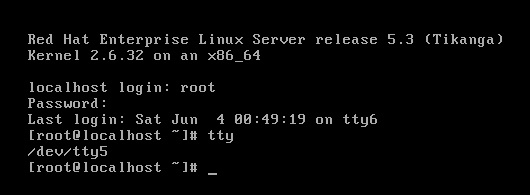
/dev/tty 与 /dev/pts
打开3个bash会话窗口
[root@server1 fd]# cd /proc/7489/fd
[root@server1 fd]# ll
总用量 0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 0 -> /dev/pts/2
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 1 -> /dev/pts/2
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 2 -> /dev/pts/2
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 255 -> /dev/pts/2
[root@server1 fd]# cd /proc/7508/fd
[root@server1 fd]# ll
总用量 0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 0 -> /dev/pts/3
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 1 -> /dev/pts/3
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 2 -> /dev/pts/3
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:55 255 -> /dev/pts/3
[root@server1 fd]# cd /proc/6734/fd
[root@server1 fd]# ll
总用量 0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:56 0 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:56 1 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:56 2 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------ 1 root root 64 6月 5 23:56 255 -> /dev/pts/0
[root@server1 fd]# cd /dev/pts
[root@server1 pts]# ll
总用量 0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 0 6月 5 18:26 0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 1 6月 5 23:57 1
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 2 6月 5 23:54 2
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 3 6月 5 23:55 3
c--------- 1 root root 5, 2 5月 16 16:23 ptmx
[root@server1 pts]# tty
/dev/pts/1
[root@server1 ~]# tty
/dev/pts/2
[root@server1 ~]# tty
/dev/pts/3
tty:命令
tty - print the file name of the terminal connected to standard input
创健6个可切换终端:
root 1019 1 0 May16 tty1 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty1
root 1021 1 0 May16 tty2 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty2
root 1023 1 0 May16 tty3 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty3
root 1025 1 0 May16 tty4 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty4
root 1027 1 0 May16 tty5 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty5
root 1029 1 0 May16 tty6 00:00:00 /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty6
ALT +F[1-6]切换,
[root@localhost dev]# tty
/dev/pts/1
[root@localhost dev]# echo "0" > /dev/tty0
所有的tty[1-6]都显示 0
1 当前控制终端(/dev/tty)
/dev/tty指的是当前所处的终端,输出到此的内容只会显示在当前工作的终端显示器上;可以使用命令”ps –ax”来查看进程与哪个控制终端相连.对于你登录的shell,
/dev/tty就是你使用的终端,设备号是(5,0).
使用命令”tty”可以查看自己具体对应哪个实际终端设备./dev/tty有些类似于到实际所使用终端设备的一个联接 2./dev/pts
/dev/pts是远程登陆(telnet,ssh等)后创建的控制台设备文件所在的目录。由于可能有好几千个用户登陆,所以/dev/pts其实是动态生成的,不象其他设备文件是构建系统时就已经产生的硬盘节点. 3.控制台终端-系统控制台(/dev/console 和 /dev/tty*)
在Linux系统中,计算机显示器通常被称为控制台终端(Console).它仿真了类型为Linux的一种终端(TERM=Linux),并且有一些设备特殊文件与之相关联:
tty0、tty1、tty2等.当你在控制台上登录时,使用的是tty1.使用Alt+[F1—F6]组合键时,我们就可以切换到tty2、tty3等上面去.tty1–tty6等称为虚拟终端,
而tty0则是当前所使用虚拟终端的一个别名,系统所产生的信息会发送到该终端上.因此不管当前正在使用哪个虚拟终端,系统信息都会发送到控制台终端上.
你可以登录到不同的虚拟终端上去,因而可以让系统同时有几个不同的会话期存在.只有系统或超级用户root可以向/dev/tty0进行写操作.
root 4665 925 0 13:53 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0
root 4667 4665 0 13:53 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 4744 925 0 14:53 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/1
root 4746 4744 0 14:53 pts/1 00:00:00 -bash
root 4843 925 0 16:24 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/2
root 4845 4843 0 16:24 pts/2 00:00:00 -bash
root 4860 925 0 16:24 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/3
root 4862 4860 0 16:24 pts/3 00:00:00 -bash
root 4877 925 0 16:24 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/4
root 4879 4877 0 16:24 pts/4 00:00:00 -bash
root 4894 925 0 16:24 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/5
root 4896 4894 0 16:24 pts/5 00:00:00 -bash
root 4911 925 0 16:25 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/6
root 4913 4911 0 16:25 pts/6 00:00:00 -bash
root 4935 925 0 16:25 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/7
root 4937 4935 0 16:25 pts/7 00:00:00 -bash
root 4954 925 0 16:25 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/8
[root@server1 ~]# cd /dev/pts
[root@server1 pts]# ll
总用量 0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 0 6月 4 16:25 0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 1 6月 4 16:25 1
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 2 6月 4 16:25 2
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 3 6月 4 16:25 3
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 4 6月 4 16:25 4
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 5 6月 4 16:25 5
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 6 6月 4 16:25 6
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 7 6月 4 16:25 7
crw--w---- 1 root tty 136, 8 6月 4 16:28 8
c--------- 1 root root 5, 2 5月 16 16:23 ptmx
linux下看到的控制台(console)是由几个设备完成的。分别是/dev/ttyN(其中tty0就是/dev/console,tty1,tty2就是不同的虚拟终端(virtual console))
通常使用热键alt+Fn来在这些虚拟终端之间进行切换。所有的这些tty设备都是由linux/drivers/char /console.c和vt.c对应。
ALT+F7切回到GUI桌面
动态创健/dev/pts: root@server1 ~]# cd /dev/pts
[root@server1 pts]# ll
总用量
crw--w---- root tty , 6月 :
crw--w---- root tty , 6月 :
c--------- root root , 5月 : ptmx [root@server1 pts]# ll
总用量
crw--w---- root tty , 6月 :
c--------- root root , 5月 : ptmx
alt+[F1-F6] 进行切换 :当前切换为:alt+F5
[root@server1 dev]# cd pts
[root@server1 pts]# ll
总用量
crw--w---- root tty , 6月 :
crw--w---- root tty , 6月 :
c--------- root root , 5月 : ptmx pts+ptmx 实现tty登陆
init 1进入单用户: tty为 /dev/console
/dev/tty 与 /dev/pts的更多相关文章
- linux – tty,ttyS,pts,ptmx,vcs,vcsa设备文件之间的区别?(/dev/tty等)
linux – tty,ttyS,pts,ptmx,vcs,vcsa设备文件之间的区别? 终端有字符终端和图形终端两种模式.在linux的图形环境下,我们可以通过鼠标点击来完成所有的管理任务,这是图形 ...
- /dev/console,/dev/null,/dev/tty
UNIX和Linux中比较重要的三个设备文件是:/dev/console,/dev/tty和/dev/null. 0 : /dev/console 这个设备代表的是系统控制台,错误信息和诊断信息通常 ...
- centos单用户 救援 运行级别 yum,单用户模式,救援模式,inittab :启动级别 e2fsck wetty mingetty 物理终端 /dev/console 虚拟终端 /dev/tty(0,6) 模拟终端 /dev/pts/# grub-md5-crypt 给grub加密码 initrd 第二节课
centos单用户 救援 运行级别 yum,单用户模式,救援模式,inittab :启动级别 e2fsck wetty mingetty 物理终端 /dev/console 虚拟终端 /d ...
- /dev/tty /dev/ttyS0 /dev/tty0,/dev/null区别
1./dev/tty表示控制终端如果当前进程有控制终端(Controlling Terminal)的话,那么/dev/tty就是当前进程的控制终端的设备特殊文件.可以使用命令”ps –ax”来查看进程 ...
- 特殊文件: /dev/null和/dev/tty
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/stephen-liu74/archive/2011/11/10/2240461.html Linux系统提供了两个对Shell编程非常有用的特殊文 ...
- /dev/tty /dev/ttyS0 /dev/tty0区别 (转载)
1.串行端口终端(/dev/ttySn) 串行端口终端(Serial Port Terminal)是使用计算机串行端口连接的终端设备. 计算机把每个串行端口都看作是一个字符设备.有段时间 ...
- What is special about /dev/tty?
ls -la /dev/tty shows the output: crw-rw-rw- 1 root tty 5, 0 Dec 14 22:21 /dev/tty The 'c' means it' ...
- 2.5.5.2 特殊文件:/dev/null 与 /dev/tty
UNIX 系统提供了两个对Shell编程特别有用的特殊文件. 第一个文件 /dev/null ,就是大家所熟知的位桶(bit bucket).传送到此文件的数据都会被丢掉.换句话说 ...
- hostapd、/dev/random、/dev/urandom
在使用hostapd做软ap时,出现了random熵不够的问题,导致节点连接不上这个ap. 下面先解释一下/dev/random和/dev/urandom 先让我们从一个工程中遇到的实际问题开始,先上 ...
随机推荐
- C++程序的编写和实现
C++程序的编写和实现 一个程序从编写到最后得到运行结果要经历以下一些步骤. 1. 用C++语言编写程序 用高级语言编写的程序称为“源程序”(source program).C++的源程序是以.cpp ...
- BZOJ 3707: 圈地 计算几何
Description 2维平面上有n个木桩,黄学长有一次圈地的机会并得到圈到的土地,为了体现他的高风亮节,他要使他圈到的土地面积尽量小.圈地需要圈一个至少3个点的多边形,多边形的顶点就是一个木桩,圈 ...
- IE连EXCHANGE的HTTPS时,出现错误
"There is a problem with this website's security certificate" 这种问题,一般是SSL或CA认证证书的问题. 一般从服务 ...
- [QuickX]xcode运行Quick-cocos2d-x项目时自动更新lua资源文件
1.项目设置 build settings ->build options ->Scan all source files and Includes = YES 2.加入script (1 ...
- 【HDOJ】1890 Robotic Sort
伸展树伤不起啊,很容易wa,很容易T,很容易M. /* 1890 */ #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <m ...
- pcDuino安装vnc进行远程控制
准备工作: 已经刷好的 pcduino : 点此购买 可选用显示器或者用ssh连接,ssh连接参考 无显示器刷机与使用 1.安装x11vnc 输入下面的命令: sudo apt-get insta ...
- POJ_2104_Kth_(主席树)
描述 http://poj.org/problem?id=2104 给出一个n个数的数列,m次询问,每次询问求区间[l,r]中第k小的数,无修改操作. K-th Number Time Limit: ...
- (转载)PHP 判断常量,变量和函数是否存在
(转载)http://www.jb51.net/article/17881.htm 如果你看懂了上面一句话,那么接下来都是废话,PHP手册写的还是很全的.一句话就把我标题中的问题全部解决了. 还是举几 ...
- vim/Gvim配置
" Sections:" -> General" -> VIM user interface" -> Colors and Fonts&quo ...
- [转]NHibernate之旅(3):探索查询之NHibernate查询语言(HQL)
本节内容 NHibernate中的查询方法 NHibernate查询语言(HQL) 1.from子句 2.select子句 3.where子句 4.order by子句 5.group by子句 实例 ...