于一个 RingBuffer 而言,判空与判满的方法如下:
- Empty 的条件:
head == tail - Full 的条件:
(tail + 1) % N == head
因此,enqueue 和 dequeue 可以是以下的实现:
inline bool enqueue(const T &item)
{
const size_t tail = m_tail.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
const size_t next = (tail + 1) % m_buffer.size();
if (next == m_head.load(std::memory_order_acquire))
return false;
m_buffer[tail] = item;
m_tail.store(next, std::memory_order_release);
return true;
}
inline bool dequeue(T &item)
{
const size_t head = m_head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if (head == m_tail.load(std::memory_order_acquire))
return false;
item = m_buffer[head];
const size_t next = (head + 1) % m_buffer.size();
m_head.store(next, std::memory_order_release);
return true;
}
std::memory_order 的使用说明:https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/atomic/memory_order
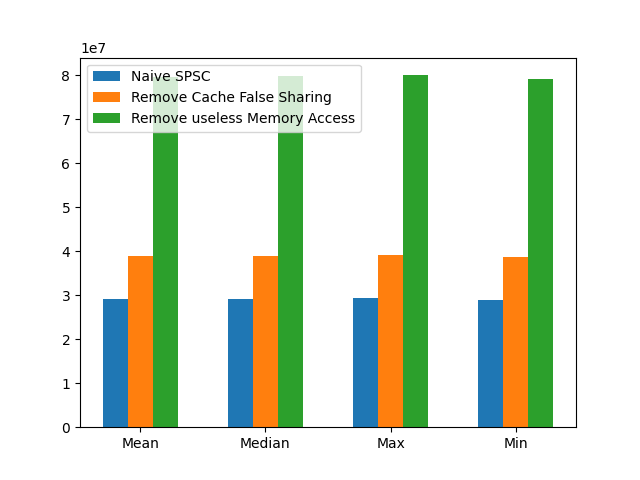
Benchmark 计算 SPSC Queue 的吞吐量:
Mean: 29,158,897.200000 elements/s
Median: 29,178,822.000000 elements/s
Max: 29,315,199 elements/s
Min: 28,995,515 elements/s
Benchmark 的计算方法为:
- Producer 和 Consumer 分别执行
1e8次enqueue和dequeue,计算队列为空所耗费的总时间t,1e8 / t即为吞吐量。 - 上述过程执行 10 次,最终计算
mean, median, min, max的值。
2. Remove cache false sharing
什么是 Cache False Sharing? 参考 Architecture of Modern CPU 的 Exercise 一节。
int *a = new int[1024];
void worker(int idx)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 1e9; j++)
a[idx] = a[idx] + 1;
}
考虑以下程序:
- P1: 开启 2 线程,执行
worker(0), worker(1) - P2: 开启 2 线程,执行
worker(0), worker(16)
P2 的执行速度会比 P1 快,现代 CPU 的 Cache Line 大小一般为 64 字节,由于 a[0], a[1] 位于同一个 CPU Core 的同一个 Cache Line,每次写入都会带来数据竞争 (Data Race) ,触发缓存和内存的同步(参考 MESI 协议),而 a[0], a[16] 之间相差了 64 字节,不在同一个 Cache Line,所以避免了这个问题。
所以,对于上述的 SPSC Queue,可以进行以下改进:
template <class T>
class spsc_queue
{
private:
std::vector<T> m_buffer;
alignas(64) std::atomic<size_t> m_head;
alignas(64) std::atomic<size_t> m_tail;
};
这里的 alignas(64) 实际上改为 std::hardware_constructive_interference_size 更加合理,因为 Cache Line 的大小取决于具体 CPU 硬件的实现,并不总是为 64 字节。
#ifdef __cpp_lib_hardware_interference_size
using std::hardware_constructive_interference_size;
using std::hardware_destructive_interference_size;
#else
// 64 bytes on x86-64 │ L1_CACHE_BYTES │ L1_CACHE_SHIFT │ __cacheline_aligned │ ...
constexpr std::size_t hardware_constructive_interference_size = 64;
constexpr std::size_t hardware_destructive_interference_size = 64;
#endif
Benchmark 结果:
Mean: 38,993,940.400000 elements/s
Median: 39,027,123.000000 elements/s
Max: 39,253,946 elements/s
Min: 38,624,197 elements/s
3. Remove useless memory access
在使用 spsc_queue 的时候,通常会有以下形式的代码:
spsc_queue sq(1024);
// Producer keep spinning
int x = 233;
while (!sq.enqueue(x)) {}
而在 dequeue/enqueue 中,存在判空/判满的代码:
inline bool enqueue(const T &item)
{
const size_t tail = m_tail.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
const size_t next = (tail + 1) % m_buffer.size();
if (next == m_head.load(std::memory_order_acquire))
return false;
// ...
}
每次执行 m_head.load,Producer 线程的 CPU 都会访问一次 m_head 所在的内存,但实际上触发该条件的概率较小(因为在实际的场景下, Producer/Consumer 都是计算密集型,否则根本不需要无锁的数据结构)。在判空/判满的时候,可以去 “离 CPU 更近” 的 Cache 去获取 m_head 的值。
template <class T>
class spsc_queue
{
private:
std::vector<T> m_buffer;
alignas(hardware_constructive_interference_size) std::atomic<size_t> m_head;
alignas(hardware_constructive_interference_size) std::atomic<size_t> m_tail;
alignas(hardware_constructive_interference_size) size_t cached_head;
alignas(hardware_constructive_interference_size) size_t cached_tail;
};
inline bool enqueue(const T &item)
{
const size_t tail = m_tail.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
const size_t next = (tail + 1) % m_buffer.size();
if (next == cached_head)
{
cached_head = m_head.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
if (next == cached_head)
return false;
}
}
Benchmark 结果:
Mean: 79,740,671.300000 elements/s
Median: 79,838,314.000000 elements/s
Max: 80,044,793 elements/s
Min: 79,241,180 elements/s
4. Summary
3 个版本的 spsc_queue 的吞吐量比较(均值,中位数,最大值,最小值)。在优化 Cache False Sharing 和优先从 Cache 读取 head, tail 之后,可得到 x2 的提升。
SPSC Queue的更多相关文章
- readerwriterqueue 一个用 C++ 实现的快速无锁队列
https://www.oschina.net/translate/a-fast-lock-free-queue-for-cpp?cmp&p=2 A single-producer, sing ...
- [数据结构]——链表(list)、队列(queue)和栈(stack)
在前面几篇博文中曾经提到链表(list).队列(queue)和(stack),为了更加系统化,这里统一介绍着三种数据结构及相应实现. 1)链表 首先回想一下基本的数据类型,当需要存储多个相同类型的数据 ...
- Azure Queue Storage 基本用法 -- Azure Storage 之 Queue
Azure Storage 是微软 Azure 云提供的云端存储解决方案,当前支持的存储类型有 Blob.Queue.File 和 Table. 笔者在<Azure File Storage 基 ...
- C++ std::queue
std::queue template <class T, class Container = deque<T> > class queue; FIFO queue queue ...
- 初识Message Queue之--基础篇
之前我在项目中要用到消息队列相关的技术时,一直让Redis兼职消息队列功能,一个偶然的机会接触到了MSMQ消息队列.秉着技术还是专业的好为原则,对MSMQ进行了学习,以下是我个人的学习笔记. 一.什么 ...
- 搭建高可用的rabbitmq集群 + Mirror Queue + 使用C#驱动连接
我们知道rabbitmq是一个专业的MQ产品,而且它也是一个严格遵守AMQP协议的玩意,但是要想骚,一定需要拿出高可用的东西出来,这不本篇就跟大家说 一下cluster的概念,rabbitmq是erl ...
- PriorityQueue和Queue的一种变体的实现
队列和优先队列是我们十分熟悉的数据结构.提供了所谓的“先进先出”功能,优先队列则按照某种规则“先进先出”.但是他们都没有提供:“固定大小的队列”和“固定大小的优先队列”的功能. 比如我们要实现:记录按 ...
- C#基础---Queue(队列)的应用
Queue队列,特性先进先出. 在一些项目中我们会遇到对一些数据的Check,如果数据不符合条件将会把不通过的信息返回到界面.但是对于有的数据可能会Check很多条件,如果一个数据一旦很多条件不 ...
- [LeetCode] Queue Reconstruction by Height 根据高度重建队列
Suppose you have a random list of people standing in a queue. Each person is described by a pair of ...
- [LeetCode] Implement Queue using Stacks 用栈来实现队列
Implement the following operations of a queue using stacks. push(x) -- Push element x to the back of ...
随机推荐
- Intrusion Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Representation Learning 笔记
Intrusion Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Representation Learning 2.2 实验数据的预处理 为了确 ...
- 五分钟k8s入门到实战-应用配置
背景 在前面三节中已经讲到如何将我们的应用部署到 k8s 集群并提供对外访问的能力,x现在可以满足基本的应用开发需求了. 现在我们需要更进一步,使用 k8s 提供的一些其他对象来标准化我的应用开发. ...
- Django框架——Django与Ajax、分页器
文章目录 1 Django与Ajax 一 什么是Ajax 优点: 二 基于jquery的Ajax实现 Ajax-->服务器-->Ajax执行流程图 三 案例 一 通过Ajax,实现前端输入 ...
- Mac 下使用 ffmpeg 制作 gif
Mac 下使用 ffmpeg 制作 gif 公众号文章,gif要求 300帧数以内 .以下是从 mp4 转为 gif 的步骤. 步骤 ffmpeg 是著名的视频处理开源软件 brew ...
- linux内核离线升级步骤详解【亲测可用】
由于种种原因,linux的内核版本需要升级,但由于生产原因往往不能在线升级,在此记录笔者本人昨晚的的离线升级步骤,亲测可用. 我们知道,红帽和CentOS同源同宗,内核升级步骤也是一样的. 目录 ■ ...
- [ABC216G] 01Sequence 题解
01Sequence 题目大意 构造一个满足 \(m\) 个形如 \((l,r,x)\) 的限制条件的 \(01\) 序列,其中 \((l,r,x)\) 表示区间 \([l,r]\) 的和不小于 \( ...
- IL编制器 --- Fody
介绍 这个项目的名称"Fody"来源于属于织巢鸟科(Ploceidae)的小鸟(Fody),本身意义为编织. 核心Fody引擎的代码库地址 :https://github.com/ ...
- 比较并交换(compare and swap, CAS)
比较并交换(compare and swap, CAS),是原子操作的一种,可用于在多线程编程中实现不被打断的数据交换操作,从而避免多线程同时改写某一数据时由于执行顺序不确定性以及中断的不可预知性产生 ...
- 【日常收支账本】【Day03】完成编辑账本界面的新增动账记录功能——通过ElementTree加XPath实现
一.项目地址 https://github.com/LinFeng-BingYi/DailyAccountBook 二.新增 1. 解析xml文件 1.1 功能详述 解析所设计的xml文件格式,并将所 ...
- 增长实验室-ab分流的流量保护功能介绍
介绍ab分流的流量保护功能之前,先普及一下ab分流的一些概念和术语 名词解释: 实验:用来验证某个决定请求处理方式的功能或策略的一部分流量,通常用来验证某个功能或策略对系统指标(如PV/UV,CRT, ...
