图解CompletableFuture源码
前言
关于CompletableFuture源码解析部分,整体上感觉还是写比较难的,不过为了推广到团队还是要好好搞一下的,我还是希望大家看到这边文章能学到点什么,废话不多说开始吧。
属性部分
首先看属性部分,我觉得可以从全貌了解他的整体的数据结构,后续我们看到一些操作的时候,也不会产生疑问,算是一种先整体后部分的思想。
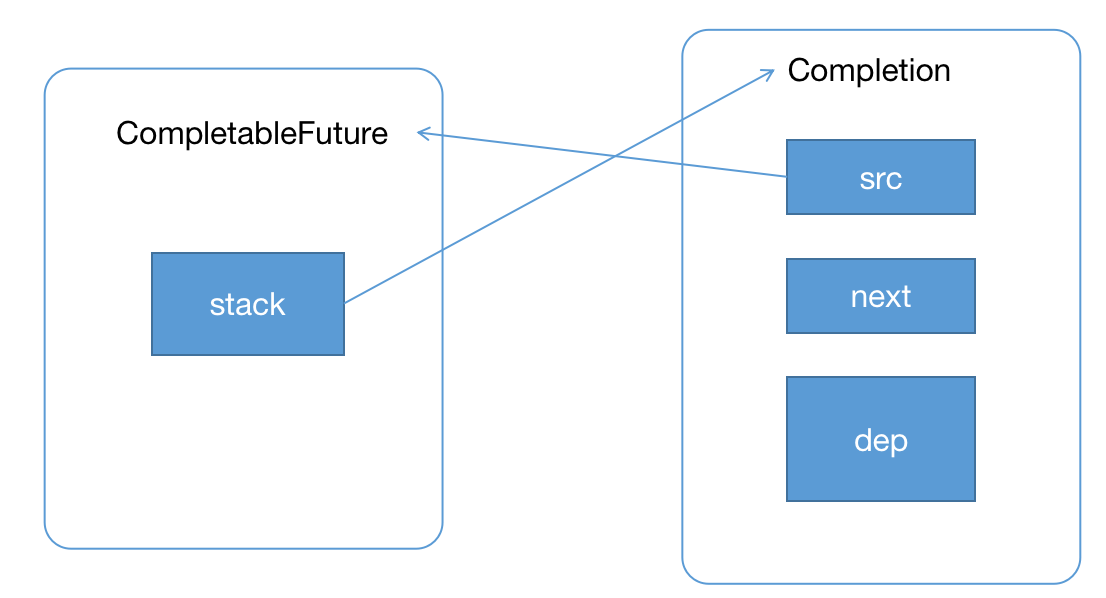
打开CompletableFuture源码以后我们首先看到是下面两个核心的关键属性result和stack,关于这两个属性也有核心的注释,result可能是返回的结果集,也可能是包装的AltResult,stack这个数据暴露出了CompletableFuture的整体的结构是一个栈。
volatile Object result; // Either the result or boxed AltResult
volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actions
接下来我们看下Completion的情况,Completion是一个抽象类,分别实现了Runnable、AsynchronousCompletionTask接口,继承了ForkJoinPoolTask类,而ForJoinPoolTask抽象类又实现了Future接口,因此Completion实际上就是一个Future。
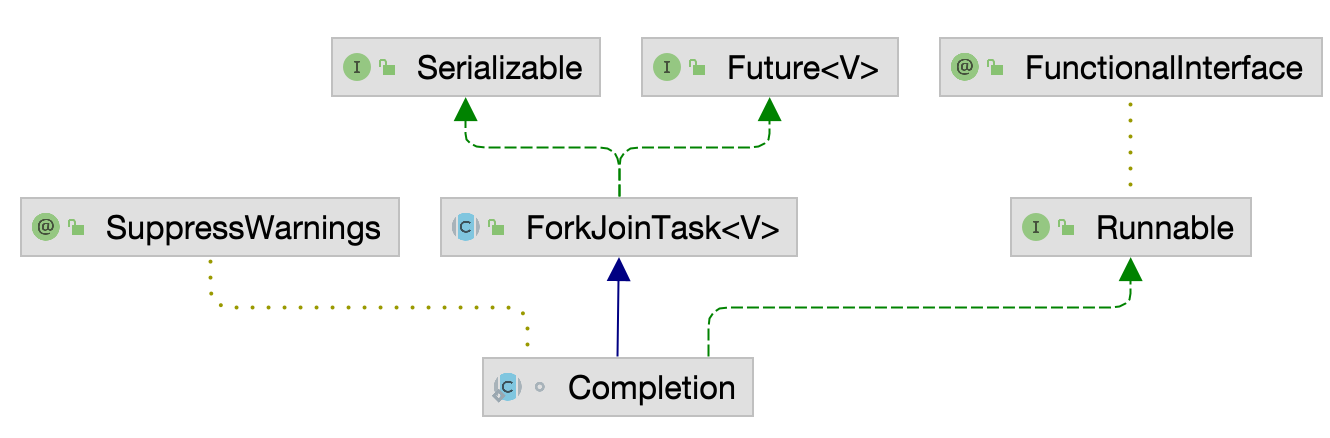
在Completion类中还有一个非常重要的成员属性,结合我们上面看到的CompletableFuture的stack属性,整好能验证CompletableFuture是一个链表的一个数据结构,Completion中的next保存了栈中下一个元素的引用,而CompletableFuture中的stack永远指向栈顶,至于是不是栈我们可以看下后续方法是如何操作的。
volatile Completion next;
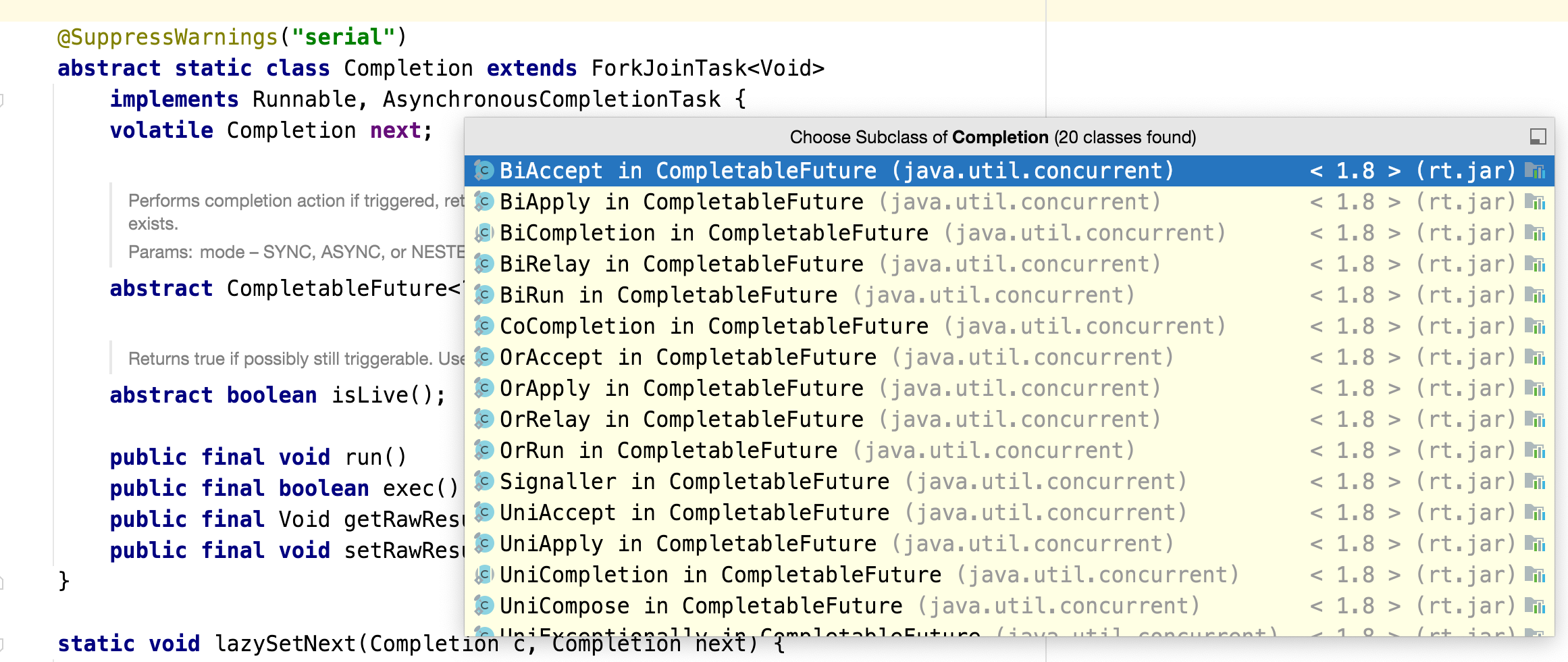
关于Completion类其实是一个抽象类,还有很多的实现,如下图,后续我们看到具体的实现的时候再来细化实现类。
核心方法源码解析
首先我们来看两个测试用例,
@Test
public void test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> base = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<String> future = base.thenApply(s -> s + " 2").thenApply(s -> s + " 3");
base.complete("1");
System.out.println(future.get());
}
@Test
public void test2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> base = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<String> future = base.thenApply(s -> s + " 2").thenApply(s -> s + " 3");
future.complete("1");
System.out.println(future.get());
}
执行这两个测试用例以后,我们会发现最终的结果的是不一致的,这里base和future对象,分别调用complete()和get()方法的排列组合,最终导致结果就发生了变化,是不是很神奇,接下来我们就来看看thenApply相关源码部分。
thenApply
关于thenApply的使用,CompletableFuture提供了类似的三个方法,以Async结尾的表示异步执行,如果传入Executor则以指定线程池执行,否则默认使用的线程池是ForkJoinPool。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(asyncPool, fn);
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {
return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
我们重点关注的thenApply的方法,整体的源码如下:
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(
Executor e, Function<? super T,? extends V> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
1.创建一个新的CompletableFuture对象
CompletableFuture<V> d = new CompletableFuture<V>();
if (e != null || !d.uniApply(this, f, null)) {
2. 构建UniApply e代表线程池 d 代表新的CompletableFuture this 代表当前
f 代表方法 这个时候 UniApply 内部的所有的引用都处于为null的状态
UniApply<T,V> c = new UniApply<T,V>(e, d, this, f);
3. c其实就是Completion对象,被push到栈中
push(c);
4. 尝试执行c
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
5. 这个d会一直返回到调用thenApply的地方,后续的链式调用会作用在这个d上面
return d;
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static final class UniApply<T,V> extends UniCompletion<T,V> {
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn;
UniApply(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,
CompletableFuture<T> src,
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn) {
2.1 向上执行
super(executor, dep, src); this.fn = fn;
}
}
abstract static class UniCompletion<T,V> extends Completion {
Executor executor; // executor to use (null if none)
CompletableFuture<V> dep; // the dependent to complete
CompletableFuture<T> src; // source for action
UniCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,
CompletableFuture<T> src) {
2.2 dep就是新创建的d src就是当前的this
this.executor = executor; this.dep = dep; this.src = src;
}
}
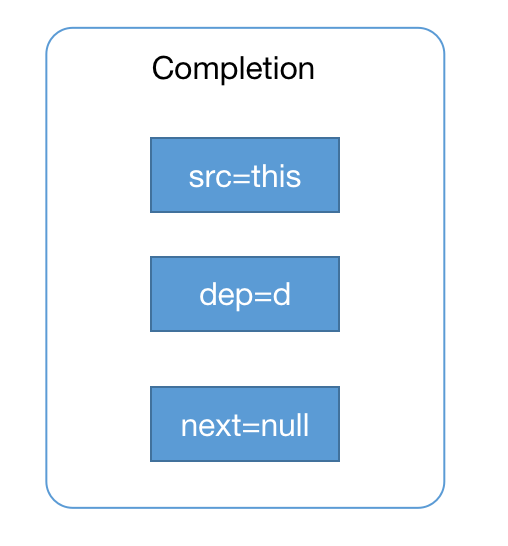
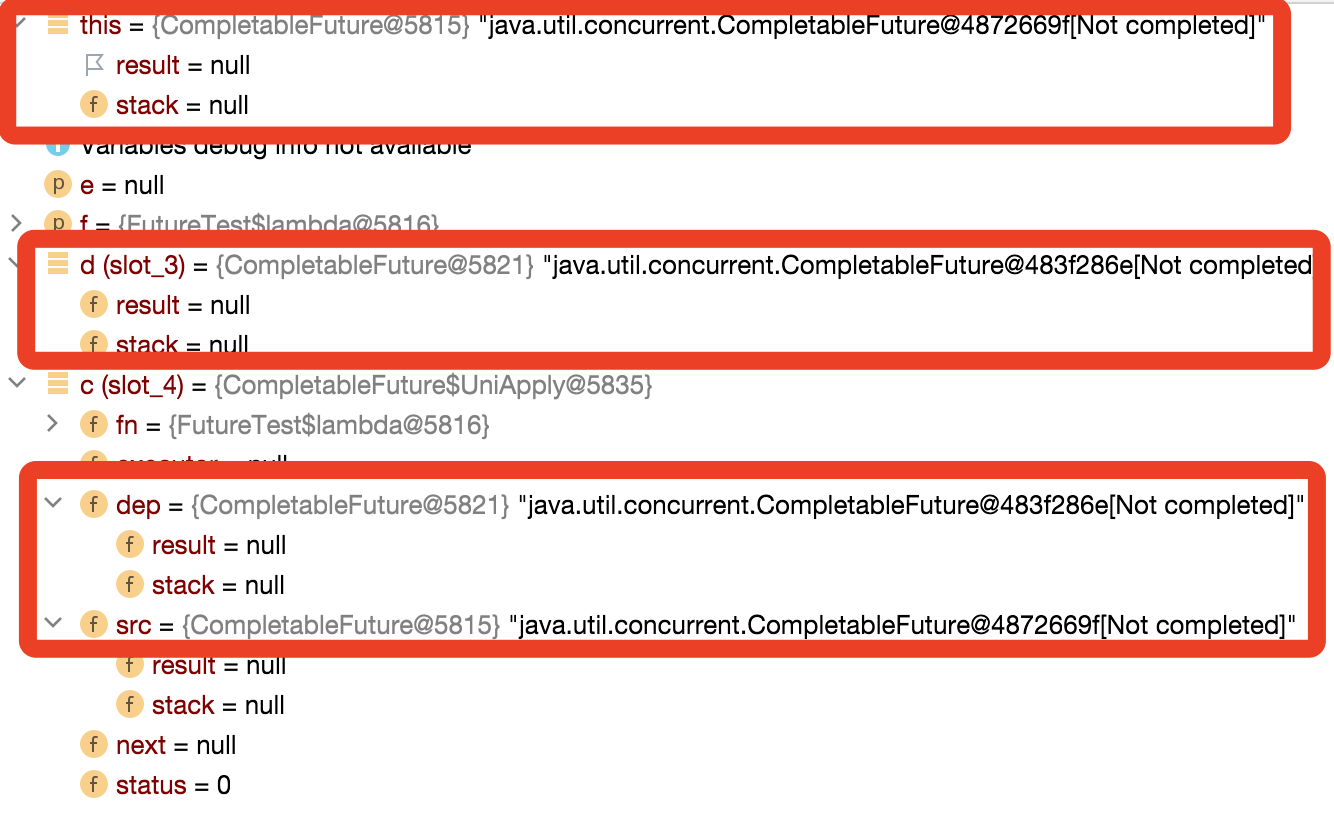
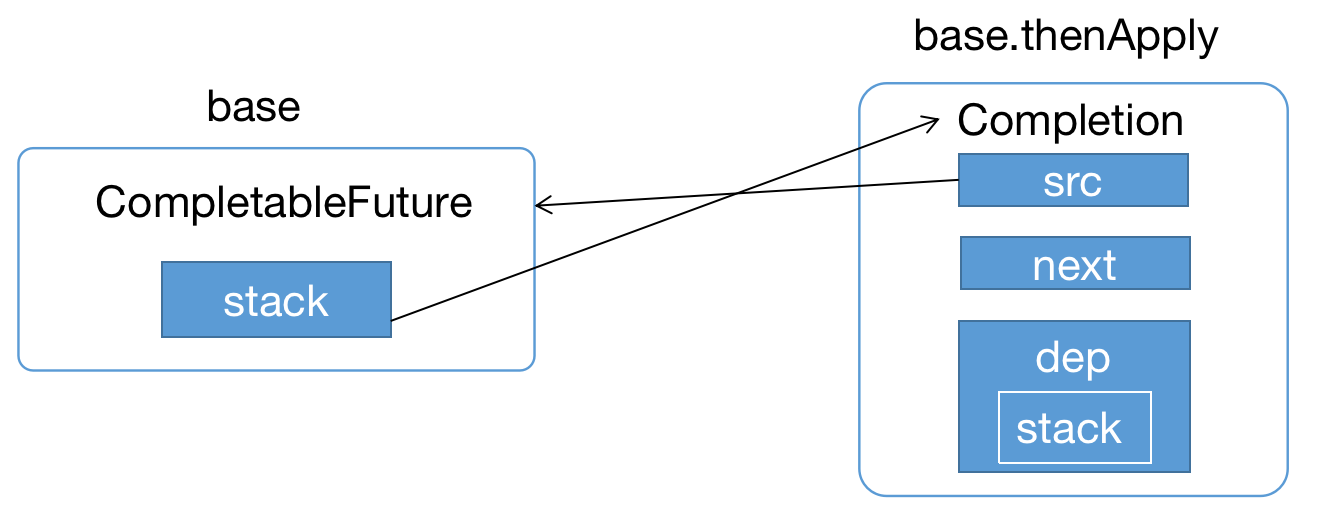
关于执行第2步的时候,构建的对象如下图, src和dep都是空的CompletableFuture,next为Null,这里我们会发现所有的都是继承Completion对象,最终所有都是构建都可以理解为Completion对象;
关于执行第3步的时候,构建的UniApply对象的内容完成压栈的操作,将CompletableFuture的stack属性指向Completion对象;
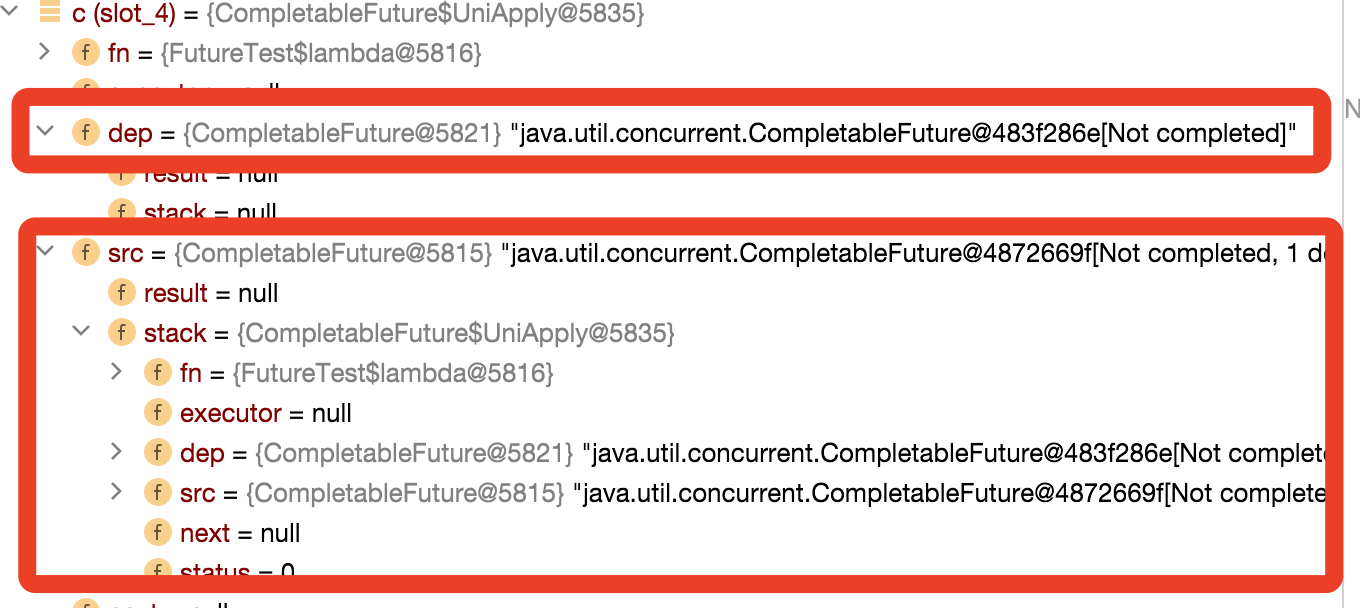
接下来看第4步操作,尝试执行Completion;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static final class UniApply<T,V> extends UniCompletion<T,V> {
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn;
UniApply(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,
CompletableFuture<T> src,
Function<? super T,? extends V> fn) {
super(executor, dep, src); this.fn = fn;
}
final CompletableFuture<V> tryFire(int mode) {
4.1 d新创建的 a(也是c中的src) 就是原来的
CompletableFuture<V> d; CompletableFuture<T> a;
4.2 如果uniApply执行成功,则会进到下面的postFire调用
否则返回null 如果返回null,就要等待以后的主动complete来再次触发
if ((d = dep) == null ||
!d.uniApply(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this))
return null;
4.5 tryFire成功后,会把以下几个属性设为null,表面此Completion已经完成任务,
变成dead状态
dep = null; src = null; fn = null;
4.6 出栈
return d.postFire(a, mode);
}
}
final <S> boolean uniApply(CompletableFuture<S> a,
Function<? super S,? extends T> f,
UniApply<S,T> c) {
Object r; Throwable x;
4.3 如果a(也是c中的src)没有准备完成,那result是空,这里就会直接返回false
if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null)
return false;
tryComplete: if (result == null) {
if (r instanceof AltResult) {
if ((x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null) {
completeThrowable(x, r);
break tryComplete;
}
r = null;
}
try {
if (c != null && !c.claim())
return false;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") S s = (S) r;
4.4 如果r不为空,则会作为f的输入参数,f的输出则成为当前CompletableFuture的完成值
completeValue(f.apply(s));
} catch (Throwable ex) {
completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
return true;
}
第5步返回d, 这个d会返回到调用thenApply的地方,后续的链式调用会作用在这个d上面,接下来我们可以看到base对象就是我们构建好的第一个链;
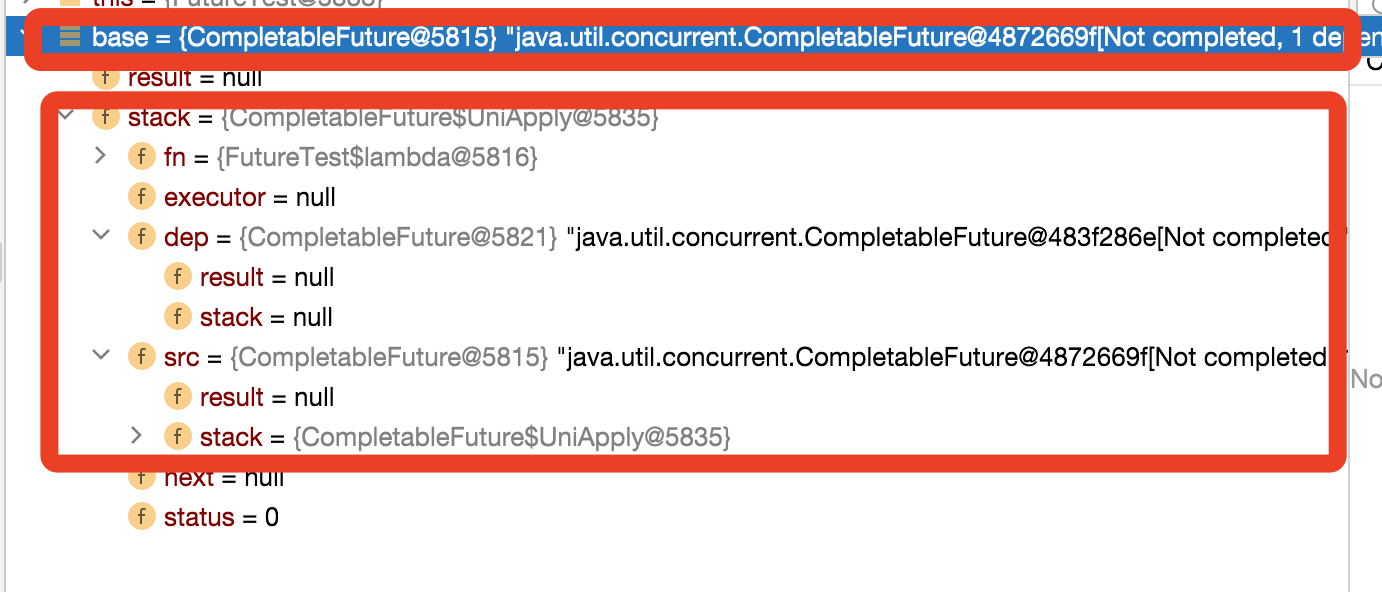
这里我们可以猜测后续的执行thenApply的方法,也就是执行完成test1的第二行代码,生成的结构如下图:
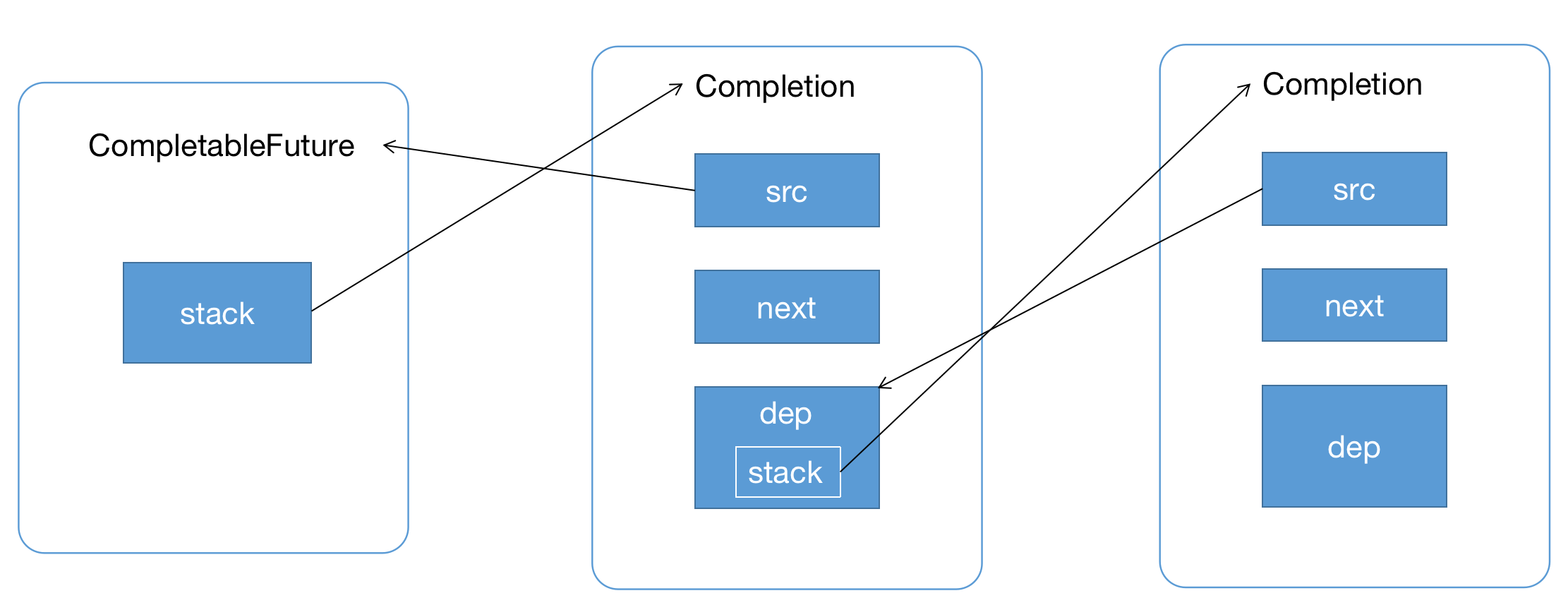
接下来我们验证一下,我们可以发现和我们猜想一致;
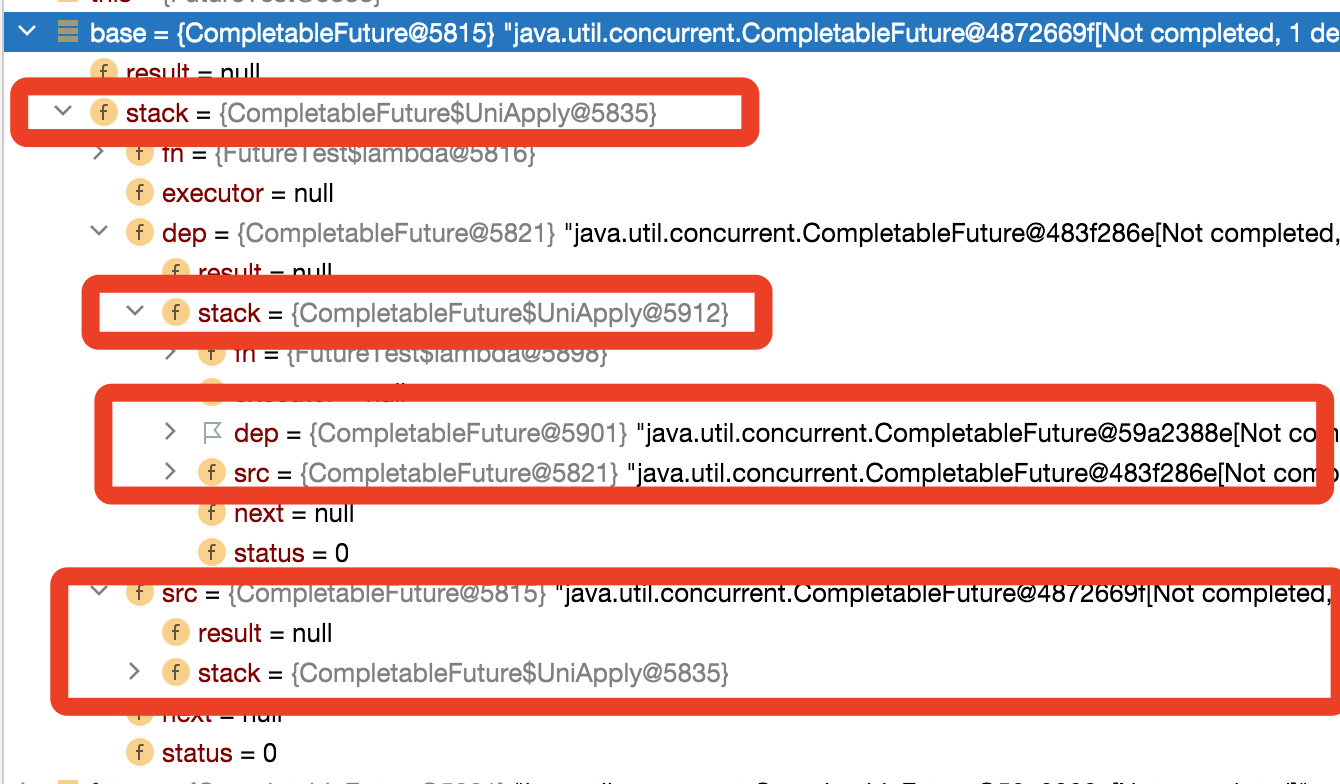
当我们的代码执行到test1的第3行的时候,也就是complete方法,该方法也就是为了解决我们执行tryFire执行失败后动作,源码如下:
public boolean complete(T value) {
boolean triggered = completeValue(value);
postComplete();
return triggered;
}
final void postComplete() {
1. this表示当前的CompletableFuture, 也就是我们base
CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;
2. 判断stack是否为空 或者如果f的栈为空且不是this则重置
while ((h = f.stack) != null ||
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;
3. CAS出栈
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) { 4.出栈的h不是最后一个元素,最后一个元素直接执行7即可
if (f != this) {
5. 如果f不是this,将刚出栈的h, 入this的栈顶
我猜测这个地方大家会有迷惑
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
h.next = null; 6. detach
}
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d; 7.调用tryFire
}
}
}
对于postComplete()方法可以理解为当任务完成之后,调用的一个后完成方法,主要用于触发其他依赖任务,也就是完成出栈的操作,关于第4、5步和的疑惑,这里我先说一下,这里的原因是每次调用产生的Completion并不在同一个stack中,接下来我们来看一个复杂的案例,可能大家就比较明白了;
复杂案例
@Test
public void test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> base = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<String> future = base.thenApply(s -> {
log.info("2");
return s + " 2";
});
base.thenAccept(s -> log.info(s + "3-1")).thenAccept(aVoid -> log.info("3-2"));
base.thenAccept(s -> log.info(s + "4-1")).thenAccept(aVoid -> log.info("4-2"));
base.complete("1");
log.info("base result: {}", base.get());
log.info("future result: {}", future.get());
}
首先看下输出,我们可以看到基本上是按照4-3-2-1的顺序输出的,证明CompletableFuture整体上是一个栈的结构,接下来我们就图解下这一过程;
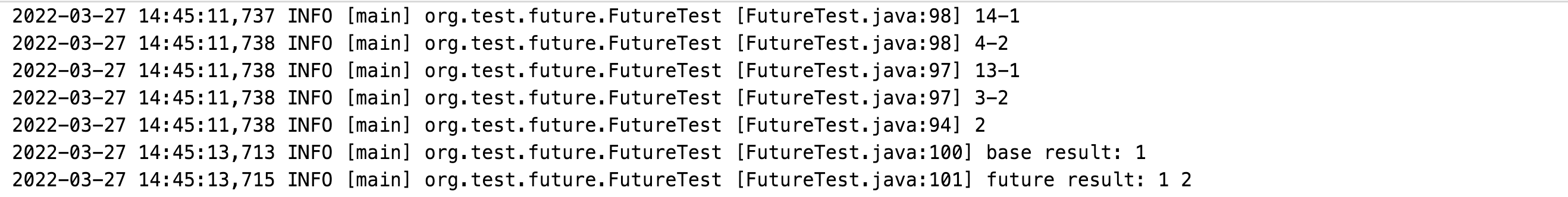
当代码执行完第7行的时候我们得到的是这样的结构:
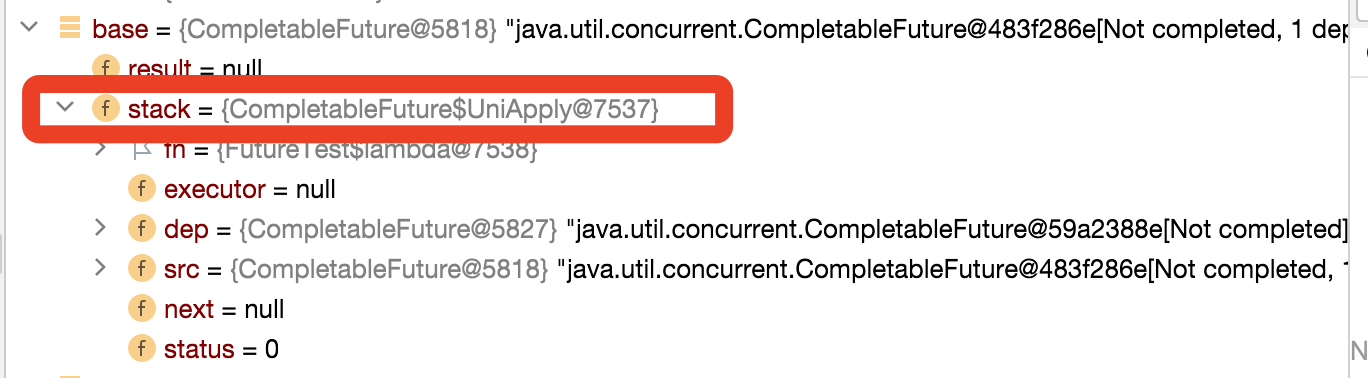
代码执行完第8行的时候,结构是这样的:
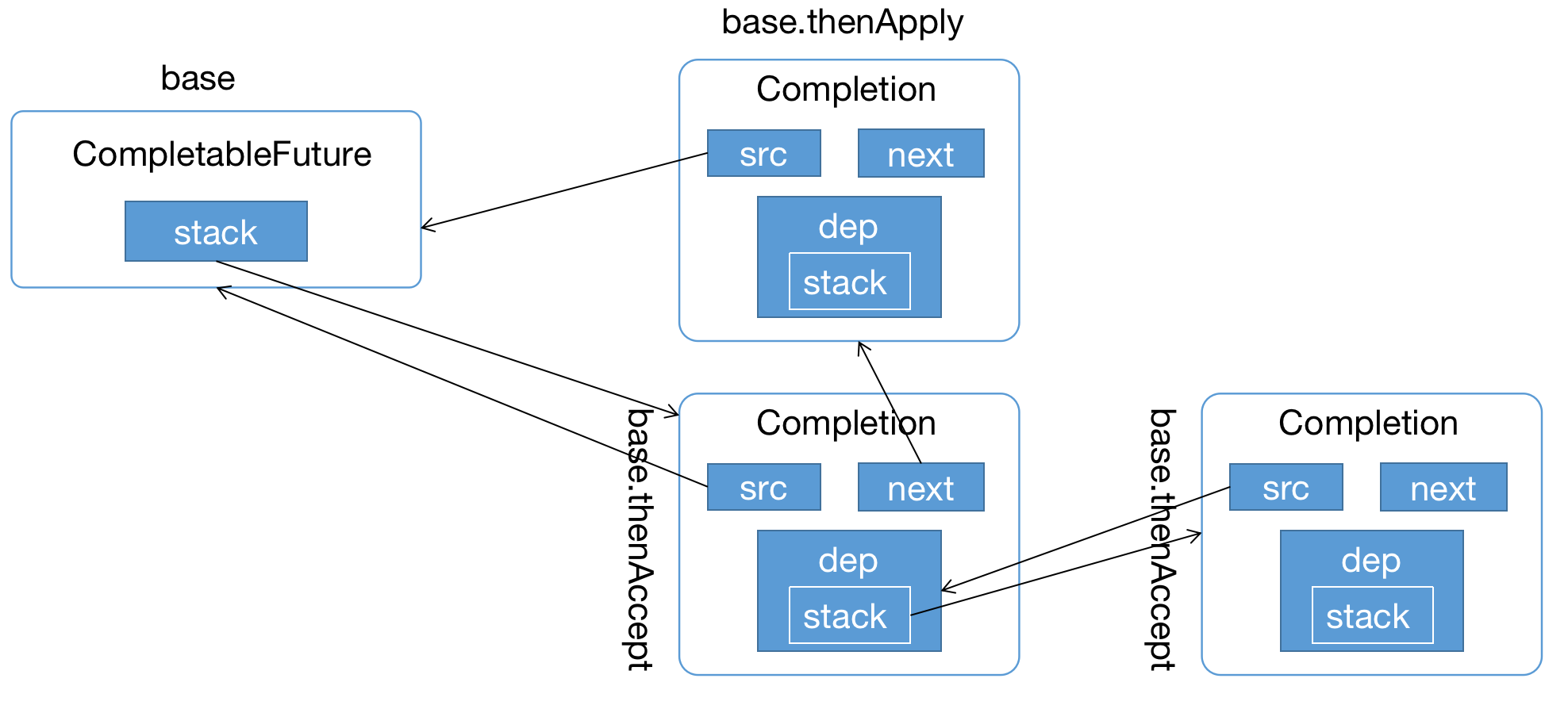
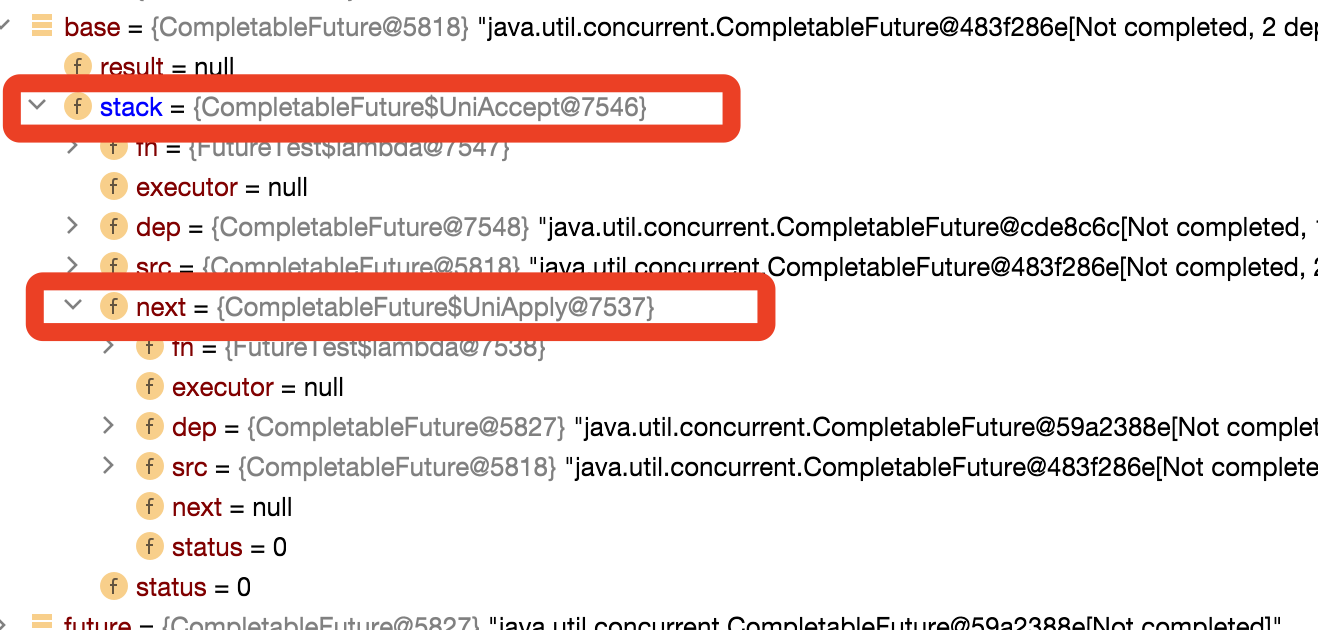
执行完第9行的时候,结构是这样的:
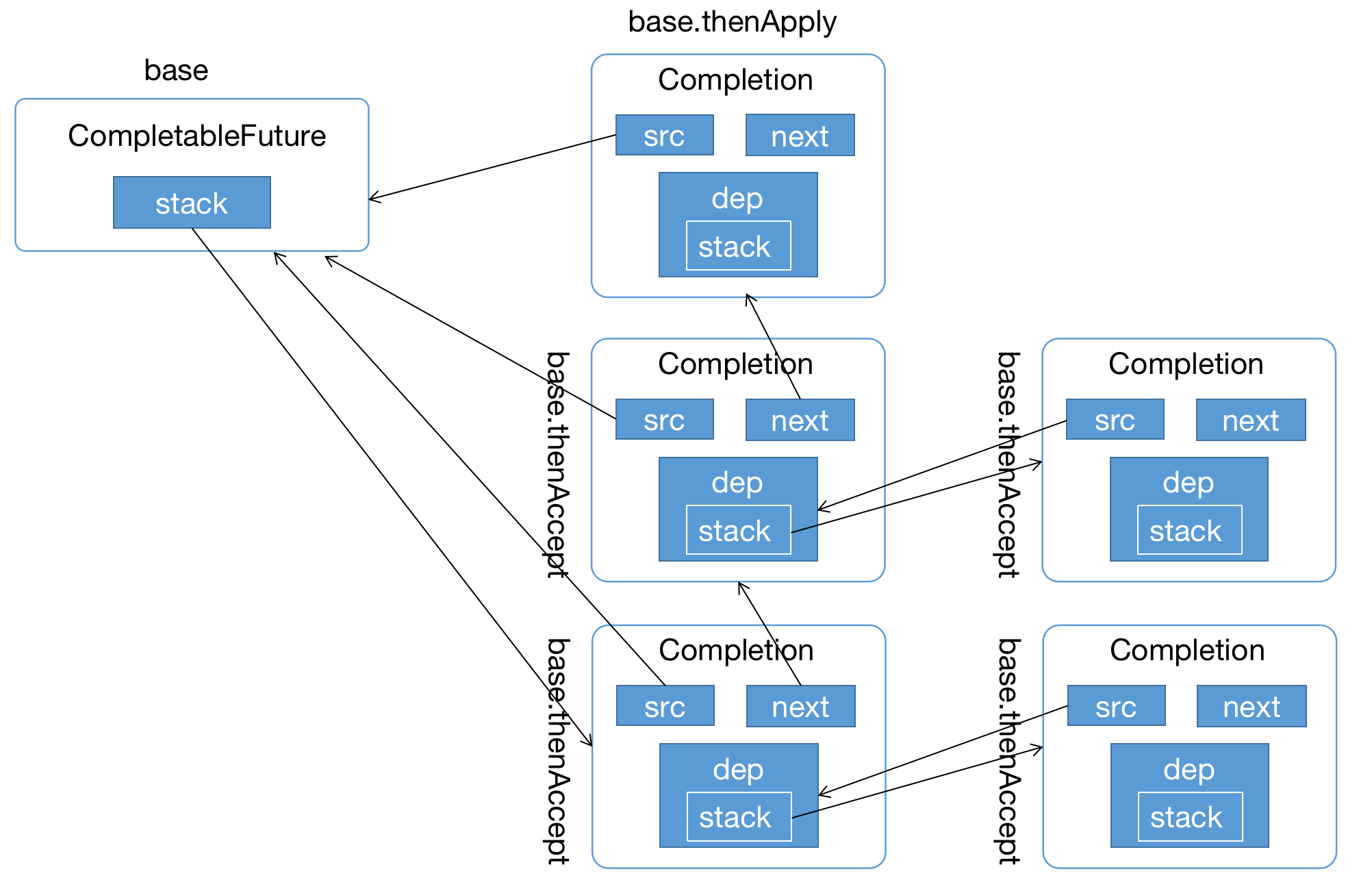
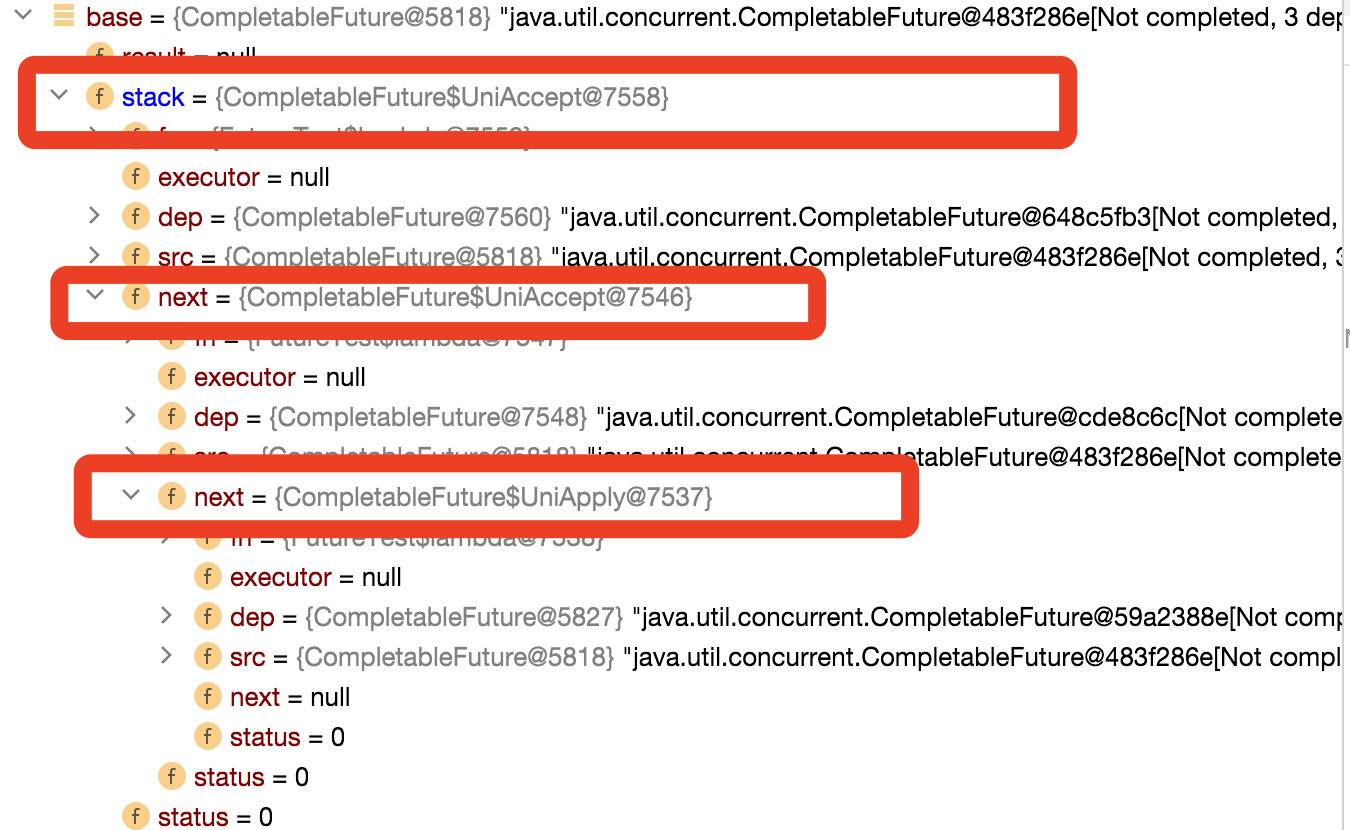
到这里就构成我们整个的调用链路,这个时候我们可以想明白为什么出栈的时候要判断下f != this了吧,因为内部又嵌套层栈的结构,构成了一个图状;
当代码执行到第10行的时候,就开始出栈,按照4-3-2-1的顺序输出,到这里这部分内容就讲解完成了。
参考以下内容:
结束
欢迎大家点点关注,点点赞!

图解CompletableFuture源码的更多相关文章
- [图解tensorflow源码] 入门准备工作附常用的矩阵计算工具[转]
[图解tensorflow源码] 入门准备工作 附常用的矩阵计算工具[转] Link: https://www.cnblogs.com/yao62995/p/5773142.html tensorf ...
- [图解tensorflow源码] [原创] Tensorflow 图解分析 (Session, Graph, Kernels, Devices)
TF Prepare [图解tensorflow源码] 入门准备工作 [图解tensorflow源码] TF系统概述篇 Session篇 [图解tensorflow源码] Session::Run() ...
- [图解tensorflow源码] 入门准备工作
tensorflow使用了自动化构建工具bazel.脚本语言调用c或cpp的包裹工具swig.使用EIGEN作为矩阵处理工具.Nvidia-cuBLAS GPU加速计算库.结构化数据存储格式prot ...
- 图解tensorflow 源码分析
http://www.cnblogs.com/yao62995/p/5773578.html https://github.com/yao62995/tensorflow
- [图解tensorflow源码] TF系统概述篇
Rendezvous 1. 定义在core/framework/rendezvous.h 2. A Rendezvous is an abstraction for passing a Tensor ...
- [图解tensorflow源码] [转载] tensorflow设备内存分配算法解析 (BFC算法)
转载自 http://weibo.com/p/1001603980563068394770 @ICT_吴林阳 tensorflow设备内存管理模块实现了一个best-fit with coales ...
- [图解tensorflow源码] Graph 图优化 (graph optimizer)
- [图解tensorflow源码] Graph 图构建 (Graph Constructor)
- [图解tensorflow源码] Graph 图模块 —— Graph Loading
随机推荐
- CentOS 7.6 部署 GlusterFS 分布式存储系统
文章目录 GlusterFS简介 环境介绍 开始GlusterFS部署 配置hosts解析 配置GlusterFS 创建文件系统 安装GlusterFS 启动GlusterFS 将节点加入到主机池 创 ...
- nginx负载均衡初体验
本例采取简单的轮询策略进行nginx的负载均衡处理. 在反向代理(参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ilovebath/p/14771571.html)的基础上增加负载均衡处理的n ...
- 我的平安夜-Merry Christmas
我的平安夜-Merry Christmas 平安夜给自己买的第一个"苹果",嘻嘻. 今夜,不想去学习技术知识点什么的, 我们就想到哪里写哪里,就简单聊聊思维方式吧. 其实我不想做今 ...
- Python-Flask框架之"图书管理系统"项目,附详解源代码及页面效果截图
该图书管理系统要实现的功能如下: 1. 可以通过添加窗口添加书籍或作者,如果要添加的作者和书籍已存在于书架上, 则给出相应的提示: 2. 如果要添加的作者存在,而要添加的书籍书架上没有,则将该书籍添加 ...
- 命令行下Git调用IDEA的diff功能
命令行下git diff, 有人欢喜有人厌, 本文以IDEA diff为例, 介绍如何更换Git的diff工具. IDEA diff IDEA作为一个图形化工具, 其实也提供了极少一部分命令行接口, ...
- MySQL explain结果Extra中"Using Index"与"Using where; Using index"区别探究
问题背景 最近用explain命令分析查询sql执行计划,时而能看到Extra中显示为"Using index"或者"Using where; Using Index&q ...
- Wireshark教程之统计功能
实验目的 1.工具介绍 2.主要应用 实验原理 Wireshark的原名是Ethereal,新名字是2006年起用的.当时Ethereal的主要开发者Gerald决定离开他原来供职的公司NIS,并继续 ...
- RENIX报文字段跳变——网络测试仪实操
什么是报文字段跳变? 报文字段跳变是指字段的值进行一些列有规则的变化,Renix支持对字段进行递增.递减.列表和随机变化. 如当用户想要仿真大量的源IP变化的数据时,就可以使用Modifier进行规则 ...
- 谁说EXCEL不能处理大数据?那是你用错了工具
我是一名数据分析师,每天需要和各种各样的数据和表格打交道,是一名名副其实的"表哥",不仅需要制作和更新公司里的日报.周报和月报,有时候也要为公司的会议准备各种数据材料.由于公司的业 ...
- springMVC整合mybatis,spring
使用spring-mvc创建一个项目的过程 spring的配置十分复杂,很难记忆. 这篇博客用于记录springmvc整合创建过程,虽然步骤有点多,但是每一步都很容易理解,便于以后忘记后参考和记忆. ...
