Objective-C Memory Management Being Exceptional 异常处理与内存
Objective-C Memory Management Being Exceptional 异常处理与内存
3.1Cocoa requires that all exceptions must be of type NSException
cocoa 需要所有的异常是NSException类型的。
so even though you can throw an exception from other objects, Cocoa isn't set up to deal with those.
所以你即使从别的类抛出异常,cocoa 也不会处理。
Exception handling is really intended for errors that are generated by your programs. Cocoa frameworks usually handle errors by exiting the program, which is not what you want. You should throw and catch exceptions in your code, instead of letting them escape to the framework level.
cocoa框架通常用已经存在的程序解决异常。你应该throw and catch exceptions 在你自己的代码中,而不是任其跑到框架层。
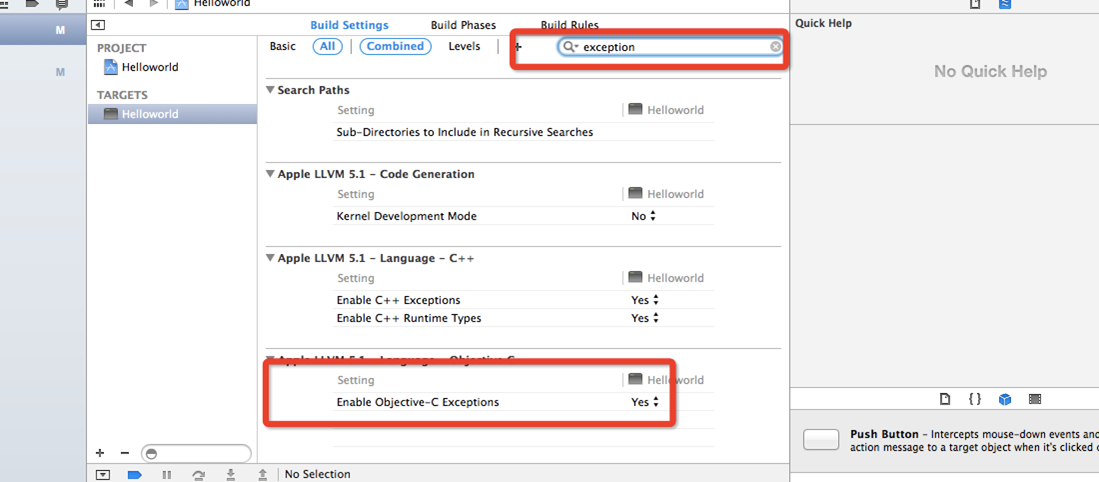
To enable support for exceptions, make sure the -fobj-exceptions flag is turned on.
为了支持异常,你应该确保-fobj-exceptions打开。
When an exception is thrown and is not caught, the program stops at the exception point and propagates the exception.
当一个异常抛出后,并没有被接到的话,则程序停在异常点。
3.2 Keywords for exceptions
All the keywords for exceptions start with @. Here's what each one does
所以的异常keyword 均以@开头。
(1)@try: Defines a block of code that will be tested to determine if an exception
should be thrown.
测试一个异常是否应该被抛出。
(2)@catch(): Defines a block of code for handling a thrown exception. Takes an
argument, typically of type NSException, but can be of other types.
处理异常
(3)@finally: Defines a block of code that gets executed whether an exception is
thrown or not. This code will always be executed.
不管是否抛出异常都运行。
(4)@throw: Throws an exception.
抛出异常
3.3 Catching Different types of exceptions
You can have multiple @catch blocks depending on which type of exception you want to handle.
可以根据exception 的类型来选择@catch 的类型
@try{
} @catch (MyCustomException *custom) {
} @catch (NSException *exception) {
} @catch (id value) {
} @finally {
}
A program throws an exception by creating an instance of NSException and using one of two techniques:
一个程序抛出异常通过创建NSException 和使用下面的技术:
(1)Using @throw exception;
(2)Sending a raise message to an NSException objectwe'll create an exception: 我们建一个NSExcepiton
NSException *theException = [NSException exceptionWithName: ...];
We can then throw with either 我们throw 通过下面:
@throw theException;
or
[theException raise];
You'll usually throw exceptions from inside the exception handling code.
也可以在一个exception handling code里再抛出异常。
@try {
NSException *e = ...;
@throw e; }
@catch (NSException *e) {
@throw; // rethrows e.
}
2.4 Exceptions need memory management too . 异常也需要内存管理
Memory management can be tricky when exceptions are involved.
- (void)mySimpleMethod
{
NSDictionary *dictionary = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWith....];
[self processDictionary:dictionary];
[dictionary release];
}
let's imagine that processDictionary throws an exception. The program jumps out of this method and looks for an exception handler. But because the method exits at this point, the dictionary object is not released, and we have a memory leak.
假如processDictionary 抛出异常,但是dictionary 还没有释放,因此有了memory leaks .
解决办法:One simple way to handle this is to use @try and @finally, doing some cleanup in @finally because it's always executed (as we said earlier).
在@finally 处处理,因为总是执行。
- (void)mySimpleMethod
{
NSDictionary *dictionary = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWith....];
@try {
[self processDictionary:dictionary];
}
@finally {
[dictionary release];
}
}
2.5 Exceptions and autorelease pools 异常和自动释放池
Exceptions are almost always created as autoreleased objects because you don't know when they will need to be released. When the autorelease pool is destroyed, all objects in that pool are destroyed also, including the exception.
Exceptions 几乎总是被创作为自动释放因为你不知道什么时候结束。
- (void)myMethod
{
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
NSDictionary *myDictionary =
[[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjectsAndKeys:@"asdfads", nil];
@try {
[self processDictionary:myDictionary];
} @catch (NSException *e) {
@throw;
} @finally {
[pool release];
}
}
There's a problem when we think about exception handling. We discussed earlier that we can rethrow exceptions in the @catch block, which causes the @finally block to execute before the exception is rethrown.
我们可以rethrow exceptions 在@catch block中。这导致了@finally在异常抛出前执行。
This will cause the local pool to be released before the exception can be delivered, thus turning it into a dreaded zombie exception.
这将导致恐怖的zombie exception.
- (void)myMethod
{
id savedException = nil;
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
NSDictionary *myDictionary =
[[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjectsAndKeys:@"asdfads", nil];
@try {
[self processDictionary:myDictionary];
} @catch (NSException *e) {
savedException = [e retain];
@throw;
} @finally {
[pool release];
[savedException autorelease];
}
}
By using retain, we saved the exception in the parent pool. When our pool is released, we already have a pointer saved, and when the parent pool is released, the exception will be released with it.
通过retain ,我们保留了这个exception 在parent pool。
Objective-C Memory Management Being Exceptional 异常处理与内存的更多相关文章
- Objective -C Memory Management 内存管理 第一部分
Objective -C Memory Management 内存管理 第一部分 Memory management is part of a more general problem in pr ...
- [译]C# 7系列,Part 10: Span<T> and universal memory management Span<T>和统一内存管理
原文:https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/mazhou/2018/03/25/c-7-series-part-10-spant-and-universal-memory- ...
- Memory Management in Open Cascade
Open Cascade中的内存管理 Memory Management in Open Cascade eryar@163.com 一.C++中的内存管理 Memory Management in ...
- Java (JVM) Memory Model – Memory Management in Java
原文地址:http://www.journaldev.com/2856/java-jvm-memory-model-memory-management-in-java Understanding JV ...
- Objective-C Memory Management
Objective-C Memory Management Using Reference Counting 每一个从NSObject派生的对象都继承了对应的内存管理的行为.这些类的内部存在一个称为r ...
- Operating System Memory Management、Page Fault Exception、Cache Replacement Strategy Learning、LRU Algorithm
目录 . 引言 . 页表 . 结构化内存管理 . 物理内存的管理 . SLAB分配器 . 处理器高速缓存和TLB控制 . 内存管理的概念 . 内存覆盖与内存交换 . 内存连续分配管理方式 . 内存非连 ...
- Android内存管理(2)HUNTING YOUR LEAKS: MEMORY MANAGEMENT IN ANDROID PART 2
from: http://www.raizlabs.com/dev/2014/04/hunting-your-leaks-memory-management-in-android-part-2-of- ...
- Android内存管理(1)WRANGLING DALVIK: MEMORY MANAGEMENT IN ANDROID PART 1
from : http://www.raizlabs.com/dev/2014/03/wrangling-dalvik-memory-management-in-android-part-1-of-2 ...
- Understanding Memory Management(2)
Understanding Memory Management Memory management is the process of allocating new objects and remov ...
随机推荐
- CSVReader
从网上找了一个开源的东东 ,网址 https://www.csvreader.com/
- socket.io中文文档
socket.io 中文文档转载于:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiezhengcai/p/3956401.html 服务端 io.on(‘connection’,function( ...
- Android控件之HorizontalScrollView 去掉滚动条
在默认情况下,HorizontalScrollView控件里面的内容在滚动的情况下,会出现滚动条,为了去掉滚动条, 只需要在<HorizontalScrollView/>里面加一句 and ...
- Ural2089:Experienced coach(二分图匹配)
Misha trains several ACM teams at the university. He is an experienced coach, and he does not undere ...
- 算法复习周------“动态规划之‘最长公共子序列’”&&《计蒜课》---最长公共子串题解
问题描述: 这个问题其实很容易理解.就是给你两个序列X={x1,x2,x3......xm} Y={y1,y2,y3......ym},要求找出X和Y的一个最长的公共子序列. 例:Xi={A, B, ...
- null、undefined和NaN的简洁比较
Null 类型也只有一个值,即null.null用来表示尚未存在的对象,常用来表示函数企图返回一个不存在的对象.Undefined 类型只有一个值,即undefined.当声明的变量还未被初始化时,变 ...
- python 面向对象九 定制类
一.定制类,实质就是我们自己重写特殊函数 看到类似__slots__这种形如__xxx__的变量或者函数名就要注意,这些在Python中是有特殊用途的. __slots__我们已经知道怎么用了,__l ...
- bzoj 4137 [FJOI2015]火星商店问题【CDQ分治+可持久化trie】
其实我不太清楚这个应该叫CDQ分治还是整体二分 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/lvzelong2014/article/details/78688727 一眼做法是线段树套可持久化t ...
- bzoj 1614: [Usaco2007 Jan]Telephone Lines架设电话线【二分+spfa】
二分答案,然后把边权大于二分值的的边赋值为1,其他边赋值为0,然后跑spfa最短路看是否满足小于等于k条边在最短路上 #include<iostream> #include<cstd ...
- concurrent包下的Exchanger练习
Exchanger可以在两个线程之间交换数据,只能是2个线程,他不支持更多的线程之间互换数据. 当线程A调用Exchange对象的exchange()方法后,他会陷入阻塞状态,直到线程B也调用了exc ...
