zookeeper系列(七)zookeeper的序列化及通讯协议
作者:leesf 掌控之中,才会成功;掌控之外,注定失败。原创地址http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6091208.html尊重作者原创,奇文共欣赏,大家共同学习;
一、前言
前面介绍了Zookeeper的系统模型,下面进一步学习Zookeeper的底层序列化机制,Zookeeper的客户端与服务端之间会进行一系列的网络通信来实现数据传输,Zookeeper使用Jute组件来完成数据的序列化和反序列化操作。
二、首先我们普及下序列化和反序列化的知识:
概念:把对象转换为字节序列的过程称为对象的序列化;把字节序列恢复为对象的过程称为对象的反序列化。
用途:把对象的字节序列永久地保存到硬盘上,通常存放在一个文件中;在网络上传送对象的字节序列;
描述:在很多应用中,需要对某些对象进行序列化,让它们离开内存空间,入住物理硬盘,以便长期保存。比如最常见的是Web服务器中的Session对象,当有10万用户并发访问,就有可能出现10万个Session对象,内存可能吃不消,于是Web容器就会把一些seesion先序列化到硬盘中,等要用了,再把保存在硬盘中的对象还原到内存中;
当两个进程在进行远程通信时,彼此可以发送各种类型的数据。无论是何种类型的数据,都会以二进制序列的形式在网络上传送。发送方需要把这个Java对象转换为字节序列,才能在网络上传送;接收方则需要把字节序列再恢复为Java对象;
综述:序列化的目的就是方便对应的传输与存储。
serialVersionUID这个也有必要说一下,若不指定serialVersionUID的值,java编译器会自动给这个class进行一个摘要算法,生成一个UID(类似于指纹算法)。只要这个文件有变动,得到的UID就会截然不同。若对当前的java文件变动并且也没有指定serialVersionUID的值,编译器会为我们生成了一个UID,这样会导致序列化前后的值不一致,从而就会导致对象的反序列化失败。若在java文件中指定serialVersionUID的值,则在序列化或反序列化时就不在生成新的UID,直接拿文件中的比对;
三、Jute
Jute是Zookeeper底层序列化组件,其用于Zookeeper进行网络数据传输和本地磁盘数据存储的序列化和反序列化工作。
2.1 Jute序列化
MockReHeader实体类
package com.hust.grid.leesf.examples; import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.jute.InputArchive;
import org.apache.jute.OutputArchive;
import org.apache.jute.Record;
/**
* 创建MockReHeader实体类,实现Record接口
*/
public class MockReHeader implements Record{
private long sessionId;
private String type; public MockReHeader() {} public MockReHeader(long sessionId, String type) {
this.sessionId = sessionId;
this.type = type;
}
/**
* 序列化
*/
public void serialize(OutputArchive archive, String tag) throws IOException {
archive.startRecord(this, tag);
archive.writeLong(sessionId, "sessionId");
archive.writeString(type, "type");
archive.endRecord(this, tag);
}
/**
* 反序列化
*/
public void deserialize(InputArchive archive, String tag)
throws IOException {
archive.startRecord(tag);
this.sessionId = archive.readLong("sessionId");
this.type = archive.readString("type");
archive.endRecord(tag);
} public void setSessionId(long sessionId) {
this.sessionId = sessionId;
} public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
} public long getSessionId() {
return sessionId;
} public String getType() {
return type;
} } package com.hust.grid.leesf.examples; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import org.apache.jute.BinaryInputArchive;
import org.apache.jute.BinaryOutputArchive;
import org.apache.zookeeper.server.ByteBufferInputStream; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
BinaryOutputArchive boa = BinaryOutputArchive.getArchive(baos);
new MockReHeader(0x3421eccb92a34el, "create").serialize(boa, "header");
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(baos.toByteArray()); ByteBufferInputStream bbis = new ByteBufferInputStream(bb);
BinaryInputArchive bia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(bbis); MockReHeader header = new MockReHeader();
System.out.println("sessionId:"+header.getSessionId()+" type:"+header.getType() );
header.deserialize(bia, "create");
System.out.println("sessionId:"+header.getSessionId()+" type:"+header.getType() );
bbis.close();
baos.close();
}
}
运行结果

说明:可以看到MockReHeader实体类需要实现Record接口并且实现serialize和deserialize方法。OutputArchive和InputArchive分别是Jute底层的序列化器和反序列化器。
在Zookeeper的src文件夹下有zookeeper.jute文件,其内容如下:
其定义了所有的实体类的所属包名、类名及类的所有成员变量和类型,该文件会在源代码编译时,Jute会使用不同的代码生成器为这些类定义生成实际编程语言的类文件,如java语言生成的类文件保存在src/java/generated目录下,每个类都会实现Record接口。
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ module org.apache.zookeeper.data {
class Id {
ustring scheme;
ustring id;
}
class ACL {
int perms;
Id id;
}
// information shared with the client
class Stat {
long czxid; // created zxid
long mzxid; // last modified zxid
long ctime; // created
long mtime; // last modified
int version; // version
int cversion; // child version
int aversion; // acl version
long ephemeralOwner; // owner id if ephemeral, 0 otw
int dataLength; //length of the data in the node
int numChildren; //number of children of this node
long pzxid; // last modified children
}
// information explicitly stored by the server persistently
class StatPersisted {
long czxid; // created zxid
long mzxid; // last modified zxid
long ctime; // created
long mtime; // last modified
int version; // version
int cversion; // child version
int aversion; // acl version
long ephemeralOwner; // owner id if ephemeral, 0 otw
long pzxid; // last modified children
} // information explicitly stored by the version 1 database of servers
class StatPersistedV1 {
long czxid; //created zxid
long mzxid; //last modified zxid
long ctime; //created
long mtime; //last modified
int version; //version
int cversion; //child version
int aversion; //acl version
long ephemeralOwner; //owner id if ephemeral. 0 otw
}
} module org.apache.zookeeper.proto {
class ConnectRequest {
int protocolVersion;
long lastZxidSeen;
int timeOut;
long sessionId;
buffer passwd;
}
class ConnectResponse {
int protocolVersion;
int timeOut;
long sessionId;
buffer passwd;
}
class SetWatches {
long relativeZxid;
vector<ustring>dataWatches;
vector<ustring>existWatches;
vector<ustring>childWatches;
}
class RequestHeader {
int xid;
int type;
}
class MultiHeader {
int type;
boolean done;
int err;
}
class AuthPacket {
int type;
ustring scheme;
buffer auth;
}
class ReplyHeader {
int xid;
long zxid;
int err;
}
class GetDataRequest {
ustring path;
boolean watch;
}
class SetDataRequest {
ustring path;
buffer data;
int version;
}
class SetDataResponse {
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
class GetSASLRequest {
buffer token;
}
class SetSASLRequest {
buffer token;
}
class SetSASLResponse {
buffer token;
}
class CreateRequest {
ustring path;
buffer data;
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
int flags;
}
class DeleteRequest {
ustring path;
int version;
}
class GetChildrenRequest {
ustring path;
boolean watch;
}
class GetChildren2Request {
ustring path;
boolean watch;
}
class CheckVersionRequest {
ustring path;
int version;
}
class GetMaxChildrenRequest {
ustring path;
}
class GetMaxChildrenResponse {
int max;
}
class SetMaxChildrenRequest {
ustring path;
int max;
}
class SyncRequest {
ustring path;
}
class SyncResponse {
ustring path;
}
class GetACLRequest {
ustring path;
}
class SetACLRequest {
ustring path;
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
int version;
}
class SetACLResponse {
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
class WatcherEvent {
int type; // event type
int state; // state of the Keeper client runtime
ustring path;
}
class ErrorResponse {
int err;
}
class CreateResponse {
ustring path;
}
class ExistsRequest {
ustring path;
boolean watch;
}
class ExistsResponse {
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
class GetDataResponse {
buffer data;
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
class GetChildrenResponse {
vector<ustring> children;
}
class GetChildren2Response {
vector<ustring> children;
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
class GetACLResponse {
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
} module org.apache.zookeeper.server.quorum {
class LearnerInfo {
long serverid;
int protocolVersion;
}
class QuorumPacket {
int type; // Request, Ack, Commit, Ping
long zxid;
buffer data; // Only significant when type is request
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.Id> authinfo;
}
} module org.apache.zookeeper.server.persistence {
class FileHeader {
int magic;
int version;
long dbid;
}
} module org.apache.zookeeper.txn {
class TxnHeader {
long clientId;
int cxid;
long zxid;
long time;
int type;
}
class CreateTxnV0 {
ustring path;
buffer data;
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
boolean ephemeral;
}
class CreateTxn {
ustring path;
buffer data;
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
boolean ephemeral;
int parentCVersion;
}
class DeleteTxn {
ustring path;
}
class SetDataTxn {
ustring path;
buffer data;
int version;
}
class CheckVersionTxn {
ustring path;
int version;
}
class SetACLTxn {
ustring path;
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.data.ACL> acl;
int version;
}
class SetMaxChildrenTxn {
ustring path;
int max;
}
class CreateSessionTxn {
int timeOut;
}
class ErrorTxn {
int err;
}
class Txn {
int type;
buffer data;
}
class MultiTxn {
vector<org.apache.zookeeper.txn.Txn> txns;
}
}
四、通信协议
基于TCP/IP协议,Zookeeper实现了自己的通信协议来完成客户端与服务端、服务端与服务端之间的网络通信;对于请求,主要包含请求头和请求体;对于响应,主要包含响应头和响应体。

4.1 请求协议
对于请求协议而言,如下为获取节点数据请求的完整协议定义
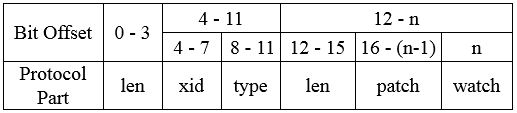
class RequestHeader {
int xid;
int type;
}
从zookeeper.jute中可知RequestHeader包含了xid和type,xid用于记录客户端请求发起的先后序号,用来确保单个客户端请求的响应顺序,type代表请求的操作类型,如创建节点(OpCode.create)、删除节点(OpCode.delete)、获取节点数据(OpCode.getData)。
协议的请求主体内容部分,包含了请求的所有操作内容,不同的请求类型请求体不同。对于会话创建而言,其请求体如下
class ConnectRequest {
int protocolVersion;
long lastZxidSeen;
int timeOut;
long sessionId;
buffer passwd;
}
Zookeeper客户端和服务器在创建会话时,会发送ConnectRequest请求,该请求包含协议版本号protocolVersion、最近一次接收到服务器ZXID lastZxidSeen、会话超时时间timeOut、会话标识sessionId和会话密码passwd。
对于获取节点数据而言,其请求体如下:
class GetDataRequest {
ustring path;
boolean watch;
}
Zookeeper客户端在向服务器发送节点数据请求时,会发送GetDataRequest请求,该请求包含了数据节点路径path、是否注册Watcher的标识watch。
对于更新节点数据而言,其请求体如下
class SetDataRequest {
ustring path;
buffer data;
int version;
}
Zookeeper客户端在向服务器发送更新节点数据请求时,会发送SetDataRequest请求,该请求包含了数据节点路径path、数据内容data、节点数据的期望版本号version。
针对不同的请求类型,Zookeeper都会定义不同的请求体,可以在zookeeper.jute中查看。
4.2 响应协议
对于响应协议而言,如下为获取节点数据响应的完整协议定义
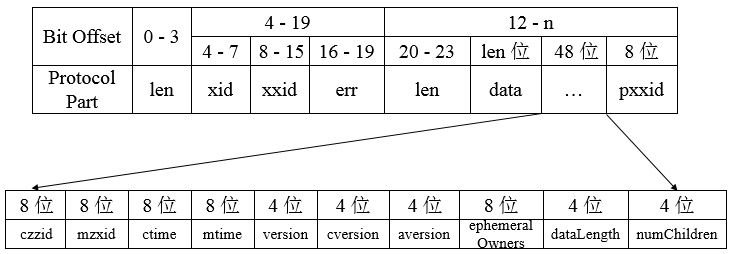
响应头中包含了每个响应最基本的信息,包括xid、zxid和err:
class ReplyHeader {
int xid;
long zxid;
int err;
}
xid与请求头中的xid一致,zxid表示Zookeeper服务器上当前最新的事务ID,err则是一个错误码,表示当请求处理过程出现异常情况时,就会在错误码中标识出来,常见的包括处理成功(Code.OK)、节点不存在(Code.NONODE)、没有权限(Code.NOAUTH)。
协议的响应主体内容部分,包含了响应的所有数据,不同的响应类型请求体不同。对于会话创建而言,其响应体如下
class ConnectResponse {
int protocolVersion;
int timeOut;
long sessionId;
buffer passwd;
}
针对客户端的会话创建请求,服务端会返回客户端一个ConnectResponse响应,该响应体包含了版本号protocolVersion、会话的超时时间timeOut、会话标识sessionId和会话密码passwd。
对于获取节点数据而言,其响应体如下:
class GetDataResponse {
buffer data;
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
针对客户端的获取节点数据请求,服务端会返回客户端一个GetDataResponse响应,该响应体包含了数据节点内容data、节点状态stat。
对于更新节点数据而言,其响应体如下
class SetDataResponse {
org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat stat;
}
针对客户端的更新节点数据请求,服务端会返回客户端一个SetDataResponse响应,该响应体包含了最新的节点状态stat。
针对不同的响应类型,Zookeeper都会定义不同的响应体,可以在zookeeper.jute中查看。
四、总结
本篇博客讲解了Zookeeper中的序列化机制和客户端与服务端、服务端与服务端的通信协议,内容相对较为简单,容易理解
zookeeper系列(七)zookeeper的序列化及通讯协议的更多相关文章
- 分布式系列七: zookeeper简单用法
zookeeper是分布式开源框架, 是Google Chubby的一个实现, 主要作为分布式系统的协调服务. Dobbo等框架使用了其功能. zookeeper特性 顺序一致性: 事务请求最终会严格 ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】ZooKeeper一致性原理(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4138580.html 一.ZooKeeper 的实现 1.1 ZooKeeper处理单点故障 我们知道可以通过Zo ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】Zookeeper简单介绍(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4033574.html 一.分布式协调技术 在给大家介绍ZooKeeper之前先来给大家介绍一种技术——分布式协调技 ...
- zookeeper系列之六—zookeeper之应用
http://www.cnblogs.com/sharpxiajun/archive/2013/06/02/3113923.html Zookeeper是hadoop的一个子项目,虽然源自hadoop ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】zookeeper面试题(转)
原文链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014479433 1.ZooKeeper是什么? ZooKeeper是一个分布式的,开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是 ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】ZooKeeper机制架构(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4133784.html 一.ZooKeeper权限管理机制 1.1 权限管理ACL(Access Control L ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】ZooKeeper管理分布式环境中的数据(转)
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4092654.html 引言 本节本来是要介绍ZooKeeper的实现原理,但是ZooKeeper的原理比较复杂,它 ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】Zookeeper命令操作(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4031881.html 一.Zookeeper的四字命令 Zookeeper支持某些特定的四字命令字母与其的交互.他 ...
- 【Zookeeper系列】ZooKeeper安装配置(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunddenly/p/4018459.html 一.Zookeeper的搭建方式 Zookeeper安装方式有三种,单机模式和集群模式以及伪 ...
随机推荐
- 【原创】大叔经验分享(59)kudu查看table size
kudu并没有命令可以直接查看每个table占用的空间,可以从cloudera manager上间接查看 CM is scrapping and aggregating the /metrics pa ...
- Django: ORM 数据库设置和读写分离
一.Django的数据库配置 (一)修改settings.py文件关于数据库的配置: Django默认使用sqlite: # Django默认的数据库库,SQLit配置 DATABASES = { ' ...
- python爬虫下正则各种字符串数据匹配
s = '*\/:?"<>|' #这9个字符在Windows系统下是不可以出现在文件名中的str1 = '\巴拉<1"!11[]>1*hgn/p:?|' # ...
- CentOS7安装Docker-CE并部署项目
前言 这是我第一次使用dokcer部署项目,现学现卖.成功之后把所有用到的安装及部署和操作命令做一个总结.如有不足,请指教. 使用的是阿里云服务器.CentOS7版本. Dokcer安装 1.Cent ...
- Redis之各版本特性
1.Redis2.6 Redis2.6在2012年正是发布,经历了17个版本,到2.6.17版本,相对于Redis2.4,主要特性如下: 1)服务端支持Lua脚本. 2)去掉虚拟内存相关功能. 3)放 ...
- 销售订单(SO)-API-登记销售订单
登记销售订单可以在新增订单的时候就登记:并不是去修改 flow_status 为booked,而是赋值action request:就下面两句 l_action_request_tbl(l_actio ...
- LINUX中lrzsz软件的使用
安装lrzsz 可以在Linux 和 windows直接相互传文件 Linux无论ssh跳过去也可以sz rz打开图像进行传输文件 [root@master2 ~]# yum install lrzs ...
- UE中正则表达式
UltraEdit(后简称UE),是我经常使用的文本编辑软件,其功能的强大,令我由衷地爱上了它.每天不用就全身不爽.从最开始的9.0到现在的 12.10a(本人只用到这个版本),UE都是系统重装后必安 ...
- linux基础—课堂随笔08_进程(转)
进程优先级 命令 pstree -p 显示各个子线程 ps 进程状态(process state) UNIX风格:ps -ef BSD风格:ps aux 还有用到o参数,选项显示定制的信息: pid. ...
- Django REST Framework(DRF)_第四篇
DRF分页(总共三种) PageNumberPagination(指定第n页,每页显示n条数据) 说明 既然要用人家的那么我们就先来看下源码,这个分页类源码中举例通过参数指定第几页和每页显示的数据:h ...
