c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(二)iterator
ITERATOR 迭代器
template<class InputIterator,class T>
InputIterator find(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,const T& value)
{
while(first != last && *first != value)
++first;
return first;
}
代码示例
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const int arraySize = ;
int ia[arraySize] = {,,,,,,}; vector<int> ivect(ia,ia+arraySize);
list<int> ilist(ia,ia+arraySize);
deque<int> ideque(ia,ia+arraySize); vector<int>::iterator it1 = find(ivect.begin(),ivect.end(),);
if(it1 == ivect.end())
cout << "4 not found." << endl;
else
cout << "4 found. " << * it1 << endl; list<int>::iterator it2 = find(ilist.begin(),ilist.end(),);
if(it2 == ilist.end())
cout << "6 not found. " << endl;
else
cout << "6 found. " << *it2 << endl; deque<int>::iterator it3 = find(ideque.begin(),ideque.end(),);
if(it3 == ideque.end())
cout << "8 not found. " << endl;
else
cout << "8 find " << *it3 << endl; return ;
}
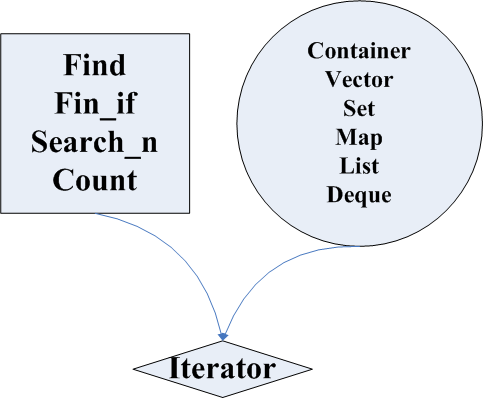
stl中容器有vector\set\list等等等等
算法有find\count等
两者独立 而他们之间的联系便是由iterator进行连接 将两者粘合起来
iterator类似智能指针
智能指针auto_ptr 除了拥有平常指针概念的功能 还具有引用计数功能
通过对该指针指向的元素的引用计数 自动释放元素内存资源 而不必手动调用delete
(auto_ptr 在c++11之后已经被智能指针shared_ptr unique_ptr取代)
示例代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T>
class auto_ptr{
public:
explicit auto_ptr(T* p = 0):pointer(p){}
template<typename U>
auto_ptr(auto_ptr<U>& rhs):pointer(rhs.release()){}
~auto_ptr(){ cout << "enter delete status\n";delete pointer;} template<class U>
auto_ptr<T>& operator=(auto_ptr<U>& rhs){
if(this != &rhs) reset(rhs.release());
return *this;
}
T& operator*()const{return *pointer;}
T* operator->()const{return pointer;}
T* get()const{return pointer;} private:
T* pointer;
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
auto_ptr<string> ps(new string("test"));
cout << *ps << endl;
cout << ps->size() << endl;
return 0;
}
要使用iterator这个智能指针 就需要识别指向的元素的相关信息,比如类别、引用等
代码使用了trait技巧将元素信息提取出来
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo> using namespace std; struct INT{
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
}; struct FLOAT{
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
}; template<class I>
struct Iterator_Traits{
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<INT>::reference).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<FLOAT>::reference).name() << std::endl; return 0;
}
至此 除了
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
还没解决 其他都解决完毕
iterator_category是什么东西呢?
iterator迭代器也是有类型区分的

那么在实际代码中是如何进行识别呢?
在代码执行时才识别区分 效率太低

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo> using namespace std; //申请五个作为迭代器iterator类别的结构
struct input_iterator_tag_{};
struct output_iterator_tag_{};
struct forward_iterator_tag_:public input_iterator_tag_{};
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag_:public forward_iterator_tag_{};
struct random_access_iterator_tag_:public bidirectional_iterator_tag_{}; struct INT{
typedef input_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
}; struct FLOAT{
typedef output_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
}; template<class I>
struct MyIterator_Traits{
typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
};
template<typename T,typename Distance>
void test(T t,Distance n){
typename MyIterator_Traits<T>::iterator_category SELECT_TYPE;
test_(t,n,SELECT_TYPE);
} template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,input_iterator_tag_){
cout << "input_iterator_tag_" << endl;
} template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,output_iterator_tag_){
cout << "output_iterator_tag_" << endl;
} int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
INT i;
FLOAT f;
char c;
test(i,c);
test(f,c); return 0;
}
我们对不同的迭代器 指定不同的tag 这样就会进入到不同的函数中去了
c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(二)iterator的更多相关文章
- c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(一)uninitialized_copy()函数
template <class InputIterator, class ForwardIterator>inline ForwardIterator uninitialized_copy ...
- c++ stl源码剖析学习笔记(三)容器 vector
stl中容器有很多种 最简单的应该算是vector 一个空间连续的数组 他的构造函数有多个 以其中 template<typename T> vector(size_type n,cons ...
- STL源码剖析 学习笔记 MiniSTL
https://github.com/joeyleeeeeee97 目录: 第二章 空间适配器 第三章 迭代器 第四章 序列式容器(vector,list,deque,stack,heap,prior ...
- STL源码剖析-学习笔记
1.模板是一个公式或是蓝图,本身不是类或是函数,需进行实例化的过程.这个过程是在编译期完成的,编译器根据传递的实参,推断出形参的类型,从而实例化相应的函数 2. 后续补充-.
- STL源码剖析读书笔记之vector
STL源码剖析读书笔记之vector 1.vector概述 vector是一种序列式容器,我的理解是vector就像数组.但是数组有一个很大的问题就是当我们分配 一个一定大小的数组的时候,起初也许我们 ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第三章
源码之前,了无秘密. --侯杰 第三章:迭代器概念与traits编程技法 迭代器是一种smart pointer auto_Ptr 是一个用来包装原生指针(native pointer)的对象,声明狼 ...
- STL源码剖析读书笔记--第四章--序列式容器
1.什么是序列式容器?什么是关联式容器? 书上给出的解释是,序列式容器中的元素是可序的(可理解为可以按序索引,不管这个索引是像数组一样的随机索引,还是像链表一样的顺序索引),但是元素值在索引顺序的方向 ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第五章
源码之前,了无秘密 ——侯杰 序列式容器 关联式容器 array(build in) RB-tree vector set heap map priority-queue multiset li ...
- 重温《STL源码剖析》笔记 第六、七、八章 next_permutation (字典序)
源码之前,了无秘密 ——侯杰 第六章算法 next_permutation 比如:01342 -> 01423 -> 01432 方法:从尾端开始往前寻找两个相邻的元素,令第一个元素为* ...
随机推荐
- Java种的String
String中的常用方法 subString()的使用,charAt的使用方法: indexof等的用法 String和byte的转换,对于程序过程的传输很重要, ==和equals的比较 1equa ...
- Android批量验证渠道、版本号(windows版)
功能:可校验单个或目录下所有apk文件的渠道号.版本号,此为windows版,稍后整理Linux版使用说明:1.copy需要校验的apk文件到VerifyChannelVersion目录下2.双击运行 ...
- 3.STM32复位系统
一.概念 复位: 使系统结束当前运行状态,重新开始运行,并根据复位种类,将系统的寄存器(特定的寄存器除外)恢复到默认状态. 二.复位的种类 1.系统复位 将除了系统后备区域寄存器(BKP)和时钟控制寄 ...
- Node学习笔记(二)
1.package.json详解Node.js 在调用某个包时,会首先检查包中 package.json 文件的 main 字段,将其作为包的接口模块,如果 package.json 或 main 字 ...
- 在HTML中限制input 输入框只能输入纯数字
限制 input 输入框只能输入纯数字 onkeyup = "value=value.replace(/[^\d]/g,'')" 使用 onkeyup 事件,有 bug ,那就是在 ...
- 如何让大小一定的span能够包含“容不下”的内容
overflow: hidden; text-overflow: ellipsis; width: 70px;(长度随意) 给span加上面的代码
- Java并发编程三个性质:原子性、可见性、有序性
并发编程 并发程序要正确地执行,必须要保证其具备原子性.可见性以及有序性:只要有一个没有被保证,就有可能会导致程序运行不正确 线程不安全在编译.测试甚至上线使用时,并不一定能发现,因为受到当时的 ...
- IIS下https配置及安全整改
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/JangoJing/p/6769759.html 1.https证书的分类 SSL证书没有所谓的"品质"和"等级 ...
- IDEA(MAC) 快捷键
从eclipse到IDEA:从Windows到MAC 有些不习惯,记录一些日常使用的快捷键 1.格式化代码 command+alt+L 2.导包 alt+ enter 3.自动生成该类型的对象 com ...
- MySQL中Checkpoint技术
个人读书笔记,详情参考<MySQL技术内幕 Innodb存储引擎> 1,checkpoint产生的背景数据库在发生增删查改操作的时候,都是先在buffer pool中完成的,为了提高事物操 ...
