DC-DC converter Control techniques
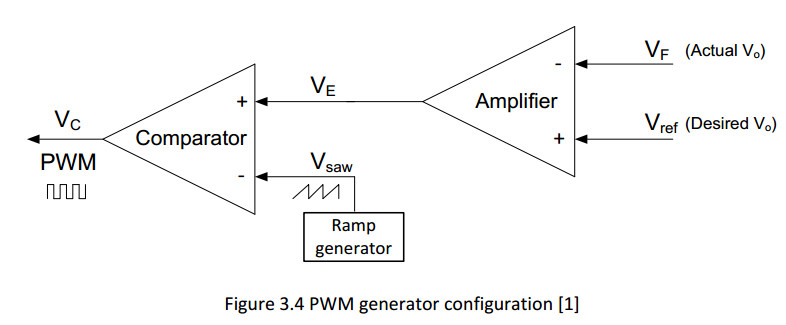
As shown in figure 3.4, PWM controller contains two main parts;
voltage error-amplifier and voltage comparator.
The error-amplifier compares the feedback voltage VF (applied to inverting input)
to reference voltage VREF (applied to non-inverting input)
then their difference which is called voltage error signal VE
after amplification is applied to noninverting input of voltage comparator.
Comparator compares this error voltage to sawtooth ramp VSAM that is generated by ramp generator,
if voltage VE is higher than VSAW output voltage of comparator goes high but
when VE is lower than VSAW the output of comparator goes low
to adjust the switching duty cycle.
error voltage VE is inversely proportional to voltage reference VREF,
for example when VREF is low, error voltage VE is increased by error amplifier to adjust the switching duty cycle.
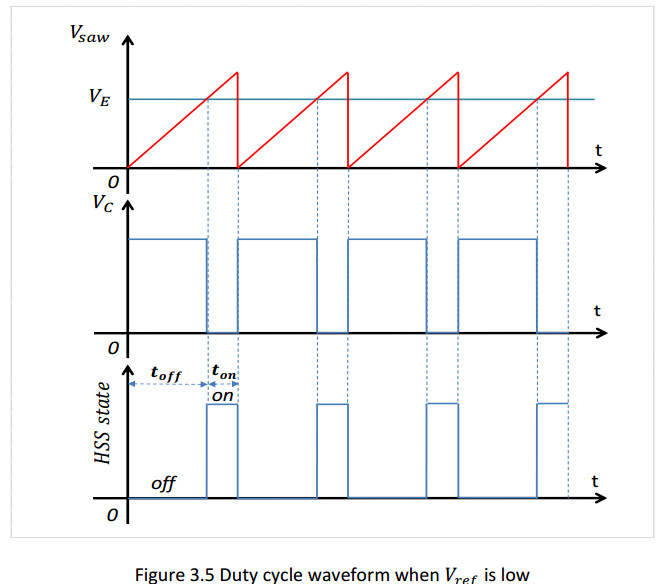
As can be seen in figure 3.5 when the error voltage is high the pulse width of PWM wave
at the output of voltage comparator (VC ) is increased to keep off High side switch (PMOS) for
the most time of the each cycle in order to reduce duty cycle to regulate output voltage.
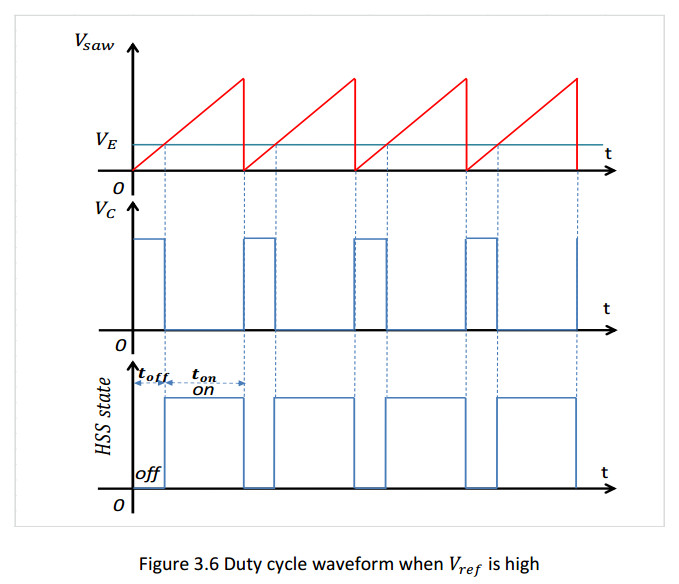
Vice versa as shown in figure 3.6 when VREF is high error amplifier reduces VE to keep on
the HSS for a most time of each period in order to adjust output voltage [14].
http://www.chinabaike.com/2011/0120/201049.html

From the derivations for the boost, buck, and inverter (flyback), it can be seen that changing the duty cycle controls the steady-state output with respect to the input voltage. This is a key concept governing all inductor-based switching circuits.
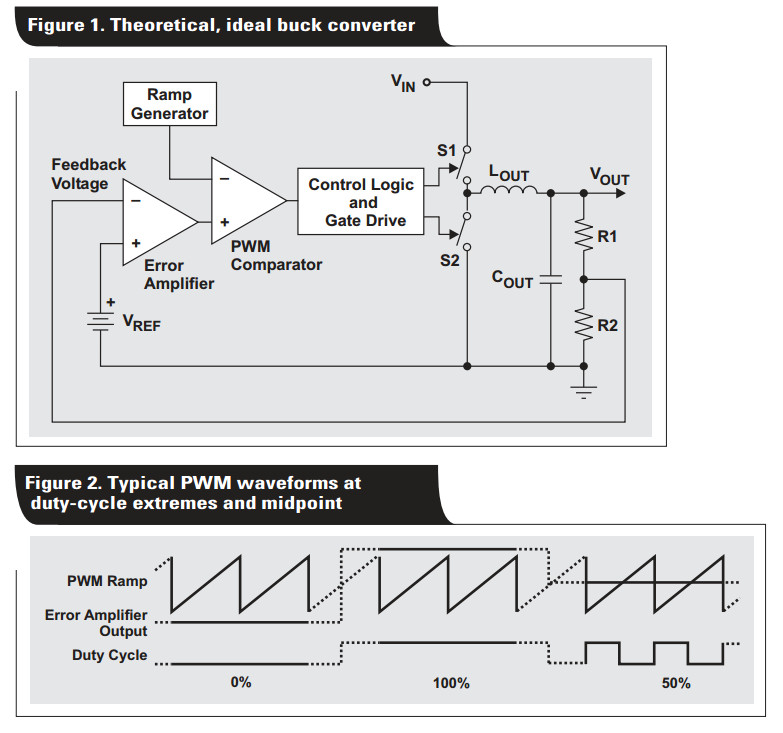
The most common control method, shown in Figure 7, is pulse-width modulation (PWM). This method takes a sample of the output voltage and subtracts this from a reference voltage to establish a small error signal (VERROR). This error signal is compared to an oscillator ramp signal. The comparator outputs a digital output (PWM) that operates the power switch. When the circuit output voltage changes, VERROR also changes and thus causes the comparator threshold to change. Consequently, the output pulse width (PWM) also changes. This duty cycle change then moves the output voltage to reduce to error signal to zero, thus completing the control loop.
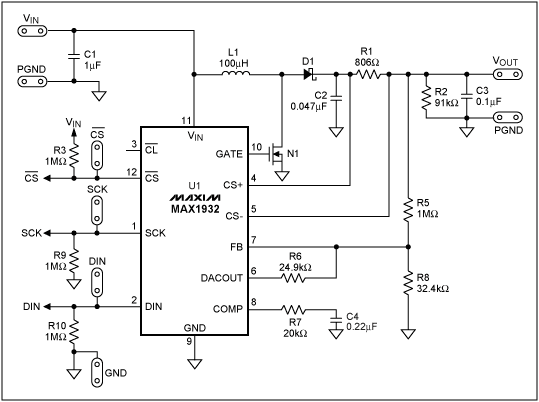
Figure 8 shows a practical circuit using the boost topology formed with the MAX1932.
This IC is an integrated controller with an onboard programmable digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
The DAC sets the output voltage digitally through a serial link.
R5 and R8 form a divider that meters the output voltage.
R6 is effectively out of circuit when the DAC voltage is the same as the reference voltage (1.25V).
This is because there is zero volts across R6 and so zero current.
When the DAC output is zero (ground), R6 is effectively in parallel with R8.
These two conditions correspond to the minimum and maximum output adjustment range of 40V and 90V, respectively.

Next, the divider signal is subtracted from the internal 1.25V reference and then amplified.
This error signal is then output on pin 8 as a current source.
This, in conjunction with the differential input pair, forms a transconductance amplifier.
This arrangement is used because the output at the error amp is high impedance (current source),
allowing the circuit's gain to be adjusted by changing R7 and C4.
This arrangement also provides the ability to trim the loop gain for acceptable stability margins.
The error signal on pin 8 is then forwarded to the comparator and output to drive the power switch.
R1 is a current-sense resistor that meters the output current.
When the current is unacceptably high, the PWM circuit shuts down, thereby protecting the circuit.
The type of switching (topology) in Figures 7 and 8 is classified as a voltage-mode controller (VMC)
because the feedback regulates the output voltage.
For analysis we can assume that if the loop gain is infinite, the output impedance for an ideal voltage source is zero.
Another commonly used type of control is current-mode control (CMC).
This method regulates the output current and, with infinite loop gain, the output is a high-impedance source.
In CMC, the current loop is nested with a slower voltage loop, as shown in Figure 9;
a ramp is generated by the slope of the inductor current and compared with the error signal.
So, when the output voltage sags, the CMC supplies more current to the load.
The advantage of CMC is its ability to manage the inductor current.
In VMC the inductor current is not metered. This becomes a problem because the inductor,
in conjunction with the output filter capacitor, forms a resonant tank that can ring and even cause oscillations.
Current mode control senses the inductor current to correct for inconsistencies.
Although difficult to accomplish, carefully selected compensation components can effectively cancel out this resonance in VCM.

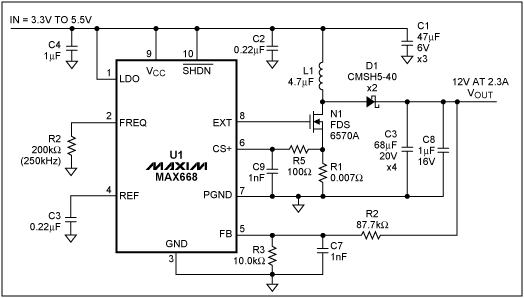
The circuit in Figure 10 uses CMC with the MAX668 controller.
This boost circuit is similar to Figures 7 and 8 except that R1 senses the inductor current for CMC.
R1 and some internal comparators provide a current limit.
R5 in conjunction with C9 filters the switching noise on the sense resistor to prevent false triggering of the current limit.
The MAX668's internal current-limit threshold is fixed; changing the resistor, R1, adjusts the current-limit setting.
The resistor, R2, sets the operating frequency.
The MAX668 is a versatile integrated circuit that can provide a wide range of DC-DC conversions.
The external components of the MAX668 can have high-voltage ratings that provide greater flexibility for high-power applications.
For portable applications that require less power, the MAX1760 and MAX8627 are recommended.
These latter devices use internal FETs, and sense the current by using the FETs' resistance to measure inductor current (no sense resistor required).
DC-DC converter Control techniques的更多相关文章
- PID DC/DC Converter Controller Using a PICmicro Microcontroller
http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=1824&appnote=en011794 ...
- Practice safe dc/dc converter
Short-circuit protection is an obvious requirement for a power supply, especially when its load conn ...
- LT1946A-- Transformerless dc/dc converter produces bipolar outputs
Dual-polarity supply provides ±12V from one IC VC (Pin 1): Error Amplifier Output Pin. Tie external ...
- Simple dc/dc converter increases available power in dual-voltage system
The schematic in Figure 1 shows a way to increase the power available from a current-limited 5V supp ...
- Add margining capability to a dc/dc converter
You can easily add margining capability—that is, the ability to digitally adjust the output voltage— ...
- [专业名词·硬件] 2、DC\DC、LDO电源稳压基本常识(包含基本原理、高效率模块设计、常见问题、基于nRF51822电源管理模块分析等)·长文
综述先看这里 第一节的1.1简单介绍了DC/DC是什么: 第二节是关于DC/DC的常见的疑问答疑,非常实用: 第三节是针对nRF51822这款芯片电源管理部分的DC/DC.LDO.1.8的详细分析,对 ...
- DC/DC与LDO的差别
转自:http://bbs.eetop.cn/thread-459121-1-1.html 在平时的学习中,我们都有接触LDO和DC/DC这一类的电源产品,但作为学生的我们队这些东西可能了解不够深刻, ...
- DC DC降壓變換器ic 工作原理
目前DC/DC轉化器大致可分為:升壓型dc dc變化器.降壓型dc dc變化器及可升壓又可降壓dc dc變換器.我們今天主要提一下降壓型dc dc變換器的原理: 見下圖降壓變換器原理圖如圖1所示, 當 ...
- DC DC電路電感的選擇
注:只有充分理解電感在DC/DC電路中發揮的作用,才能更優的設計DC/DC電路.本文還包括對同步DC/DC及異步DC/DC概念的解釋. DCDC電路電感的選擇 簡介 在開關電源的設計中電感的設計為 ...
随机推荐
- 教你如何修改FireFox打开新标签页(NewTab Page)的行列数
FireFox的打开新建标签页(即NewTab Page)默认只能显示3x3个网站缩略图,这9个自定义的网站,非常方便快捷,什么hao123的弱爆了,本人从未用过此类导航网站,曾经用过的也只是abou ...
- java并发编程实战笔记---(第五章)基础构建模块
. 5.1同步容器类 1.同步容器类的问题 复合操作,加容器内置锁 2.迭代器与concurrentModificationException 迭代容器用iterator, 迭代过程中,如果有其他线程 ...
- C#取色器
闲来无事,就写了一个取色器.原理其实很简单,只需要两步, 获取鼠标光标的位置, 获取当前鼠标光标的位置的RGB颜色值. 获取鼠标光标的位置: System.Drawing.Point p = Mous ...
- IEnumerable的几个简单用法
咋一看到IEnumerable这个接口,我们可能会觉得很神奇,在一般的编程时,基本上我们是想不到去用它的,可是,俗话说得好,存在便是道理,那么,它对我们来说,能够带来哪些奇妙的事情呢? 要想弄懂它,我 ...
- IEEEXtreme 10.0 - Counting Molecules
这是 meelo 原创的 IEEEXtreme极限编程大赛题解 Xtreme 10.0 - Counting Molecules 题目来源 第10届IEEE极限编程大赛 https://www.hac ...
- Hadoop案例(八)辅助排序和二次排序案例(GroupingComparator)
辅助排序和二次排序案例(GroupingComparator) 1.需求 有如下订单数据 订单id 商品id 成交金额 0000001 Pdt_01 222.8 0000001 Pdt_05 25.8 ...
- 趣味js【练习题】
1.无限极函数递归,使每次的参数相乘 需求:add(1)(2)(3)(4)(5) 1.1首先要知道一个东西,就是function每次调用,都会默认执行tosting 1.2利用递归,每次返回的都是函数 ...
- 【caffe-Windows】微软官方caffe之matlab接口配置,以及安装caffe的注意事项
1.在此之前,记录一下之前的错误,在参考博客[caffe-Windows]caffe+VS2013+Windows+GPU配置+cifar使用进行caffe的安装时,其中的一些步骤可以不做,具体见下图 ...
- ul>li中自定义属性后取值的问题
动态赋值的li: $.ajax({ type: "POST", url: "${base}/before/subDemand/listType", succes ...
- Python 爬虫笔记(三)
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains #Act ...
