3.线性表-cursor
fatal.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define Error(Str) FatalError(Str)
#define FatalError(Str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", Str), exit(1)
cursor.h
typedef int ElementType;
#define SpaceSize 100
#ifndef _Cursor_H
#define _Cursor_H
typedef int PtrToNode;
typedef PtrToNode List;
typedef PtrToNode Position;
void InitializeCursorSpace(void);
List MakeEmpty(List L);
int IsEmpty(const List L);
int IsLast(const Position P, const List L);
Position Find(ElementType X, const List L);
void Delete(ElementType X, List L);
Position FindPrevious(ElementType X, const List L);
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P);
void DeleteList(List L);
Position Header(const List L);
Position First(const List L);
Position Advance(const Position P);
ElementType Retrieve(const Position P);
#endif
cursor.c
#include "cursor.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "fatal.h"
/* Place in the interface file */
struct Node
{
ElementType Element;
Position Next;
};
struct Node CursorSpace[SpaceSize];
static Position CursorAlloc(void)
{
Position P;
P = CursorSpace[0].Next;
CursorSpace[0].Next = CursorSpace[P].Next;
return P;
}
static void CursorFree(Position P)
{
CursorSpace[P].Next = CursorSpace[0].Next;
CursorSpace[0].Next = P;
}
void InitializeCursorSpace(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < SpaceSize; i++)
CursorSpace[i].Next = i + 1;
CursorSpace[SpaceSize - 1].Next = 0;
}
List MakeEmpty(List L)
{
if (L != 0)
DeleteList(L);
L = CursorAlloc();
if (L == 0)
FatalError("Out of memory!");
CursorSpace[L].Next = 0;
return L;
}
/* Return true if L is empty */
int IsEmpty(const List L)
{
return CursorSpace[L].Next == 0;
}
/* Return true if P is the last position in list L */
/* Parameter L is unused in this implementation */
int IsLast(const Position P, const List L)
{
return CursorSpace[P].Next == 0;
}
/* Return Position of X in L; 0 if not found */
/* Uses a header node */
Position Find(ElementType X, const List L)
{
Position P;
P = CursorSpace[L].Next;
while (P && CursorSpace[P].Element != X)
P = CursorSpace[P].Next;
return P;
}
/* Delete from a list */
/* Assume that the position is legal */
/* Assume use of a header node */
void Delete(ElementType X, List L)
{
Position P, TmpCell;
P = FindPrevious(X, L);
if (!IsLast(P, L)) /* Assumption of header use */
{ /* X is found; delete it */
TmpCell = CursorSpace[P].Next;
CursorSpace[P].Next = CursorSpace[TmpCell].Next;
CursorFree(TmpCell);
}
}
/* If X is not found, then Next field of returned value is 0 */
/* Assumes a header */
Position FindPrevious(ElementType X, const List L)
{
Position P;
P = L;
while (CursorSpace[P].Next &&
CursorSpace[CursorSpace[P].Next].Element != X)
P = CursorSpace[P].Next;
return P;
}
/* Insert (after legal position P) */
/* Header implementation assumed */
/* Parameter L is unused in this implementation */
void Insert(ElementType X, List L, Position P)
{
Position TmpCell;
TmpCell = CursorAlloc();
if (TmpCell == 0)
FatalError("Out of space!!!");
CursorSpace[TmpCell].Element = X;
CursorSpace[TmpCell].Next = CursorSpace[P].Next;
CursorSpace[P].Next = TmpCell;
}
/* Correct DeleteList algorithm */
void DeleteList(List L)
{
Position P, Tmp;
P = CursorSpace[L].Next; /* Header assumed */
CursorSpace[L].Next = 0;
while (P != 0)
{
Tmp = CursorSpace[P].Next;
CursorFree(P);
P = Tmp;
}
}
Position Header(const List L)
{
return L;
}
Position First(const List L)
{
return CursorSpace[L].Next;
}
Position Advance(const Position P)
{
return CursorSpace[P].Next;
}
ElementType Retrieve(const Position P)
{
return CursorSpace[P].Element;
}
testcurs.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cursor.h"
void PrintList(const List L)
{
Position P = Header(L);
if (IsEmpty(L))
printf("Empty list\n");
else
{
do
{
P = Advance(P);
printf("%d ", Retrieve(P));
} while (!IsLast(P, L));
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
List L;
Position P;
int i;
InitializeCursorSpace();
L = MakeEmpty(0);
P = Header(L);
PrintList(L);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Insert(i, L, P);
PrintList(L);
P = Advance(P);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i += 2)
Delete(i, L);
for (i = 10; i < 15; i++)
{
Insert(i, L, P);
PrintList(L);
P = Advance(P);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
if (Find(i, L) == 0)
printf("Element %d Find fails\n", i);
printf("Finished deletions\n");
PrintList(L);
DeleteList(L);
return 0;
}
函数调用关系图(Call graph)
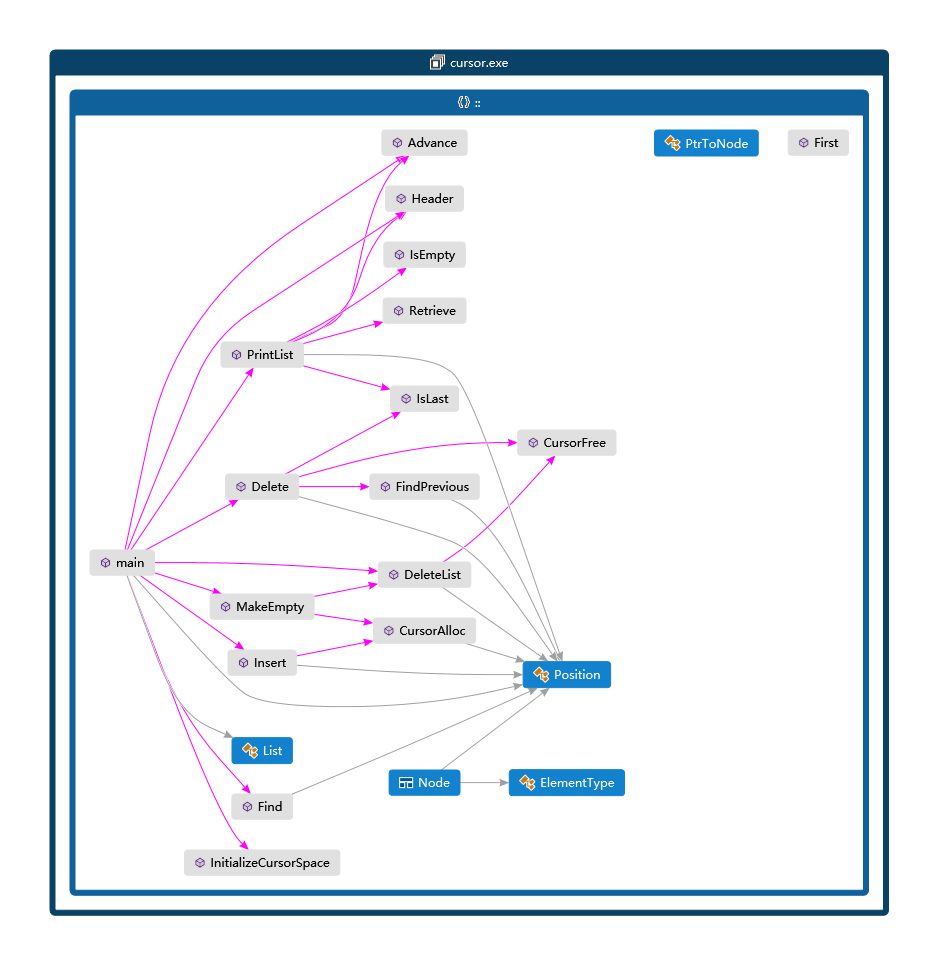
3.线性表-cursor的更多相关文章
- 算法与数据结构(一) 线性表的顺序存储与链式存储(Swift版)
温故而知新,在接下来的几篇博客中,将会系统的对数据结构的相关内容进行回顾并总结.数据结构乃编程的基础呢,还是要不时拿出来翻一翻回顾一下.当然数据结构相关博客中我们以Swift语言来实现.因为Swift ...
- 顺序存储线性表_ArrayList
相信大家在日常开发过程中 List 应该使用的非常非常多,今天就来简单学习一下 List 的数据结构 顺序存储线性表. 一.什么是顺序存储线性表 顺序存储线性表是最基本.最简单.也是最常用的一种数据结 ...
- 线性表Linearlist
顺序存储,链式存储,索引存储,散列存储 基本运算 SLIST 1.置空表 void SetNull(&L) 2.求长度 int Length(L) 3.取元素 ...
- 数据结构(Java描述)之线性表
基础概念 数据结构:是相互之间存在一种或多种关系的数据元素的集合. 逻辑结构和物理结构 关于数据结构,我们可以从逻辑结构和物理结构这两个维度去描述 逻辑结构是数据对象中数据元素之间的关系,是从逻辑意义 ...
- JAVASE02-Unit04: 集合框架 、 集合操作 —— 线性表
Unit04: 集合框架 . 集合操作 -- 线性表 操作集合元素相关方法 package day04; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Co ...
- 数据结构代码整理(线性表,栈,队列,串,二叉树,图的建立和遍历stl,最小生成树prim算法)。。持续更新中。。。
//归并排序递归方法实现 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; #define maxn 100 ...
- Java集合类学习笔记(各种线性表性能分析)
ArrayList.LinkedList是线性表的两种典型实现:基于数组的线性表和基于链的线性表. Queue代表了队列,Deque代表了双端队列. 一般来说,由于数组以一块连续内存区来保存所有的数组 ...
- 动态分配的顺序线性表的十五种操作—C语言实现
线性表 定义:是最常用的,也是最简单的数据结构,是长度为n个数据元素的有序的序列. 含有大量记录的线性表叫文件 记录:稍微复杂的线性表里,数据元素为若干个数据项组成,这时把一个数据元素叫记录 结构特点 ...
- Java Se :线性表
Java的集合框架分为两个系列,Collection和Map系列.在大学期间,学习数据结构时,好像学习了线性表.非线性表.树,哎,都给忘了.其实,在Collection系列内部又可以分为线性表.集合两 ...
随机推荐
- App提交Appstore审核流程
原文: https://www.douban.com/note/461351420/ 这是一个app提交到iTunces Connect被拒了4次摸索出来的经验,说多了都是泪,先让我擦擦...好了,话 ...
- linux mingling
grep 文本搜索工具 -i 忽略大小写 -v 不显示匹配行 -c 显示符合条件的行数值 文本搜索支持正则表达式 1 2 3 cat /etc/passwd | grep root // 显示包含ro ...
- MySQL 5.7 学习:功能性能的提升
背景: 继上次介绍 初识 MySQL 5.6 新功能.参数完之后,刚好MySQL 5.7又GA了,在官方测试里看到,MySQL5.7在功能.性能.可用性.安全和监控上又提升了很高.现在看看和MySQL ...
- 【转】android中ListView的定位:使用setSelectionFromTop实现ListView的position的保持
如果一个ListView太长,有时我们希望ListView在从其他界面返回的时候能够恢复上次查看的位置,这就涉及到ListView的定位问题: 解决的办法如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 // 保存 ...
- eclipse中如何安装插件ADT及SDK工具
1.如何在eclipse中安装ADT 首先下载ADT Plugin 下载地址: http://tools.android-studio.org/index.php/adt-bundle-plugin ...
- C# 获取时间差状态
/// <summary> /// 根据时间获取时间状态 /// </summary> /// <param name="dt"></pa ...
- Keywords Search(hdu 2222)
题意:给出n个单词,一篇文章,询问有几个单词在文章中出现过. /* AC自动机的裸题. 题目标号牛的一比. */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring& ...
- tp框架之空方法与空控制器
对于空方法的两种方法: 1.建立一个empty模板(不建议,除非打算指定静态页面) 2.在控制器里面加一个empty方法 public function _empty() { echo "控 ...
- rename
重命名文件名: # rename hosts.conf.正式配值文件 hosts.conf.正式配置文件 hosts.conf.正式配值文件 [root@monitor- vhost]# ls hos ...
- python环境变量自动配置脚本(setx使用)
前言 setx不是windows系统自带的工具,需要到微软官网下载,但是有的系统也会自带.(是官方提供的,可放心食用) set和setx都可以用来配置环境变量.他们的不同点在于,set只是临时的修改环 ...
