Java(30)集合五Set
作者:季沐测试笔记
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/testero/p/15228440.html
博客主页:https://www.cnblogs.com/testero
1.Set集合
1.1Set集合概述和特点
- Set集合的特点
- 元素存取无序
- 没有索引、只能通过迭代器或增强for循环遍历
- 不能存储重复元素
- Set集合的基本使用
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
//添加元素
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("java");
//不包含重复元素的集合
set.add("world");
//遍历
for(String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
1.2哈希值
哈希值简介
是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数字算出来的int类型的数值
如何获取哈希值
Object类中的public int hashCode():返回对象的哈希码值
哈希值的特点
- 同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
- 默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不同的。而重写hashCode()方法,可以实现让不同对象的哈希值相同
获取哈希值的代码
- 学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} // @Override
// public int hashCode() {
// return 0;
// }
}
- 测试类
public class HashDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张三",30); //同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); //1510467688
System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); //1510467688
System.out.println("--------"); Student s2 = new Student("张三",30); //默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不相同的
//通过方法重写,可以实现不同对象的哈希值是相同的
System.out.println(s2.hashCode()); //1995265320
System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("hello".hashCode()); //99162322
System.out.println("world".hashCode()); //113318802
System.out.println("java".hashCode()); //3254818 System.out.println("world".hashCode()); //113318802
System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("重地".hashCode()); //1179395
System.out.println("通话".hashCode()); //1179395
}
}
1.3HashSet集合概述和特点
HashSet集合的特点
- 底层数据结构是哈希表
- 对集合的迭代顺序不作任何保证,也就是说不保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
- 没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
- 由于是Set集合,所以是不包含重复元素的集合
HashSet集合的基本使用
public class HashSetDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>(); //添加元素
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java"); hs.add("world"); //遍历
for(String s : hs) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
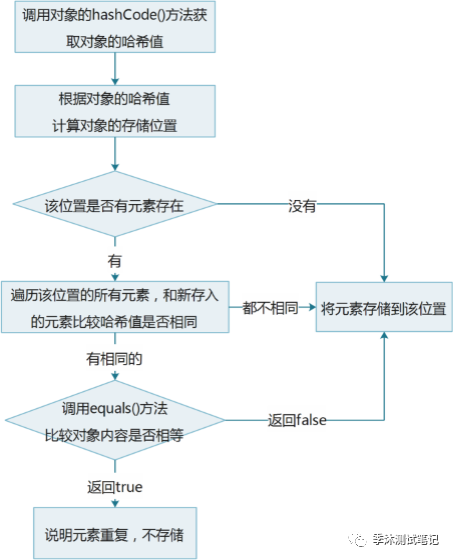
1.4HashSet集合保证元素唯一性源码分析
HashSet集合保证元素唯一性的原理
1.根据对象的哈希值计算存储位置
如果当前位置没有元素则直接存入
如果当前位置有元素存在,则进入第二步
2.当前元素的元素和已经存在的元素比较哈希值
如果哈希值不同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果哈希值相同,则进入第三步
3.通过equals()方法比较两个元素的内容
如果内容不相同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果内容相同,则不存储当前元素
HashSet集合保证元素唯一性的图解
1.5HashSet集合存储学生对象并遍历
案例需求
- 创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
- 要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
代码实现
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student student = (Student) o; if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
} @Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
}
测试类
public class HashSetDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建HashSet集合对象
HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>(); //创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 30);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 35);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 33);
Student s4 = new Student("王五", 33); //把学生添加到集合
hs.add(s1);
hs.add(s2);
hs.add(s3);
hs.add(s4); //遍历集合(增强for)
for (Student s : hs) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}
1.6LinkedHashSet集合概述和特点
LinkedHashSet集合特点
- 哈希表和链表实现的Set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序
- 由链表保证元素有序,也就是说元素的存储和取出顺序是一致的
- 由哈希表保证元素唯一,也就是说没有重复的元素
LinkedHashSet集合基本使用
public class LinkedHashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); //添加元素
linkedHashSet.add("hello");
linkedHashSet.add("world");
linkedHashSet.add("java");
linkedHashSet.add("world"); //遍历集合
for(String s : linkedHashSet) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
2.Set集合排序
2.1TreeSet集合概述和特点
TreeSet集合概述
- 元素有序,可以按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
- TreeSet():根据其元素的自然排序进行排序
- TreeSet(Comparator comparator) :根据指定的比较器进行排序
- 没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
- 由于是Set集合,所以不包含重复元素的集合
- 元素有序,可以按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
TreeSet集合基本使用
public class TreeSetDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>(); //添加元素
ts.add(10);
ts.add(40);
ts.add(30);
ts.add(50);
ts.add(20);
ts.add(30); //遍历集合
for(Integer i : ts) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
2.2自然排序Comparable的使用
案例需求
- 存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用无参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
实现步骤
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,无参构造方法使用的是自然排序对元素进行排序的
- 自然排序,就是让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(T o)方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
代码实现
学生类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int age; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} @Override
public int compareTo(Student s) {
// return 0;
// return 1;
// return -1;
//按照年龄从小到大排序
int num = this.age - s.age;
// int num = s.age - this.age;
//年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
int num2 = num==0?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num;
return num2;
}
}
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(); //创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29);
Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28);
Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30);
Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33);
Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33); //把学生添加到集合
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6); //遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}
2.3比较器排序Comparator的使用
案例需求
- 存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用带参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
实现步骤
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,带参构造方法使用的是比较器排序对元素进行排序的
- 比较器排序,就是让集合构造方法接收Comparator的实现类对象,重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
代码实现
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
//this.age - s.age
//s1,s2
int num = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
return num2;
}
}); //创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29);
Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28);
Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30);
Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33);
Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33); //把学生添加到集合
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6); //遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}
2.4成绩排序案例
案例需求
- 用TreeSet集合存储多个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩),并遍历该集合
- 要求:按照总分从高到低出现
代码实现
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int chinese;
private int math; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int chinese, int math) {
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getChinese() {
return chinese;
} public void setChinese(int chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
} public int getMath() {
return math;
} public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
} public int getSum() {
return this.chinese + this.math;
}
}
测试类
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建TreeSet集合对象,通过比较器排序进行排序
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// int num = (s2.getChinese()+s2.getMath())-(s1.getChinese()+s1.getMath());
//主要条件
int num = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
//次要条件
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese() : num;
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num2;
return num3;
}
}); //创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 98, 100);
Student s2 = new Student("张曼玉", 95, 95);
Student s3 = new Student("王祖贤", 100, 93);
Student s4 = new Student("柳岩", 100, 97);
Student s5 = new Student("风清扬", 98, 98);
Student s6 = new Student("左冷禅", 97, 99);
Student s7 = new Student("赵云", 97, 99); //把学生对象添加到集合
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7); //遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getChinese() + "," + s.getMath() + "," + s.getSum());
}
}
}
2.5不重复的随机数案例
案例需求
- 编写一个程序,获取10个1-20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复,并在控制台输出
代码实现
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Set集合对象
// Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<Integer>(); //创建随机数对象
Random r = new Random(); //判断集合的长度是不是小于10
while (set.size()<10) {
//产生一个随机数,添加到集合
int number = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
set.add(number);
} //遍历集合
for(Integer i : set) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Java(30)集合五Set的更多相关文章
- Java之集合(五)LinkedList
转载请注明源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7298017.html 1.前言 Java中另一个常见的list就是本章将要讲的LinkedList.ArrayL ...
- Java面试集合(三)-30道面试题
前言 大家好,我是 Vic,今天给大家带来Java面试集合(三)的概述,希望你们喜欢 三 1.在Java中是否可以含有多个类?答:可以含有多个类,但只有一个是public类,public类的类名与文件 ...
- Java实习生常规技术面试题每日十题Java基础(五)
目录 1.启动一个线程是用run()还是start()? . 2.线程的基本状态以及状态之间的关系. 3.Set和List的区别,List和Map的区别? 4.同步方法.同步代码块区别? 5.描述Ja ...
- Java 字符串拼接 五种方法的性能比较分析 从执行100次到90万次
[请尊重原创版权,如需引用,请注明来源及地址] > 字符串拼接一般使用“+”,但是“+”不能满足大批量数据的处理,Java中有以下五种方法处理字符串拼接,各有优缺点,程序开发应选择合适的方法实现 ...
- Java学习-集合(转)
在编写java程序中,我们最常用的除了八种基本数据类型,String对象外还有一个集合类,在我们的的程序中到处充斥着集合类的身影!java中集合大家族的成员实在是太丰富了,有常用的ArrayList. ...
- Java中的五种单例模式实现方法
[代码] Java中的五种单例模式实现方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 2 ...
- 浅谈Java的集合框架
浅谈Java的集合框架 一. 初识集合 重所周知,Java有四大集合框架群,Set.List.Queue和Map.四种集合的关注点不同,Set 关注事物的唯一性,List 关注事物的索引列表,Q ...
- Java面试集合(三)
前言 大家好,给大家带来Java面试集合(三)的概述,希望你们喜欢 三 1.在Java中是否可以含有多个类? 答:可以含有多个类,但只有一个是public类,public类的类名与文件名必须一致. 2 ...
- 算法篇(前序)——Java的集合
菜鸟拙见,望请纠正:附上JDK参考文档(中文文档和英文文档):链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/14KDmCtQxeGCViq7e0zENjA 密码:e9xs 以及算法篇全文链接 ...
- Java基础-集合的嵌套
Java基础-集合的嵌套 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.静态导入 静态导入是在JDK1.5后的新特性,可以减少开发的代码量,但是实际用处是很一般,静态导入的标准 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL主库手动复制至从库
原文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/itzgr/p/10233932.html作者:木二 目录 一 主库手动复制至从库 1.1 Master主库锁表 1.2 主库备份 1.3 从 ...
- MySQL-SQL基础1
p.p1 { margin: 0; font: 11px Menlo; background-color: rgba(128, 128, 128, 0.5); min-height: 13px } p ...
- Python之pyyaml模块
pyyaml模块在python中用于处理yaml格式数据,主要使用yaml.safe_dump().yaml.safe_load()函数将python值和yaml格式数据相互转换.当然也存在yaml. ...
- 学了这么多年C语言,你真的知道全局变量,局部变量,静态变量,本地函数,外部函数是如何区分标识的吗?
动态库内容分析 文章目录 动态库内容分析 1. 动态库编译 1.1 第一个C文件:basic.c 1.2第二个C文件:demo.c 1.3第三个C文件:main.c 2.动态库编译 3.二进制内容分析 ...
- C#中的文本到语音
本演示说明了如何使用c#.net Windows Forms应用程序中的system.speech库将文本转换为语音.Microsoft .NET框架提供System.Speech.Synthesis ...
- python库--pandas--文本文件读取
.read_table() / read_csv() filepath_or_buffer 文件路径 sep='\t' 分隔符. 设置为N, 将尝试自动确定 delimiter=N sep的备 ...
- sort-uniq-tr-cut命令 对文件处理相关操作
目录: 一.sort命令 二.uniq命令 三.tr命令 四.cut命令 五.eval命令 一.sort命令 以行为单位对文件内容进行排序,也可以根据不同的数据类型来排序 语法格式 sort [选项] ...
- 使用ECS和OSS搭建个人网盘
体验简介 本场景将提供一台配置了Centos 7.7版本的ECS实例(云服务器)和对象存储OSS实例.通过本教程的操作,您可以基于ECS和OSS快速搭建一个个人网盘. 体验此场景后,可以掌握的知识有: ...
- 洛谷P1781——宇宙总统(高精度排序)
题目描述 地球历公元6036年,全宇宙准备竞选一个最贤能的人当总统,共有n个非凡拔尖的人竟选总统,现在票数已经统计完毕,请你算出谁能够当上总统. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第一行为一个整数n,代表竞选 ...
- 【tp3.2】根据不同域名来加载不同的配置文件
遇到问题: 最近遇到一个需求,需要多个公众号使用同一个项目,这就导致了不同公众号访问的数据库和公众号配置不同. 解决思路: 查看文档:http://document.thinkphp.cn/manua ...
