《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 6.28

代码:
% The following 3 lines produce filter coefficients shown in Table 6.1
wp = [0.35, 0.65]; ws = [0.25, 0.75]; Rp = 1; As = 50;
[N, wn] = ellipord(wp, ws, Rp, As);
[b, a] = ellip(N, Rp, As, wn);
w = [0:500]*pi/500; H = freqz(b, a, w);
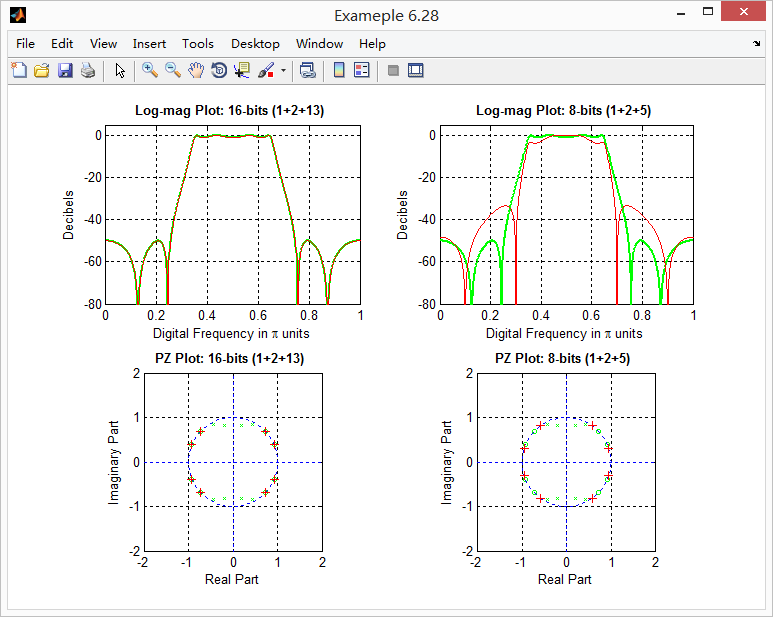
magH = abs(H); magHdb = 20*log10(magH); % 16-bit word-length quantization
N1 = 15; [bahat, L1, B1] = QCoeff([b; a], N1);
TITLE1 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N1+1, L1, B1);
bhat1 = bahat(1, :); ahat1 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat1 = freqz(bhat1, ahat1, w); magHhat1 = abs(Hhat1);
magHhat1db = 20*log10(magHhat1); zhat1 = roots(bhat1); % 8-bit word-length quantization
N2 = 7; [bahat, L2, B2] = QCoeff([b; a], N2);
TITLE2 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N2+1, L2, B2);
bhat2 = bahat(1, :); ahat2 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat2 = freqz(bhat2, ahat2, w); magHhat2 = abs(Hhat2);
magHhat2db = 20*log10(magHhat2); zhat2 = roots(bhat2); % Comparison of Magnitude Plots
Hf_1 = figure('paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 5], 'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.28');
%figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.26a')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 1); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat1db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 3); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [a]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat1), imag(zhat1), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off; % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 2); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat2db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 4); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [a]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat2), imag(zhat2), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off;
运行结果:
《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 6.28的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.28
昨晚手机在看X信的时候突然黑屏,开机重启都没反应,今天维修师傅说使用时间太长了,还是买个新的吧,心疼银子啊! 这里只放前两个小题的图. 代码: 1. %% ++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.28
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.28
又是一年五一节,朋友圈都是晒名山大川的,晒脑袋的,我这没钱的待在家里上网转转吧 频率采样法设计带通滤波器,过渡带中有一个样点 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu18.04里更新系统源和pip源
一.修改ubuntu系统源 我的ubuntu系统是在清华的开源网站上下的,所以我还以为他应该就帮我弄好源了,可是没想到下载的还是非常慢,看到下载的时候网址前还有个us,就知道不是国内源了.所以这里我们 ...
- 关于http请求ContentType:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
在又一次http请求过程中,模拟post请求提交form表单数据一直提示部分参数为空,后面检查发现是缺少ContentType:application/x-www-form-urlencoded的原因 ...
- w3c标准盒模型与IE传统模型的区别
一.盒子模型(box model) 在HTML文档中的每个元素被描绘为矩形盒子.确定其大小,属性——比如颜色.背景.边框,及其位置是渲染引擎的目标. CSS下这些矩形盒子由标准盒模型描述.这个模型描述 ...
- 关于 MongoDB 复制集
为什么要使用复制集 1.备份数据通过自带的 mongo_dump/mongo_restore 工具也可以实现备份,但是毕竟没有复制集的自动同步备份方便. 2.故障自动转移部署了复制集,当主节点挂了后, ...
- vs2012 在调试或运行的过程中不能加断点
在使用VS2012 的过程中,突然发现在调试的过程中,不能加断点,显示断点未能绑定.在搜寻了很多解决方案后未能解决,3.23这一天,重装了VS也没有用. 便想着把网上所有的方法都试个遍也要解决这个问题 ...
- ctci1.8
bool isSub(string str0, string str1){ if(str0.length() != str1.length()) return false; ...
- Java中unicode增补字符(辅助平面)相关用法简介
转载自 http://blog.csdn.net/gjb724332682/article/details/51324036 前言 Java从1.5版本开始,加入了unicode辅助平面的支持.相关的 ...
- Ansible 小手册系列 十九(常见指令表)
Play 指令 说明 accelerate 开启加速模式 accelerate_ipv6 是否开启ipv6 accelerate_port 加速模式的端口 always_run any_error ...
- ansible入门一(Ansible介绍及安装部署)
本节内容: 运维工具 Ansible特性 Ansible架构图和核心组件 安装Ansible 演示使用示例 一.运维工具 作为一个Linux运维人员,需要了解大量的运维工具,并熟知这些工具的差异,能够 ...
- lvs fullnat部署手册(一)fullnat内核编译篇
标签:kernel rpm lvs fullnat 原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.http://shanks.blog.51c ...
