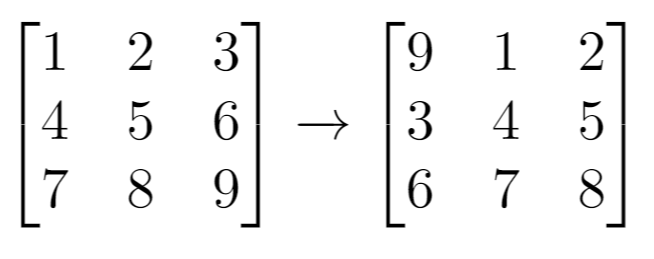【leetcode】1260. Shift 2D Grid
题目如下:
Given a 2D
gridof sizen*mand an integerk. You need to shift thegridktimes.In one shift operation:
- Element at
grid[i][j]becomes atgrid[i][j + 1].- Element at
grid[i][m - 1]becomes atgrid[i + 1][0].- Element at
grid[n - 1][m - 1]becomes atgrid[0][0].Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation
ktimes.Example 1:
Input:grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]Example 2:
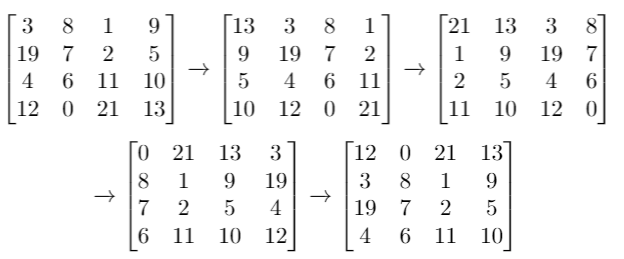
Input:grid= [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]Example 3:
Input:grid= [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]Constraints:
1 <= grid.length <= 501 <= grid[i].length <= 50-1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 10000 <= k <= 100
解题思路:记grid的行数为row,列数为col,显然经过row*col次移动后和不移动效果是一样的,所以可以首先令k = k%(row*col)。剩下的k就是每一个元素需要移动的次数,我的方法是给grid的每个元素编号,从左到右,从上到下,依次为0,1,1....row*col - 1,这样方便计算。
代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def shiftGrid(self, grid, k):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
row = len(grid)
col = len(grid[0])
k = k%(row * col)
res = [[0] * col for _ in range(row)]
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
inx = (i*col + j) + k
if inx >= (row*col):inx -= row*col
newrow = inx/col
newcol = inx%col
res[newrow][newcol] = grid[i][j]
return res
【leetcode】1260. Shift 2D Grid的更多相关文章
- 【leetcode】Search a 2D Matrix
Search a 2D Matrix Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This m ...
- 【leetcode】 Search a 2D Matrix (easy)
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the follo ...
- 【LeetCode】764. Largest Plus Sign 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]764. Largest Plus Sign 解题报告(Python) 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn ...
- 【leetcode】657. Robot Return to Origin
Algorithm [leetcode]657. Robot Return to Origin https://leetcode.com/problems/robot-return-to-origin ...
- 【LeetCode】Permutations 解题报告
全排列问题.经常使用的排列生成算法有序数法.字典序法.换位法(Johnson(Johnson-Trotter).轮转法以及Shift cursor cursor* (Gao & Wang)法. ...
- 【LeetCode】分治法 divide and conquer (共17题)
链接:https://leetcode.com/tag/divide-and-conquer/ [4]Median of Two Sorted Arrays [23]Merge k Sorted Li ...
- 【LeetCode】1162. 地图分析 As Far from Land as Possible(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 这个题想考察什么? 剩下的任务就是套模板! 日期 题目 ...
- 【LeetCode】代码模板,刷题必会
目录 二分查找 排序的写法 BFS的写法 DFS的写法 回溯法 树 递归 迭代 前序遍历 中序遍历 后序遍历 构建完全二叉树 并查集 前缀树 图遍历 Dijkstra算法 Floyd-Warshall ...
- 【LeetCode】Island Perimeter 解题报告
[LeetCode]Island Perimeter 解题报告 [LeetCode] https://leetcode.com/problems/island-perimeter/ Total Acc ...
随机推荐
- 再谈mysql锁机制及原理—锁的诠释
加锁是实现数据库并发控制的一个非常重要的技术.当事务在对某个数据对象进行操作前,先向系统发出请求,对其加锁.加锁后事务就对该数据对象有了一定的控制,在该事务释放锁之前,其他的事务不能对此数据对象进行更 ...
- Centos7 安装多版本php 并添加swoole拓展
服务器默认安装了php7 直接使用lnmp工具包安装php5.6 使用之前的lnmp安装包,切换到root sudo su - 运行 选择5.6 安装完成 没有安装swoole拓展 由官方https: ...
- php 二维数据排序 排行榜
php 二维数据排序 排行榜 $rateCount = array(); foreach($groupUsers as $user){ $rateCount[] = $user['rate']; } ...
- nginx一些高级配置
参数: https://www.wangbokun.com/%E8%BF%90%E7%BB%B4/2018/07/21/Nginx.html 免费证书等 1/ nginx代理hue限制上传文件大小 ...
- Swagger中paramType
paramType:表示参数放在哪个地方 header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader(代码中接收注解) query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestPa ...
- Python学习【day03】- Python基础练习题(列表、元组、字典)
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- # 1.有两个列表 # l1 = [11,22,33] # l2 = [22,33,44] # a.获取内容相同 ...
- Spring实现构造注入
Spring通过setter访问器实现对属性的赋值,这种做法称为设值注入:Spring还提供了通过构造方法赋值的能力,称为构造注入.使用设值注入时,Spring通过JavaBean的无参构造方法实例化 ...
- Git 实习一个月恍然大悟合集
从开始实习到现在大概有一个月了,这个月时间接触了很多新东西,其中就包括了git版本控制.分支管理等等.我在这段时间里,深深地感受到了git对公司项目代码管理和控制.团队合作带来的益处和其重要性.其实在 ...
- 附录1:arrayanalysis的本地使用(质量控制)
访问:https://github.com/BiGCAT-UM/affyQC_Module,点击“Download ZIP”,下载得到affyQC_Module-master.zip,解压得到一个af ...
- HTML5-placeholder属性
HTML 5<input> placeholder属性 placeholder属性提供可描述输入字段预期值的提示信息(hint). 该提示会在输入字段为空时显示,并会在字段获得焦点时消失. ...