关联,聚合和组合(复合)--Association, Aggregation and Composition
概要
Association, Aggregation and Composition are terms that represent relationships among objects. They are very basic stuff of Object Oriented Programming.
关联
Association is a relationship among the objects. Association is "*a*" relationship among objects. In Association, the relationship among the objects determine what an object instance can cause another to perform an action on its behalf. We can also say that an association defines the multiplicity among the objects. We can define a one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one and many-to-many relationship among objects. Association is a more general term to define a relationship among objects. Association means that an object "uses" another object.
For example Managers and Employees, multiple employees may be associated with a single manager and a single employee may be associated with multiple managers.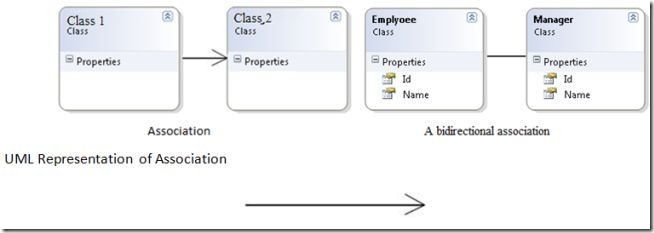
聚合
Aggregation is a special type of Association. Aggregation is "*the*" relationship among objects. We can say it is a direct association among the objects. In Aggregation, the direction specifies which object contains the other object. There are mutual dependencies among objects.
For example, departments and employees, a department has many employees but a single employee is not associated with multiple departments.
UML Representation of Aggregation (white diamond):
The UML representation of the example above (relation between employee and department):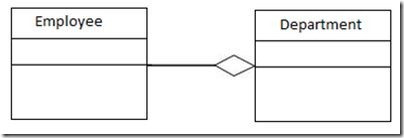
Here, the lives of both objects are independent of each other. That means that in this Association (Aggregation) the object has their own life cycle. Employees may exist without a department. Here, department can be called an owner object and the employee can be called a child object. The owner and child objects cannot belong to a different parent object.
组合(复合)
Composition is special type of Aggregation. It is a strong type of Aggregation. In this type of Aggregation the child object does not have their own life cycle. The child object's life depends on the parent's life cycle. Only the parent object has an independent life cycle. If we delete the parent object then the child object(s) will also be deleted. We can define the Composition as a "Part of" relationship.
For example, the company and company location, a single company has multiple locations. If we delete the company then all the company locations are automatically deleted. The company location does not have their independent life cycle, it depends on the company object's life (parent object).
UML Representation of Composition (black diamond):
UML representation of the example above (relation between Company and Company Location):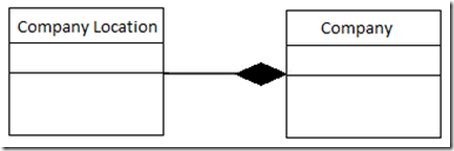
Here, the lives of both objects are not independent. The life of the company location object can be determined by the life of the company object. The company object is responsible for creating and destroying company location objects.
关联,聚合和组合三者之间的关系图
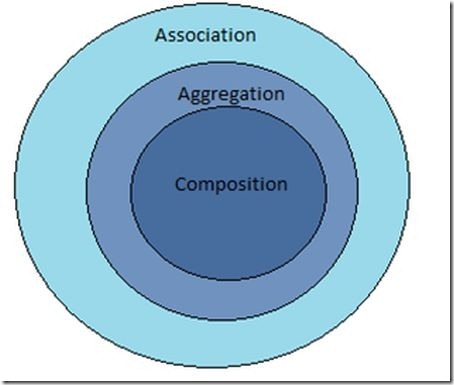
Aggregation and Composition are a special type of Association. Composition is again a special type of Aggregation. We can define Aggregation and Composition as "has a" relationships. Composition is more restrictive or more specific. In Composition, composed objects cannot exist without the other object. This type of restriction does not exist in Aggregations. In Aggregation, the existence of a composed object is optional. In Aggregation, the child object can exist beyond the life cycle of its parent whereas in Composition the child object cannot exist beyond the life cycle of its parent.
Combined example of Aggregation and Composition: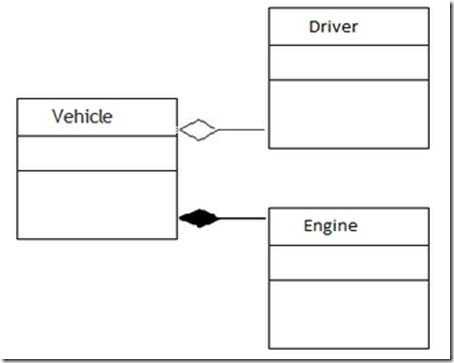
聚合VS组合
| Aggregation | Composition |
| Aggregation is a special type of Association. | Composition is a special type of Aggregation. |
| All objects have their own life cycle. | In Composition, the child object does not have their own life cycle and it depends on the parent's life cycle. |
| A parent class is not responsible for creating or destroying the child class. | The parent class is responsible for creating or destroying the child class. |
| Aggregation can be described as a "Has-a" relationship. | Composition can be described as a "Has-a" relationship as well as a "Part of" relationship, but here the difference is the length of the relationship among the objects. |
| Aggregation is a weak Association. | Composition is a strong Association. |
| Aggregation means one object is the owner of another object. | Composition means one object is contained in another object. |
| The direction of a relation is a requirement in both Composition and Aggregation. The direction specifies which object contains the other one. | |
| Both have a single direction of association. | |
| Both have a single owner. | |
结论
These three terms are more important in the object oriented world. They denote or represent the relations among objects. If you are confused or unable to decide whether a specific relation best describes an Association, Aggregation or Composition then it can be decribed as an Association.
引用:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/ff2f08/association-aggregation-and-composition/
关联,聚合和组合(复合)--Association, Aggregation and Composition的更多相关文章
- UML类关系:依赖,关联,聚合和组合
UML图示例:(可使用StartUML来画图,小巧^_^) http://www.blogjava.net/lukangping/archive/2010/08/01/327693.html 聚合:表 ...
- Inheritance, Association, Aggregation, and Composition 类的继承,关联,聚合和组合的区别
在C++中,类与类之间的关系大概有四种,分别为继承,关联,聚合,和组合.其中继承我们大家应该都比较熟悉,因为是C++的三大特性继承Inheritance,封装Encapsulation,和多态Poly ...
- UML类关系(依赖,关联,聚合,组合,泛化,实现)
转自https://blog.csdn.net/k346k346/article/details/59582926 在学习面向对象设计时,类关系涉及依赖.关联.聚合.组合和泛化这五种关系,耦合度依 ...
- UML类图关系(泛化 、继承、实现、依赖、关联、聚合、组合)
UML类图关系(泛化 .继承.实现.依赖.关联.聚合.组合) 继承.实现.依赖.关联.聚合.组合的联系与区别 分别介绍这几种关系: 继承 指的是一个类(称为子类.子接口)继承另外的一个类(称为父类.父 ...
- java--依赖、关联、聚合和组合之间区别的理解
在学习面向对象设计对象关系时,依赖.关联.聚合和组合这四种关系之间区别比较容易混淆.特别是后三种,仅仅是在语义上有所区别,所谓语义就是指上下文环境.特定情景等. 依赖(Dependency)关系是类与 ...
- java_UML:继承/泛化、实现、依赖、关联、聚合、组合的联系与区别 (2016-07-12)
分别介绍这几种关系: UML关系:继承(泛化).实现.依赖.关联.聚合.组合的联系与区别 一.表示符号上的区别 二.具体区别与联系 1. 继承/泛化(Generalization) [泛化关系]:是一 ...
- UML[1] UML类图关系(泛化 、继承、实现、依赖、关联、聚合、组合)(转)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoxu0312/article/details/7212152 继承.实现.依赖.关联.聚合.组合的联系与区别 分别介绍这几种关系: 继承 指的是 ...
- UML图中类之间的关系:依赖,泛化,关联,聚合,组合,实现
UML图中类之间的关系:依赖,泛化,关联,聚合,组合,实现 类与类图 1) 类(Class)封装了数据和行为,是面向对象的重要组成部分,它是具有相同属性.操作.关系的对象集合的总称. 2) 在系统中, ...
- UML类图及依赖,泛化,关联,聚合,组合,实现
UML图中类之间的关系:依赖,泛化,关联,聚合,组合,实现 类与类图 1) 类(Class)封装了数据和行为,是面向对象的重要组成部分,它是具有相同属性.操作.关系的对象集合的总称. 2) 在系统中, ...
随机推荐
- LCN协调者服务集群
官方文档: https://github.com/codingapi/tx-lcn/wiki/TxManager%E9%9B%86%E7%BE%A4%E8%AF%B4%E6%98%8E 核心原理 通过 ...
- 搭建confluence参考文献
https://www.cnblogs.com/kevingrace/p/7607442.html https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/144747?t=t1 jira: h ...
- QT QMimeData类
http://blog.csdn.net/xie376450483/article/details/5863810 QMimeData类提为数据提供一个容器,用来记录关于MIME类型数据的信息 QMi ...
- Spring Cloud Ribbon实现客户端负载均衡
1.构建microservice-consumer-movie-ribbon项目,在pom.xml中引入ribbon依赖 在引入Eureka依赖的时候,默认里面含有ribbon依赖 2.添加@Load ...
- html5 pc端参考网址
http://huodong.baidu.com/zhuanpan/?SEM&PC&refer=107255
- 本地的html服务
本地的调试的时候, 我们服务器返回的cookie就会变的失效,因为你的本地服务器的域名不太对.
- java:system根据输入的内容,然后输出(字节流)
把输入的内容输出来:根据system.in的内容System.out.println输出出来 都是字节流,的形式: //限制读取的字符长度 //字节流 InputStream ips = System ...
- poj2112 最大流+floyd+二分
题意:给一堆点,一部分是牛,一部分是机器,每头牛必须要走到一个机器,每个点之间有距离,要求每头牛都能找得到一台机器(机器有最大容量)的情况下,走的最远的牛距离最小 题解:二分答案,小于该距离的边才能加 ...
- Android自定义组件之ListView
1-ListView简介 在android开发中ListView是比较常用的组件,它以列表的形式展示具体内容,并且能够根据数据的长度自适应显示.一个ListView通常有两个职责. (1)将数据填充到 ...
- getBytes()详解
在java中,getBytes()方法如果不指定字符集,则得到的是一个操作系统默认的编码格式的字节数组:如果指定字符集,则得到的是在指定字符集下的字节数组,如: byte[] b_gbk = &quo ...
