D3D Deferred Shading
在3D图形计算中,deferred shading是一个基于屏幕空间的着色技术。之所以被称为deferred shading,是因为我们将场景的光照计算与渲染"deferred"到第二个pass。在第一个pass中,我们会将所有需要的数据(例如diffuse,normals,materials)渲染到一系列render targets中,这些render targets通常被称为geometry buffer(G-Buffer)。然后,在第二个pass中,从这些render targets中取出数据来执行光照计算与渲染。
Deferred shading技术的主要优点是它分离了场景中的光源与几何体。在我们熟悉的forward rendering技术中,为了渲染一盏光源的效果,我们不得不将在这盏光源范围内的几何体数据提交给GPU来进行计算与渲染。这个过程包含了许多states和shaders的切换,并且会产生大量的draw calls。而在deferred shading技术中,我们可以将许多光源甚至所有光源的计算与渲染在一个draw call中完成。所以当场景中的光源数量急剧增加时,deferred shading的优势将有巨大的体现。
Deferred shading技术的缺点在于它需要消耗更多的内存,带宽以及着色器指令。
下面通过一个例子来说明deferred shading的工作流程,在这个例子中,我在场景中发射了1024个粒子,每个粒子都被当作是一个点光源,最终效果如图:

首先来看下粒子的生成过程,我没有使用CPU来计算和生成粒子,而全部都是在GPU上完成的。我创建了四张32*32大小的纹理,纹理中的每个像素都代表了一个粒子,格式都是DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32A32_FLOAT。其中两张用于存储粒子的位置和生命周期,另外两张用于存储粒子的方向。这里各创建两张的原因是需要做ping-ponging,因为同一张纹理是不能同时读取和写入的(在渲染时,我们将其中两张作为输入,另外两张作为输出。在下一帧,将它们互换)。
存储粒子位置和生命周期的纹理如图(随意截取了一帧的数据),其中x, y, z存储粒子的位置,而w存储粒子的生命周期:
存储粒子方向的纹理如图(随意截取了一帧的数据),其中x, y, z存储粒子的方向,w没有使用:
每一帧,我都会根据上一帧粒子的位置和方向来计算出这一帧粒子的位置和方向:
PSOut main( PSIn pIn )
{
PSOut psOut; int3 texCoord = int3( int2(pIn.position.xy), ); // 采样上一帧粒子的位置和方向
float4 position = texPositions.Load( texCoord );
float4 direction = texDirections.Load( texCoord ); // Tick
position.w += frameTime;
if ( position.w >= 4.0f ) // 粒子的生命周期是4秒
{
// 重置粒子
direction.xyz = sprinkleDir;
position.xyz = float3( 0.0f, -235.0f, 0.0f );
position.w -= 4.0f;
}
else
{
// 计算重力
direction.y -= (500.0f * frameTime); // 更新位置
position.xyz += (direction.xyz * frameTime); // 伪物理,不让粒子超出场景的边界
direction.xyz = ((position.xyz > sceneBound) ? -0.8f * abs(direction.xyz) : direction.xyz);
direction.xyz = ((position.xyz < -sceneBound) ? 0.8f * abs(direction.xyz) : direction.xyz);
position.xyz = clamp( position.xyz, -sceneBound, sceneBound );
} //
psOut.position = position;
psOut.direction = direction; //
return psOut;
}
接着,在渲染粒子时,直接从计算完毕的纹理中采样粒子的位置数据,利用geometry shader生成朝向摄像机的面片,就完成了粒子的渲染:
[Geometry shader] Texture1D texColors;
SamplerState samColors; float4x4 viewProjMatrix;
float3 dirX, dirY; [maxvertexcount()]
void main( point GSIn gIn[], inout TriangleStream<PSIn> triStream )
{
PSIn gsOut; //
gsOut.color = texColors.SampleLevel(samColors, gIn[].position.w * 0.25f, ).rgb; // 输出朝向摄像机的面片
gsOut.position = mul( viewProjMatrix, float4(gIn[].position.xyz - dirX - dirY, 1.0f) );
gsOut.texCoord = float2( 0.0f, 1.0f );
triStream.Append( gsOut ); gsOut.position = mul( viewProjMatrix, float4(gIn[].position.xyz - dirX + dirY, 1.0f) );
gsOut.texCoord = float2( 0.0f, 0.0f );
triStream.Append( gsOut ); gsOut.position = mul( viewProjMatrix, float4(gIn[].position.xyz + dirX - dirY, 1.0f) );
gsOut.texCoord = float2( 1.0f, 1.0f );
triStream.Append( gsOut ); gsOut.position = mul( viewProjMatrix, float4(gIn[].position.xyz + dirX + dirY, 1.0f) );
gsOut.texCoord = float2( 1.0f, 0.0f );
triStream.Append( gsOut );
}

在计算完粒子的位置数据后,接着我们就渲染场景,在这个pass中,我们不计算光照,而仅仅是将场景的diffuse以及normal渲染到两张render targets中:
[Fragment shader] struct PSOut
{
float3 base : SV_TARGET0;
float3 normal : SV_TARGET1;
}; Texture2D texDiffuse;
Texture2D texBumpMap;
SamplerState samTrilinearAnisoWrap; PSOut main( PSIn pIn )
{
float3 base = texDiffuse.Sample(samTrilinearAnisoWrap, pIn.texCoord).rgb; float3 bump = texBumpMap.Sample(samTrilinearAnisoWrap, pIn.texCoord).xyz;
bump = 2.0f * bump - 1.0f; // Convert from [0, 1] to [-1, 1] // 计算法线
float3 normal = pIn.tangent * bump.x + pIn.binormal * bump.y + pIn.normal * bump.z;
normal = normalize( normal ); //
PSOut psOut;
psOut.base = base;
psOut.normal = normal * 0.5f + 0.5f; // Convert from [-1, 1] to [0, 1] return psOut;
}
这样,我们就有了用于在第二个pass中计算光照的G-Buffer数据:

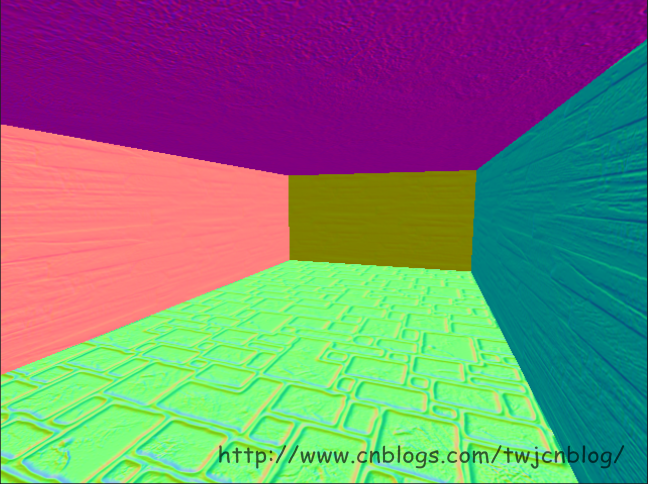
至此,我们可以开始我们的deferred shading了。具体流程是这样的:每个粒子我们都把它作为一个点光源,一种简单的方法是针对每个粒子,我们都绘制一个全屏四边形,触发屏幕上每个像素的着色器,然后去计算光照,但是这种方法的效率太低了。所以我采用的方法是计算每个点光源的覆盖范围,然后生成一个表示覆盖范围的四边形,来触发在范围内的像素的着色器。计算覆盖范围的方法为,将粒子的位置转换到视图空间,然后根据设置的点光源的范围来生成四边形的四个顶点,再将这四个顶点转换到clip-space:
// 投影矩阵分量:
// projMatrix[0][0]
// projMatrix[1][1]
// projMatrix[2][2]
// projMatrix[3][2]
float4 projMatrixComponoents; bool getScreenBox(
const float3 pos,
const float radius,
out float xProjLeft, out float xProjRight,
out float yProjTop, out float yProjBottom,
out float zProjNear, out float zProjFar )
{
// 初始化
xProjLeft = -;
xProjRight = ;
yProjTop = ;
yProjBottom = -;
zProjNear = ;
zProjFar = ; //
float4 viewLightPosition = mul( viewMatrix, float4(pos, 1.0f) ); // 计算z
float zViewFar = viewLightPosition.z + radius;
if ( zViewFar <= 0.0f )
{
// 光源完全位于摄像机之后
return false;
} //
float zViewNear = max( viewLightPosition.z - radius, 0.00001f ); //
zProjNear = projMatrixComponoents.z + projMatrixComponoents.w / zViewNear;
zProjFar = projMatrixComponoents.z + projMatrixComponoents.w / zViewFar; //
// 计算clip-space的四边形
//
float xViewLeft = viewLightPosition.x - radius;
xProjLeft = projMatrixComponoents.x * xViewLeft / viewLightPosition.z;
if ( xProjLeft >= 1.0f )
{
// 光源完全位于投影范围的右边
return false;
} float xViewRight = viewLightPosition.x + radius;
xProjRight = projMatrixComponoents.x * xViewRight / viewLightPosition.z;
if ( xProjRight <= -1.0f )
{
// 光源完全位于投影范围的左边
return false;
} float yViewTop = viewLightPosition.y + radius;
yProjTop = projMatrixComponoents.y * yViewTop / viewLightPosition.z;
if ( yProjTop <= -1.0f )
{
// 光源完全位于投影范围的底部
return false;
} float yViewBottom = viewLightPosition.y - radius;
yProjBottom = projMatrixComponoents.y * yViewBottom / viewLightPosition.z;
if ( yProjBottom >= 1.0f )
{
// 光源完全位于投影范围的顶部
return false;
} // Clamp all
xProjLeft = clamp( xProjLeft, -1.0f, xProjLeft );
xProjRight = clamp( xProjRight, xProjRight, 1.0f );
yProjTop = clamp( yProjTop, yProjTop, 1.0f );
yProjBottom = clamp( yProjBottom, -1.0f, yProjBottom ); return true;
}

接着,在光源范围内的像素的着色器被触发,我们就可以开始计算它们的光照了,从G-Buffer中采样diffuse和normal数据,进行常规的点光源光照计算即可:
[Fragment shader] Texture2D texBaseGBuffer;
Texture2D texNormalGBuffer;
Texture2D texDepth;
SamplerState samPointClamp; float4x4 invViewProjMatrix; float3 main( PSIn pIn ) : SV_TARGET0
{
float depth = texDepth.Sample(samPointClamp, pIn.texCoord).x; // 只计算在深度范围内的像素的光照
[branch]
if ( (depth >= pIn.zBounds.x) && (depth <= pIn.zBounds.y) )
{
float3 base = texBaseGBuffer.Sample(samPointClamp, pIn.texCoord).rgb;
float3 normal = texNormalGBuffer.Sample(samPointClamp, pIn.texCoord).xyz * 2.0f - 1.0f; // Clip-space position,x和y的偏移量已经计算在invViewProjMatrix中,所以这里就不需要转换了
float4 clipPosition = float4( pIn.texCoord, depth, 1.0f ); // World-space position
float4 worldPosition = mul( invViewProjMatrix, clipPosition );
worldPosition.xyz /= worldPosition.w; // Lighting
float3 lightDir = (pIn.lightPosition - worldPosition.xyz) / LIGHT_SIZE; //
float atten = saturate( 1.0f - dot(lightDir, lightDir) ); //
lightDir = normalize( lightDir );
float diffuse = saturate( dot(lightDir, normal) ); return (0.7f * atten * pIn.color * (diffuse * base));
} return ;
}
至此,我们的deferred shading就完成了 o(∩_∩)o

D3D Deferred Shading的更多相关文章
- 引擎设计跟踪(九.14.3.1) deferred shading: Depthstencil as GBuffer depth
问题汇总 1.Light support for Editor编辑器加入了灯光工具, 可以添加和修改灯光. 问题1. light object的用户互交.point light可以把对应的volume ...
- 引擎设计跟踪(九.14.3) deferred shading 准备
目前做的一些准备工作 1.depth prepass for forward shading. 做depth prepass的原因是为了完善渲染流程, 虽然架构上支持多个pass, 但实际上从来没有测 ...
- Deferred Shading延迟渲染
Deferred Shading 传统的渲染过程通常为:1)绘制Mesh:2)指定材质:3)处理光照效果:4)输出.传统的过程Mesh越多,光照处理越费时,多光源时就更慢了. 延迟渲染的步骤:1)Pa ...
- 引擎设计跟踪(九.14.3.2) Deferred shading的后续实现和优化
最近完成了deferred shading和spot light的支持, 并作了一部分优化. 之前forward shading也只支持方向光, 现在也支持了点光源和探照光. 对于forward sh ...
- Deferred Shading 延迟着色(翻译)
原文地址:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferred_shading 在3D计算机图形学领域,deferred shading 是一种屏幕空间着色技术.它被称为Def ...
- opengl deferred shading
原文地址:http://www.verydemo.com/demo_c284_i6147.html 一.Deferred shading技术简介 Deferred shading是这样一种技术:将光照 ...
- Deferred Shading,延迟渲染(提高渲染效率,减少多余光照计算)【转】
Deferred Shading,看过<Gems2> 的应该都了解了.最近很火的星际2就是使用了Deferred Shading. 原帖位置: http://blog.csdn.net ...
- Deferred shading rendering path翻译
Overview 概述 When using deferred shading, there is no limit on the number of lights that can affect a ...
- Unity的Deferred Shading
什么是Deferred Shading Unity自身除了支持前向渲染之外,还支持延迟渲染.Unity的rendering path可以通过Edit/Project Settings中的Graphic ...
随机推荐
- Java 第七天 动态代理
代理类需实现InvocationHandler接口: public interface InvocationHandler { public Object invoke(Object proxy,Me ...
- ASP.NET Core文章汇总
现有Asp.Net Core 文章资料,2016 3-20月汇总如下 ASP.NET Core 1.0 与 .NET Core 1.0 基础概述 http://www.cnblogs.com/Irvi ...
- 实战Django:官方实例Part1
[写在前面] 撰写这个实战系列的Django文章,是很久之前就有的想法,问题是手头实例太少,一旦开讲,恐有"无米下锅"之忧. 随着对Django学习的深入,渐渐有了些心得,把这些心 ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 Key Task Description The Czech Technical Univers ...
- hdu 5131 Song Jiang's rank list
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5131 Song Jiang's rank list Description <Shui Hu Z ...
- hdu 5264 pog loves szh I
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5264 pog loves szh I Description Pog has lots of stri ...
- SVN中的常见错误(长期更新)
一 svn中的简写含义. A:add,新增 C:conflict,冲突 D:delete,删除 M:modify,本地已经修改 G:modify and merGed,本地文件修改并且和服务器的进行合 ...
- How to Notify Command to evaluate in mvvmlight
How to Raize Command to evalituate in mvvm In mvvmlight, we bind our control to the relaycommand obj ...
- Think in java备忘录
1..new在内部类中的使用 .new可以用使用外部类对象创建一个内部类,对象 DotNew.java package com.gxf.innerclass; public class DotNew ...
- OA Framework - How to Find the Correct Version of JDeveloper to Use with E-Business Suite 11i or Release 12.x (Doc ID 416708.1)
APPLIES TO: Oracle Applications Framework - Version 11.5.10.0 to 12.2.2 [Release 11.5.10 to 12.2] In ...
