Spring 源码(7)Spring的注解是如何解析的?
上一篇 https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/p/16196359.html 介绍了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行过程,这篇文章介绍Spring中配置的注解是如何通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor解析的,另外分析下Spring Boot自动装配是如何处理的。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 解析了哪些注解?
在上一篇文章https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/p/16196359.html 我们知道ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实际上是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的一个实现类,他特殊的地方是他还实现了BeanDefinitionRegisterPostProcessor接口,所以ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 既要实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的接口方法postProcessBeanFactory也要实现BeanDefinitionRegisterPostProcessor的接口方法postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,并且在解析的时候先执行了postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,再执行了postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
接下来我们看看postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry做了什么?
上源码:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
// 处理配置的BeanDefinition
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
整个方法核心是执行了processConfigBeanDefinitions方法,这个方法非常的长并且逻辑也复杂,代码我就不贴了,说一下大概的流程(较详细):
- 先进行合格的
beanDefinition的检查- 获取到注解的元数据信息
- 判断是包含
@Configuration注解,包含则合格,否则判断是否包含了@Component、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource注解,包含则合格,如果都不包含则不合格
- 对合格的
BeanDefinition排序 - 创建一个解析
@Configuration注解的解析器 - 对合格的
BeanDefinition集合进行解析- 循环解析,最终调用
processConfigurationClass方法 - 判断是否跳过解析,比如配置了
@Conditional注解的 - 调用
doProcessConfigurationClass方法开始解析(下面的解析中可能会存在递归调用)- 解析
@Component注解- 判断是否包含内部类标记了
@Component,比如在标有@Component注解的类里面创建一个内部类也标记了@Component注解,如果有就会进行递归调用processConfigurationClass方法
- 判断是否包含内部类标记了
- 解析
@PropertySources和@PropertySource注解- 比如标记
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties"),这样就会把这个属性的值全部解析到环境信息的propertySources属性中
- 比如标记
- 解析
@ComponetScans和@ComponentScan注解- 比如配置了扫描的包,那么就会扫描出合格的
BeanDefinition,然后递归解析
- 比如配置了扫描的包,那么就会扫描出合格的
- 解析
@Import注解(Spring Boot自动装配的实现)- 递归解析出标记了
@Import注解的类放在imports属性中 - 解析
ImportSelector接口的实现类 - 调用
ImportSelector#selectImports方法解析需要注册的类 - 递归调用
processImports方法,然后将需要注册的类注册到importBeanDefinitionRegistrars(这里会在后面进行loadBeanDefinition)
- 递归解析出标记了
- 解析
@ImportResource注解- 比如解析配置的
Spring的xml配置文件,最终放到importedResources属性中(后面会进行loadBeanDefinition)
- 比如解析配置的
- 解析
@Bean注解- 比如解析当前类标记了
@Bean的方法 - 然后放在
beanMethods属性中(后面会进行loadBeanDefinition)
- 比如解析当前类标记了
- 解析
- 加载
BeanDefinition从上面解析出来的类中- 循环遍历加载
BeanDefinition - 判断是否跳过,比如实现了
Condition接口的类 - 加载标有
@Bean的BeanDefinition - 加载从
ImportResource中解析的BeanDefinition - 加载从
ImportSelector中配置的解析的BeanDefinition
- 循环遍历加载
- 循环解析,最终调用
整个过程非常复杂,而且存在递归操作,读者可以按照我写的步骤进行debug调试,当然可能会出现到处跳转不知所措的情况,多调几遍就好了,只要知道大致的流程,应该还是不难的。
总的来说就是解析了这些注解:@Component、@PropertySource、@PropertySources、@ComponentScan、@ComponentScans、@Import、@ImportResource、@Bean,然后将标有这些注解的解析成BeanDefinition,如果加上了@Conditionnal注解,那么按照条件进行解析。

自定义自动装配
现在开发都是用SpringBoot,原因在于他非常的方便,引入即可使用,那么他是做到的呢?众所周知Spring Boot有几个注解非常重要,比如:@SpringBootApplication、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@SpringBootConfiguration,其中最重要的是@EnableAutoConfiguration,这个注解里面标记了@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),当然还标记了其他的,我们现在只关心这个@Import,里面放入了一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector类。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,这个DeferredImportSelector接口是ImportSelector的子接口,表示延迟导入的意思。在上面的分析中,其实最主要的是实现他的接口selectImports,直接源码:
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
// 获取自动装配的实体
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 获取合格(候选)的配置
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 加载配置,根据factoryType,这里的FactoryType就是@EnableAutoConfiguration注解
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
// 直接返回@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// 加载spring.factories文件并解析
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try
// 这里获取的url就是:
// public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 读取属性文件,获取到key为EnableAutoConfiguration,value为需要加载的类
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
所以我们也可以自己写一个进行自动装配,接下来实现一个简单的自动装配。
定义自动装配注解
/**
* @author <a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/">redwinter</a>
* @since 1.0
**/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableRedwinterAutoConfiguration {
}
创建MyInportSelector类
/**
* @author <a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/">redwinter</a>
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
// 加载需要装配的类
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getFactoryTypeClass(), classLoader);
return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
}
private Class<?> getFactoryTypeClass() {
return EnableRedwinterAutoConfiguration.class;
}
}
创建启动类
/**
* @author <a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/">redwinter</a>
* @since 1.0
**/
@Configuration
@EnableRedwinterAutoConfiguration
public class RedwinterApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.redwinter.test.config");
context.refresh();
}
}
创建需要装配的类
/**
* @author <a href=""https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/">redwinter</a>
* @since 1.0
**/
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
@Conditional(RedwinterStrCondition.class)
public String myStr() {
return "redwinter";
}
public static class RedwinterStrCondition implements ConfigurationCondition {
@Override
public ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase() {
return ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN;
}
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
System.out.println("开始匹配。。。");
return true;
}
}
}
创建spring.factories文件
com.redwinter.test.config.EnableRedwinterAutoConfiguration=\
com.redwinter.test.config.MyConfiguration
启动验证
debug断点:
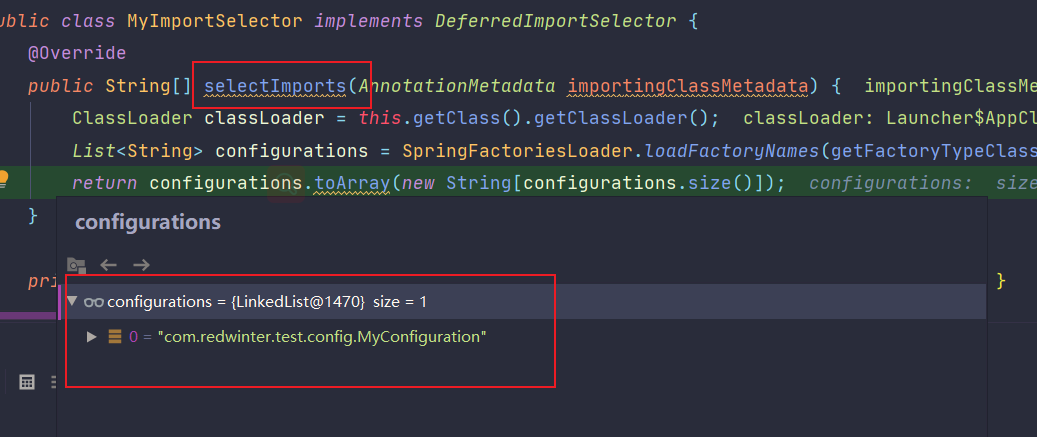
这就是Spring Boot自动装配的简化版,总得来说我们完成了Spring 对BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行过程的解析,包括Spring是如何进行注解解析的,其实就是Spring在对BeanDefinition在正式初始化为Bean的前置处理,所以我们可以这个阶段进行很多扩展,比如占位符的处理PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer等。
接下来接续解读AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法对BeanPostProcessor的注册。
Spring 源码(7)Spring的注解是如何解析的?的更多相关文章
- Spring源码情操陶冶-PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser注解配置解析器
本文针对spring配置的context:property-placeholder作下简单的分析,承接前文Spring源码情操陶冶-自定义节点的解析 spring配置文件应用 <context: ...
- Spring源码情操陶冶-AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser注解配置解析器
本文承接前文Spring源码情操陶冶-自定义节点的解析,分析spring中的context:annotation-config节点如何被解析 源码概览 对BeanDefinitionParser接口的 ...
- Spring源码分析-从@ComponentScan注解配置包扫描路径到IoC容器中的BeanDefinition,经历了什么(一)?
阅前提醒 全文较长,建议沉下心来慢慢阅读,最好是打开Idea,点开Spring源码,跟着下文一步一步阅读,更加便于理解.由于笔者水平优先,编写时间仓促,文中难免会出现一些错误或者不准确的地方,恳请各位 ...
- Spring源码解读Spring IOC原理
一.什么是Ioc/DI? IoC 容器:最主要是完成了完成对象的创建和依赖的管理注入等等. 先从我们自己设计这样一个视角来考虑: 所谓控制反转,就是把原先我们代码里面需要实现的对象创建.依赖的代码,反 ...
- 初探Spring源码之Spring Bean的生命周期
写在前面的话: 学无止境,写博客纯粹是一种乐趣而已,把自己理解的东西分享出去,不意味全是对的,欢迎指正! Spring 容器初始化过程做了什么? AnnotationConfigApplication ...
- Spring源码阅读-spring启动
web.xml web.xml中的spring容器配置 <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.C ...
- spring源码系列(一)sring源码编译 spring源码下载 spring源码阅读
想对spring框架进行深入的学习一下,看看源代码,提升和沉淀下自己,工欲善其事必先利其器,还是先搭建环境吧. 环境搭建 sping源码之前是svn管理,现在已经迁移到了github中了,新版本基于g ...
- Spring源码:Spring IoC容器加载过程(2)
Spring源码版本:4.3.23.RELEASE 一.加载XML配置 通过XML配置创建Spring,创建入口是使用org.springframework.context.support.Class ...
- Spring源码:Spring IoC容器加载过程(1)
Spring源码版本:4.3.23.RELEASE 一.加载过程概览 Spring容器加载过程可以在org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplic ...
- 【Spring 源码】Spring 加载资源并装配对象的过程(XmlBeanDefinitionReader)
Spring 加载资源并装配对象过程 在Spring中对XML配置文件的解析从3.1版本开始不再推荐使用XmlBeanFactory而是使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader. Class ...
随机推荐
- System.getenv和getProperty的区别
/** * System.getenv()是获取---环境变量(environment variables), * 系统层面的,好比我linux系统里的.bash_profile文件里面的变量 * 返 ...
- memcached 与 redis 的区别?
1.Redis 不仅仅支持简单的 k/v 类型的数据,同时还提供 list,set,zset,hash 等数据结构的存储.而 memcache 只支持简单数据类型,需要客户端自己处理复 杂对象 2.R ...
- 如何获取所有的参数名和参数值?用request.getParameterNames(); Enumeration enu=request.getParameterNames(); while(enu.hasMoreElements()){ String paraName=(String)enu.nextElement(); System.out.println(paraName+"
用request.getParameterNames(); Enumeration enu=request.getParameterNames(); while(enu.hasMoreElemen ...
- 您对 Distributed Transaction 有何了解?
分布式事务是指单个事件导致两个或多个不能以原子方式提交的单独数据源的突 变的任何情况.在微服务的世界中,它变得更加复杂,因为每个服务都是一个工 作单元,并且大多数时候多个服务必须协同工作才能使业务成功 ...
- Linux分区问题
一.基本分区的作用及其大小 /boot分区: 存放引导文件和Linux内核文件等. 引导文件:判断启动哪一个操作系统或启动哪个内核. 内核:管理硬件和软件资源,程序与硬件之间的桥梁. 分区大小:100 ...
- 分布式存储---FastDFS+GlusterFS
一. 存储概念 1.块存储的多种实现: 块存储: 就好比硬盘一样, 直接挂在到主机,一般用于主机的直接存储空间和数据库应用的存储 1.磁盘+LVS: 单机硬盘纯存储 2.DAS(DELL MD系列): ...
- 学习Redis(三)
一.安装部署 1.常规安装 1.安装 # wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.0.7.tar.gz # tar xf redis-3.0.7. ...
- vue循环时设置多选框禁用状态,v-for
<div v-for="user in users" > <el-radio v-bind:disabled="user.id== ...
- Python - 字符串基础知识
- ubuntu 20.04 安装 ros1 和ros2
ubuntu 选择Hong Kong 源 1. ROS1安装 添加 sources.list(设置你的电脑可以从 packages.ros.org 接收软件.) sudo sh -c '. /etc ...
