Tuple元组 、 ValueTuple 值元组详解
Tuple元组
Tuple是C# 4.0时出的新特性,.Net Framework 4.0以上版本可用。
元组是一种数据结构,具有特定数量和元素序列,与数组不同,元祖中的元素可以不同的数据类型。比如设计一个三元组数据结构用于存储学生信息,一共包含三个元素,第一个是名字,第二个是年龄,第三个是身高。
元组的具体使用如下:
1. 如何创建元组
默认情况.Net Framework元组仅支持1到7个元组元素,如果有8个元素或者更多,需要使用Tuple的嵌套和Rest属性去实现。另外Tuple类提供创造元组对象的静态方法。
- 利用构造函数创建元组:
var testTuple7 = new Tuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int>(, , , , , ,);
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple7.Item1}, Item 7: {testTuple7.Item7}"); var testTuple10 = new Tuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, Tuple<int, int, int>>
(, , , , , , , new Tuple<int, int, int>(, , ));
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple10.Item1}, Item 10: {testTuple10.Rest.Item3}");
- 利用Tuple静态方法构建元组,最多支持八个元素:
var testTuple7 = System.Tuple.Create<int, int, int, int, int, int, int>(, , , , , , );
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple7.Item1}, Item 7: {testTuple7.Item7}"); var testTuple8 = System.Tuple.Create<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, int>
(, , , , , , , );
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple8.Item1}, Item 8: {testTuple8.Rest.Item1}");
Note:这里构建出来的Tuple类型其实是Tuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, Tuple<int>>,因此testTuple8.Rest取到的数据类型是Tuple<int>,因此要想获取准确值需要取Item1属性。
2. 表示一组数据
如下创建一个元组表示一个学生的三个信息:名字、年龄和身高,而不用单独额外创建一个类。
var studentInfo = Tuple.Create<string, int, uint>("Bob", , );
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
3. 从方法返回多个值
当一个函数需要返回多个值的时候,一般情况下可以使用out参数,这里可以用元组代替out实现返回多个值。
void Main()
{
var studentInfo = GetStudentInfo("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
}
static dynamic GetStudentInfo(string name)
{
return new Tuple<string, int, uint>("Bob", , );
}
4. 用于单参数方法的多值传递
当函数参数仅是一个Object类型时,可以使用元组实现传递多个参数值。
void Main()
{
var t = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ParameterizedThreadStart(WriteStudentInfo));
t.Start(new Tuple<string, int, uint>("Bob", , ));
while (t.IsAlive)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep();
}
}
static void WriteStudentInfo(Object student)
{
var studentInfo = student as Tuple<string, int, uint>;
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
}
尽管元组有上述方便使用的方法,但是它也有明显的不足:
- 访问元素的时候只能通过ItemX去访问,使用前需要明确元素顺序,属性名字没有实际意义,不方便记忆;
- 最多有八个元素,要想更多只能通过最后一个元素进行嵌套扩展;
- Tuple是一个引用类型,不像其它的简单类型一样是值类型,它在堆上分配空间,在CPU密集操作时可能有太多的创建和分配工作。
因此在C# 7.0中引入了一个新的ValueTuple类型,详见下面章节。
ValueTuple值元组
ValueTuple是C# 7.0的新特性之一,.Net Framework 4.7以上版本可用。
值元组也是一种数据结构,用于表示特定数量和元素序列,但是是和元组类不一样的,主要区别如下:
- 值元组是结构,是值类型,不是类,而元组(Tuple)是类,引用类型;
- 值元组元素是可变的,不是只读的,也就是说可以改变值元组中的元素值;
- 值元组的数据成员是字段不是属性。
值元组的具体使用如下:
1. 如何创建值元组
和元组类一样,.Net Framework值元组也只支持1到7个元组元素,如果有8个元素或者更多,需要使用值元组的嵌套和Rest属性去实现。另外ValueTuple类可以提供创造值元组对象的静态方法。
- 利用构造函数创建元组:
var testTuple6 = new ValueTuple<int, int, int, int, int, int>(, , , , , );
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple6.Item1}, Item 6: {testTuple6.Item6}"); var testTuple10 = new ValueTuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, ValueTuple<int, int, int>>(, , , , , , , new ValueTuple <int, int, int>(, , ));
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple10.Item1}, Item 10: {testTuple10.Rest.Item3}");
- 利用Tuple静态方法构建元组,最多支持八个元素:
var testTuple6 = ValueTuple.Create<int, int, int, int, int, int>(, , , , , );
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple6.Item1}, Item 6: {testTuple6.Item6}"); var testTuple8 = ValueTuple.Create<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, int>(, , , , , , , );
Console.WriteLine($"Item 1: {testTuple8.Item1}, Item 8: {testTuple8.Rest.Item1}");
注意这里构建出来的Tuple类型其实是Tuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, Tuple<int>>,因此testTuple8.Rest取到的数据类型是Tuple<int>,因此要想获取准确值需要取Item1属性。
优化区别:当构造出超过7个元素以上的值元组后,可以使用接下来的ItemX进行访问嵌套元组中的值,对于上面的例子,要访问第十个元素,既可以通过testTuple10.Rest.Item3访问,也可以通过testTuple10.Item10来访问。
var testTuple10 = new ValueTuple<int, int, int, int, int, int, int, ValueTuple<int, int, int>>(, , , , , , , new ValueTuple<int, int, int>(, , ));
Console.WriteLine($"Item 10: {testTuple10.Rest.Item3}, Item 10: {testTuple10.Item10}");
2. 表示一组数据
如下创建一个值元组表示一个学生的三个信息:名字、年龄和身高,而不用单独额外创建一个类。
var studentInfo = ValueTuple.Create<string, int, uint>("Bob", , );
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
3. 从方法返回多个值
值元组也可以在函数定义中代替out参数返回多个值。
static ValueTuple<string, int, uint> GetStudentInfo(string name)
{
return new ValueTuple<string, int, uint>("Bob", , );
} static void Main()
{
var studentInfo = GetStudentInfo("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
}
优化区别:返回值可以不明显指定ValueTuple,使用新语法(,,)代替,如(string, int, uint):
static (string, int, uint) GetStudentInfo1(string name)
{
return ("Bob", , );
} static void Main()
{
var studentInfo = GetStudentInfo1("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
}
调试查看studentInfo的类型就是ValueType三元组。
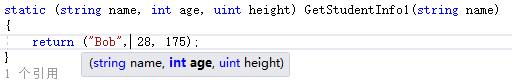
优化区别:返回值可以指定元素名字,方便理解记忆赋值和访问:
static (string name, int age, uint height) GetStudentInfo1(string name)
{
return ("Bob", , );
} static void Main()
{
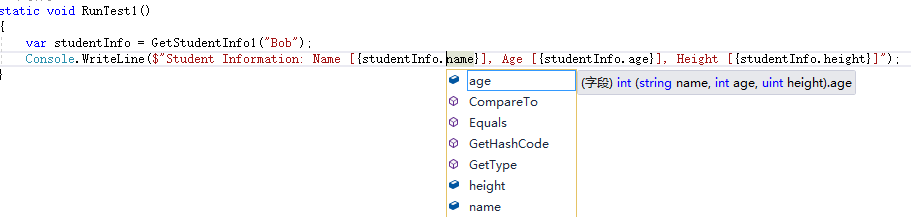
var studentInfo = GetStudentInfo1("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.name}], Age [{studentInfo.age}], Height [{studentInfo.height}]");
}
方便记忆赋值:
方便访问:
4. 用于单参数方法的多值传递
当函数参数仅是一个Object类型时,可以使用值元组实现传递多个值。
static void WriteStudentInfo(Object student)
{
var studentInfo = (ValueTuple<string, int, uint>)student;
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{studentInfo.Item1}], Age [{studentInfo.Item2}], Height [{studentInfo.Item3}]");
} static void Main()
{
var t = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ParameterizedThreadStart(WriteStudentInfo));
t.Start(new ValueTuple<string, int, uint>("Bob", , ));
while (t.IsAlive)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep();
}
}
5. 解构ValueTuple
可以通过var (x, y)或者(var x, var y)来解析值元组元素构造局部变量,同时可以使用符号”_”来忽略不需要的元素。
static (string name, int age, uint height) GetStudentInfo1(string name)
{
return ("Bob", , );
} static void Main()
{
var (name, age, height) = GetStudentInfo1("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{name}], Age [{age}], Height [{height}]"); (var name1, var age1, var height1) = GetStudentInfo1("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Name [{name1}], Age [{age1}], Height [{height1}]"); var (_, age2, _) = GetStudentInfo1("Bob");
Console.WriteLine($"Student Information: Age [{age2}]");
}
由上所述,ValueTuple使C#变得更简单易用。较Tuple相比主要好处如下:
- ValueTuple支持函数返回值新语法”(,,)”,使代码更简单;
- 能够给元素命名,方便使用和记忆,这里需要注意虽然命名了,但是实际上value tuple没有定义这样名字的属性或者字段,真正的名字仍然是ItemX,所有的元素名字都只是设计和编译时用的,不是运行时用的(因此注意对该类型的序列化和反序列化操作);
- 可以使用解构方法更方便地使用部分或全部元组的元素;
- 值元组是值类型,使用起来比引用类型的元组效率高,并且值元组是有比较方法的,可以用于比较是否相等,详见:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.valuetuple。
Tuple元组 、 ValueTuple 值元组详解的更多相关文章
- 详解C# Tuple VS ValueTuple(元组类 VS 值元组)
C# 7.0已经出来一段时间了,大家都知道新特性里面有个对元组的优化,并且网上也有大量的介绍,这里利用详尽的例子详解Tuple VS ValueTuple(元组类VS值元组),10分钟让你更了解Val ...
- C#关键字扫盲——Tuple(元组类) 、ValueTuple(值元组)
原文:C#关键字扫盲--Tuple(元组类) .ValueTuple(值元组) 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,随意转载. https://blog.csdn.net/Michel4Liu/articl ...
- C# 元组和值元组
C# 7.0已经出来一段时间了,大家都知道新特性里面有个对元组的优化:ValueTuple.这里利用详尽的例子详解Tuple VS ValueTuple(元组类VS值元组),10分钟让你更了解Valu ...
- C#进阶系列——WebApi 接口返回值不困惑:返回值类型详解
前言:已经有一个月没写点什么了,感觉心里空落落的.今天再来篇干货,想要学习Webapi的园友们速速动起来,跟着博主一起来学习吧.之前分享过一篇 C#进阶系列——WebApi接口传参不再困惑:传参详解 ...
- C++11 左值、右值、右值引用详解
C++11 左值.右值.右值引用详解 左值.右值 在C++11中所有的值必属于左值.右值两者之一,右值又可以细分为纯右值.将亡值. 在C++11中可以取地址的.有名字的就是左值,反之,不能取地址的.没 ...
- (转)C# WebApi 接口返回值不困惑:返回值类型详解
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/landeanfen/p/5501487.html 正文 前言:已经有一个月没写点什么了,感觉心里空落落的.今天再来篇干货,想要学习Webapi ...
- [转]C#进阶系列——WebApi 接口返回值不困惑:返回值类型详解
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/landeanfen/p/5501487.html 阅读目录 一.void无返回值 二.IHttpActionResult 1.Json(T c ...
- Web Api 接口返回值不困惑:返回值类型详解
前言:已经有一个月没写点什么了,感觉心里空落落的.今天再来篇干货,想要学习Webapi的园友们速速动起来,跟着博主一起来学习吧.之前分享过一篇 WebApi 接口参数:传参详解,这篇博文内容本身很基础 ...
- 【RMQ】 区间最值查询详解
1. 概述 RMQ(Range Minimum/Maximum Query),即区间最值查询,是指这样一个问题:对于长度为n的数列A,回答若干询问RMQ(A,i,j)(i,j<=n),返回数列A ...
随机推荐
- 安装caffe(opencv3+anaconda3)
目录 仅安装CPU版本的caffe 1.下载相关的依赖包: 2.安装opencv3 3.安装caffe 参考文献: 仅安装CPU版本的caffe 1.下载相关的依赖包: sudo apt-get in ...
- Nginx proxy buffer相关的设置和解释
proxy_buffer_size 4k; proxy_buffering on;proxy_buffers 4 4k;proxy_busy_buffers_size 8k;proxy_max_tem ...
- JavaScript的原型链继承__propt__、prototype、constructor的理解、以及他们之间相互的关系。
回想自己已经工作了有一段时间了,但是自己对JavaScript的原型链.和继承的理解能力没有到位,最近他们彻底的整理并且复习了一遍. 本案例中部分文案来自网络和书籍,如有侵权请联系我,我只是把我的理解 ...
- python 3.x 爬虫基础---Requersts,BeautifulSoup4(bs4)
python 3.x 爬虫基础 python 3.x 爬虫基础---http headers详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Urllib详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Requer ...
- 从CentOS官网下载系统镜像详细教程
很多新手小白鼠想学习CentOS系统,但是不知道镜像去哪里搞,随便去个第三方发现要么要注册,要么各种广告病毒,或者好不容易找到官网,点进去一看却一脸懵逼,不仅全英文,有些专业术语也不懂啊,不要担心 ...
- 局域网内配置虚拟机的hostname
一般上我们在局域网内访问,比如宿主机访问虚拟机的时候可以直接使用IP去访问,大多数情况下也都适用.但是对于有的情况,比如像新版的hbase的配置,它默认将localhost作为hbase.master ...
- 使用xml4j xml与字符串之间转换
jar准备:dom4j-2.1.1.jar jaxen-1.1.6.jar jaxen/jaxen/ Maven依赖写法 <dependency> <groupId>jaxe ...
- java EE 新手入门了解
郑重申明:本文转载至https://blog.csdn.net/Neuf_Soleil/article/details/80962686,在此深表感谢! 为什么选择java? 想必有很多初学者会像我一 ...
- 一图解析 React组件生命周期 (React Component Lifecycle)
React LifeCycle v1 参考官方文档作成 可放大 参考:https://reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html 数字补丁数字补丁数字补丁数字补丁数 ...
- 阿里云CentOS7.3配置Java Web应用和Tomcat步骤
阿里云的Linux系统包括CentOS7.3配置了密钥对 怎样将自己ECS实例绑定密钥对,并启用秘钥: https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/51798.ht ...
